| 283. The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Lecture VI
30 Sep 1920, Dornach Translated by Maria St. Goar Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Just as the child should comprehend only fifths during the first year of school—at most also fourths, but not thirds; it begins to grasp thirds inwardly only from age nine onward—one can also say that the child easily understands the element of melody, but it begins to understand the element of harmony only when it reaches the age of nine or ten. Naturally, the child already understands the tone, but the actual element of harmony can be cultivated in the child only after the above age has been reached. |
| It would not actually be so difficult to popularize the understanding of the threefold human being if only people today were conscious of their musical experiences. |
| 283. The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Lecture VI
30 Sep 1920, Dornach Translated by Maria St. Goar Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Though they are quite fragmentary and incomplete and must be elaborated further at the next opportunity, I wish to emphasize again that yesterday's lecture and today's are intended to give teachers in school what they need as background for their instruction. Yesterday, I spoke on the one hand of the role that the interval of the fifth plays in musical experience and on the other hand of the roles played by the third and the seventh. You have been able to gather from this description that music progressing in fifths is still connected with a musical experience in which the human being is actually brought out of himself; with the feeling for the fifth, man actually feels transported. This becomes more obvious if we take the scales through the range of seven octaves—from the contra-tones up to the tones above c—and consider that it is possible for the fifth to occur twelve times within these seven scales. In the sequence of the seven musical scales, we discover hidden, as it were, an additional twelve-part scale with the interval of the fifth. What does this really mean in relation to the whole musical experience? It means that within the experience of the fifth, man with his “I” is in motion outside his physical organization. He paces the seven scales in twelve steps, as it were. He is therefore in motion outside his physical organization through the experience of the fifth. Returning to the experience of the third—in both the major and minor third—we arrive at an inner motion of the human being. The “I” is, so to speak, within the confines of the human organism; man experiences the interval of the third inwardly. In the transition from a third to a fifth—though there is much in between with which we are not concerned here—man in fact experiences the transition from inner to outer experience. One therefore can say that in the case of the experience of the third the mood is one of consolidation of the inner being, of man's becoming aware of the human being within himself. The experience of the fifth brings awareness of man within the divine world order. The experience of the fifth is, as it were, an expansion into the vast universe, while the experience of the third is a return of the human being into the structure of his own organization. In between lies the experience of the fourth. The experience of the fourth is perhaps one of the most interesting for one who wishes to penetrate the secrets of the musical element. This is not because the experience of the fourth in itself is the most interesting but because it arises at the dividing line between the experience of the fifth of the outer world and the experience of the third in man's inner being. The experience of the fourth lies right at the border, as it were, of the human organism. The human being, however, senses not the outer world but the spiritual world in the fourth. He beholds himself from outside, as it were (to borrow an expression referring to vision for an experience that has to do with hearing). Though man is not conscious of it, the sensation he experiences with the fourth is based on feeling that man himself is among the gods. While he has forgotten his own self in the experience of the fifth in order to be among the gods, in the experience of the fourth he need not forget his own being in order to be among the gods. With the experience of the fourth, man moves about, as it were, in the divine world; he stands precisely at the border of his humanness, retaining it, yet viewing it from the other side. The experience of the fifth as spiritual experience was the first to be lost to humanity. Modern man does not have the experience of the fifth that still existed, let us say, four to five hundred years before our era. At that time the human being truly felt in the experience of the fifth, “I stand within the spiritual world.” He required no instrument in order to produce outwardly the interval of a fifth. Because he still possessed imaginative consciousness, he felt that the fifth, which he himself had produced, took its course in the divine realm. Man still had imaginations, still had imaginations in the musical element. There was still an objectivity, a musical objectivity, in the experience of the fifth. Man lost this earlier than the objective experience of the fourth. The experience of the fourth, much later on, was such that during this experience man believed that he lived and wove in something etheric. With the experience of the fourth he felt—if I may say so—the holy wind that had placed him into the physical world. Based on what they said, it is possible that Ambrose and Augustine still felt this. Then this experience of the fourth was also lost. One required an outer instrument in order to be objectively certain of the fourth. We thus have pointed out at the same time what the musical experience was like in very ancient ages of human evolution. Man did not yet know the third; he descended only to the fourth. He did not distinguish between, “I sing,” and “there is singing.” These two were one for him. He was outside himself when he sang, and at the same time he had an outer instrument. He had an impression, an imagination, as it were, of a wind instrument, or of a string instrument. Musical instruments appeared to man at first as imaginations. Musical instruments were not invented through experimentation; with the experimentation of the piano they have been derived from the spiritual world. With this, we have described the origin of song as well. It is hard today to give an idea of what song itself was like in the age when the experience of the fifth was still pure. Song was indeed something akin to an expression of the word. One sang, but this was at the same time a speaking of the spiritual world. One was conscious that if one spoke of cherries and grapes one used earthly words; if one spoke of the gods, one had to sing. Then came the time when man no longer had imaginations. He still retained the remnants of imaginations, however, though one does not recognize them as such today—they are the words of language. The spiritual element incarnated into the tones of song, which in turn incarnated into the elements of words. This was a step into the physical world. The inner emancipation of the song element into arias and the like took place after that; this was a later development. If we return to the primeval song of humanity, we find that it was a speaking of the gods and of the proceedings of the gods. As I mentioned earlier, the fact of the twelve fifths in the seven scales is evidence that the possibility of motion outside the human realm existed in music in the interval of the fifth. Only with the fourth does man really approach himself with the musical element. Yesterday, someone said quite rightly that man senses an emptiness in the interval of the fifth. Naturally, he must experience something empty in the fifth, since he no longer has imaginations, and the fifth corresponds to an imagination while the third corresponds to a perception within man's being. Today, therefore, man feels an emptiness in the fifth and must fill it with the substantiality of the instrument. This is the transition of the musical element from the more spiritual age to the later materialistic age. For earlier ages, the relationship of musical man to his instrument must be pictured as the greatest possible unity. A Greek actor even felt the need of amplifying his voice with an instrument. The process of drawing the musical experience inward came later. Formerly, man felt that in relation to music he carried a certain circle of tones within himself that reached downward, excluding the realm of tones below the contra-c. Upward, it did not reach the tones beyond c but was a closed circle. Man then had the consciousness, “I have been given a narrow circle of the musical element. Out there in the cosmos the musical element continues in both directions. I need the instruments in order to reach this cosmic musical element.” Now we must take the other aspects of music into consideration if we wish to become acquainted with this whole matter. The center of music today is harmony. I am referring to the sum total of music, not song or instrumental music. The element of harmony takes hold directly of human feeling. What is expressed in harmonies is experienced by human feeling. Now, feeling passes into thinking [Vorstellen].1 In looking at the human being, we can say that we have feeling in the middle; on the one hand we have the feeling that passes into thinking, on the other hand we have the feeling that passes into willing. Harmony directly addresses itself to feeling and is experienced in it. The whole emotional nature of man, however, is actually twofold. We have a feeling that is more inclined to thinking—when we feel our thoughts, for instance—and we have a feeling more inclined to willing. When we engage in an action, we feel whether it pleases or displeases us; in the same way, we feel pleasure or displeasure with an idea. Feeling is actually divided into these two realms. The peculiar thing about the musical element is that neither must it penetrate completely into thinking—because it would cease to be something musical the moment it was taken hold of by the brain's conceptual faculty—nor should it sink down completely into the sphere of willing. We cannot imagine, for example, that the musical element itself could become a direct will impulse without being an abstract sign. When you hear the ringing of the dinner bell, you will go because it announced that it is time to go for dinner, but you will not take the bell's musical element as the impulse for the will. This illustrates that music should not reach into the realm of willing any more than into that of thinking. In both directions it must be contained. The musical experiences must take place within the realm situated between thinking and willing. It must unfold in that part of the human being that does not belong at all to ordinary day-consciousness but that has something to do with that which comes down from spiritual worlds, incarnates, and then passes again through death. It is present in the subconscious, however. For this reason, music has no direct equivalent in outer nature. In adapting himself to the earth, man finds his way into what can be grasped conceptually and what he wills to do. Music, however, does not extend this far into thinking and willing; yet, the element of harmony has a tendency to stream, as it were, toward thinking. It must not penetrate thinking, but it streams toward it. This streaming into the region of our spirit, where we otherwise think [vorstellen], is brought about by the harmony out of the melody. The element of melody guides the musical element from the realm of feeling up to that of thinking. You do not find what is contained in thinking in the thematic melody, but the theme does contain the element that reaches up into the same realm where mental images are otherwise formed. Melody contains something akin to mental images, but it is not a mental image; it clearly takes its course in the life of feeling. It tends upward, however, so that the feeling is experienced in the human head. The significance of the element of melody in human nature is that it makes the head of the human being accessible to feelings. Otherwise, the head is only open to the concept. Through melody the head becomes open to feeling, to actual feeling. It is as if you brought the heart into the head through melody. In the melody you become free, as you normally are in thinking; feeling becomes serene and purified. All outer aspects are eliminated from it, but at the same time it remains feeling through and through. Just as harmony can tend upward toward thinking, so it can tend downward toward willing. It must not penetrate the realm of willing, however; it must restrain itself, as it were, and this is accomplished through the rhythm. Melody thus carries harmony upward; rhythm carries harmony in the direction of willing. This is restricted willing, a measured will that runs its course in time; it does not proceed outward but remains bound to man himself. It is genuine feeling that extends into the realm of willing. Now it becomes understandable that when a child first enters school, it comprehends melodies more readily than harmonies. Of course, one must not take this pedantically; pedantry must never play a role in the artistic. It goes without saying that one can introduce the child to all sorts of things. Just as the child should comprehend only fifths during the first year of school—at most also fourths, but not thirds; it begins to grasp thirds inwardly only from age nine onward—one can also say that the child easily understands the element of melody, but it begins to understand the element of harmony only when it reaches the age of nine or ten. Naturally, the child already understands the tone, but the actual element of harmony can be cultivated in the child only after the above age has been reached. The rhythmic element, on the other hand, assumes the greatest variety of forms. The child will comprehend a certain inner rhythm while it is still very young. Aside from this instinctively experienced rhythm, however, the child should not be troubled until after it is nine years old with the rhythm that is experienced, for example, in the elements of instrumental music. Only then should the child's attention be called to these things. In the sphere of music, too, the age levels can indicate what needs to be done. These age levels are approximately the same as those found elsewhere in Waldorf education. Taking a closer look at rhythm, we see that since the rhythmic element is related to the nature of will—man must inwardly activate his will when he wishes to experience music—it is the rhythmic element that kindles music in the first place. Regardless of man's relationship to rhythm, all rhythm is based on the mysterious connection between pulse and breath, the ratio of eighteen breaths per minute to an average of seventy-two pulse beats per minute. This ratio of 1:4 naturally can be modified in any number of ways; it can also be individualized. Each person has his own experience regarding rhythm; since these experiences are approximately the same, however, people understand each other in reference to rhythm. All rhythmic experience bases itself on the mysterious relationship between breathing and the heartbeat, the circulation of the blood. One thus can say that while the melody is carried from the heart to the head on the stream of breath—and therefore in an outer slackening and inner creation of quality—the rhythm is carried on the waves of the blood circulation from the heart to the limbs, and in the limbs it is arrested as willing. From this you can see how the musical element really pervades the whole human being. Picture the whole human being who experiences the musical element as a human spirit: the ability to experience the element of melody gives you the head of this spirit. The ability to experience the element of harmony gives you the chest, the central organ of the spirit; and the ability to experience rhythm gives you the limbs of the spirit. What have I described for you here? I have described the human etheric body. If only you depict the whole musical experience, and if you do this correctly, you actually have before you the human etheric body. It is just that instead of “head” was say, “melody”; instead of “rhythmic man”—because it is lifted upward—we say, “harmony”; and instead of “limb man”—we cannot say here, “metabolic man”—we say, “rhythm.” We have the entire human being etherically before us. The musical experience is nothing else than this. The human being really experiences himself as etheric body in the experience of the fourth, but a kind of summation forms within him. The experience of the fourth contains a touch of melody, a touch of harmony, a touch of rhythm, but all interwoven in such a way that they are no longer distinguishable. The entire human being is experienced spiritually at the threshold in the experience of the fourth: one experiences the etheric human being. If today's music were not a part of the materialistic age, if all that man experiences today did not contaminate the musical element, then, based on what man possesses today in the musical element—which in itself has attained world-historical heights—he could not but be an anthroposophist. If you wish to experience the musical element consciously, you cannot but experience it anthroposophically. If you take these things as they are, you can ponder, for example, over the following point: everywhere in ancient traditions concerning spiritual life, mention is made of man's sevenfold nature. The theosophical movement also adopted this view of the sevenfold nature of the human being. When I wrote my Theosophy, I had to speak of a ninefold nature, further dividing the three individual members. I arrived at a sevenfold from a ninefold organization. 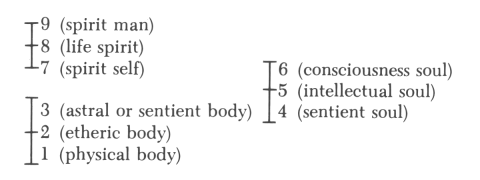 Since three and four overlap, as do six and seven, I too, arrived at the sevenfold human being in Theosophy. This book, however, never could have been written in the age dominated by the experience of the fifth. The reason is that in that age all spiritual experience resulted from the awareness that the number of planets was contained in the seven scales, and the number of signs in the Zodiac was contained in the twelve fifths within the seven scales. The great mystery of man was revealed in the circle of fifths, and in that period you could not write about theosophy in any way but by arriving at the sevenfold human being. My Theosophy was written in an age during which predominantly the third is experienced by human beings, in other words, in the age of introversion. One must seek the spiritual in a similar way, descending from the interval of the fifth by division to the interval of the third. I therefore also had to divide the individual members of man. You can say that those other books that speak of the sevenfold human being stem from the tradition of the age of fifths, from the tradition of the circle of fifths. My Theosophy is from the age in which the third plays the dominant musical role and in which, because of this, the complication arises that the more inward element tends toward the minor side, the more outward element toward the major side. This causes the indistinct overlapping between the sentient body and sentient soul. The sentient soul relates to the minor third, the sentient body to the major third. The facts of human evolution are expressed in musical development more clearly than anywhere else. As I already told you yesterday, however, one must forego concepts; abstract conceptualizing will get you nowhere here. When it comes to acoustics, or tone physiology, there is nothing to be gained. Acoustics has no significance, except for physics. A tone physiology that would have significance for music itself does not exist. If one wishes to comprehend the musical element, one must enter into the spiritual. You see how the interval of the fourth is situated between the fifth and the third. Man feels transported in the fifth. In the third he feels himself within himself; in the fourth he is on the border between himself and the world. Yesterday I told you that the seventh was the dominant interval for the Atlanteans. They had only intervals of the seventh, though they did not have the same feeling as we have today. When they made music they were transported completely beyond themselves; they were within the great, all-pervading spirituality of the universe in an absolute motion. They were being moved. This motion was still contained in the experience of the fifth as well. Again, the sixth is in between. From this we realize that man experiences these three steps, the seventh, the sixth, and the fifth, in a transported condition; he enters into his own being in the fourth; he dwells within himself in the third. Only in the future will man experience the octave's full musical significance. A bold experience of the second has not yet been attained by him today; these are matters that lie in the future. When man's inner life intensifies, he will experience the second, and finally he will be sensitive to the single tone. If you focus on what is said here, you will grasp better the forms that appear in our tone eurythmy. You will also grasp something else. You will, for example, grasp the reason that out of instinct the feeling will arise to interpret the lower segments of the octave—the prime, second and third—by backward movements and in the case of the upper tones—the fifth, sixth, and seventh—by forward movements.  These are more or less the forms that can be used as stereotypical forms, as typical forms. In the case of the forms that have been developed for individual musical compositions, you will be able to sense that these forms express the experience of the fourth or the fifth. 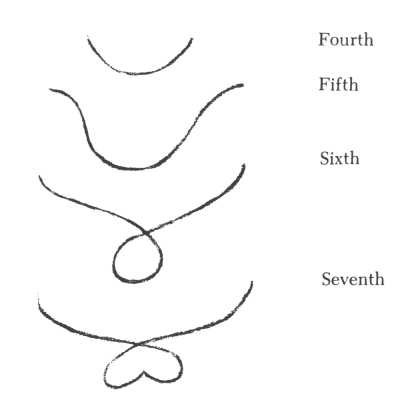 In eurythmy it is necessary that this part here—the descent of harmony through rhythm into willing—finds emphatic expression in form. The individual intervals thus are contained in the forms as such, executed by the eurthymist. Then, however, that which passes from the intervals into rhythm must be experienced fully by the performer in these forms; and quite by itself the instinct will arise to make as small a movement as possible without standing still in the case of the fourth. You see, the fourth is in fact a real perceiving, but a perceiving from the other side. It would be as if the eye, in perceiving itself, would have to look back upon itself; this, then, is the experience of the fourth gained from the soul. The interval of the fifth is a real experience of imagination. He who can experience fifths correctly is actually in a position to know on the subjective level what imagination is like. One who experiences sixths knows what inspiration is. Finally, one who fully experiences sevenths—if he survives this experience—knows what intuition is. What I mean is that in the experience of the seventh the form of the soul's composition is the same as clairvoyantly with intuition. The form of the soul's composition during the experience of the sixth is that of inspiration with clairvoyance. The experience of the fifth is a real imaginative experience. The same composition of soul need only be filled with vision. Such a composition of soul is definitely present in the case of music. This is why you hear everywhere that in the older mystery schools and remaining mystery traditions clairvoyant cognition is also called musical cognition, a spiritual-musical cognition. Though people today no longer know why, the mysteries refer to the existence of two kinds of cognition, ordinary bodily, intellectual cognition and spiritual cognition, which is in fact a musical cognition, a cognition living in the musical element. It would not actually be so difficult to popularize the understanding of the threefold human being if only people today were conscious of their musical experiences. Certainly to some extent people do have sensitivity for the experience of the musical element. They actually stand alongside it. The experience of the musical element is as yet quite limited. If it were really to become alive in man, he would feel: my etheric head is in the element of melody, and the physical has fallen away. Here, I have one aspect of the human organization. The element of harmony contains the center of my etheric system; again, the physical has fallen away. Then we reach the next octave; again in the limb system—it is obvious and goes without saying—I find the element that appears as the rhythmic element of music. How, indeed, does the musical evolution of man proceed? It begins with the experience of the spiritual, the actual presence of the spiritual in tone, in the musical tone structure. The spiritual fades away; man retains the tone structure. Later, he links it with the word, which is a remnant of the spiritual; and what he had earlier as imaginations, namely the instruments, he fashions here in the physical, out of physical substance, as his musical instruments. To the extent that they arouse the musical instruments, man simply filled the empty spaces that remained after he no longer beheld the spiritual. Into those spaces he put the physical instruments. It is correct to say that in music more than anywhere else one can see how the transition to the materialistic age proceeds. In the place where musical instruments resound today, spiritual entities stood formerly. They are gone, they have disappeared from the ancient clairvoyance. If man wishes to take objective hold of the musical element, however, he needs something that does not exist in outer nature. Outer nature offers him no equivalent to the musical element; therefore, he requires musical instruments. The musical instruments basically are a clear reflection of the fact that music is experienced by the whole human being. The wind instruments prove that the head of man experiences music. The string instruments are living proof that music is experience in the chest, primarily expressed in the arms. All percussion instruments—or those in between string and percussion instruments—are evidence of how the musical element is expressed in the third part of man's nature, the limb system. Also, however, everything connected with the wind instruments has a more intimate relation to the melody than that which is connected with string instruments which have a relation to the element of harmony. That which is connected with percussion possesses more inner rhythm and relates to the rhythmic element. An orchestra is an image of man; it must not include a piano, however. Why is that? The musical instruments are derived from the spiritual world; the piano, however, in which the tones are abstractly lined up next to each other, is created only in the physical world by man. All instruments like the flute or violin originate musically from the higher world. A piano is like the Philistine who no longer contains within him the higher human being. The piano is the Philistine instrument. It is fortunate that there is such an instrument, or else the Philistine would have no music at all. The piano arises out of a materialistic experience of music. It is therefore the instrument that can be used most conveniently to evoke the musical element within the material realm. Pure matter was put to use so that the piano could become an expression of the musical element. Naturally, the piano is a beneficial instrument—otherwise, we would have to rely from the beginning on the spiritual in musical instruction in our materialistic age—but it is the one instrument that actually, in a musical sense, must be overcome. Man must get away from the impressions of the piano if he wishes to experience the actual musical element. It is therefore always a great experience when a composition by an artist who basically lives completely in the element of music, such as Bruckner, is played on the piano. In Bruckner's compositions, the piano seems to disappear in the room! One forgets the piano and thinks that one is hearing other instruments; this is indeed so in Bruckner's case. It proves that something of the essentially spiritual, which lies at the basis of all music, still lived in Bruckner, though in a very instinctive way. These are the things that I wished to tell you today, though in a fragmentary, informal way. I believe we will soon have an opportunity to continue with these matters. Then, I shall go into more detail concerning this or that aspect.
|
| 283. The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Lecture VII
20 Dec 1920, Dornach Translated by Maria St. Goar Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Without spiritual scientific insight into this matter, one actually no longer understands how human beings sensed and felt before the fourth century A.D. We have frequently described, however, this composition of soul, this feeling. |
| The consciousness of the soul ceased to see supersensibly, to perceive, because this human soul surrendered itself to the earth. You perhaps will understand this more clearly if we shed light on it from yet another angle. What is really implied here? |
| From this the conviction must grow in us that we must return to that human soul composition, and it will arise again if the soul perceives [erkennt], through the religious welling up in it, the artistic streaming through it. Such a composition of soul will understand vividly once again what Goethe meant when he said, “Beauty is a manifestation of secret natural laws without which these phenomena would have remained forever hidden.” |
| 283. The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Lecture VII
20 Dec 1920, Dornach Translated by Maria St. Goar Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Recently, I have called attention repeatedly to the fact that, just as one can give a biographical description of man's waking life, so one could offer one of the time spent during sleep. Everything the human being experiences during his waking hours is experienced through his physical and etheric bodies. By virtue of the appropriately developed sense organs in the physical and etheric bodies he is conscious of this world, which, as his environment, is related to the physical and etheric bodies; it is at one with them, so to speak. Since man at his present level of evolution has not similarly developed soul-spiritual organs in his astral body and “I” that would serve as super-sensible sense organs—to coin a paradoxical expression—he cannot bring his consciousness into what he experiences between falling asleep and awakening. Only spiritual vision, therefore, could survey that which would be contained in the biography of this “I” and astral body, which runs parallel to the biography that we come to with the help of the physical and the etheric bodies. If one speaks of man's waking experiences, they necessarily include what, together with him and caused by him, takes place in his physical-etheric environment. One therefore must speak of a physical-etheric environment or world in which man exists during this waking life. Likewise, man is in another world during sleep; this world, however, is totally different from the physical-etheric world. Just as the physical world is our environment when we are awake, so super-sensible vision is in a position to speak of a world that surrounds us similarly when we sleep. In this lecture we shall bring before our souls some of the aspects that can illuminate that world. The basic elements for it are described in my book, An Outline Of Occult Science. There you will find described in a certain way, though in a sketchy form, how the realms of the physical-etheric world—the mineral, plant, animal, and human realms—continue upward into the realms of the higher hierarchies. We shall now take a closer look at this. When in the waking state, we turn our eyes or other sense organs in the direction of our physical-etheric environment, we perceive the three, or four, realms of nature, namely, the mineral, plant, animal, and human realms. Ascending to those regions that are accessible only to super-sensible consciousness, we find a continuation, as it were, of these realms: the realms of the Angeloi, Archangeloi, Archai, Exusiai, Dynamis, Kyriotetes, and so forth (see following diagram.) We therefore have two worlds interpenetrating one another, the physical-etheric world and the super-sensible world. We already know that during sleep we are indeed in this super-sensible world and have experiences there, despite the fact that, due to the absence of soul-spiritual organs, these experiences do not reach ordinary consciousness. To arrive at a more specific comprehension of what the human being experiences in this super-sensible world, one must describe this world in the same way as one describes the physical-etheric world by means of natural science and history. Regarding the super-sensible science that concerns the actual course of events in the world in which we exist as sleeping human beings, we naturally must select particular details to begin with. Today, I shall select one event of profound significance for the whole evolution of humanity in the last few thousand years. We have already discussed this event repeatedly from the viewpoint of the physical-etheric world and its history. Today, we shall discuss it from another viewpoint, that of the super-sensible world. The event to which I refer is one that falls in the fourth century A.D. I have described how the whole composition of human souls in the West becomes different in that century. Without spiritual scientific insight into this matter, one actually no longer understands how human beings sensed and felt before the fourth century A.D. We have frequently described, however, this composition of soul, this feeling. We have described in different words what human beings experienced in the course of that age. Now we shall take a brief glance at what the beings who belong to the super-sensible realm experienced during that same time. We shall turn to the other side of life, as it were, and take the viewpoint of the super-sensible realm. It is a prejudice of contemporary, so-called enlightened human beings to believe that their thoughts are confined only to their heads. We would discover nothing of the things around us through thoughts if these thoughts were only within the heads of man. He who believes that thoughts are only in the human head is as prejudiced as one—paradoxical as this might sound—who believes that the drink of water with which he quenches his thirst originated on his tongue instead of flowing into his mouth from the glass of water. It is as ridiculous to claim that thoughts originate in the human head as it is to claim that the drink of water originates in the mouth. Indeed, thoughts are spread out all through the world. Thoughts are forces that dwell in all things. Our organ of thinking is simply something that partakes of the cosmic reservoir of thought forces, absorbing thoughts of itself. We therefore cannot speak of thoughts as if they were the possession only of the human being. Instead, we must be aware that thoughts are world-dominating forces, spread out everywhere in the cosmos. These thoughts, however, do not freely float about, as it were, but are always borne and worked upon by some beings; and, most important, they are not always borne by the same beings. When we make use of the super-sensible world, we find through super-sensible research that, up into the fourth century A.D., the thoughts with which human beings made the world comprehensible to themselves were borne outside in the cosmos (I could also say, “they flowed out”—our earthly terms are ill-suited for these sublime occurrences and states of being), that these thoughts were borne or flowed from those hierarchical beings that we designate as the Exusiai or beings of form (see following diagram). If, out of the science of the mysteries, an ancient Greek wished to give an account of how he actually had acquired his thoughts, he would have had to do it in the following way. He would have said, “I turn my spiritual sight up toward those beings who, through the science of the mysteries, have been revealed to me as the beings of form, the forces or beings of form. They are the bearers of cosmic intelligence, they are the bearers of cosmic thoughts. They let thoughts stream through all the world events, and they bestow these human thoughts upon the world so that it can experience them consciously.” A person who, through a special initiation, had gained access to the super-sensible world in those ancient Greek times and had come to experience and behold these form beings, would, in order to form a correct picture, a true imagination of them, have had to attribute to them the thoughts that stream and radiate through the world. As an ancient Greek he beheld how, from their limbs, as it were, these form beings let stream forth radiant thought forces which then entered the world processes and there continued to be effective as the world-creative powers of intelligence. 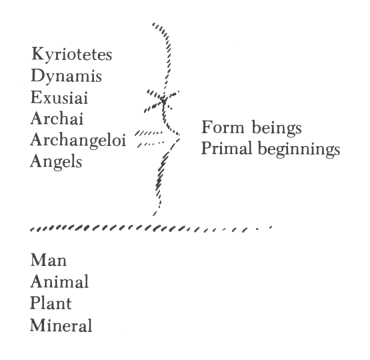 He thus could say that in the cosmos, the universe, the Exusiai, the forces of form, have the task of pouring thoughts into all the world processes. A material science describes human deeds by noting what people do individually or together. In focusing on the activity of the form forces of that particular age, a super-sensible science would have to describe how these super-sensible beings let the thought forces stream from one to the other, how they received them from one another, and how, in this streaming and receiving, the world processes are incorporated that appear outwardly to man as natural phenomena. The evolution of humanity now approached the fourth century A.D. In the super-sensible world, thought brought about an extremely significant event; namely, the Exusiai—the forces or beings of form—gave their thought forces up to the Archai, to the primal forces or primal beginnings. (See diagram above) The primal beginnings, or Archai, took over the task formerly executed by the Exusiai. Such things happen in the super-sensible world. This was a particularly sublime and significant cosmic event. From that time on, the Exusiai, the form beings, retained only the task of regulating the outer sense perceptions, therefore ruling with the particular cosmic forces over everything existing in the world of colors, tones, and so forth. Concerning the age that now dawned after the fourth century A.D. a person who can discern these matters must say that he beholds how the world-dominating thoughts are passed on to the Archai, the primal beginnings, how what eyes see and what ears hear, the manifold world phenomena engaged in perpetual metamorphosis, are the tapestry woven by the Exusiai. They formerly bestowed the thoughts on human beings; they now give human beings their sense impressions, while the primal beginnings bestow the thoughts on human beings. This fact of the super-sensible world was mirrored below in the sense world. In the ancient age in which lived the Greek, for example, thoughts were objectively perceived in all things. Just as today we believe that we perceive the color red or blue streaming forth from an object, so the ancient Greek found not only that he grasped a thought with his brain but that the thought streamed forth out of the things, just as red or blue streams forth. In my book, The Riddles of Philosophy, I have described the human side, so to speak, of the matter, how this important process of the super-sensible world is reflected in the physical-sensible world. There, I employed philosophical expressions, because philosophical terminology is a language for the material world. When one discusses the matter from the viewpoint of the super-sensible world, however, one must speak of the super-sensible fact that the task of the Exusiai passed on to the Archai. Such things are prepared in humanity through whole epochs of time and are connected with fundamental changes in human souls. I said that this super-sensible event took place in the fourth century A.D., but this is only an approximation, a mean point in time, as it were. This transference of a spiritual task took place over a long period of time. It had been prepared already in pre-Christian times and was completed only in the twelfth, thirteenth, and fourteenth centuries A.D. The fourth century is just the mean century, which is mentioned so as to pinpoint something definite in the historical development of humanity. This is also the point of time in humanity's evolution when the view of the super-sensible world began to vanish completely for man. The consciousness of the soul ceased to see supersensibly, to perceive, because this human soul surrendered itself to the earth. You perhaps will understand this more clearly if we shed light on it from yet another angle. What is really implied here? What am I trying to point out so intensely? It is the fact that human beings feel themselves more and more in their individuality. As the world of thoughts passes from the form beings to the primal beginnings, from the Exusiai to the Archai, man increasingly senses the thoughts in his own being, because the Archai live one level nearer man than the Exusiai. Now, when man begins to see supersensibly, he has the following impression. He realizes that this [see diagram] is the world that he perceives as the sense world. One side [yellow in diagram] is turned toward his senses, the other [red] is already hidden from the senses. Ordinary consciousness knows nothing of the relationships that are to be considered here. Supersensible consciousness, on the other hand, has the impression that between man [see diagram] and the sense impressions there are the Angeloi, Archangeloi, and Archai; they are really on this side of the sense world. Though one does not see them with ordinary eyes, they actually are situated between man and the whole tapestry of sense impressions. The Exusiai, Dynamis, and Kyriotetes are actually located beyond this realm; they are concealed by the tapestry of sense impressions. 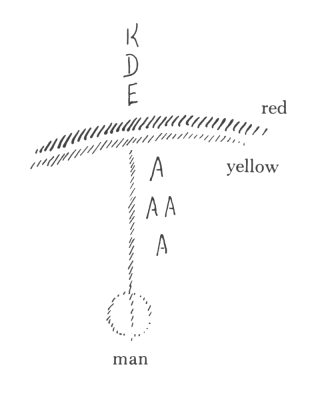 A human being having super-sensible consciousness senses that the thoughts are coming closer to him since having been given over to the Archai. He senses them as being located more in his world, whereas formerly they were located behind the appearance of things; they approached man, as it were, through the red or blue color, or the tone of c-sharp or g. Since this transference of thoughts, man feels a freer association with the world of thoughts. This also gives rise to the illusion that man himself produces the thoughts. In the course of time, the human being evolved to the point where he could enclose in himself, as it were, what formerly offered itself to him as objective outer world. This came about only gradually in human evolution. Going back into the distant past of human evolution, to the ancient Atlantean time preceding the Atlantean catastrophe, picture to yourselves the human configuration at that time, as described in my books, An Outline Of Occult Science or Cosmic Memory. As you know, human beings of that time were formed completely differently. The substance of their bodies was more delicate than it became later in the post-Atlantean age. For this reason, the soul element also stood in a different relationship to the world—all this is described in the above books—and these Atlanteans experienced the world completely differently. I just wish to point out one aspect of their particular kind of experience. Atlanteans could not yet experience musical intervals of thirds, not even fifths. Their musical experience really began with feeling the sevenths. They then felt further intervals, of which the seventh was the smallest. They missed hearing thirds and fifths; these intervals did not exist for Atlanteans. The experience of tone structure was completely different, and the soul had a completely different relationship to the tone structure. One who lives musically only in sevenths, with no intervals in between, as naturally as did the Atlanteans does not even perceive the musical element as something that occurs around or within him. The moment he perceives the musical element he feels transported out of his body into the cosmos. This was the case with the Atlanteans. Their musical experience converged with a direct religious experience. Their experience of the seventh did not make them feel that they themselves had something to do with the appearance of the interval of the seventh. Instead, they sensed how the gods, who pervaded and wove through the world, revealed themselves in sevenths. The statement, “I make music,” would have made no sense to them. The only meaningful thing for them to say was, “I live in music made by the gods.” In a much diminished form, this musical experience still existed in the post-Atlantean age during the period when people lived mainly in the interval of the fifth. This must not be compared to man's present-day feeling for the fifth. Today, the fifth gives man an impression of being something external that lacks content. Man experiences something empty in the fifth, though in a positive sense of the word empty. The fifth has become empty because the gods have withdrawn from human beings. Still, in the post-Atlantean age too, man experienced in the internal of the fifth that the gods actually lived in these fifths. Only later, when the third appeared in the musical element—both major and minor thirds—the musical element submerged itself, as it were, into human feeling [Gemüt]; hence, man no longer felt transported from his body while experiencing music. Man was definitely transported in musical life during the true era of the fifth. In the era of thirds, however, which as you know dawned only relatively recently, man is within himself when he experiences music. He brings the musical element close to his corporeality. He interweaves it with his corporeality. Along with the experience of the third, therefore, the difference between major and minor keys arises. Man becomes aware of what can be experienced through the major key on the one hand and the minor key on the other. With the third and the appearance of major and minor keys, the musical experience now links itself with uplifting, joyous human moods and with depressed, sad moods, which the human being experiences as a bearer of his physical and etheric bodies. In a manner of speaking, man withdraws his experiences as a bearer of his physical and etheric bodies. In a manner of speaking, man withdraws his experience of the world from the cosmos and unites it with himself. Formerly, his most important experience of the world was such—this was definitely still the case in the “fifth-era,” if I may put it like this, but much more so in the “seventh-era”—that it directly transported him, that he could say, “The world of tones draws my ‘I’ and my astral body out of my physical and etheric bodies. I interweave my earthly existence with the divine-spiritual world, and, on the wings of the tone structure, the gods move through the world. I participate in their moving when I perceive the tones.” In this specific area you can see how cosmic experience draws near to man, as it were; how the cosmos penetrates man; how, when we go back to earlier ages, we must seek in the super-sensible for the most important human experiences; and how the age is approaching when man as an earthly sense phenomenon must be taken along, as it were, when the most important world events are described. This occurs in the age before which the dominion over thoughts passed from the form beings to the primal beginnings. This is also reflected in the fact that the ancient “fifth-era,” which preceded the above cosmic event, passes on to the “era of thirds” and the experience of major and minor modes. It is of special interest regarding man's musical experience to go back into a still earlier time, an age of human earthly evolution reaching back into the dimmest primeval past, which can be brought into view by super-sensible vision. We arrive at an age—you find it described as the “Lemurian Age” in my Occult Science—in which generally man cannot perceive the musical element that can become conscious in him in an interval within one octave. In that age, man perceives only an interval that surpasses one octave: cdefgabcd He perceives only the above interval c to d above c1. In the Lemurian age we discover a musical experience that excludes hearing any interval within one octave; the interval instead reaches to the first tone of the following octave. It is difficult to put into words what the human being experienced then, but perhaps one can form an idea of it if I say that Lemurian man experienced the second of the next higher and the third of the second higher octave. He experienced a kind of objective third, and there he also experienced both major and minor thirds. It is not a third in our sense, of course, because one has an actual third only when I take the prime in the same octave and the tone that I refer to as being the second-nearest to the prime. Because ancient man was able to experience such intervals, however—we should say today, prime in the first octave, second in the next, third in the third octave—he perceived something like an objective major and minor mode, not one experienced within himself but one that was felt to be an expression of the soul experiences of the gods. One cannot say that Lemurians experienced joy and suffering, exaltation and depression, but one must say that, due to the particular musical sensation of the Lemurian age, when, in a completely transported state, human beings perceived these intervals, they experienced the god's cosmic sounds of joy and lamentation. We thus can look back upon an epoch of the earth actually experienced by human beings when what man experiences today in major and minor modes was projected, so to speak, into the universe. What today he experiences inwardly was once projected out into the universe. What today wells up in his life of feeling [Gemüt], in his sensation, he perceived—transported from his physical body—as the experience of the gods. Our present inner experience of a major musical mood was perceived by Lemurian man, when he was transported from his physical body, as the cosmic song of jubilation, as the cosmic music of jubilation, produced by the gods as an expression of joy over their world creation. What today we know as an inner minor mood experience, man perceived in the Lemurian age as the overwhelming lamentation of the gods concerning the possibility that humanity could fall victim to what subsequently has been described by the Bible as the fall into sin, the falling away from the benevolent divine-spiritual powers. This is something that sounds forth to us from the wonderful knowledge of the ancient mysteries, which at the same time was in itself artistic; it is not an abstract description of how humanity once passed through the Luciferic and Ahrimanic seduction and temptation and experienced such and such a thing. Human beings actually heard how, in primeval times, the gods made jubilant music in the cosmos because they rejoiced over their cosmic creativity. They also heard how the gods prophetically envisioned man's fall from the divine-spiritual powers and brought this to expression in their cosmic lamentation. This knowledge, which later took on increasingly intellectual forms, resounds as an artistic conception from the ancient mysteries. From this we can gain the profound conviction that it was only a single source from which flowed knowledge, art and religion. From this the conviction must grow in us that we must return to that human soul composition, and it will arise again if the soul perceives [erkennt], through the religious welling up in it, the artistic streaming through it. Such a composition of soul will understand vividly once again what Goethe meant when he said, “Beauty is a manifestation of secret natural laws without which these phenomena would have remained forever hidden.” The secret of human evolution within earthly existence, within earthly becoming, betrays itself to us by this inner unity of everything that man, perceiving religiously and artistically, must go through with the world, so that along with the world he can experience his entire development. The time has come when man must become conscious again of these matters, because otherwise the soul qualities of human nature will simply deteriorate. Through the increasingly intellectual, one-sided form of knowledge, man of today and the immediate future would have to become arid in his soul; the arts, grown one-sided, would dull his soul; and the one-sided religion would drain him of his soul altogether, if he were unable to find the path that could lead him to an inner harmony and union of these three; if he could not find the way to rise out of himself—in a more conscious way than was formerly the case—and once again to see and hear the super-sensible together with the sense world. When, with the air of the science of the spirit, one looks back at the ancient, great personalities of the dawning Greek culture, whose descendants were men like Aeschylus or Heraclitus, one finds that, in so far as they were initiated into the mysteries, these personalities all had the same feeling born out of their knowledge and their artistic forces of creativity just as Homer did, who said, “Sing, O Muse, to me of the wrath of Achilles,” not as something personal pervading them but as something they accomplished in their religious experience in community with the spiritual world. It motivated them to say the following: in primeval times, human beings actually experienced themselves as human beings by withdrawing from themselves during their most important human activities—I explained to you that this was in the case of music, but it was like this also in forming thoughts—and communing with the gods. Human beings have lost what they thus experienced. This mood of the loss of an ancient cognitive, artistic and religious treasure of humanity weighted heavily on the deeper Greek souls. Another mood must come over modern man. By unfolding the appropriate forces of his soul experience he must reach the point where he rediscovers what once was lost. I would like to put it like this: man must develop a consciousness—after all, we live in the age of consciousness—of how that which has become inward can once again find the way out to the divine-spiritual. In one realm, for example, this will be accomplished when the inner wealth of feeling experienced in a melody one day will be discovered in the single tone, at which time the secret of individual tone will be experienced by man. In other words, man not only will experience intervals but will be able to experience the single tone with the same inner richness and inner variation of experience that he can experience today with melody. As yet, today, man can hardly imagine what this will be like. You see, however, how matters proceed from the seventh to the fifth, from the fifth to the third, and from the third down to the prime, the single tone, and so forth. What was once the loss of the divine must transform itself for human evolution if humanity on earth is not to perish but to continue its development. The loss must transform itself for earthly humanity into a rediscovery of the divine. We understand the past correctly only if we are able to confront it with the right image for our evolution in the future; if deeply, deeply shaken we are able to feel what a profound person could feel in ancient Greek times, “I have lost the presence of the gods”: if, with a shaken, but intensely and warmly striving soul, we are able to counter this with the resolve, “We shall bring the spirit that is within us like a seed to blossoming and fruition so that we can find the gods once again!” |
| The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Foreword
Translated by Maria St. Goar Erika V. Asten |
|---|
| Since every night during sleep man's soul lies in the spiritual world—essentially a light-filled ocean of sounds—it is understandable why music speaks so directly and powerfully to almost everyone. The creative musician translates what he has experienced in the spiritual world into harmonies, melodies, and rhythms of music that is physically manifest. |
| In the remaining lectures, given in 1922–23, Steiner discusses man and his experience of the world of tones, an experience that has undergone profound changes during the course of evolution. Before the Atlantean catastrophe, described in detail in Steiner's An Outline of Occult Science, man perceived only those intervals that were larger than the seventh; such intervals lifted him outside his body and made any musical experience a cosmic-spiritual one. |
| The Inner Nature of Music and the Experience of Tone: Foreword
Translated by Maria St. Goar Erika V. Asten |
|---|
This volume contains the only two sets of lectures that Rudolf Steiner gave primarily on musical subjects. The first group of three lectures, given in 1906, explains why music has always held a special position among the arts. Music is the only art form whose archetypal origin is in the spiritual rather than in the physical world, as is the case with architecture, sculpture, or painting. Since every night during sleep man's soul lies in the spiritual world—essentially a light-filled ocean of sounds—it is understandable why music speaks so directly and powerfully to almost everyone. The creative musician translates what he has experienced in the spiritual world into harmonies, melodies, and rhythms of music that is physically manifest. Music, therefore, is a messenger from the spiritual world, speaking to us through tones as long as we are unable to partake in super-sensible events directly. In the remaining lectures, given in 1922–23, Steiner discusses man and his experience of the world of tones, an experience that has undergone profound changes during the course of evolution. Before the Atlantean catastrophe, described in detail in Steiner's An Outline of Occult Science, man perceived only those intervals that were larger than the seventh; such intervals lifted him outside his body and made any musical experience a cosmic-spiritual one. In the early post-Atlantean period man's experience of the interval narrowed to that of the fifth; in our modern age, the period of the experience of the third, we now perceive the fifth to be empty. This feeling of emptiness actually is caused, as Steiner explains, by the withdrawal of the gods from man. An extensive course for singers and other practicing musicians planned for the later part of the year 1924 could not take place due to the onset of Rudolf Steiner's mortal illness. The only other lecture cycle musicians can turn to is the tone eurythmy course, given in Dornach in February 1924 and published as Eurythmy as Visible Music. The collection of lectures presented here is thus an unusual treasure. Erika V. Asten |
| 283. The Occult Basis of Music
03 Dec 1906, Cologne Translated by Charles Waterman Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| For those who think of music from the aesthetic point of view, there is something puzzling about it; for simple human feeling it is a direct experience which penetrates the soul; and for those who want to understand how it produces its effects, it is a rather difficult problem. Compared with other arts—sculpture, painting, poetry—music has a special character. |
| The primal image, the archetype, of music is in Devachan; and having understood this, we can now examine the effect of music on human beings. Man has his physical body, and an etheric model for it, the ether-body. |
| 283. The Occult Basis of Music
03 Dec 1906, Cologne Translated by Charles Waterman Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
For those who think of music from the aesthetic point of view, there is something puzzling about it; for simple human feeling it is a direct experience which penetrates the soul; and for those who want to understand how it produces its effects, it is a rather difficult problem. Compared with other arts—sculpture, painting, poetry—music has a special character. All the other arts have some kind of model in the external world. The sculptor works from a model, and if he creates a statue of Zeus or Apollo, it takes an idealised human form. It is the same with painting—and today the tendency is to give an exact impression of what the senses perceive. Poetry, similarly, tries to deal with some aspect of the real world. But if one tried to apply this theory to music, one would get nowhere—for how could one copy, for example, the song of birds! What is the origin of musically-shaped sounds? How are they related to anything in the objective world? It is precisely in connection with this art of music that Schopenhauer has advanced some interesting views; in a certain respect they are indeed clear and striking. He assigns to music a quite special place among the arts, and to art itself a quite special value in human life. His philosophy has a fundamental ground-note which may be expressed as follows: Life is a sorry business, and through thinking I try to make it bearable. Pervading everything in the world is a blind, unconscious Will. It shapes the stone and then the plant—but always, in all its manifestations, with a restless yearning for something higher. The savage feels this less than does the genius, who experiences the painful cravings of the Will in the highest, most intense, degree. Besides the activity of the Will—Schopenhauer continues—man has the faculty of forming mental images. These are like a fata morgana, like pictures in the mist, like the spray thrown up by the waves of the Will. The Will surges up to shape these illusory pictures. When in this way man perceives the working of the Will, he is less than ever satisfied; but a release from the blind driving-force of the Will comes to us through art. Art is something through which man can escape from the restless craving of the Will. How does this happen? When man creates a work of art, it springs from his image-forming faculty; but genuine art, Schopenhauer insists, is not merely a copy of external reality. A statue of Zeus, for example, is not produced by copying; the sculptor draws for his model on the characteristics of many men, and so he creates the archetypal image, which in nature is distributed among numerous separate individuals. So the artist surpasses nature. He extracts her archetypal essence, and this is what the true artist renders. By penetrating into the creative depths of nature, he creates something real and achieves a certain release for himself. So it is with all the arts except music. All the other arts have to work through images and produce only pictures of the Will. But musical sound is a direct expression of the Will itself. The composer listens to the pulse-beat of the Will, and renders it in the sequence of musical sounds. Music is thus intimately related to the working of the Will in nature, to “things in themselves”; it penetrates into the elemental archetypal being of the cosmos and reflects the feeling of it; that is why music is so deeply satisfying. Schopenhauer was no occultist, but in these matters he had an instinctive apprehension of the truth. Why does music speak so intimately to the heart, and so widely, and why is its influence so powerful, even in early childhood? For answers to these questions we must turn to the realm where the true models for music are to be found. When a composer is at work, he has nothing to copy from; he has to draw his music from out of his own soul. Whence he derives it we shall find out if we turn our attention to the worlds which are not perceptible to the ordinary senses. Human beings are so made that it is possible for them to release in themselves faculties which are normally asleep; in the same way that someone born blind may be given sight by an operation, so can a man's inner eyes be opened, enabling him to gain knowledge of higher worlds. When a man develops these slumbering faculties through concentration, meditation and so on, he advances step by step. First of all he experiences a special configuration of his dream life. His dreams take on a much more orderly character; on waking, he feels as though he were rising from out of the waves of an ocean in which he had been submerged, a world of flowing light and colour. He knows that he has experienced something; that he has seen an ocean of which he had no previous knowledge. Increasingly his dream-experiences gain in clarity. He remembers that in this world of light and colour there were things and beings which differed from anything physical in being permeable, so that one can pass right through them without meeting any resistance. He comes to know beings whose element, whose bodies, the colours are. Gradually he extends his consciousness over this world, and on waking he remembers that he has been active within it. The next step occurs when he—as it were—carries this world back with him into waking life. Then he sees the astral bodies of other men and of much else, and he experiences a world which is much more real than the physical one—a world which in relation to the physical world appears as a densification, a crystallisation, from out of the astral world. Now it is also possible to transform into a conscious condition the unconscious state of dreamless sleep. The disciple who attains to this stage learns to extend his consciousness over those parts of the night which are not filled with dreams, but are normally spent in complete unconsciousness. He then finds himself conscious in a world of which previously he knew nothing, a world which is not intrinsically one of light and colour; it first announces itself as a world of musical sound. The disciple acquires the capacity to hear spiritually; he hears sequences and combinations of sounds which are not audible to the physical ear. This world is called the devachanic world (Deva=spirit, chan=home). One must not think that when a man enters this world and hears its tones resounding, he loses the world of light and colours. The world of tones is shot through with light and colours, but they belong to the astral world. The essential element of the devachanic world is the endlessly flowing and changing ocean of musical tones. When continuous consciousness extends to this world, its tones can be brought over, and it is then possible to hear also the ground-tones of the physical world. For every physical thing has its ground-note in the devachanic world, and in every countenance devachanic ground-notes are figured forth. It was on this account that Paracelsus said: “The kingdoms of nature are the letters of the alphabet, and Man is the word formed from them.” Whenever anyone falls asleep, his astral body goes out from his physical body; his soul then lives in the devachanic world. Its harmonies make an impression on his soul; they vibrate through it in waves of living sound, so that every morning he wakes from the music of the spheres, and out of this realm of harmony he passes into the everyday world. Just as the human soul has a sojourn in Devachan between incarnations, so we can say that during the night the soul rejoices in flowing tones of music: they are the very element out of which it is itself woven and they are its true home. The composer translates into physical sounds the rhythms and harmonies which at night imprint themselves on his astral body. Unconsciously he takes his model from the spiritual world. He has in himself the harmonies which he translates into physical terms. That is the secret connection between the music which resounds in the physical world and the hearing of spiritual music during the night. But the relation of physical music to this spiritual music is like that of a shadow to the object which casts it. So the music of instruments and voices in the physical world is like a shadow, a true shadow, of the far higher music of Devachan. The primal image, the archetype, of music is in Devachan; and having understood this, we can now examine the effect of music on human beings. Man has his physical body, and an etheric model for it, the ether-body. Connected with his ether-body is the sentient body, which is a step towards the astral. Inwardly bound up with him, as though membered into him, is the Sentient Soul. Just as a sword and its scabbard form a single whole, so do the Sentient Soul and the sentient body. Man has also the Intellectual Soul, and as a still higher member the Spiritual Soul, which is linked with the Spirit-self, or Manas. In completely dreamless sleep the higher members, and so also the Sentient Soul, are in the devachanic world. This is not like living in the physical realm, where everything we see and hear is outside ourselves. The beings of Devachan interpenetrate us, and we are within everything that exists there. In occult schools, accordingly, this devachanic-astral realm is called the world of interpenetrability. Man is played through by its music. When he returns from this devachanic world, his Sentient Soul, his Intellectual Soul and his Spiritual Soul are permeated with its rhythms; he carries them down into his denser bodies. He is thus able to work from out of his Intellectual Soul and his Sentient Soul on to his ether-body, and to carry the rhythms into it. As a seal stamps itself on the wax, so the astral body imprints the devachanic rhythms on the ether-body, until the ether-body vibrates in harmony with them. Ether-body and astral body bear witness in their own being to the spiritual tones and rhythms. The ether-body is lower than the astral body, but in activity it is superior. From out of his Ego man works on his bodies in so far as he transmutes the astral body into Manas, the ether-body into Buddhi, the physical body into Atma. Since the astral body is the most tenuous, the transmutation of it calls for the least strength. Man can work on his astral body with forces drawn from the astral world. But to work on his etheric body he has to call on forces from the devachanic world, and for working on his physical body he needs forces from the higher devachanic world. During the night he draws from the world of flowing tones the strength to carry them over into his sentient body and his etheric body. Although on waking in the morning he is not conscious of having absorbed this music of the night, yet on listening to music he has an inkling that these impressions of the spiritual world are within him. When a man listens to music, the seer can observe how the rhythms and colours flow into and lay hold of the firmer substance of the ether-body, causing it to vibrate in tune with them, and from the harmonious response of the ether-body comes the pleasure that is felt. The more strongly the astral body resounds, the more strongly do its tones echo in the ether-body, overcoming the ether-body's own natural rhythms, and this gives feelings of pleasure both to a listener and to a composer. In certain cases the harmonies of the astral body penetrate to some extent into the sentient body, and a conflict then arises between the sentient body and the ether-body. If the tones set up in the sentient body are so strong that they master the tones of the ether-body, the result is cheerful music in a major key. A minor key indicates that the ether-body has prevailed over the sentient body; and the painful feeling that ensues gives rise to the most serious melodies. So, when someone lives in the experience of music, he is living in the image of his spiritual home. It naturally elevates the soul to feel this intimate relationship to its primal ground, and that is why the simplest souls are so receptive to music. A man then feels himself truly at home, and whenever he is lifted up through music he says to himself: “Yes, you come from other worlds, and in music you can experience your native place.” It was an intuitive knowledge of this that led Schopenhauer to assign to music a central place among the arts, and to say that the composer discerns with his spiritual ear the pulse-beat of the Will. In music, man feels the echo of the inmost life of things, a life related to his own. Because feelings are the most inward part of the soul, and because they are related to the spiritual world and are indwelt by musical sound—that is why man, when he listens to music, lives in the pleasure of feeling himself in harmony with its tones, and in touch with the true home of his spirit. |
| 283. Speech and Song
02 Dec 1922, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| We lose the life within the cosmic language, and acquire here on earth the language which serves us in the first place to express our thoughts—our earthly thoughts. This earthly language serves our mutual understanding—understanding as between human beings, all of whom are living on the earth. And so it is with our thoughts themselves—our earthly thinking. |
| How deeply and fully he is contained, we only begin to see when we understand more in detail what the human being is in that he speaks or sings. Let us take our start from speech. |
| Thus we may say, the very process which man must undergo here on earth, in that he adapts his language to earthly conditions, is reversed in a certain sense when we pass from speech to song. |
| 283. Speech and Song
02 Dec 1922, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
I have already pointed out in recent lectures how certain functions or activities of the human being, which emerge in early childhood, are in reality a metamorphosis of activities which belong to man between death and a new birth, i.e. in his pre-earthly life. At birth the child is not yet fully adapted to the earthly gravitation, the earthly conditions of equilibrium. We see the child slowly and gradually adapt himself to these earthly conditions as he learns to stand and walk. Thus the adaptation of the body to the position of equilibrium for earthly life is a faculty which man does not bring with him. He must acquire it during his earthly life. Now we know that the physical body of man in all its form is the result of a mighty spiritual activity—an activity which man performs in unison with Beings of the Higher Worlds between death and a new birth. Yet that which man forms and creates in this activity—we may call it in a sense the spiritual germ of his future physical earthly body—is not so formed as already to contain the faculty of upright gait and posture. This faculty is only incorporated in man's nature when, after his birth, he gradually finds his way into the conditions of equilibrium, into the forces of earthly existence. For in the pre-earthly life, balance or equilibrium is not the same as it is on earth, where it signifies the power to walk and stand. In the pre-earthly life, balance and equilibrium signify the relation man has to the Angeloi, Archangeloi and so forth—to the Beings of the Hierarchies—a relation manifold and differentiated according as one feels oneself drawn more towards one Being or more towards another. This constitutes the state of equilibrium in the spiritual worlds. And this, man loses in a certain sense when he descends on to the earth. In the mother's womb he is neither in the conditions of equilibrium of his spiritual existence, nor is he yet in the conditions of equilibrium of his earthly life. He has left the former and has not yet entered into the latter. It is similar in the case of speech. The language which we speak here on earth is, of course, essentially adapted to earthly conditions. In the first place it is an expression of our earthly thoughts. These earthly thoughts contain earthly information and earthly knowledge; and to all this our speech or language is adapted during our life on earth. But in the pre-earthly life as I have already explained, man has a very different language—one which does not go from within outwards, which does not mainly follow the out-breathing process, but the spiritual in-breathing or inspiration (which we observe to correspond to breathing in the pre-earthly life). Thus in pre-earthly existence, man's language is a living with the cosmic Logos; it is a living within the cosmic Word—the cosmic language from out of which all things of the world are made. This too we lose when we descend on to the earth. We lose the life within the cosmic language, and acquire here on earth the language which serves us in the first place to express our thoughts—our earthly thoughts. This earthly language serves our mutual understanding—understanding as between human beings, all of whom are living on the earth. And so it is with our thoughts themselves—our earthly thinking. Here on earth, our thinking is gradually adapted to the earthly conditions. In pre-earthly existence on the other hand, our thought is a living within the creative thoughts of the Cosmos. Walking, Speaking and Thinking:—let us now consider, of these three, the middle member—human speech. We may indeed say that in speech there lies a most essential element of all earthly culture and civilisation. By speech, human beings come together here on earth, and one man finds the way to another. Bridging the gulf that lies between, soul meets with soul through speech. We feel that we have in speech something essential to our nature here on earth. And indeed our speech is the earthly reflection of our life in the Logos, in the cosmic Word. Thus it is particularly interesting to understand the connection of what man attains by great efforts here on earth, as speech and language, with the metamorphosis of speech and language yonder in the pre-earthly life. Indeed, when we study this relationship, we are led to perceive how the human being is inwardly constructed and organised out of the very element of spoken sound and music. And it is a happy coincidence at the present moment that in the cosmological studies we have pursued for some weeks, I can to-day insert the chapter on the expression of the human being through the words of speech and the sounds of song. It is our great pleasure in these days to be having so excellent a performance of song, here in our Goetheanum building.1 Allow me therefore to-day, if I may say so, to express my personal gratitude for this happy artistic event in our midst, by telling you a little of the connection between the speech and song of man here on earth, and his life in that element which corresponds to the Sound in speech and song, in the spiritual world. If we study the human organism as it stands before us here on earth, we know that it is through and through an image of the spiritual. Everything here—not only what man bears in himself, but also what surrounds him in external nature—is an image of the spiritual. Now when man expresses himself in speech or in song, he is really manifesting his whole nature—body, soul and spirit—not only outwardly but inwardly. In all that he brings forth by way of sound—whether the articulate sounds of speech or the musical notes of song—the full human being is in fact contained. How deeply and fully he is contained, we only begin to see when we understand more in detail what the human being is in that he speaks or sings. Let us take our start from speech. In the historic evolution of mankind, speech, as we know, proceeded from something which originally was song. The farther we go back into pre-historic ages, the more does speech become recitative and eventually song. In distant ages of human evolution upon earth, the expression of the human being through sound was not really differentiated into song and speech, but these two were one. What is so often referred to as the primeval language of man was such that we might as well speak of it as a primeval song. But we will now study speech in its present condition, where it has become very far removed from the pure element of song, and is steeped in the prosaic and intellectual quality. If we take speech as we have it to-day, we find in it two essential elements—consonant and vowel, All that we bring forth in speech is composed of a consonantal and of a vowel element. Now, the consonantal element is in reality entirely based upon the finer plastic structure of our body. Whether we pronounce a B or a P, an L or an M, in each case it rests upon the fact that something or other in our body has a certain plastic form. Nor is this confined by any means to the organs of speech and song alone. These organs only represent the highest culmination of what is here meant. For when the human being brings forth a musical note in song or an articulate sound in speech, his whole body really takes part in the process. The process that goes on in the organ of speech or song is but the final culmination of something that is taking place through the whole human being. Our human body therefore, as to its plastic form and structure, may really be conceived as follows. We take all the consonants there are in any language. They are always variations of twelve primary consonants, and indeed in the Finnish language you still find these twelve preserved very nearly in their pure, original nature; eleven are quite distinct, only the twelfth has grown a little indistinct, but it, too, is still present. Now, these twelve original consonants when rightly understood (and each of them can at the same time be conceived as a form), these twelve consonants taken together really represent the entire plastic structure of the human body. We may say therefore, without speaking figuratively in the least:—the human being is plastically expressed by the twelve primeval consonants. What then is this human body? From the point of view—the musical point of view—we are now taking, the human body is nothing else than a great musical instrument. Even the external musical instruments—the violin or any other instrument of music—even these you can best understand by somehow perceiving in their form and shape a consonant or consonants. You must see them, as it were, built up out of the consonants. When we refer to the consonant element in speech, there must always be something in our feeling reminiscent of musical instruments; and the totality, the harmony of all consonants, represents the plastic sculpture of the human body. And the vowel element—in this we have the soul which plays upon the instrument. The soul provides the vowel nature. Thus when you embody in speech the consonant and vowel elements, you have in every manifestation of speech or of song a self-expression of the human being. The soul of the human being plays in vowels upon the consonants of the musical instrument—the human body. Now if, as I said, we are considering the speech that forms a part of present-day civilisation, we find that our soul, whenever it brings forth vowel sounds, makes use to a very great extent of the brain, the system of head and nerves. In earlier ages of human evolution, this was not the case to the same degree. Let us consider for a minute the system of head and nerves. The whole structure of the head is permeated by forces which run along the nerve-strands. Now the activity which the nerve-strands here develop is entered and permeated by another activity, namely that which comes about through our breathing-in the air. The air which we breathe in passes through the spinal canal right up into the head, and the impact of the breathing beats in unison with the movements that are executed along the nerve-strands. Pressing upward to the head through the spinal canal, the current of the breath is perpetually meeting with the activity of the nerves in the head. We have not a separate nervous activity, and a separate breathing activity; we have in the head a harmony and mutual resonance of breathing activity and nervous activity. Now the man of to-day, having grown prosaic in his ordinary life, sets more store by the nerve forces than by the breathing impulses. He makes more use of his nervous system when he speaks; he permeates with nerve, if we might put it so, the instrument which through its consonantal nature shapes and forms the vowel currents. In earlier ages of human evolution, this was not the case. Man lived not so much in his nervous system; he lived in the breathing system. Hence the primeval language was more like song. Now when the man of to-day sings, he takes what he does in speech—where he permeates it with the nervous activity of the nervous system—and restores it to the current of the breath. He consciously calls into activity this second stream—the breathing. It is the continuation of the breathing into the head which is directly called into activity when, as in song, the uttering of the vowel is added to the bringing forth of the note. But here in song man does not leave the element of breath; he takes back his now prosaic language into the poetic and artistic nature of the rhythmic breathing process. The poet of to-day still strives to maintain the rhythm of the breath itself in the way he shapes and moulds the language of his poems. And he who writes for song takes it all back again into the breathing process (including the breathing process of the head). Thus we may say, the very process which man must undergo here on earth, in that he adapts his language to earthly conditions, is reversed in a certain sense when we pass from speech to song. Song is indeed a. real recollection—though by earthly means—of that which we experienced in the pre-earthly life. For in our rhythmic system we are far nearer to the spiritual world than in our thinking system. And it is of course the thinking system which takes hold of speech when speech becomes prosaic. When we utter the vowel sounds, we press what is living in our soul down into the body; and the body, by adding the consonantal element, does but provide the musical instrument for our soul to use. You will certainly have the feeling that in every vowel there is something of the soul, immediate and living. The vowel can be taken by itself. The consonant on the other hand is perpetually longing for the vowel, tending towards it. The plastic instrument of the body is in fact a dead thing until the vowel nature—the soul—strikes its chords. You can see this in detailed examples. Take for instance, in certain dialects of Middle Europe, the word mir as in the phrase Es geht mir gut. When I was a little boy, I simply could not conceive that the word should be written as it is. I always wrote it mia; for in the r the longing towards the a is quite inherent. Thus when we perceive the human organism as the harmony of all consonants, we find in it everywhere the longing for the vowel nature, that is to say for the soul. Now we are driven to ask, what is the origin of all these things? This human body, in the whole arrangement of its plastic structure here on earth, has to adapt itself to the earthly conditions. It is shaped as it is, because the earthly position of equilibrium and the whole system of the earthly forces would not allow it to be otherwise. And yet all the time it is shaped out of the spiritual world. This matter can be understood only by deeper spiritual-scientific research. The soul-nature, manifesting itself through the vowels, strikes upon the consonantal nature, which is plastically shaped and formed in accordance with earthly conditions. If we lift ourselves into the spiritual world, in the way I have described in my book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and its Attainment, we first attain Imagination or Imaginative Cognition, as I have often told you. Now when we reach this point, we find that we have lost the consonants. We still possess the vowels, but the consonants—to begin with at any rate—are lost. In the Imaginative condition, we have in effect lost our physical body—i.e. we have lost the consonants. In the Imaginative world, the consonants no longer appeal to us. To describe what we have in that world adequately in spoken words, our words would have to consist, to begin with, of vowels only. We have lost the instrument, and we enter a pure world of sound, where the vowels are indeed coloured and shaded in manifold variety, but all the consonants of earth are in effect dissolved away in the vowels. You will therefore find that in those languages which were not yet so far removed from the primeval, the things of the super-sensible world were named in words consisting of vowels only. The word Jahve for example did not contain our present form of J or V. It consisted only of vowels, and was half-scanned, half-sung. We enter here into a vowel-language which it is only natural to sing. And when we reach from Imaginative to Inspired Cognition—when therefore we receive the direct manifestations of the spiritual world—then all the consonants we have on earth are changed into something quite different. The consonants, as such, we lose. But in place of it, a new thing comes forth in the spiritual perception which comes to us in Inspiration. And this new thing we find to be none other than the spiritual counterparts of the consonants. But the spiritual counterparts of the consonants are not there between the vowels; they live in them. In your speech here on earth you have the consonants and vowels side by side. You lose the consonants as you ascend into the spiritual world. You live your way into a vowel world of song. To put it truly one must say, “It sings,” for you yourself no longer sing. The World itself becomes cosmic song. But all this vowel world is variedly coloured or shaded in a spiritual sense. In effect, there is something living in the vowels—namely the spiritual counterparts of the consonants. Here on earth we have the vowel sound A for example, and—if you will the note C sharp in a certain octave. But when we reach the spiritual world, we do not have one A, or one C sharp in a given octave, but countless ones differing in inner quality. For it is another thing, whether a Being from the Hierarchy of the Angeloi speaks A to one, or a Being of the Hierarchy of the Archangeloi, or some other Being. Outwardly the manifestation is the same, but it is filled in each case with a different inner soul. We may say therefore:—Here on earth we have our body. The vowel sound strikes into it. Yonder in the spiritual world we have the vowel sound; and the soul strikes into it, and lives in it, so that the sound becomes the body for the soul. You are immersed in cosmic music, cosmic song; you are within the creative sound—within the creative Word. Let us now consider sound as it is on earth, including spoken sound. Sound has its earthly life in the element of air. It is, however, but a childish conception of Physics to believe that the peculiar forms in the air are the reality of sound. It is really childish. Imagine, for a moment, you have a piece of ground, and on it stands a man. The ground is most certainly not the man, yet the ground must be there for the man to stand on. Without it, the man himself could not be there. It will not therefore occur to you to seek to understand the man by examining the soil beneath his feet. In the same way the air must be there for the sound to have a basis of support. Just as man stands on the soil—only in a rather more complicated way the sound has its “soil,” its necessary basis or resistance in the air. For the sound itself, the air signifies no more than does the soil for the man who stands on it. The sound presses forward to the air, and the air gives it the possibility to stand. But the sound itself is spiritual. Just as the man is different from the earthly soil on which he stands, so, is the sound different from the air upon which it stands—in which it finds its support though of course in a more complicated way, in a manifold and varied way. Through the fact that we on earth can only speak and sing by means of the air, we have in the airy forming of the sound the earthly image of a thing of soul and spirit. The soul-and-spirit of sound belongs to the super-sensible world, and that which dwells here in the air is fundamentally the body of the sound. We need not therefore be surprised if we find the sound again in the spiritual world, though shorn of that which comes from the earthly—the earthly consonant-articulation. The vowel only is carried over there. The sound as such in its spiritual content goes with us when we rise into the spiritual world, only there it becomes filled with soul. Instead of being shaped and moulded outwardly by the nature of the consonants, the sound is inwardly ensouled. Now all this runs parallel with man's entry into the spiritual world in the widest sense. Think for a moment, my dear friends, man passes through the gate of death. The consonants he soon leaves behind, but the vowels—and especially the manifold intonations of the vowels—these he experiences all the more strongly, only with this difference. He no longer feels the sound proceeding from his own larynx, but he feels that there is singing all around him, and that in every sound of the song, he himself is living. It is so in the very first days after man passes through the gate of death. He is dwelling in a musical element, which is at the same time an element of speech; and this musical element reveals ever more and more as it becomes filled with living soul from the spiritual world. Now, as I have told you, man's going forth into the Universe after he has passed through the gate of death is at the same time a passing from the earthly world into the world of the stars. When we describe such a thing as this, we seem to be speaking in images, but our images none the less are reality. Imagine here the Earth. Around it are the planets, then the heavens of the fixed stars, conceived from time immemorial—and rightly so—as the Animal Circle or Zodiac. Man standing on the Earth sees the planets and the fixed stars in their shadowed radiance. He sees them from the Earth—or, shall we say, with due respect to earthly man, he sees them “from in front?” (The Old Testament, as you know, expressed it differently.) After death, when man goes farther and farther from the earth, he gradually comes to see the planets as well as the fixed stars “from behind.” But there he does not see these points of light or surfaces of light which are seen from the earth. Rather does he see the spiritual—the corresponding spiritual Beings. On all sides it is a world of spiritual Beings. Wherever he looks back, whether it be towards Saturn, Sun or Moon, or towards Aries, Taurus and the other constellations, he sees from yonder side the spiritual Beings. But this seeing is at the same time a hearing; and when he says:—Man sees from the other side—or from behind—Moon, Venus, Aries, Taurus and so forth, we might equally well express it thus:—Man hears the Beings, who have their dwelling in these heavenly bodies, resounding forth into the cosmic spaces. Try to imagine it in its totality. (It really looks as though we were speaking figuratively, but we are not, it is absolutely real.) Imagine yourself out there in the Cosmos—the planetary world farther from you now, the Zodiac with its twelve constellations nearer. From all the heavenly bodies it is singing, speaking as it sings to you, singing as it speaks; and all your perception is a listening to the speaking song, the singing speech of the World. You look out in the direction of Aries, and as you do so, receive the impression of a consonant soul-nature. Behind Aries maybe, is Saturn, a vowel element of soul. And in this vowel element as it radiates out into the cosmic space from Saturn—in it there dwells the soul-and-spirit Consonant:—Aries, or in another instance, Taurus. Thus you have the planetary sphere singing to you in vowels—singing forth into the cosmic spaces; and the fixed stars permeate the song of the planetary sphere with soul from the consonants. Picture it to yourselves as vividly as you can:—the sphere of the fixed stars at rest, and behind it the wandering planets. Whenever a planet in its course passes a constellation of the fixed stars, there bursts forth not a single note, but a whole world of sound. Then as the planet passes on from Aries to Taurus, a different world of sound rings forth. But behind it there follows, let us say, another planet:—Mars. Mars passing through the constellation of Taurus, causes a different world of sounds to ring forth once more. Thus you have in the heavens of the fixed stars, or the Zodiac, a wondrous cosmic instrument of music, while from behind it our planetary Gods are playing upon this instrument. We may truly say, my dear friends, when man down here on earth takes back his speech (which is now formed for his earthly needs, just as his walking is transformed, for earthly needs, from his spiritual power of orientation in the Cosmos)—when therefore man takes speech back again into the element of song, he really inclines himself to that cosmic pre-earthly existence from out of which he is born for earthly life. And indeed, all Art comes before man in this sense. It is as though, whenever he expresses himself in Art, he were to say, “’Tis human destiny—and rightly so that man as he begins his earthly course of life is placed into the midst of earthly conditions and must adapt himself to these. But in Art he goes back again a little step, leaves the earthly life to take its course around him, and retreating for a moment approaches once more the world of Soul and Spirit—the pre-earthly life from which he has come forth.” We do not understand Art, my dear friends, unless we feel in it the longing to experience the Spiritual—though it be but manifested, to begin with, in a world of beautiful semblance. Our creative fancy, whereby we develop all artistic things, is at bottom nothing else than the power of clairvoyance in an earthly form. We are tempted to say:—As sound dwells on earth in the element of air, so it is with the nature of the soul itself. That which is truly spiritual in the pre-earthly life has its earthly dwelling in the image of the spiritual. For when man speaks, he makes use of his whole body. The consonant nature becomes in him the plastic sculpture of the human frame, and the Soul makes use of the current of the breath which does not enter into solid form, to play upon this plastic instrument of music and now, in a twofold way we can turn once more to the Divine, what we thus are as human beings speaking upon earth. Take the consonantal human frame. Suppose we loosen it as it were from the solid form wherein the earthly forces—gravity and the like—or the chemical forces in the foodstuffs have enchained it. Suppose we liberate the consonant nature that permeates the human being for so we may now describe it. When we place a lung on the dissection table we find chemical substances in it, which we can investigate by chemical methods. But this is not the lung. What is the lung? It is a consonant, spoken forth out of the Cosmos, which has taken plastic form. The heart, if we lay it on the dissection table, consists of cells which we can investigate chemically and find the substances composing it. But this is not the heart. The heart again is a consonant—another consonant, spoken forth out of the Cosmos. And if we conceive the whole twelve consonants, cosmically spoken and resounding forth, we have in all essentials the human bodily frame. Thus as we look to the consonants, if we have the necessary clairvoyant power of imagination to see them in their real connection, there arises before us the human body in its plastic shape. If then we take the consonants out of the human being, we have the Art of Sculpture. If on the other hand we take the breath, which the soul uses to play upon the bodily instrument in song—if we take the vowel nature out of the human being, there arises the musical art, the Art of Song. Once more:—Take the Consonant-nature out of the human being, and there arises Form, which you must mould in plastic art. Take the Vowel-nature out of the human being, and there arises Song—Music, which you must sing. Man as he stands before us here on earth proceeds out of the two Cosmic Arts—a Cosmic Art of Sculpture from the one side, and a cosmic Art of Song or Music from the other. Two kinds of spiritual Beings join their activity together. The one provides the instrument, the other plays upon it; the one forms and moulds the instrument, the other plays upon it. Can we wonder that in olden time, when things like these were felt, it was said of the greatest of all artists, Orpheus, that his command over the soul was such that he was able, not only to use the ready-moulded human body as an instrument, but to cast even amorphous matter into plastic forms—forms which correspond to the notes of his music. My dear friends! You will understand that when we describe such things as these we must depart a little in our use of words from what is usual in this prosaic age. Nevertheless what I have said is not intended in a figurative or symbolic but in a most real sense. These things are indeed such as I have described them, albeit to describe them we must sometimes bring our language into greater flow and movement than is customary in its use to-day.
|
| 284. Two Paintings by Raphael
05 May 1909, Berlin Translated by Rick Mansell Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The picture called “The School of Athens” (so-called in Baedeker, but it would be better if this name were allowed to disappear), and the picture called the “Disputa”—what do these, pictures represent when we study them in order to discover the great thoughts that underlie them, as well as the artistic impression they make upon us? I have had the opportunity of seeing these pictures several times; as you know, they are in Rome, at the Vatican, in the famous Raphael Room ... |
| Her expression conveys to us that which is living in the heads and souls of the men, until we come to her white garment, the garment of innocence, showing us that the force which comes from the mere working of the things of sense has not yet been active in her. We understand the countenances of the men when we understand what this female figure expresses. And now let us pass to the other female figure on the right-hand side of the same picture. |
| We could really reconstruct a great part of the history of man from the whole way in which Raphael has worked out this motif, with his great knowledge and understanding and his wonderful artistic powers. All that is living in the souls of the men is brought to expression in this woman figure, which we find four times repeated in the pictures. |
| 284. Two Paintings by Raphael
05 May 1909, Berlin Translated by Rick Mansell Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A study of two of the most significant pictures in the world can help us to see the way in which the Theosophist should make his life's ideal into the very content of his soul. By means of these two pictures Raphael was able, in an age of great artistic development, to give utterance to the impressions and feelings which passed through his soul concerning the evolution of mankind through many centuries. The picture called “The School of Athens” (so-called in Baedeker, but it would be better if this name were allowed to disappear), and the picture called the “Disputa”—what do these, pictures represent when we study them in order to discover the great thoughts that underlie them, as well as the artistic impression they make upon us? I have had the opportunity of seeing these pictures several times; as you know, they are in Rome, at the Vatican, in the famous Raphael Room ... You can always see people standing there with their guide-books and reading: This is Socrates, that is Plato, that other is Aristotle, and so on. They are immensely pleased when Baedeker enables them to discover whom this or the other figure represents, whether this one here is a bishop or an early Father of the Church, whether another is Paul or Peter or Moses … But how little has all this to do with the artistic value of the pictures! I should like to suggest by rather a grotesque supposition how one can approach such pictures in an artistic way. In this case the artistic and theosophical methods of approach are one and the same. We know that there are inhabitants of Mars, although they are of course very different in appearance from the inhabitants of Earth. For us however they are very real beings. To be sure, we do not interest ourselves in that wild idea of some modern visionaries as to whether it might not be possible to draw the theorem of Pythagoras in lines of electric light over a great tract of Siberia and in this way set up communication with the inhabitants of Mars. We will leave such dreaming to the materialistic visionaries of our day. Anyone who takes his stand on the ground of reality knows that the inhabitants of Mars are of quite a different nature from those of Earth. But now let us suppose that one of these Mars inhabitants were to descend to Earth and let us imagine that he visited the Vatican picture-galleries and saw there these two pictures by Raphael. We could not expect that he should at once study the whole history of Greek philosophy and the whole spiritual development of the Middle Ages, in order that we might be able to converse with him in our own way. For it would, you know, seem quite ridiculous to him if we were to begin explaining, “Here is Augustine, there is Ambrose,” and so on. If he could speak an earthly language at all, he would probably reply, “I do not know these gentlemen!” We have a general acquaintance with them, having assimilated certain ideas about them—whether right or wrong need not concern us now. The artistic impression produced upon one by these pictures is not altered in the least because the beholder happens to be an inhabitant of Mars, who knows nothing of Mr. Aristotle or Mr. Plato or Mr. Socrates; for the artistic impression depends solely and entirely upon what confronts us in the picture, and makes itself best felt when we pay no attention at all to anything but what speaks from the picture itself. The inhabitant of Mars would therefore really be the best observer from a purely artistic point of view. Let us try to enter into the feelings of such a one on his first descent to Earth, who has not been given a handbook of Greek and Mediaeval philosophy. He would say to himself: “I see figures, human figures, in these pictures—but I see no figures like them among the men of to-day.” For indeed it is hardly likely that among the people standing there with him and looking at the pictures he should recognise any as being persons of like dignity and importance. He would however become aware in the pictures of something that must have grown out of the life of Earth itself. He would read in them that the inhabitants of Earth desire to say something which is not connected with any particular moment of time, but with the whole of Earth. He could contemplate the one picture and say “Here I see very remarkable forms,—two figures in the centre, and on their right and left other figures. I notice a certain expression—the uplifted hand of the one, the hand of the other pointing to the ground,”—and so on. (He would see all this without having any knowledge of Plato or Aristotle.) “There are also persons doing something or other in various parts of the picture. And around all these human beings is nothing but quite simple architectural forms. It can however also be seen that in the hearts and souls of these people something is living. That can quite clearly be noticed!” Now suppose the inhabitant of Mars turns his attention to the other picture. It has quite a different appearance. There he sees, down below, a world which looks much the same as our external world to-day. Up above, he finds a scene that could only be represented by bringing together things which do not belong together in the external world. For there we behold human forms among the clouds—and yet in such a way as to recall something quite real and true. And higher up still, above this interweaving of the forms of clouds and men, figures are to be seen on a golden background which have little left to remind one of the human form. What would the visitor from Mars say,—who knows nothing of the spiritual life of Earth, and only judges the pictures by what they themselves tell him? He would be compelled to say: “These men have the Earth around them; but there are times when they feel the need to express a world the physical eyes do not see, a world completely remote from the senses, and which they can only represent by clouds and human forms interwoven together, and by forms on a golden background that bear no resemblance to man. There must therefore be something by means of which these men are able to raise themselves; they must have inner forces, stronger than all, they meet with in the world of sense. That other world must have come into some relation with them.” And he would ask himself the question: “How did these men come into touch with that other world?” He would then see the wonderful group which we call “God the Father,” “God the Son,” and “The Dove” as the expression of the Spirit; and, below, an Altar, and upon it the Host, the symbol of the Lord's Supper. Since the evolution of Mars is not yet so far advanced as the evolution of Earth, there is nothing on Mars like what we have on Earth in the two thousand years' tradition of Christianity. The visitor from Mars would accordingly not know what this picture represents. But from the relation of the groups on the right and left to the central group he could see that through the power of the symbol something is being given to the souls which opens to them the higher worlds. Our visitor would then examine the pictures more closely and discover that in the first picture there are all manner of figures, but among them in particular two female figures, one on the right hand and one on the left. And remarkable figures they are! As one looks at them it is evident that they differ totally in their expression and even in their dress. Let us study them a little. Looking at the one on the left (we are standing in front of the so-called “School of Athens”), we see in the whole expression something indicative of the Earthly kingdom of sense here below, and of what the senses directly give us. Male figures stand all around; and one dimly feels that what dwells in the heads of these men belongs to the world of sense. What presents itself to us in the female figure? Her expression conveys to us that which is living in the heads and souls of the men, until we come to her white garment, the garment of innocence, showing us that the force which comes from the mere working of the things of sense has not yet been active in her. We understand the countenances of the men when we understand what this female figure expresses. And now let us pass to the other female figure on the right-hand side of the same picture. She is quite different, and already begins to notice what the men are doing. Whereas the left-hand figure indicates only the physical environment, the right-hand figure is following what the men have done, her gaze follows what the human spirit has brought forth. Even if we know nothing of Greek Philosophy, we can quite clearly see that there is an advance from the left to the right side of the picture. On the right hand we see what the men have made of their environment. (It really goes much further; it is expressed also in the colour.) Now these two women appear also in the other picture, which is called the “Disputa.” Here again we see the figure first on the left, where people are standing, contemplating with rapture the symbol in the centre. We are looking into early times when the Christian religion was still entirely a religion of feeling, when Wisdom itself was still nothing but feeling. On every countenance we can see a kind of enthusiasm for Christianity, and all hearts are filled with warm feeling. This is reflected too in the female figure. And now when we pass to the other side of the picture we see again a progress. Here we have the Christian philosophers who have brought their knowledge to bear on the whole content of the Christian Wisdom. There is St. Augustine dictating, and the woman writing it down. We could really reconstruct a great part of the history of man from the whole way in which Raphael has worked out this motif, with his great knowledge and understanding and his wonderful artistic powers. All that is living in the souls of the men is brought to expression in this woman figure, which we find four times repeated in the pictures. The above is no more than a first rough sketch for a consideration of these pictures. The two paintings have to be studied together one after the other. They are an expression of what happened from the pre-Christian age down to the later part of the Middle Ages, and they express it in artistic form. Just imagine how great and mighty must have been the impression made upon a really sensitive soul who saw these pictures, first one and then the other, and said to himself:—“I am myself inter woven into this onward path of Wisdom, which mankind follows in the course of evolution; I am part of it, I belong to the march of events as it is shown in these pictures.” For the man who understood the sense of evolution in those days really felt this. He looked back to the pre-Christian age when men were surrounded only by the world of sense, just as the architecture surrounds the people in the picture; and he beheld too a time when through the entrance of Christ Jesus into human evolution the spiritual was revealed to mankind. He felt that he belonged to all this; he felt how his own existence takes part in the life of thousands and thousands of years. What lived in men's souls was borne along the flow of fantasy and streamed into the hand of the painter, who painted these pictures in order that men should meet in the outer world that which dwells in the inner world. For the Theosophist these pictures can he an earnest call and summons to inscribe the great ideal into his soul. Let us look with the eye of the spirit at the “Disputa.” In the centre we see “God the Father,” then “God the Son” or Christ, and below, the Dove or the Holy Spirit. And now let us recall many other pictures that are to be found in various galleries. Whenever you have opportunity to visit picture galleries, you will find pictures of this kind, created out of good and great traditions. You will often meet with the following motif,—Christ coming forth from a figure like a bird, Christ being born as it were from a winged being. For the whole mystery of Christ, His whole descent from the higher worlds was formerly felt as a kind of breaking loose from a nature which had itself been born as a higher world,—higher even in the spatial sense. Hence the descent out of a birdlike form. Christ born from the bird,—let us hold the motif before our soul, and with that study the “Disputa.” Here we find another “bird-being,”—the. Dove of the Spirit. The Dove of the Spirit, what a great riddle that is among all the Christian symbols! Much, very much is contained within it. The painters of the future will have to paint what comes to birth from out of this Dove of the Spirit. This Dove of the Spirit is a transitory symbol; something else will take its place in the Trinity. The day will come when from the Dove of the Spirit will be born, as it were, the human soul that is liberated by the wisdom of Theosophy. Every human soul that has the will to receive the spirit of Theosophy will be born again at a higher stage—spiritually, in a new form. This Dove of the Spirit will break its form, and from it will come forth the human soul which will have for its life-blood the spiritual conception of the world which meets us to-day in its first form as Theosophy. Other figures, new figures, will be around the symbol. And these liberated ones will show in their countenances what is living in their souls,—how through the events of the spiritual world as they reveal themselves to one who can rise above the world of sense, the soul is set free, and how then these liberated souls can each confront every other with real brotherly love. And so it seems to me good that we should sometimes have these pictures before us, inasmuch as they are at the same time a prophetic foreshadowing of a third picture, A pre-Christian conception of the world is expressed in the first picture; the second expresses what has come about through Christ in the world of form; and what will come about through the Spirit, which has been sent by Christ and will divest itself of its coverings, will be expressed in the third picture that can stand before the soul of every Theosophist as a great and mighty ideal. This picture cannot be painted yet, for the models are not yet here; but in our own souls the two pictures must already be finding their completion in the third … |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Acanthus Leaf
07 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The acanthus motif, as we have seen, was created purely from the spirit and only in its late development came to bear a remote resemblance to the acanthus leaf. Artistic understanding in future ages will simply be unable to understand this attitude of mind which in our time influences not only the art experts who are supposed to understand their subject, but all artistic creation as well. |
| Some time, my dear friends, we shall understand what really underlies the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, but not until we grow out of the unfortunate habit which makes us perpetually ask, ‘What is the meaning of this or that?’ |
| When this habit is eliminated from our Movement we shall really come to understand what underlies artistic form—that is to say, we shall either have direct perception of true spiritual movement, or of the corresponding etheric phenomenon. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Acanthus Leaf
07 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A thought that may often arise in connection with this building is that of our responsibility to the sacrifices which friends have made for its sake. Those who know how great these sacrifices have been, will realise that the only fit response is a strong sense of responsibility, for the goal at which we must aim is the actual fulfilment of the hopes resting in this building. Anyone who has seen even a single detail—not to speak of the whole structure, for no conception of that is possible yet—will realise that this building represents many deviations from other architectural styles that have hitherto arisen in the evolution of humanity and have been justified in the jugdment of man. An undertaking like this can of course only be justified if the goal is in some measure attained. In comparison to what might be, we shall only be able to achieve a small, perhaps insignificant beginning. Yet, may be, this small beginning will reveal the lines along which a spiritual transformation of artistic style must come about in the wider future of humanity. We must realise that when the building is once there, all kind of objections will be made, especially by so-called ‘experts,’ that it is not convincing, perhaps even dilettante. This will not disconcert us, for it lies in the nature of things that ‘expert’ opinion is least of all right when anything claiming to be new is placed before the world. We shall not, however, be depressed by derogatory criticism that may be levelled at our idea of artistic creation, if we realise, as a compensation for our sense of responsibility, that in our age, the origin of the Arts and of their particular forms and motifs is greatly misunderstood by technical experts. And then, gradually, we shall understand that all we are striving to attain in this building stands much closer to primordial forces of artistic endeavour which are revealed when the eye of the Spirit is directed to the origin of the Arts, than do the conceptions of art claiming to be authoritative at the present time. There is now little understanding of what was once implied by the phrase “true artistic conception.” It need not therefore astonish us if a building like ours, which strives to be in harmony with primordial Will and in accordance with the origin of the arts, is not well or kindly received by those who adhere to the direction and tendency of the present age. In order to bring home these thoughts to you, I should like to start to-day by considering a well-known motif in art—that of the so-called acanthus leaf—showing the sense in which our aims are in harmony with the artistic endeavours of humanity as expressed in the origin of this acanthus leaf as a decorative motif. Now because our endeavours are separated by many hundreds, nay even thousands of years, from the first appearance of this acanthus motif, they must naturally take a very different form from anything that existed in the days when, for instance, the acanthus leaf was introduced into the Corinthian capital. If I may be permitted a brief personal reference here, let me say that my own student days in Vienna were passed during the time when the buildings which have given that city its present stamp, were completed—the Parliament Buildings, the Town Hall, the Votivkirche and the Burgtheatre. The famous architects of these buildings were still living: Hanson who revived Greek architecture, Schmidt who elaborated Gothic styles with great originality, Ferstel who built the Votivkirche. It is perhaps not known to you that the Burgtheatre in Vienna was built according to the designs of an artist who in the seventies and eighties of the last century was the leading influence in artistic appreciation and development of form in architecture and sculpture. The Burgtheatre was built according to the designs of the great Architect, Gottfried Semper. At the Grammar School I myself had as a teacher a gifted admirer and disciple of Gottfried Semper, in the person of Josef Baier, so that I was able to live, as it were, in the whole conception of the world of architectural, sculptural and decorative form as inaugurated by the great Semper. Now, in spite of all the genius that was at work, here was something that well-nigh drove one to despair in the whole atmosphere of the current conceptions of the historical development of art, on the one side, and of the way to artistic creation on the other. Gottfried Semper was undoubtedly a highly gifted being, but in those days the usual conception of man and the universe was an outcome of the materialistic interpretation of Darwin, and the doctrine of evolution was also apparent in the current ideas of art. Again and again this materialistic element crept into the conceptions of art. It was, above all, considered necessary to possess a knowledge of the technique of weaving and interlacing. Architectural forms were derived in the first place from the way in which substances were woven together, or fences constructed so that the single canes might interpenetrate and hold together. In short, people were saturated with the principle that decoration and ornamentation were forms of external technique. This subject of course might be further elaborated, but I only want to indicate the general tendency which was asserting itself at that time—namely, the tendency to lead everything artistic back to external technique. The standpoint had really become one of ultilitarianism and the artistic element was considered to be an outcome of the use to which things were put. All treatises on the subject of art, and especially on decoration, invariably made mention of the special idiosyncrasies of the different technical experts. This of course was a stream running parallel to the great flood of materialistic conceptions that swept over the 19th century, chief among them being the materialistic conception of art. The extent to which materialism asserted itself in all spheres of life during the second half of the 19th century was enough to drive one to despair. Indeed I still remember how many sleepless nights I had at that time over the Corinthian capital. Now the main feature, the principal decoration of the Corinthian capital—although in the days of which I am speaking it was almost forbidden to speak of such a thing as ‘decoration’—is the acanthus leaf. What could be more obvious than to infer that the acanthus leaf, on the Corinthian capital was simply the result of a naturalistic imitation of the leaf of the common acanthus plant? Now anyone with true artistic feelings finds it very difficult to conceive that a beginning was somewhere made by man taking a leaf of a weed, an acanthus leaf, working it out plastically and adding it to the Corinthian column. Let us think for a moment of the form of the acanthus leaf. The basis of all artistic creation is a consciousness that comes to a standstill before the portals of the historical evolution of humanity as depicted by external documents. A certain consciousness that was once active in man, a remnant of the old clairvoyance, belonged to the fourth Post-Atlantean period, the Graeco-Roman. Although Egyptian culture belongs to the third Post-Atlantean epoch, all that was expressed in Egyptian art belongs to the fourth epoch. In the fourth epoch this consciousness gave rise to such intense inner feeling in men that they perceived how the movement, bearing and gestures of the human being, nay even the human form itself, develop outwards into the physical and etheric. You will understand me if you realise that in those times, when there was a true conception of artistic aim, the mere sight of a flower or a tendril was of much less importance than the feeling: ‘I have to carry something heavy; I bend my back and generate with my own form the forces which make me, as a human being, able to bear the weight.’ Men felt within themselves what they must bring to expression in their own postures. This was the sense in which they made movements when it was a question of taking hold of something or of carrying something in the hand. They were conscious of a sense of carrying, of weight, where it was necessary to spread the hands and finger outwards. Then there arose the lines and forms which passed over into artistic creation. It is as though one felt in humanity itself how man can indeed go beyond what he sees with his eyes and perceives with his other senses:—he can go beyond it when he enters into and adapts himself to a larger whole. Even in this case of a larger whole, when a man no longer merely lets himself go as he walks along, but is obliged to adapt himself to the carrying of a load—already here he enters into the organism of the whole universe.
I have drawn it diagrammatically, from the side view: a number of men are walking one behind the other. They form the procession which then passes round inside the circle; others are sitting in the circle looking on.
If you think of these two figures in alternation, you have the earth-motif and the sun-motif that were always carried by the people who formed the procession. This was one thing that in olden times was presented in circling procession. The people sat around in a circle and the actors passed around in a procession. Some of them carried emblems representing man's connection with the sun; and they alternated: earth-sun, sun-earth and so on:
Man sensed this cosmic power: earth-sun, and then he began to think how he could portray it. The best medium for purposes of art proved to be a plant or tree whose forms runs upwards to a point from a wider base. This was alternated with palms. Plants having a form like a wide bud were alternated with palms. Palms represented' the sun forces; bud-forms running upwards to a point, the earth forces. Feeling his place in the cosmos, man created certain forms, merely using the plants as a means of expression. He used plants instead of having to invent some other device. Artistic creation was the result of a living experience of cosmic connections; this is in accordance with the evolution of the creative urge in man and the process is no mere imitation of outer phenomena of nature. The artistic representation of the elements of outer nature only entered into art later on. When men no longer realised that palms were used to express the sun forces, they began to think that the ancients simply imitated the palm in their designs. This was never the case; the ancients used the leaves of palms because they were typifying the sun forces. Thus has all true artistic creation arisen, from a ‘superabundance’ of forces in the being of man—forces which cannot find expression in external life, which strive to do so through man's consciousness of his connection with the universe as a whole. Now all contemplation and thought both in the spheres of natural science and art, have been misled and confused by a certain idea which it will be very difficult to displace. It is the idea that complexity has arisen from simplicity. Now this is not the case. The construction of the human eye, for instance, is much more simple than that of many of the lower animals. The course of evolution is often from the complex to the simple; it often happens that the most intricate interlacing finally resolves itself into the straight line. In many instances, simplification is the later stage, and man will not acquire the true conception of evolution unless he realises this. Now all that was presented to the spectators in those ancient times, when it was always a question of portraying living cosmic forces, was later on simplified into the decoration, the lines of which expressed man's living experience when he presented these things. This alternation of Sun-motif, Earth-motif, presented itself to the artistic feeling of mankind as a decorative motif in the truest sense. Later on man no longer realised that he must see in this decorative motif a reproduction that had passed into the subconscious realm, of a very ancient dance motif, a ceremonial dance. This was preserved in the palmette motif. Now it is interesting to consider  the following:—On the decorations of certain Doric columns one often finds a very interesting motif which I will sketch thus. In Greece, that wonderful land where the fourth Post-Atlantean period was expressed in all its fulness, there was a union of what came over from Asia with all that I have now described and which, as an after-image is there, on Doric columns together with the truly dynamic-architectonic principle of weight-bearing. This union came about because it was in Greece that the Ego was fully realised within the human body, and therefore this motif could find expression in Greek culture. Now you need only imagine what is merely indicated in the Ionic pillars, the middle portion, developing downwards to the perfect volute and you have the Corinthian column. The essential forms of art can no more arise from an imitation of nature than music can be created by an imitation of nature. Even in the so-called imitative arts, the thing that is imitated is fundamentally secondary, an accessory as it were. Naturalism is absolutely contrary to true artistic feeling. If we find that people think our forms here are grotesque we shall be able to comfort ourselves with the knowledge that this kind of artistic conception sees in the acanthus motive nothing but a naturalistic imitation. The acanthus motif, as we have seen, was created purely from the spirit and only in its late development came to bear a remote resemblance to the acanthus leaf. Artistic understanding in future ages will simply be unable to understand this attitude of mind which in our time influences not only the art experts who are supposed to understand their subject, but all artistic creation as well. The materialistic attitude of mind in Darwinism also confronts us in artistic creation, in that there is a greater and greater tendency to make art into a mere imitation of nature. My discovery of these connections in regard to the acanthus leaf has really been a source of joy to me, for it proves circumstantially that the primordial forms of art have also sprung from the human soul and not from imitation of external phenomena. I was only able really to penetrate to the essence of art after I had myself moulded the forms of our building here. When one moulds forms from out of the very well-springs of human evolution, one feels how artistic creation has arisen in mankind. It was a strange piece of karma that during the time when I was deeply occupied with following up a certain artistic intuition (this was after the forms for the buildings had already been made)—an intuition that had arisen during the General Congress in Berlin—it happened that I began to investigate what I had created in these forms, in order to get a deeper understanding. One can only think afterwards about artistic forms; if one “understands” them first and then carries them out, they will have no value. If one creates from concepts and ideas nothing of value will ensue, and the very thing that I perceived so clearly in connection with the acanthus leaf, and have shown to be erroneous, is an indication of the inner connections of the art in our building. I came upon a remarkable example which is purely the result of clairvoyant investigation. At one point I discovered a curious point of contact with Rigl, a fellow-countryman of mine. It is a curious name, not very aristocratic, but typically Austrian. This man Rigl did not achieve anything of great importance but while he was Curator of an Architectural Museum in Vienna he had an intuitive perception of the fact that these architectural decorations had not arisen in the way described by “Semperism” at the end of the 19th century. Rigl hit upon certain thoughts which are really in line with the metamorphosis of the palmette motif into that of the acanthus leaf. Quite recently, therefore, I have discovered a perfect connection between the results of occult investigation, and external research which has also hit upon this development of the so-called acanthus motif from the palmette. ‘Palmette’ is of course merely a name; what is really there in the palmette is the Sun-motif. In the first place, of course, one feels in despair about an idea like that of Rigl. He simply could not realise whence the palmette motif had originated and that it was connected with forces working and moving in man. Rigl remonstrates with the learned art critics who have brought Semper's ideas into everything and are for the most part mere naturalists, but in spite of this he did not get very far. He says that in regard to the acanthus leaf the learned art critics are still feeding upon the old anecdote quoted by Vitruvius. (It cannot be said that they are all feeding upon it, but it is true that they constantly quote it.) Rigl, however, only mentions this anecdote briefly; he does not think it worth while to go into all the details because it is too well known. What he leaves out is very characteristic. He says that Callimachos had seen a basket surrounded by acanthus leaves and that then the idea of the Corinthian column came to him. Rigl, too, leaves something out and this very thing shows that the typical conceptions of our age must despair of ever having real knowledge in this sphere. He leaves out the most important factor in the whole anecdote, which is that what Callimachos saw was over the grave of a Corinthian girl. That is the important thing, for it implies no less than that Vitruvius, although he wisely holds his tongue about it, intends to indicate that Callimachos was clairvoyant and saw, over a girl's grave, the Sun-motif struggling with the Earth-motif, and above this the girl herself, hovering in her etheric body. Here indeed is a significant indication of how the motifs of Sun and Earth came to be used on the capitals of columns. If we are able to see clairvoyantly what is actually present in the etheric world above the grave of a girl who had died, we realise that the palmette motif has arisen out of this, growing, as it were, around the etheric body that is rising like the sun. It seems as though men have never really understood the later Roman statues of Pytri-Clitia for they are nothing else than a clairvoyant impression that can be received over the graves of certain people; in these statues, the head of an extraordinarily spiritual, though not virginal Roman woman, seems to grow upwards as if from a flower chalice. Some time, my dear friends, we shall understand what really underlies the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, but not until we grow out of the unfortunate habit which makes us perpetually ask, ‘What is the meaning of this or that?’ and is always looking for symbolic interpretations such as, ‘this signifies the physical body, that the etheric body, this or that the astral body.’ When this habit is eliminated from our Movement we shall really come to understand what underlies artistic form—that is to say, we shall either have direct perception of true spiritual movement, or of the corresponding etheric phenomenon. It is actually the case that in clairvoyant vision the acanthus leaf can be seen, in its true form, above a grave. If you will consider all these things; my dear friends, you will realise how important it is to understand the forms in the interior of our building, the forms that should adorn it, and to know the artistic principle from which they have arisen. On previous occasions I used a somewhat trivial comparison, but it is only a question of understanding the analogy. Although it is trivial, it does, nevertheless, convey what it is intended to convey. When we are trying to understand what will be placed in the interior of the building in these two different sized spaces, we may with advantage think of the principle of the mould in which German cakes are baked. It would have been my wish—only it was not to be—that we should have had no such surfaces as these (pointing to an architrave). They will only be right—when something is taken away from them. This roundness here must be eliminated. It would have been better if from the very beginning we had worked with the graver's chisel for then there would have been no protuberance but only a surface. What we must do is to feel from the models how the interior decoration is the plastic vesture for the Spiritual Science that is given its in the building. Just as the interior decoration has the quality of being ‘in-carved,’ so the outer decoration will seem as though it is ‘laid on.’ The interior decoration must always have the character of being in-carved. One can feel this in the model, for the essential thing is a true inner feeling for form in space. It is this that leaves one unsatisfied even in such writings as those of a man like Hildebrandt. He has a certain idea of the workings of form but what he lacks is the inner feeling of form—the inner feeling that makes one live wholly within the form. He simply says that the eye should feel at home when it looks at form. In our building we must learn to experience the forms inwardly, so that, holding the chisel in a particular way, we learn to love the surface we are creating—the surface that is coming into being under the mallet. I, for my part, must admit that I always feel as if I could in some way caress such a surface. We must grow to love it, so that we live in it with inner feeling and not think of it as something that is merely there for the eye to look at. Just recently someone told me after a lecture that a certain very clever man had accused us of straining after ‘externalities,’ as instanced by the fact that different kinds of wood have been used for the columns in the interior. This shows how little our work has been understood. Such a thing is considered to be a dreadful externality. This very intelligent man, you see, simply cannot realise that the columns must be of different woods. The real reason why he cannot understand, is that he has not paused to consider what answer he would have to make if he were asked: ‘Why must there be different strings on a violin? Would it not be possible simply to stretch four A strings instead?’ The use of different woods is a reality in just the same sense. We could no more use only one kind of wood than we could have only A strings on a violin. Real inner necessities are bound up with this. One can never do more than mention a few details in these matters. The whole conception of our building and what must be expressed in it, is based upon deep wisdom, but a wisdom that is at the same time very intimate. Of course there will be forms which are nowhere to be found in the outer physical world. If anything bears an apparent resemblance to a form in the animal or human body, this is simply due to the fact that higher Spirits who work in nature, create according to these forces; nature is expressing the same things as we are expressing in our building. It is not a question of an imitation of nature, but of the expression of what is there as pure etheric form. It is as though a man were to ask himself: ‘What idea must I have of my own being when I look away from the outer sense-world, and try to find an environment that will express my inner being in forms?’ I am sure that everyone will be struck by the plastic forms on the capitals and in the rest of the interior. Not a single one of these forms is without its own raison d'étre. Suppose anyone is carving the column just here (pointing to an architrave motif). At another place he will carve more lightly or deeper down into the wood. It would be nonsense to demand symmetry. There must be living progression, not symmetry. The columns and architraves in the interior are a necessary consequence of the two circular buildings with the two incomplete domes. And I cannot express this any more precisely than by saying that if the radius of the small dome were at all larger or smaller in proportion to the large dome, each of these forms would have to be quite different, just as the little finger of a dwarf is different from that of a giant. It was not only the differences in dimension, but the differences in the forms that called forth the overwhelming feeling of responsibility while we were erecting the building; down to the smallest detail it could not be other than it is. Each single part of a living organism has to exist within and in accordance with the whole living organism. It would be nonsense to say: I want to change the nose and put a different organ in the place where the nose now is.' It is a matter of actual fact that the big toe, and the small toe as well, would have to be different if the nose were different. Just as nobody in his senses would wish to re-model the nose, so it is impossible that the form here should be other than it is. If this form were different, the whole building would have to be different, for the whole is conceived in living, organic form. The advance we must make is this: all that was, in the early days of art, a kind of instinctive perception of a human posture transformed into artistic form must now enter with consciousness into the feeling life of man. In this way we shall have, in our interior decorations, etheric forms that are true and living, and we shall feel them to be the true expression of all that is to live in our building. It simply cannot be otherwise. Now the other day I received two letters from a man who, ten years ago, it is true, did belong to the Anthroposophical Movement, but who since then has left it. He asked me if he could be allowed to make the windows, for he was so well qualified for the work. He was really very insistent. But when you see the windows you will understand that they could only be made by somebody who has followed our work right up to the present. Suppose I were to press my hand into a soft substance: the impress could only be that of my hand, it could not be the head of an ox for instance! It is Spiritual Science that must be impressed into the interior decoration; and Spiritual Science must let in the sunlight through the windows in a way that harmonises with its own nature. The whole building is really constructed—forgive this analogy—according to the principle of the cake mould, only of course instead of a rising cake, it is filled with Spiritual Science and all the sacred things that inspire us. This was always the case in art, and above all it was so in the days when men perceived in their dim, mystical life of feeling the alternation of the principles of earth and sun in the living dance and then portrayed the dance in the palmette motif. So it must be when it is a question of penetrating the outer sense- veil of natural and human existence and expressing in forms things that lie behind the realm of sense perception—if, that is to say, we are fortunate enough to be able to carry this building through. How inner progress is related to the symptoms of onward-flowing evolution—this is what will be expressed in the building, in the dimensional proportions, forms, designs and paintings. I wanted to place these thoughts before you in order that you may not allow yourselves to be misled by modern conceptions of art, which have put all true understanding on one side. A good example of this is the belief that the Corinthian capital arose primarily from the sight of a little basket with acanthus leaves around it. The truth is that something springing from the very depths of human evolution has been expressed in the Corinthian capital. So also we shall feel that what surrounds us in our building is the expression of something living in the depths of human nature behind the experiences and events of the physical plane. To-day I only wanted to speak of this particular detail in connection with our building and with a certain chapter in the history of art. There may be opportunities during the coming weeks to speak to you of other things in connection with some of the motifs in the building. I shall seize every available opportunity to bring you nearer to what is indeed full of complexity, but yet absolutely natural and necessary, in a spiritual sense, for our building. In our days it is not at all easy to speak about problems of art, for naturalism, the principle of imitation, really dominates the whole realm of art. So far as the artist himself is concerned, naturalism has arisen out of a very simple principle; so far as other people are concerned it seems to have arisen from something less simple. The artist, when he is learning must, of course, copy the productions of his master; he must imitate in order to learn. Man now imitates nature out of instinct—for he has made the principle of pupil into that of master and has then put the master on one side because he will brook no authority. This principle is very convenient for artists, for they do not want to get beyond an artistic reproduction of the models before them. The layman to-day understands the principle of naturalism as a matter of course. Where can he find anything to take hold of when he sees forms like those in our building? How are these forms to stimulate any thought at all? He will tear his hair and ask, with a shrug of his shoulders: ‘Whatever is this?’ And he will be lucky if he finds anything at all to take hold of, for instance, if he discovers that some detail has a slight resemblance, maybe to a nose! Although this may be negative, he is delighted that he has discovered anything at all. To-day the layman is pleased if when he finds in the different arts something that transcends the purely naturalistic element, he can say: ‘This has a resemblance to something or other.’ Art will most certainly be misunderstood if people continue to think that it is only legitimate to express things that resemble something or other in the external world. Real art does not ‘resemble’ anything at all; it is something in itself, sufficient unto itself. And again from this point of view it was despairing to find that as a result of the materialism of the second half of last century, painters (not to speak of sculptors) were asking themselves for instance: ‘How am I to get the effect of that mist in the distance?’ And then all kinds of attempts were made to reproduce nature by pure imitation. It really was enough to drive one to despair! Ingenious things were produced, it is true, but what is the value of them? It is all far better in nature herself. The artists were wasting their time in their efforts to imitate, for nature has it all in a much higher form. The answer to this problem is to be found in the Prologue to “The Portal of Initiation.” [The first of Dr. Steiner's Mystery Plays.] Not long ago we happened to be going through the Luxemburg Gallery in Paris, and we saw a statue there. At first sight it was exceedingly difficult to make out what it was supposed to be, but by degrees it dawned on one that perhaps it was meant to represent a human figure. It was so distorted .... I will not imitate the posture, for it would be too much of a strain on the shoulders and knees! It is an absolutely hideous production, but I assure you that if it were to meet one in nature it would be much easier to understand than this “work of art.” People to-day do not realise the absurdity of giving plastic form to a motif that has been thought out, for there is, as a matter of fact, no real necessity to give it plastic form. That which is to be given plastic form must from the very beginning be there in itself and only conceived of plastically. No true sculptor will say that Rodin's productions are an expression of true plastic art. Rodin models non-plastic motifs very well, in an external sense, but true artistic feeling will always be prompted to ask if it amounts to anything, for true plastic conception is entirely lacking. All these things are connected, my dear friends. I have told you what happened in my young days, when I was about 24 or 25 years old, when I absorbed the doctrines of Semper. Already then they were enough to drive one to despair and their influence has not been got rid of yet. Therefore I ask you—and more particularly those who are working so devotedly and unselfishly at our building with all the sacrifices that their work entails—always to try to proceed from inner feeling for what this building ought to contain and to feel in life itself the forms which must arise, in order that we may free ourselves from the trammels of much so-called modern “art.” We must realise, in a new sense, that art is born from the depths of man's being. So greatly is this prone to be misunderstood in our age that people have taken the metamorphosis of of the Earth and Sun motifs to be an imitation of the acanthus leaf. If people will stop believing the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, that Callimachos saw a basket strewn around with acanthus leaves and then used it as a motif on columns, and will listen to what he says about Callimachos having had a vision over the grave of a Corinthian girl, they will also realise that he had clairvoyant sight and they will have a better understanding of the evolution of art. They will realise that development of clairvoyance leads man to the realm lying behind the world of sense. Art is the divine child of clairvoyant vision—although it only lives as unconscious feeling in the soul. The forms that are seen by the clairvoyant eye in the higher worlds cast their shadow pictures, as it were, down to the physical plane. When people understand all that lives in the Spirit—the Spirit which has the power to impress itself into what surrounds us here in our building, finding its expression in the outer framework around us—they will also understand the goal we have set ourselves, and see in the forms of art the impress of what has to be accomplished and proclaimed in living words in our building. It is a living word this building of ours! Now that I have tried, scantily, it is true, to indicate something in regard to the interior we shall, before very long, be able to speak of the painting and also of the outside of the building.   |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The House of Speech
17 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| When I come to speak of the real nature of painting we shall understand the significance of the connection between colour and the inner element of soul in the universe. |
| Then each one of us will sit within the building and we shall say to ourselves: “The organs of the great Spirits themselves are round about us; it is for us to understand the language spoken though these forms.” But we must understand it in the heart and not merely be able to grasp it intellectually. |
| A man who tries to ‘interpret’ the myths and explain external forms may be clever and ingenious but he is like one who tries to look under his chin to explain the symbolism of his larynx. We understand the speech of the Gods by learning how to listen with our hearts, not by using intellectual agility and giving symbolic or allegorical meanings to myths and artistic forms. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The House of Speech
17 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Even more than on the last occasion when I spoke to you about our building am I reminded to-day of the attitude we must have to this edifice, dedicated as it is to the cause of Spiritual Science. The sacrifices of those who have befriended the cause of Anthroposophy call for a sense of great responsibility. To-day is a splendid occasion for reminding ourselves of this responsibility, for the first of our auxiliary buildings is to be given over to its own tasks. We can be reminded of this responsibility by studies that arise naturally out of the tasks before us and the goal we are striving to attain. The immediate use to which these rooms will be put is the production of the glass windows for our building, and we cannot help being moved by the thought that our human faculties are not really mature enough as yet to accomplish the full task before us. I think it is healthy and good that all our work should be permeated by the feeling that we have not as yet grown equal to our task, for only this can enable us to accomplish the highest that lies within our power. We shall be able to create the first beginnings of an artistic vesture for Spiritual Science—to the extent to which our epoch and our means allow—if we are always pervaded by the feeling that we are, in truth, little qualified for the full task. The site on which our building stands is pervaded by an atmosphere which seems to say: “Do the very utmost of which your powers and faculties are capable, for you cannot do nearly enough in comparison with what ought to be achieved; and even when you have done your very utmost, it will not by any means suffice.” When we look at the site of our building we should be pervaded by an indefinable feeling—a presentiment that a mighty task is hovering before us. And more particularly should this be the case to-day when we are handing over this auxiliary building to our friend Rychter and his workers, in order that they may create something that in the fairest sense may be a living member in the whole organism of our building. Entering the room through this door, our feeling will be that we are indeed blessed, as individuals, in having the opportunity to co-operate in work like this. And when we think of the functions of the windows in the building, an atmosphere of the soul and spirit will hover around us, whispering of the deep spirituality which we pray may flow like purifying waves of healing through this room. When the building is once ready we shall again and again be conscious of a feeling which I may perhaps express as follows: ‘How infinitely necessary it is to grow beyond everything personal, if the forms of this framework for our Spiritual Science are to have real meaning for us.’ This again is, in a certain sense, the satisfying element in our building. Our architects, engineers, and all the other workers may well derive strength from the comforting feeling that apart from all the cares and troubles which the building involves, it can itself be for us a wonderful education—an education leading us above everything personal. The building demands a great deal more than the expression of any personal element. As we set about our work, and permeate the single forms with thought and feeling, we become conscious of new tasks of which we previously had no inkling. We feel that a mystery is there around us, calling out to the highest forces of soul, heart and mind to create something that transcends personality. This building can teach us how to fulfil the tasks which arise every day. It brings home to us a feeling that can ring in such sacred tones in the soul: How infinitely greater are the potentialities of the Universe than insignificant human beings! The highest we can create must be infinitely greater if it is to prove equal to the tasks before us in the objective world.' All that can ever be enclosed within the limits of the personal self must be transcended. The building itself, and the auxiliary house we have been able to open to-day can be a means of education for us. Indeed, the more they become a means of education, the greater understanding we shall have. Already now, as we look at the incomplete building and at this house, we cannot help thinking of what our feeling should be as we enter. How often we shall feel, ‘Ah, if only all human beings could be led here!’ Do we really deserve so sacred a framework—a framework we ourselves have helped to create—if we have any desire to exclude other human beings? Shall it not rather be our dearest wish to bring all men into the building? This will certainly be our desire if we realise the mission that such buildings will have to humanity, if they find imitators and followers? Think for a moment of many buildings erected in our times by clever architects. Some of them, although they show no signs of a new style and are not permeated with any new spirituality, are really creations of architectural genius. Yet they all have one thing in common. We may admire them from outside and think them beautiful inside, but they do not make us feel, as our building will do, that we are enclosed as if by organs of sense. The reason for this is that these other buildings are dumb—they do not speak. This is the thought that I would like to press home to you this evening. Let us think of buildings which express all the characteristics of our times. People pass in and out without in any way growing into their architecture, forms or art. Everywhere we feel that what ought to be expressed through the forms of art has to-day to be communicated to humanity by other means. In the present age man is more and more compelled to bring about order, stability, peace and harmony by means of external laws, decrees or institutions, definitions in words. This implies no syllable or thought of criticism, for it must be so in our age. But something must be added to this—something that signifies the onward evolution of humanity in a different sense. It is probable that our building will not be able fully to attain its goal—indeed we are only aiming at a primitive beginning. Yet if human culture is able to take what is expressed in our building (in so far as we fulfil the tasks set us by the higher Spirits) and develop it; if the ideas underlying such works of art find followers—then people who allow themselves to be impressed by these works of art and who have learnt to understand their language, will never do wrong to their fellow men either in heart or intellect, because the forms of art will teach them how to love; they will learn to live in harmony and peace with their fellow beings. Peace and harmony will pour into all hearts through these forms; such buildings will be ‘Lawgivers’ and their forms will be able to achieve what external institutions can never achieve. However much study may be given to the elimination of crime and wrong-doing from the world, true redemption, the turning of evil into good, will in future depend upon whether true art is able to pour a spiritual fluid into the hearts and souls of men. When men's hearts and souls are surrounded by the achievements of true architecture, sculpture and the like, they will cease to lie if it happens they are untruthfully inclined; they will cease to disturb the peace of their fellow men if this is their tendency. Edifices and buildings will begin to speak, and in a language of which people to-day have no sort of inkling. Human beings are wont to gather together in Congresses to-day for the purpose of putting their affairs in order, for they imagine that what passes from mouth to ear can create peace and harmony. But peace and harmony, and man's rightful position can only be established when the Gods speak to us. When will the Gods speak to us? Now when does a human being speak to us?—When he possesses a larynx. He would never be able to speak to us if he had no larynx. The spirits of nature have given us the larynx and we make this gift an organic part of the whole cosmos when we find the true forms of art, for they become instruments through which the Gods speak to us. We must, however, first learn how to make ourselves part of the great cosmos, and then our desire to lead all mankind through these doors will be the stronger. Out of this desire—for its fulfilment is not yet—the longing will develop to work so intensely for our spiritual movement that this aim may gradually be attained. Art is the creation of an organ through which the Gods are able to speak to mankind .... I have already spoken of many things in this connection. I have spoken of the Greek Temple and have shown how all its forms express the fact it is a dwelling place of the God. To-day I want to add something to this. If we try to understand the basic nature of the Greek art of building we shall realise that the very being and essence of the fourth Post-Atlantean epoch flowed into the Greeks' mode of perception and thence into their art of building. What is the basis of Greek perception and feeling? It is, of course, a wide subject, but I will only speak of one aspect. Here (see diagram) we have the wall surrounding the Greek Temple, with the horizontal structure resting upon it. When anything rises above the horizontal it is so constructed that it is upheld by its own forces which balance each other; just as when, in building, we place two beams together.
The presupposition here is that the earth with its gravity lies beneath. And translating this feeling into words, we may say: ‘In the fourth Post-Atlantean epoch man felt that the site of the earth was a gift of the God; it was as though Divine power overflowed into the creations of art.’ Therefore, by means of the forces in the earth given to man by the Gods, it was felt that gravity could be overcome. In the Greek Temple man controls the force of gravity and thereby creates a dwelling place for the God who has given him the earth. Neither this “dwelling-place of the God” nor the later Roman Temples can be thought of apart from the surrounding land. The land is part of the Temple itself. A Greek Temple is complete in itself even if nobody is within it, for its whole conception is that of the dwelling-place of the God; it is the sanctuary of the God. Human beings may live for miles around in the district; if nobody enters the Temple, it stands there, none the less, complete in itself—a dwelling-place of the God. In every detail we see how man expresses in the decorative forms of these dwelling- places of the Gods all that his feeling of veneration makes him feel he ought to do for the Gods. In the last lecture I tried to show you that the motif on the capitals has its origin in a dance motif—a dance that was performed as homage to the Gods of nature. And now let us pass on to the forms of the earliest Christian architecture. One thought in particular arises within us when we pass from the Greek Temple to the Church of Christendom. The Greek Temple stands within its surrounding territory, belongs to the territory. Human beings are not necessarily within the Temple; they live around it, outside it. The Temple belongs to the surrounding territory, is thought of as the altar of the land around it. The Temple hallows everything, even the trivial daily occupations of the human beings who live on the land. Service rendered to the earth becomes a divine office because the God stands or is enthroned as Lord and participates in the work on the land and in the pursuits of human beings living around the Temple. Man feels himself united with the God as he works on the land. Worship of the God is not yet separated from service to the earth. The Temple grows out of the human element, sometimes indeed out of the ‘all-too-human,’ and hallows everything around it. ‘Earth, be thou strong!’—This is the prevailing mood of the fourth Post-Atlatean epoch, when human beings are still at one with the earth which the Gods have given into their charge, when the Ego is still slumbering in a kind of dream consciousness, when man still feels himself connected with the Group-Soul of the whole of humanity. Then man grows out of this Group-Soul, becomes more and more individual, and he separates from the land, from daily life and activity, the worship he performs in his spiritual life. In the early days of Christianity the feelings of men were no longer the same as in the Greek age. Looking into the soul of the Greek, we see him sowing his fields and working at his industrial pursuits, pervaded by this unshakable feeling: There stands the Temple with the in-dwelling God and I am near. I may be carrying out my pursuits and working on the land but all the while the God is dwelling there within the Temple. Then man grows more individual, a strong sense of Ego, of “I” arises within him, and Christendom represents the emergence of something that had been prepared through the course of long ages by the ancient Hebrew civilisation. Out of the human soul arises the need to separate off from the affairs of everyday life the worship that is offered to the God. The building is separated from the land and the Church of Christendom comes into being. The land becomes independent; the building becomes an entity independent of the territory; it is an ‘individuality’ complete in itself. The Greek Temple was still a kind of altar for the whole territory, whereas the walls of the Christian Church now form a space set apart for those who are to worship. The forms of the Churches of Christendom and also of Roman architecture gradually come to express this individual, spiritual need of man, and they can only be understood in this sense. The place of the Greek within earthly existence was such that he said to himself: ‘I can remain here with my flocks, carrying out my occupations, doing my work on the land, for the Temple stands there like an altar for the whole countryside: the God is dwelling within it.’ In Christendom, man says: ‘I must leave my work and repair to this building, for there I must seek for the Spirit.’ The service of earth and the service of heaven are separated and the Christian Church more and more assumes a form where Greek and Roman architecture would no longer be suitable. It is a form which reveals that the community belongs to the church; the church is intended to enclose the community. Then, once again set apart from the community, we find the house of the priests, of those who teach. An image of the universe comes into being; the Spirit speaks to those who seek for the spirit, in precincts where they are enclosed within walls. The whole world was felt by the Greeks and Romans in former times in the same way in which the Christians afterwards felt the precincts of the Church with its enclosing walls. And what the Greek Temple itself had been now became the chancel. Men sought now for a distinct image of the world whereas formerly they had taken the world itself and only placed within it, visible to outer senses, the Temple as the dwelling-place of God. Gothic architecture is really only a branch of what was already being prepared. The essential feature of Gothic architecture is that the weight is taken away from the walls and placed upon the pillars. What is the origin of this whole mode of construction, where the weight rests on pillars, which are so moulded that they are able to bear it? It is based on a quite different conception from that of the Greek Temple. When we pass to the pillars of Gothic architecture which take away the weight from the walls, we are no longer concerned with the pure force of gravity. Here, man himself is working. In the Greek Temple it is as though he frees himself from the earth's gravity and having gained knowledge of it within the earthly realm, now rises above it. In that man makes use of the force of gravity, he overcomes it. In the weight-bearing Gothic pillars we are no longer concerned with the pure working of the force of gravity; in the Gothic building the art of handicraft is necessary, of higher and lower handicraft. The need for the creation of precincts which enclose the community also gives rise, in Gothic architecture, to the need for something wherein the activity of the community plays a part. In the single forms we see a continuation, as it were, of what the people have learnt. The art of the hand-workers flows into the forms, and in studying these forms we see the art of human beings who have contributed their share, who have worked together. The old Roman Churches are still edifices which enclose the God. The Gothic Church is an edifice built by the community to enclose the God but one where the people have contributed their own handicraft. They do not only enter the Churches but they themselves work at the building as a community. In Gothic architecture this labour of human beings unites itself with the Divine. The souls of men no longer receive the Divine as a matter of course; they do not only come together and listen to the word of the Spirit proceeding from the chancel, but they gather around the God in their labours. Gothic Churches are really crystallised handicraft. We can quickly pass over what came next, for it really amounted to a revival of classic architecture. In this connection it is not necessary to speak of the Renaissance; we will speak of what the fifth Post-Atlantean epoch demands of us. Let us consider the element of weight and support, following it to the point where it becomes crystallised handicraft in Gothic architecture. If we penetrate this with artistic feeling we realise that here is something at rest within itself, at rest within the earthly forces. All the forces of these edifices rest within the earthly element. The Greek Temple everywhere indicates the force of gravity and its own union with the earth. In the Greek Temple we can everywhere observe some manifestation of the force of gravity. Its very forms reveal a union with the earth. And now let us compare the basic form in our building that will confront everyone even from the outside. I will make a rough diagram of it. What is the characteristic of this motif? I should have to speak for a long time if I wanted to show that this is how the art of relief first assumes its real meaning, but I will only give you an indication of what I really have in mind. A certain eminent artist of modern times has spoken a great deal about the art of relief and has said some clever things. He tells us to think of two panes of glass standing parallel to each other and between them an intersected figure. We should then be looking in the direction of the arrow through the panes of glass at the figure ... Now there is in the world a relief which is full of meaning, only we pay no proper attention to it. There is a certain relief that has been created in accordance with the true idea—it is the earth with her plant kingdom. We must, however, pass away from the surface of the earth into cosmic space before we can study this relief. The earth is the living surface which brings forth its creatures from its own being. Our own art of relief must be based upon the conception that the wall is a living thing even as the earth brings forth her plants. This is how a true art of relief is attained. To go beyond this principle is to sin against the essence of the art of relief. When we look down upon the great relief of the earth, we see human beings and animals moving upon it, but they do not belong to the relief. They can be introduced into the relief, of course, because the arts can be developed in all directions, but this is no longer the pure essence of the art of relief. Our building must speak through the forms in its interior, but the speech must be that of the Gods. Think for a moment of the life of human beings on the earth, that is to say, immediately on the surface of the earth. Here we need not draw directly on our teachings—we need only turn to the Paradise Legend. If man had remained in Paradise he would have looked upon the wonderful relief of the earth with her plant kingdom from outside. He himself, however, was transplanted, as it were, into this relief. He could not observe it from outside for he was taken out of Paradise. The speech of the Gods cannot ascend from the earth to men for the speech of the earth drowns the speech of the Gods. Nothing in this architecture is there for its own sake alone. The one form leads over into the other; or, if the forms have a threefold character, the central form is the bridge between the other two. Here we have a rough sketch of the forms of the doors and windows.
Now all that lives in the sculptured forms is three dimensional; relief is a conquest of the second dimension, surface, which is then brought into the third dimension. This is not realised if we merely take the standpoint of an observer or spectator: for we need a living feeling of how the earth allows the plants to grow out of her being. When I come to speak of the real nature of painting we shall understand the significance of the connection between colour and the inner element of soul in the universe. There would be no sense in painting with colours if colour were not something quite different from what physics imagines it to be. The principles of colour as the speech of the soul of nature, of the soul of the universe, will be the subject of a later lecture. I will now indicate how our glass windows are to represent the union of the outer with the inner. They will each in themselves be of one single colour, but different colours will be used at the various positions in the building. This expresses the spiritual, musical harmony of the outer with the inner world. And the single coloured window will only express this harmony in the thicker and thinner strata of the glass. That is to say, we shall have surfaces where the glass is thicker, more solid, and surfaces where the glass is thinner. The light will shine more strongly through the thinner places in the windows; it will shine less strongly, and produce darker colours, through the places where the glass is thicker. The connection between spirit and matter will be expressed in the glass windows; but the whole interior will strive to be an organ for the speech of the Gods. The larynx makes it possible for man to speak, and in the same way the whole of our relief-moulding is an organ for the Gods who should speak to us from all sides of the universe. So that when we make an aperture for the windows in the walls which allow the Gods to speak to us, we are seeking the path to the Spirits of the cosmos. These windows are intended to signify in their coloured shadings: ‘Thus, O man, thou findest the path to the Spirit.’ We shall see how the soul is connected with the spiritual world when it sleeps during the night and is living outside the body. We shall see the way in which the soul is connected with the spiritual world between death and a new birth in the disembodied state. The windows will show us how, when man approaches the threshold, he becomes aware of the abyss; the stations on the path to the spiritual world will be revealed. They will arise as light formations from the West, revealing to us the mysteries of Initiation. We are trying to create walls, the forms of which make the wall themselves seem to pass away. The designs must express how we pierce the walls, showing us how we find the path to the spiritual worlds, or traverse these worlds unconsciously, showing us what our relation to the spiritual worlds must be. The Greek Temple, the dwelling place of the God, and the later edifice, which was built for the community desiring to be united with their God, were building-sheaths which enclosed and shut off. Our building must not shut off anything in the universe; its walls must live, but live in accordance with truth itself. Truth flows into the beauty of our relief-moulding. If we had not been driven out of Paradise we should be conscious of the ' speaking ' relief proceeding from the earth herself in the plant forms, which grow even above the geological formations of the mountains and only allow these strata to be bare in places where it is right that they should be bare. The moment however when we find in our perceptual life the transition from the 'repose' where the Gods speak to us, from that ‘repose’ to our own activity, to what we must do in order to find the way to the Gods—in that moment we must have movement, inner movement; we must pierce the wall. We must have these windows which call to our souls to tread the path to those regions whence the words expressed by the forms of the walls have proceeded. Then each one of us will sit within the building and we shall say to ourselves: “The organs of the great Spirits themselves are round about us; it is for us to understand the language spoken though these forms.” But we must understand it in the heart and not merely be able to grasp it intellectually. Those who begin to, explain' the meaning of these forms are on the wrong track. They stand on the same ground as those who interpret the old myths symbolically and allegorically, and imagine for instance, that they are advancing the cause of Theosophy. A man who tries to ‘interpret’ the myths and explain external forms may be clever and ingenious but he is like one who tries to look under his chin to explain the symbolism of his larynx. We understand the speech of the Gods by learning how to listen with our hearts, not by using intellectual agility and giving symbolic or allegorical meanings to myths and artistic forms. ‘Here you sit and the Spirits of the Universe are speaking to you’—this must become a living feeling within us. When this becomes a living perception of what the soul must do if it is to find the way to those regions whence the speech of the Spirits proceeds, we shall direct our gaze to where the walls are pierced by the windows; and at those places there will be revealed to us the mysteries enacted in man as he consciously or unconsciously treads the path from the physical to the spiritual. I have tried to express the feelings of our hearts and souls to-day when this house is being given over to the charge of our friend Rychter and his colleagues for their work. May they feel, as they receive it, the sacred nature of their task and something of the holiness of which I have spoken. Up on the hill itself we are still working at the building which will reveal, to those who seek, organs through which the Gods may speak to them. But there must arise in these seekers a holy longing to find the ways and paths to the realms of the Gods. The work of Rychter and his colleagues in the rooms of this house will be taken up the hill and placed in the positions where the walls are pierced. It will move the souls of those gathered together in the building at the top of the hill and show them the path to the Spirit. May this holy mood pervade this house; may each drilling in the glass be carried out with the feeling: ‘Here I have to mould something that will lead to the realms of the Spirits those who see it up there in the building. My creations must make the soul's perception so living that the shadings in the coloured glass will represent the channels by which the spiritual worlds are speaking through the forms in the interior.’ The difficulties may be very great, indeed there may be only partial success in many cases and in other cases total failure, but the attitude I have described will be an unfailing help. I did not intend to-night merely to speak of matters which may help to make art more intelligible. I have spoken as I have because I pray that something of what I feel may flow from my heart to yours. I want your hearts to be livingly permeated with a feeling inwardly vibrant with the sense of the holiness of this work. We dedicate this house of labour most fitly if as we leave the doors we concentrate with all the forces of our hearts on love for the world of man and of spirit, to the end that the way to the Spirit may be found through what is accomplished here—to the Spirit whence peace and harmony can flow among men on the earth. If all our labours are made living by the Spirit, if all the work on this hill is filled with the Spirit of Love—which is at the same time the Spirit of true art—then from our building there will flow out over the earth the spirit of Peace, of Harmony, of Love. The possibility will be created for the work on this hill to find successors; many such centres of earthly and spiritual peace, harmony and love may thus spring up in the world. Let us realise the living nature of our work in this mood of peace and loving harmony, knowing that our labours flow from the Spirit of Life itself. There have been dwelling-places of the Gods, sanctuaries of the community, and there yet will be an organ of speech for the Spirit, a building which points out the way to the Spirit. The God dwelt in the Greek Temple; the spirit of the community may dwell within the Roman or Gothic edifice; but the world of the Spirit itself must speak through the building of the future. We have seen the house of earthly forces and forms arise and pass away in the course of human evolution; we have seen the house of the union of human souls arise and pass away in the spiritual evolution of the earth. It is for us to build the house of speech out of our love for true art, which is at the same time love for true spirituality and for all mankind.    |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The New Conception of Architecture
28 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The lecture referred to the evolution of thought and conception underlying the art of building and I will just briefly recapitulate what I was then only able to indicate. |
| A speech which has a message for man of the present day will arise. But all this requires that we endeavour to understand the Spirit in its forms of expression. In order to understand the Greek Temple, we tried, last time, to grasp the purely physical qualities of space and of gravity. |
| Nobody who begins to think out all kinds of ingenious interpretations will Understand our building. It can only be understood by a living feeling of the development and being of the forms. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The New Conception of Architecture
28 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
During the time when the construction of our building is proceeding I think it is a very good thing for us to try to grow more and more into its meaning. We have already made a beginning with the two previous lectures and we will try as far as we can, by means of further study, really to become one with what is to be accomplished here. In the first place I should like to remind you of what I said when we opened the house dedicated to the work of constructing the glass windows. The lecture referred to the evolution of thought and conception underlying the art of building and I will just briefly recapitulate what I was then only able to indicate. In regard to the Greek Temple, I said that in a certain sense it formed a unity with the whole countryside—the whole countryside was one with it. The Temple stood there as the ‘dwelling place of the God.’ Nothing need be in the Greek Temple save the spiritual presence of the God and his physical image. The essence of the construction of the Temple was the fact that every man engaged in his daily pursuits on the land knew that within the region where he was carrying on his work he was not merely alone with the earth but united with the spiritual world. And the token for the fact that man, as he lived on the earth, was also united with the spiritual world, was the Temple standing there like an altar in the land. We then saw evidence of progress in architectural thought, in that the Christian art of building separated off the edifice from the land. Everyday life and the mood of exaltation by which man raised himself to the Spirit were separated from each other. The Church of Christendom is no longer actually one with the land; it serves the Spirit, apart from the countryside, and expresses the fact that when man is to rise to the Spirit he must leave the affairs of daily life, repair for a time to a place set apart and there be united with the spirit. The Church of Christendom, therefore, could no longer be what the buildings of Greece and also of Rome were in their real being. The Church of Christendom was in itself a duality, the house of the community and the house set apart for the altar and the priesthood. Man leaves the affairs of everyday life and enters into the precincts where he feels himself gazing upwards to the Spirit which comes to him from the chancel where the altar stands. This evolution in architectural thought naturally implies the transformation of the ancient Greek form of building (which was derived purely from static and dynamic factors, the factors of space and gravity) into the form corresponding to the conception of the community being set apart. Passing to the Gothic Cathedral we have a still later form of architectural conception. We have the striving of the community not only to bear their own personalities into the sanctuary but also their individual work, and this is expressed in the forms of Gothic architecture. We feel as if the work performed in the environment has passed into the architectural forms and rises to the Spirit like a prayer, a folding of the hands. I also said that a real advance in architectural conception must come to pass again in our times and that this is only possible if the nearness to the Spirit which was achieved to an ever-increasing extent from the period of the Greek conception of architecture onwards to that of Gothic building—if this nearness is gradually transformed into a complete union with the Spirit. This means that buildings which should now be dedicated to life in union with the Spirit must in their very form express inner correspondence with the Spiritual. We can indeed say—if we try not to explain the thing in abstractions but to grasp it with the whole of our feeling and soul—‘All that is embodied in our life of soul through Spiritual Science implies an actual penetration into the form that is created. The Spirit is revealed in freedom, having now descended to mankind.’ Whereas the Greek placed the Temple like an altar in the land, the future and, inasmuch as we are working from out of the future in our building, the present, are placing a true expression of the Spirit in the land as the result of what the Spirit expresses in its forms. A speech which has a message for man of the present day will arise. But all this requires that we endeavour to understand the Spirit in its forms of expression. In order to understand the Greek Temple, we tried, last time, to grasp the purely physical qualities of space and of gravity. But the Spirit does not only work according to the laws of mechanics and dynamics; it does not only reveal itself in conditions of space and energy. The Spirit is living, hence it must be expressed in our building in a living way, a truly living way. We shall not understand this any better by interpreting the Spirit symbolically, but by beginning to feel that the forms are living, that they are organs of speech flowing from the spiritual world. Is it possible for forms to speak from the spiritual world? It is indeed possible, in many ways. Let us take a thought that is specially near to us because on the one hand it is the expression of the highest, and on the other, in its Luciferic aspect it is submerged in the lowest—let us take the idea of the Ego, of Selfhood. The mere utterance of the word “I” or “Self” does not as yet evoke much thought in man. Many epochs will have to run their course in human history before a fully conscious idea can arise in the soul when the word “I” or “Self” is uttered. Nevertheless, Selfhood, Ego-hood, can be felt in form, and above all when we pass from a purely mathematical conception of form to a feeling in form we can acquire a perception of Ego-hood, Selfhood, in the perfect circle. If you realise this you will readily understand what follows from it. If the true, living, sentient human being, confronting a circle, senses the feeling of Ego-hood, Selfhood, arising in his soul, or if when he sees a fragment of a circle he feels that it typifies the independent Self, he is learning to live in forms. And the characteristic of really living feeling is the capacity for living in forms. If you keep this in mind you will easily be able to pass on to other things that follow from it. The first circle I have drawn here has an unbroken line (1).  This line however can be varied so that it shows these wavy projections (2).  Another characteristic variation is the third figure (3). Another characteristic variation is the third figure (3).  Both figures are only variations of the circle. What do these variations signify? The second (2) expresses the fact that the Self, the Ego has entered into relation with the outer world. The simple circle makes us feel that nothing of the rest of the world is there, only what is shut off within the circle. If we observe the circle in variation we can no longer feel that what is expressed by the circle is alone in the world. The variation in the line expresses a struggle, a kind of interplay with the outer world. If we really live into the form of the second variation (2) we shall feel: “The inner is stronger than the outer.” And in the case of the jagged circle (3): “The outer has bored its way in and is stronger than that which lies within the circle.” And now if we go into any building containing fragments of circles or rounded surfaces, and perceive variations of this kind, we shall feel in the case of the jagged lines, “here the outer has conquered,” and in the case of the wavy lines, “here the inner has conquered!” Our souls begin to live with the forms. We do not merely behold the forms but in our souls we have the living, pulsating feeling of “conquest and encroachment,” “victory and mastery.” The very soul lives with the form. And this union with form, this living in form is the very essence of true artistic feeling. Both figures are only variations of the circle. What do these variations signify? The second (2) expresses the fact that the Self, the Ego has entered into relation with the outer world. The simple circle makes us feel that nothing of the rest of the world is there, only what is shut off within the circle. If we observe the circle in variation we can no longer feel that what is expressed by the circle is alone in the world. The variation in the line expresses a struggle, a kind of interplay with the outer world. If we really live into the form of the second variation (2) we shall feel: “The inner is stronger than the outer.” And in the case of the jagged circle (3): “The outer has bored its way in and is stronger than that which lies within the circle.” And now if we go into any building containing fragments of circles or rounded surfaces, and perceive variations of this kind, we shall feel in the case of the jagged lines, “here the outer has conquered,” and in the case of the wavy lines, “here the inner has conquered!” Our souls begin to live with the forms. We do not merely behold the forms but in our souls we have the living, pulsating feeling of “conquest and encroachment,” “victory and mastery.” The very soul lives with the form. And this union with form, this living in form is the very essence of true artistic feeling.  But we can go further. Let us picture to ourselves a less simple variation (4). The form moves in one direction and becomes action. If we live in this form we have the feeling that it advances, that it moves. In the forms themselves we find the quality of movement. I have here made a simple sketch of something that will appear in a complicated form in the building, but you will find that there is an absolute correspondence. Passing from the entrance at the West and thence towards the smaller structure (at the East) you will find that all the forms in the interior will evoke the feeling that the whole structure is proceeding from the West onwards to the East. This is expressed in the forms. At the West you will feel in thought that you are within a vehicle that is bearing you to the East. The very essence and meaning of these relief variations is that they do not merely appear as dead, dynamic or mechanical forms; we seem to enter a vehicle that bears us onwards. In a spiritual sense we shall not “rest” in our building; we shall be led onwards. From this you will realise that the basic character of the forms here is quite different from the forms of the three stages of architectural thought which I have described. Up to our time architectural thought has been concerned with the qualities of lifeless, mechanical rest. Now, however architectural thought becomes the thought of speech, of inner movement, of that which draws us along with it. This is what is new in the whole conception, and the basic form must of course correspond to it. In what way does the basic form correspond to it? Now I have said that the most intimate of all impressions is that of the Self, the Ego, as expressed in the circle or sphere. Why is this? It is because the simple circle or sphere is of all forms the most easily perceptible. It is an absolutely simple matter to recognise a circle. All that is necessary is the most trivial thought that everything is equidistant from the central point. As soon as we picture to ourselves points standing at an equal distance from this centre, we have the sphere, or circle. It is the very easiest process that can be carried out in thought. As form, then, the circle is the simplest of all entities. This is also in accordance with external reality, for the Selfhood in every being, from the simplest cell to the complex human being, is the simplest of all impressions, just like the circle or sphere. Behind all this there is something much deeper and I want you now to follow me in a thought that will lead those who really understand it, to great profundities. Now the form of an ellipse is more complex than that of the circle. I will draw the form of an ordinary ellipse. It need not be exact but merely have the general character of an ellipse. The simplicity of the thought is no longer there when we pass to the ellipse. Although the ellipse is still spherical, we have no longer the nature of equality as in the case of the circle. Here I must ask those who have studied geometry—although for politeness sake we will assume that you all know a little of geometry though you may have forgotten some of it—to try to understand the following ideas. There is also order and regularity in the ellipse. Just as the circle is related to one point, the ellipse is related to two. In the case of the circle there is no such feeling of satisfaction, for the circle is so immediately obvious. The ellipse causes us greater joy because there we have to be inwardly active. The more one is inwardly active, the greater joy one has. What is often so difficult to realise is that man, in his inner being, craves for activity. If he wants to be lazy this is merely an affair of his conscious life. The astral body is not only wiser, but also more industrious and would like always to be active. Now there is another line consisting, of course, always of two portions. Those who have studied geometry will know that the hyperbola consists of two symmetrical curves. Man is thus a mathematician in the substrata of his consciousness and by means of subconscious calculation we create for ourselves regularity of form. We add and subtract, but we can also multiply. Here again we have two points. Multiplying the one by the other we again get a line that looks somewhat like the ellipse but is not the same. This line contains an inner process of multiplication.
This line has something mysterious about it. The circle is a simple entity, the ellipse already more complicated, the hyperbola still more so, for I do not think that the ordinary person sees only one single line in the two curves. The ordinary intellect believes there are two curves. The ordinary intellect believes there are two lines, but in reality this is not so. The other line is mysterious for another reason, for according to what is produced by multiplication the line is changed into this curious form. It is the curve of multiplication, the curve of Cassini, the lemniscate which plays so important a rôle in occult investigations. The line can develop in such a way that it assumes these forms. There are two lines, you see, but in the inner sense there is really one line, and when we feel it as one line in the astral world we know that this form (o-o) is only a specialisation of this form ( ∞ ). But now think—this form ( ∞ ) disappears into the fourth dimension—then appears again and enters the physical world. It is an unity because it ever and again disappears into the fourth dimension. This multiplication process has really three different forms. We have therefore a line of addition, a line of subtraction, a line of multiplication. Someone may say that there must then be a line of division, the fourth method of calculation.
Now we have something very remarkable indeed. When we really try to penetrate into the depths of nature they appear before the soul in all their wonder. The circle appears to be an utterly simple entity but it is, nevertheless, full of mystery. The circle can also be understood by taking two points and dividing, and inasmuch as the same result is arrived at, we get the circle. The circle is thus something very remarkable. It is the simplest of all entities and yet it is the product of an occult process of division that is brought into consciousness. It is just the same in the case of the self of man: the ordinary self is the simple entity and the higher self the mysterious entity resting in the depths of being—a self that can only be found when we transcend its limits and pay heed to the world with which it is connected. The circle is the same whether we say that it is the simplest of all forms or that the product of division from two points is always the same. Just as we have the same circle, so we have within ourselves a duality: something that belongs to everyday life and is readily perceptible, and something that we only grasp when we go out to the whole universe, conceiving of this entity as the most complicated product of the great cosmic struggle where Ahriman and Lucifer carry out the division and where our own higher self has to maintain itself as the quotient if it is ever to come to expression. Portions of the ellipse and of the hyperbola and also of the curves of Cassini will be found everywhere in our building, and your astral bodies will have plenty of opportunity to make these calculations! Here I will only mention one instance: when people go into our building and stand in the gallery where the organ and the singers will stand, their souls will be able to carry out this process of multiplication. The soul may not do so consciously but it will feel this process in the depths of its being, because this is the line of the structure around the organ. This line will be found in many places in the building. After what I have now told you about the twofold meaning of the circle you will be able to realise that when you enter the building from the West and feel yourselves surrounded by the circular structure, by the cupola above, that here is the image of the human self. But the other smaller space in the East is not at first sight so intelligible. The smaller structure will seem to be full of mystery because, although its form is also circular, it must be conceived of as the result of a process of division and it only outwardly resembles the larger space. There are two circles, but the one corresponds to the life of everyday and the other is connected with the whole cosmos. We bear within us a lower self and a higher self. Both again are one. Thus our building had to be a twofold structure. Its form expresses—not in any symbolical sense but in its very being—the dual nature of man. When the curtain in front of the stage is open we shall perceive an image of man not only as he is in everyday life, but as complete man. The forms themselves express a movement from West to East, the path of the lower to the higher Self. All that I have told you can actually be felt in the forms. The erection of a building of this kind reveals how the spiritual form of nature and the higher spiritual world can be expressed. Nobody who begins to think out all kinds of ingenious interpretations will Understand our building. It can only be understood by a living feeling of the development and being of the forms. For this reason I do not want to describe the building pictorially but to speak of the mode of its development, how spiritual being itself has become form and movement and has flowed into it. Suppose anyone were to look at the interior and begin to speculate thus: ‘Yes, two cupolas, two circular structures—lower Self, higher Self; a lower Self, a higher Self—a unity.’ This may be a neat interpretation but it would be of no more value than if it were said that Maria and Johannes Thomasius in the Mystery Plays are really one being. This is a mere speculation, for it results in an abstraction. The unity lies in the living ‘becoming.’ Naturally the living powers of becoming can bring forth both Maria and Thomasius but only as the result of a differentiation. Even in similarity the true occultist will always seek for diversity, for it would be false occultism to desire always to lead back diversity to unity. Hence the example of the circle. The circle is the simplest of all entities, where all points are equidistant from the centre—but it is also the result of division. In the circle we have something that is a unity in the outer world and complex in the spiritual world. These are some of the remarks I desired to make. On another occasion I shall speak further on these matters. I shall now speak briefly of other things. Man, as he enters the world, is really a highly complicated being. When he enters the world—as I have often said—he cannot at first stand upright; lie crawls, and at the very beginning of his existence he does not even crawl. Gradually he learns to control the forces which make him able to stand upright. The advance from Gothic architecture to that of Spiritual Science may be described as follows: Gothic architecture contains the prayer: ‘O Father of the Universe, may we be united with Thee, in Thy Spirit.’ Those who know what this prayer contains, who really understand the living development of Spiritual Science, will solve the riddle of the evolution of man. And then, when the forms of architectural thought strive to be united with the Spirit—expressing this striving in their very being—man will feel how he has been permeated with the hidden Spirit and can have around him a building which is a direct expression of the living, inner development of his being. ‘We dwell in the land, but the Spirit is among us.’ This is the Greek thought of architecture. ‘We dwell for a season in the sanctuary and the Spirit comes to us.’ This is the thought behind Christian architecture. ‘We dwell for a season in the sanctuary, but we uplift the soul by raising ourselves to the Spirit.’ This is the thought behind Gothic architecture. ‘We enter with reverence into the Spirit in order that we may become one with the Spirit poured out around us in the forms—the Spirit that moves and is active, because behind the Spirits of Form stand the Spirits of Movement.’ This is the thought behind the new architecture. Existence thus advances through earthly evolution and it is man's task to understand the inner meaning and purport of this existence. He only advances in the wake of true evolution when he endeavours, in every epoch, to experience what the spiritual world bestows in that epoch. Why do our souls pass through different, successive incarnations? Not in order that we may repeat the same experiences, nor that we may pass through re-birth, re-naissance, again and again, but in order that we may assimilate, ever and again, the new that pours into our souls from out the spiritual worlds. We are standing at a definite point in the evolution of humanity in the sphere of art and in many other spheres of spiritual life—at a point where the Spirit speaks clearly to us of new riddles. And just as in the time of the Renaissance man was destined primarily to orientate himself to the past in order to work his way through to the new, so it is with our own external knowledge and perception of the universe. All that has been produced by the modern age since the sixteenth century is only the preparation for a living experience of the universe in its forms and movements which now stand before us as riddles. This, then, is all for to-day. In another lecture I will try to approach questions of a still more intimate character—questions relating to the living soul of nature in connection with colour and the art of painting.  to the left the model made by him; in the middle, Christ, the Representative of humanity; above, Lucifer fallen; below, Ahriman imprisoned. From a drawing by W. S. Pyle.  Architraves and Capitals of Pillars during the Building Work.  Architraves and Capitals of Pillars during Building.  In the background the small Cupola with Stage (X) Here the great wooden sculptured group of the Representitive of Humanity was to have stood. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: True Aesthetic Laws of Form
05 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| In the present materialistic epoch, where there is no knowledge of Spiritual Science, there will be little understanding for these deeper laws of ‘being and becoming.’ We may therefore find ourselves faced with the question—and it is a wholly understandable one from the point of view of external knowledge—‘Why are the columns made of different kinds of wood?’ |
| Before very long, the so-called science of to-day will undergo an overwhelming expansion, and only then will there be understanding of the true and deeper laws of aesthetic form. |
| Think, by way of comparison, of certain animals which always swim under water and never come to the surface. They have water in their environment. They adapt themselves to what they take into themselves from the water. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: True Aesthetic Laws of Form
05 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In the last lecture we spoke of the Spirit which should pervade the forms in our building. From all that has been said you will have gathered that these forms are no more the result of imitation of the external physical world than of mere speculation. Your feeling will have been that the forms have been derived from the spiritual world of which man is an integral part and of which he may hope to become conscious in the development of his knowledge of Spiritual Science. I want to remind you once again of an important fact, of which mention has already been made, namely, that human life runs its course in periods of approximately seven years each, and—as I tried last time to explain to you from spiritual-scientific cosmology—when we observe the whole course of these periods of seven years, we may say that after each period a certain support is added to man's being. When he has passed through seven such periods, therefore, he has reached approximately his fiftieth year, he possesses seven pairs of these ‘life-supports.’ If we were now to imagine ourselves entering the building from the West, in the first two pillars we have the expression of the supports which man has raised in his own being after the first period of seven years has run its course; the second pair of pillars are an expression of the supports he has added after the second period of seven years; and so it goes on, only it must be remembered that in man these supports are intermingled, whereas in the building they have had to be placed one behind the other in space. We may then be permeated with the feeling that when we pass through the building from the West towards the East, all that works upon us from left and right is a revelation of processes in human life itself. This shows us that there are firmly established cosmic laws of which man is a part but which are infinitely deeper than the so-called ‘natural laws’ of the outer physical world, and furthermore that the forms in our building have been evolved from these deep cosmic laws. To study every detail from this point of view would lead us very far, although it could be done. In the present materialistic epoch, where there is no knowledge of Spiritual Science, there will be little understanding for these deeper laws of ‘being and becoming.’ We may therefore find ourselves faced with the question—and it is a wholly understandable one from the point of view of external knowledge—‘Why are the columns made of different kinds of wood?’ There is no allegorical or symbolical meaning in this, and anyone who raises such a question merely proves that life has afforded him no opportunity for the contemplation of deeper cosmic laws. The only rejoinder we can make is this: ‘Why, then, do you consider it necessary for a violin not to have only A strings?’ A man who wanted to use only A strings on a violin would be in exactly the same position as one who—perhaps quite unconsciously and naïvely—were to ask as the result of superficial knowledge, why our pillars are made of different woods. We can develop these matters slowly, for we shall often meet together here. We can allow subjects that may prove fruitful to enter gradually into our feelings. To-day, therefore, I only want to speak of one matter that will help to stimulate our perception of what underlies the laws of true aesthetic form, on the one hand in the cosmos, and on the other in the microcosm, in the constitution of man. Before very long, the so-called science of to-day will undergo an overwhelming expansion, and only then will there be understanding of the true and deeper laws of aesthetic form. In order to evoke a concrete perception of what I have here mentioned in mere abstract words, let us consider the following. I am going to place before you something that corresponds to a cosmological fact, a mighty cosmic fact. Now these three heavenly bodies (see diagram) stand in a certain mutual relationship to each other; they reveal their activities to each other and I want to speak of one particular aspect of these activities. To this end I will first divide the Sun diagrammatically as it actually appears to the occult seer when he directs his attention to these things. The Sun is seen divided into a kind of cross, into four chambers. The remarkable thing is that in the first moments of vision we see a kind of streaming current, but closer scrutiny reveals the fact that here we have to do with hosts of beings passing to and fro. We can see such a stream of spiritual beings passing from a certain “chamber” of the Sun to the Earth, penetrating the Earth and vitalising the Earth with solar essence, that is to say, with the spiritual force of the Sun, and thence streaming to their own chamber in the Sun. This is cosmic reality but one sees still more—one sees migrations of hosts of spiritual beings who are flowing around and through the Moon (see diagram). They proceed from another chamber of the Sun: but they also flow in the other direction and pour through the Moon. Up to this point we are perceiving the activities of the inhabitants of three chambers in the Sun. Another migration or stream arises from the fact that these beings always return to the Sun after having passed through the Moon; thus a double stream has arisen. On the one hand the beings return into the fourth chamber in the Sun after having poured through the Moon, but another stream is formed because certain beings do not take part in the migration to the Moon; before reaching the Moon they turn back again to the Sun. This configuration reveals to us a kind of mirror-image in the cosmos, but we will leave this image out of consideration for the moment. It would be formed by a symmetrical expansion of the figure that is engraved there in the cosmos. This means, in effect, that there is revealed to clairvoyant consciousness a marvellous combination of forms, a figure engraved in the cosmos representing the interplay between the forces of Sun, Moon and Earth. Now I will draw the diagram rather differently, with the Sun rather turned (Diagram II). The cross must also be turned. Now I will draw the diagram again differently (Diagram III). Here I have assumed hypothetically that Ahriman and Lucifer have entered, bringing disorder in their train. I will draw the Sun, Moon and Earth more irregularly and again trace the connections between them. What have I now drawn? Exactly the same thing as in the other diagrams, only somewhat distorted as a result of the intervention of Ahriman and Lucifer. I have now drawn a sketch of the blood circulation in man, a sketch of how the blood flows from the left ventricle of the heart through the body, on the one hand through the brain on the other through the rest of the body, returning as venous blood; you also see the course of the small circulatory stream through the right ventricle and lungs back again to the so-called left auricle. Thus we can read from the cosmos what man is as a microcosmos, only it must be remembered that Ahriman and Lucifer have approached him. If a figure were made of this diagram—that is to say, a figure copied from the cosmos and expressed in some motif—we should have before us a profound cosmic mystery merely in the combination of form. When a certain combination of lines underlies a figure of this kind—where perhaps only a few of these lines are expressed and the others drawn in quite another way—those who have real feeling and not merely intellectual understanding, will perceive a cosmic mystery in the very form itself. They will say to themselves: ‘What is it that this form expresses? I do not actually know, but I feel that it expresses a mystery.’ It is this that inspires our souls and makes our hearts glow when we look at certain forms. We cannot always be conscious of what lies behind them, but our astral body, our subconscious being, contains the mysteries of the cosmos and senses them in the depths just as it contains the secrets of mathematics, as I told you in the previous lecture. When a man says, ‘I feel beauty here, but I cannot explain to myself what it really is,’ something is taking place in his astral body. This he may express by saying that he senses the existence of deep and mysterious secrets of the cosmos which do not take the form of ideas and thoughts but are expressed in a feeling, ‘Ah, how beautiful this form is.’ The reason why he feels this as warmth pouring through his heart and soul is that if he were as conscious in his astral body as he is in his ego he would have a deep knowledge of the cosmos. These things must teach us to understand how art has gradually developed in human evolution and to realise that true works of art in the Goethean sense are ‘a manifestation of higher laws of nature than the ordinary intellect of man can divine.’ We find an inkling of the truth of these things more especially when we go back to what modern opinion holds to be the “primitive art” of earlier periods of human evolution. This is because in those olden times a certain primitive, atavistic clairvoyance was a common attribute of humanity and because man then created forms from out of this clairvoyance. Many of the forms to be found in primitive art can only be understood when we realise that they were the outcome of this primordial clairvoyant consciousness. Men experienced the content of their astral bodies as living movement, tried to express it in a kind of noble dance, and then converted it from the Dionysian dance into Apollonian design and painting. Such is the origin of certain forms of early art which often seem to us merely primitive, but which in truth have sprung from a deeper understanding of the spiritual world imparted by the clairvoyance of those times. This, I think, will show you that in the sense of true, genuine art, the easy phrase ‘there can be no disputing about taste’ is wholly incorrect in its ordinary sense. Fundamentally speaking, of course, one can dispute about everything, even about mathematical principles. When one man applies a mathematical principle and gets a different result from another who also applies it, disputes can naturally arise and even become acute, but one of the two has made an error. The error, of course, is not so easy to discover in the case of beauty or art. Nevertheless man can attain to a point of view which convinces him that the forms and laws of true art are firmly established and based upon the deeper laws of cosmic being. Perhaps it may be admitted that the principle ' there is no disputing about taste' only penetrates into life by dint of effort, that it is a conception only to be evolved very gradually. But in the course of his life a man can be convinced of the truth of it when he realises that art is a manifestation of higher laws of nature which without art would never be revealed. Here again I am using Goethe's words. Man can indeed be convinced that art is this manifestation of higher laws of nature about which there can fundamentally be no disputing. In the light of what now should be living within us, not so much as thought, but as feeling, we must gradually be able to work our way to another perception. What is really happening to us when we delight in forms that are truly artistic? We are passing out of ourselves, penetrating with the soul into something that is real, outside ourselves. Therefore it is not at all unnatural that in a building which belongs to the present and future we should set out in full consciousness to create forms which will help man to conquer the consciousness of merely physical and material actuality and feel himself expanded out into the cosmos through the architecture, sculpture and all that this work of art may contain. Much will have to be done, however, before this feeling will be able to penetrate into every sphere of art and be admitted by modern science. Darwinism, and all that it brought in its train in the nineteenth century, rendered great service to the progress of human knowledge and culture, but it gave rise to many one-sided conceptions, for instance, in the law of so-called “selection” which has been laid down as a universal law, although it only holds good in one connection. The knowledge of this law is very important, but to lay it down as a universal law is the result of distorted, one-sided conceptions. People have been led to think somewhat as follows. They ask, ‘Why is it that the structure of living beings is contrived in accordance with expediency? What is the origin of this?’ The monistic materialist of the present day answers: ‘We are no longer as stupid as our ancestors. We have great intelligence and do not therefore believe that some spiritual being or other has endowed living organisms with this “expedient” structure. It is part of nature that the expedient and the inexpedient (the fit and the unfit) should originally have arisen, concomitantly. These two elements then entered into the struggle for existence where the fit conquered and the unfit was exterminated. The fit passes down through heredity, so that after a certain time it alone remains.’ The ‘fitness’ of the organic structure was thus explained by the law of causality. This conception is then applied in a special instance. Some creature lives in a certain environment and has this remarkable characteristic, that its colouring is the same as that of its environment. Certain creatures live, let us say, in sand of a particular colour. In such cases observation shows that the creatures take on the colour of the sand. Those who adhere to the theory of selection and expediency say: ‘It is expedient for these creatures to have the colour of their environment, for their enemies do not see them and hence cannot pursue them. They are not destroyed. They have this advantage over other creatures whose colour differs from that of the sand. Once upon a time there were creatures who colours resembled the sand, while others were of every possible hue. But these latter were seen by their foes and destroyed; they were at a disadvantage in the struggle for existence.’ The others, however, who were, by chance of the same colour as the sand, remained, and this quality was transmitted to the following generations. The creatures who were differently coloured died out and those like the sand maintained themselves in the struggle for existence.' This is a highly plausible train of thought and it has dominated the minds of men for decades. In sandy places hosts of these tiny creatures of exactly the same colour as the sand are to be found. According to materialistic, monistic Darwinism they are supposed to have originated as I have described. But actual facts upset the conclusion, for, in spite of it all, as soon as these creatures show themselves they are destroyed by their foes. The whole conception is based upon a chain of argument that does not reckon with the actual facts. All these materialistic speculations and fantasies will one day be replaced by true insight which may indeed seem grotesque and paradoxical to many people but which will explain, for instance, why the polar bear is white and not black or brown. The insight will arise that there is an astral nature, that every animal has an astral body and that soul processes have their seat in this astral body. The greyish coloured creatures in the sand have of course no ego, but they have an astral body, primitive though it may be. An interplay arises between this astral body and the colour of the environment, and the effects produced by this interplay between the greyness, let us say, of the environment, and the astral body, pass into the dimmer consciousness of the astral body and permeate the whole being. It is just as if you were to look around here and say, ‘This is wood, I know that it is wood.’ The creature lives in the sand, its astral body is permeated with the colour of the sand and the consciousness of the colour of the sand' flows through its whole being. It takes on the colour, saturates itself with the colour of the environment which has been consciously absorbed. The colour is of course modified by every struggle arising between the immediate colour of the environment and the direct light of the sun. The influence of the direct light of the sun on the astral body, however, is such that, by way of the soul nature, something that in turn streams out and permeates the the whole being enters into the astral body. In the very colours of birds' feathers and skins of animals man will recognise the deeper effects of the consciousness, which is the result of the interplay between the astral body and the environment. The living being lives and moves in the flowing ocean of colour and identifies itself with this flowing colour essence. The human being also does this below the threshold of his ego, but in a higher sense. Our life, therefore, is bound up with the life of the flowing sea of colour. As human beings we have the advantage of the animals in one thing only. I can now do no more than hint at it. Think, by way of comparison, of certain animals which always swim under water and never come to the surface. They have water in their environment. They adapt themselves to what they take into themselves from the water. Others have to come to the surface and they too adapt themselves to what is above the surface of the water. Instead of the water, think now of a flowing sea of colour and light. All animals live, as it were, under the surface of the sea of colour and light, hence they adjust their outer covering primarily in accordance with this flowing colour and light. Man with his ego consciousness stretches out beyond the sea of colour and light and the very fact that he can do this gives him his ego consciousness. When man's colouring is influenced, as in the different races, the influence is not, in his case, the outcome of colour and light, but of the conditions of warmth and climate. The reason why humming birds in certain regions are decked with such a variety of colours is very different from the reason which causes human beings in the same region to be of a negroid black. The birds have been worked upon by colour conditions, and man by the warmth condition, because, in effect, the human being with his ego rises above the sea of colour and this only works in his astral body. Otherwise—to use a radical and therefore paradoxical expression—if the agricultural labourer who is perpetually surrounded by green had no ego whereby he reaches beyond the sea of colour, he would go about with a greenish skin; and the skin of the city man, living perpetually among grey houses and seldom leaving them, would have a horrible greyish tint—that is to say if primordial forces were at work., Our astral body none the less is immersed in the flowing sea of colour, but all that the astral body absorbs from this sea of colour has taken on a different activity. Our hair is not coloured, nor if we had feathers would they be coloured by what the astral body absorbs; instead of this, we have perceptions and feelings in connection with colour without diffusing the colours through our being. If we were simply to absorb the green or blue or red into our astral body and diffuse them through our being, thus giving ourselves the colouring of the outer world, we should have quite a different relationship to the world of colour than is actually the case. We do not, however, do this. We absorb the colours into our being in a spiritual sense, so that blue, for instance, becomes the expression of rest; red the expression of all that is passionate, fiery. Colour is changed into flowing perception or feeling in man, because he reaches out with his ego beyond the flowing sea of colour. Here is a proof that we float in the colour essence of the cosmos and that even when we are merely contemplating the colours of nature we must try to perceive in the aesthetic sense, to establish standards of beauty. This however implies that we must learn to grow into colours, to live in them as within our own element. One seldom finds this feeling for colour, even among people who think a great deal about art. Take, for instance, Hildebrand, who is an exceedingly good artist and who has written an ingenious book on the subject of artistic forms. We read there that colour alone cannot suffice for the real portrayal of things; there must first be the design, the drawing. This, however, is not correct. Hildebrand thinks that when he has a coloured wall in front of him, he is simply looking at colour, possibly blue or red, whereas if he draws contours or designs upon it he has an expression of something. If a surface is covered with blue or red it does not express anything definite—at least according to Hildebrand. Nor this is not the case. A surface covered with blue produces an impression which may be expressed in the following way. Instead of the area that appears blue, the feeling arises that blue takes one into greater and greater depths, to distances ever more remote, to the Infinite, as it were. The blue colour takes one along with it—on and on. Red seems to fight with one, to approach. This of course is somewhat radically expressed, but the whole colour scale thus reveals itself as living being. Just as forms with clear contours express something definite, so does colour place before us something quite definite, differentiated. To fathom these things, however, will be the task of future Art—and in what sense? To understand this we will consider the real nature of the spirit of human evolution. Human evolution proceeded from conditions of primitive, atavistic clairvoyant consciousness. Man gradually worked his way upwards through the different civilisations until, during the Graeco-Latin age, his ego came to birth in the intellectual or mind-soul. We are now living in an age when the ego rises into the consciousness soul (spiritual soul) and has then gradually to rise to Spirit-Self or Manas. In the ages preceding the birth of the ego, of the ego consciousness, art proceeded from direct inspiration which flowed into man from the spiritual world, and all the different forms in art were an expression of this. Suppose a man went out into the on-coming night and looked at the moon. The atavistic clairvoyant consciousness he still possessed gave him the knowledge that here was a revelation of the connection between his brain and the moon, that his lungs breathed in all that the earth's being was communicating to him. The sun had set, but he knew that in the pulsating beat of his heart he bore the sun workings within him. Then man felt—or rather he ‘saw’ it in the atavistic clairvoyance of those ancient times—he felt: ‘Yes indeed there is a connection between earth, sun and moon. Spiritual Beings are hovering up and down between the sun and moon!’
... Then came the age in human evolution when this old clairvoyance gradually passed away; man entered into a condition where he could only perceive the external world of sense. Nothing flowed into him from the spiritual world and it became necessary to resort to a different realm. Every artistic impulse lived originally in the moving being of man himself. He tried to imitate or copy what he perceived in the cosmos by expressing through his hands and with his hands the form that he felt to be living in his hands like a cosmic force. At that time he had to translate into form what he expressed in gestures. It did not occur to him to copy or imitate an object in the external sense. All that lived and pulsated within him, flowing and breathing into him from the cosmos, developed into art without any mere imitation, because the inner life surging within him used him as an instrument. He was the instrument guided by the cosmos itself. This was no longer the case after the old clairvoyant consciousness, which linked man to the cosmos, ceased. Imitative art came into being, for man no longer possessed within himself the power which guided the lines and other factors of art; he no longer felt, I will draw near to the Godhead. ‘There is the Godhead and I will approach.’ When a man felt himself rising to the Godhead he was conscious of the perception of blue, and if he wanted to give expression to this feeling he used the colour blue. But if he was conscious of the approach of an enemy, an alien being bearing down upon him, then he used red. He experienced the flowing sea of colour within himself and there was no need to imitate or copy. This was no longer the case when atavistic connection with the cosmos ceased. Imitative art came into being and attained its summit, so far as sculpture was concerned, in the Graeco-Latin epoch, and so far as painting was concerned, in the age which marked the transition to the fifth Post-Atlantean period. To those who have eyes to see, external history would also be able to prove the truth of these things. Try to think why it is that peoples from Northern and Central Europe who came into contact with Graeco-Latin culture remained so long in a state of barbarism and could not find their way to art. The reason is that these Celtic, Germanic, Slavonic peoples had remained at an earlier stage of evolution than the Graeco-Latin peoples. They had not reached the stage of the full birth of the ego and understood nothing of true imitative art. They came along afterwards with a reinforcing impulse. Hence when we study the art of the Middle Ages we find that the significant elements there are not those of imitative art. The characteristic qualities of mediaeval art are to be found in architecture where man does not imitate but creates out of his inner being. It is only gradually that the imitative element in art entered into the northern peoples. Nowadays, however, we are living in an epoch when man must again find his way into the spiritual world, when he must pass over from imitative art to a new form of artistic creation, when there must be a true renewal of art. The imitative arts reached their prime in the sculpture of antiquity, in Raphael, Michelangelo and others. Something different hovers before us now—a consciousness that penetrates into the spiritual world and at the same time brings down all that exists in forms and colours in the cosmic ocean flowing spiritually around us. A beginning must be made. Something that is not achieved by imitation and which is all around us must be brought down from the spiritual world. I have already spoken of the extent to which this conception has flowed into certain forms in our building and on another occasion we will speak of the new conception of the art of painting. To-day I only wanted to try to deepen the feelings and perceptions which must be ours if we are really to understand the transition which must come about before the old forms of art can pass over to the new. I hope that those friends whose unselfish and devoted labours are revealed each day that passes, will work in such a way towards a mastery of the forms which are necessary to our building, that although it be only a primitive beginning, there will none the less be a real beginning of a spiritualised art. I hope that they will find more and enthusiasm, greater and greater joy, in the consciousness that the World-Spirit demands us to help in the task of establishing in human evolution those things which must be established in our own fifth epoch and during the transition into the sixth. If we understand this, we link ourselves with the World-Spirit working in human evolution, of Whom we try to gain knowledge through true Spiritual Science. All the impulses of this Spiritual Science can pass over into artistic feeling, artistic activity and experience of the cosmos. True enthusiasm and devotion are necessary, but they will grow in us if we lovingly rise to the Spirit Who has guided mankind from the beginning of evolution. That Spirit will not forsake us if we dedicate ourselves to Him with upright hearts and in the real sense—if our labours are not a sentimental prayer, but a true one arising from the power flowing into our inner being from the World-Spirit Who is leading us, and if we are filled with the inspiration of the knowledge that we allow the work of our hands and souls to be guided by the power of the Spirit within us. In this sense, then, let us continue our work.   (Centaur and Slavonic Man) |


 I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us.
I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us. And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
 Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’
Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’ In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.
In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.
 I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal.
I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal. Underneath what has to bear the capital we find the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column, but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns, introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns, carried out in such a way that it forms a procession: Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on.
Underneath what has to bear the capital we find the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column, but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns, introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns, carried out in such a way that it forms a procession: Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on. The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer.
The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer. The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically.
The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically.  If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being.
If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being. The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.
The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.
 If you compare it with the Greek Temple you will discover the difference. The Greek motif is complete in itself. This other motif, when it is a wall—for instance the separate perpendicular wall—only has meaning when it is not merely wall, but when it grows out of the whole. The wall is not merely wall, it is living, just like a living organism that allows elevations and depressions to grow out of itself. The wall lives—that is the difference. Think of a Greek Temple. Although there are many columns, the whole is none the less governed by gravity. In our building, however, nothing is mere wall. The forms grow out of the wall. That is the essential thing. And when we pass around inside our building we shall find one plastic form, a continuous relief sculpture on the capitals, plinths, architraves. They grow out of the wall, and the wall is their basis, their soil, without which they could not exist. There will be a great deal of relief carving in wood in the interior of the building, and forms which, although they are not to be found elsewhere in the physical world, represent an onward flowing evolution. Beginning between the Saturn columns at the back, there will be a kind of symphonic progression to the culmination in the East. But the forms are no more present in the outer physical world than melodies are present there. These forms are walls that have become living. Physical walls do not live, but etheric walls, spiritual walls are indeed living.
If you compare it with the Greek Temple you will discover the difference. The Greek motif is complete in itself. This other motif, when it is a wall—for instance the separate perpendicular wall—only has meaning when it is not merely wall, but when it grows out of the whole. The wall is not merely wall, it is living, just like a living organism that allows elevations and depressions to grow out of itself. The wall lives—that is the difference. Think of a Greek Temple. Although there are many columns, the whole is none the less governed by gravity. In our building, however, nothing is mere wall. The forms grow out of the wall. That is the essential thing. And when we pass around inside our building we shall find one plastic form, a continuous relief sculpture on the capitals, plinths, architraves. They grow out of the wall, and the wall is their basis, their soil, without which they could not exist. There will be a great deal of relief carving in wood in the interior of the building, and forms which, although they are not to be found elsewhere in the physical world, represent an onward flowing evolution. Beginning between the Saturn columns at the back, there will be a kind of symphonic progression to the culmination in the East. But the forms are no more present in the outer physical world than melodies are present there. These forms are walls that have become living. Physical walls do not live, but etheric walls, spiritual walls are indeed living. (Dr. Steiner here read a passage from a book) ... The author is trying to form a conception of what relief really is. But the conception is built up simply from what the eye perceives, as he plainly shows when he says that the relief is produced when one thinks of the background as a pane of glass and that which lies in front of the pane as shut off by another pane of glass. He therefore bases his conception of relief on the eye and in order to make it clear he uses the two panes of glass on which the whole figure is projected. As against this conception we have our own which passes over from what is made visible by glass and projection to that which lives. We want to make relief a living thing. Relief has no meaning when one simply designs figures on a wall. It only has meaning when it calls forth the intuition that the wall itself is living and can bring forth the figures.
(Dr. Steiner here read a passage from a book) ... The author is trying to form a conception of what relief really is. But the conception is built up simply from what the eye perceives, as he plainly shows when he says that the relief is produced when one thinks of the background as a pane of glass and that which lies in front of the pane as shut off by another pane of glass. He therefore bases his conception of relief on the eye and in order to make it clear he uses the two panes of glass on which the whole figure is projected. As against this conception we have our own which passes over from what is made visible by glass and projection to that which lives. We want to make relief a living thing. Relief has no meaning when one simply designs figures on a wall. It only has meaning when it calls forth the intuition that the wall itself is living and can bring forth the figures. If we pay heed to the organs of the Gods which they themselves created when, as the Elohim, they gave the earth to man, if we pay heed to the etheric forms of the plants and mould in accordance with them, we are creating in the same way as nature created the larynx in man in order that he might speak—we are indeed creating a larynx through which the Gods may speak to us. If we hearken to the music of the forms on our walls which are the larynx for the speech of the Gods, we are seeking the way back to Paradise. I will speak of painting in another lecture. To-day I want to speak of the relief work and sculpture which will be produced in this house we have opened to-day. I have tried to explain how relief may become an organ for the speech of the Gods and on some future occasion we will speak of how colours become soul-organs for the speech of the Gods. Our age has little understanding for the kind of conceptions that must inspire us if we are really to fulfil our task. The Greek Temple was the dwelling place of the God, the Church of Christendom the framework around the community who would fain be united with the Spirit. What is our building to be? This is already revealed in its ground-plan and rounded form. The building is bipartite but the architectural forms of the two sections have equal importance. There is no difference as in the case of the chancel and the space for the congregation in a Christian Church.
If we pay heed to the organs of the Gods which they themselves created when, as the Elohim, they gave the earth to man, if we pay heed to the etheric forms of the plants and mould in accordance with them, we are creating in the same way as nature created the larynx in man in order that he might speak—we are indeed creating a larynx through which the Gods may speak to us. If we hearken to the music of the forms on our walls which are the larynx for the speech of the Gods, we are seeking the way back to Paradise. I will speak of painting in another lecture. To-day I want to speak of the relief work and sculpture which will be produced in this house we have opened to-day. I have tried to explain how relief may become an organ for the speech of the Gods and on some future occasion we will speak of how colours become soul-organs for the speech of the Gods. Our age has little understanding for the kind of conceptions that must inspire us if we are really to fulfil our task. The Greek Temple was the dwelling place of the God, the Church of Christendom the framework around the community who would fain be united with the Spirit. What is our building to be? This is already revealed in its ground-plan and rounded form. The building is bipartite but the architectural forms of the two sections have equal importance. There is no difference as in the case of the chancel and the space for the congregation in a Christian Church.  The difference in the dimensions of the two sections of our building merely signifies that in the large cupola the physical preponderates and that in the small cupola we have tried to make the spiritual predominate. This very form expresses aspiration to the Spirit. Every single detail must express this aspiration to the Spirit, inasmuch as we are striving to create an organ for the speech of the Gods. I have said that those who really understand our building fully will put away lying and unrighteousness; the building may indeed become a ‘Lawgiver,’ and the truth of this can be studied in the different forms and in the architraves. Everything in the building will have an inner value. Every part of the larynx has inner value; no words could be uttered if the larynx did not contain a a particular form at the right place. If, for instance, we were to make an indention here (see diagram) and think of a kind of roofing over it, the whole form expresses the fact that this building must be filled with the feeling of hearts striving together in love.
The difference in the dimensions of the two sections of our building merely signifies that in the large cupola the physical preponderates and that in the small cupola we have tried to make the spiritual predominate. This very form expresses aspiration to the Spirit. Every single detail must express this aspiration to the Spirit, inasmuch as we are striving to create an organ for the speech of the Gods. I have said that those who really understand our building fully will put away lying and unrighteousness; the building may indeed become a ‘Lawgiver,’ and the truth of this can be studied in the different forms and in the architraves. Everything in the building will have an inner value. Every part of the larynx has inner value; no words could be uttered if the larynx did not contain a a particular form at the right place. If, for instance, we were to make an indention here (see diagram) and think of a kind of roofing over it, the whole form expresses the fact that this building must be filled with the feeling of hearts striving together in love.
 The lines between any point of the ellipse and the two foci will naturally differ, but the two lines together will come to the same length (a + b = c + d in diagram). You can add the distances of each point from these two foci and you will always get the same length. This is so simple in the case of the circle that there is no need for an mental process. In the case of the ellipse, however, we must make an addition. All lines to the centre of the circle are equal, but in the ellipse we have to make an addition. Now you will say: ‘Yes, but I do not add when I see an ellipse.’ You yourself do not, it is true, but your astral body does; what the geometrician does consciously the astral body does unconsciously. The astral body is a finished geometrician. You have no idea of all the knowledge that is contained in your astral bodies; in the astral body you are all the wisest of geometricians, only of course the geometry you know in the astral body can only be brought into consciousness by the ‘sweat of the brow.’ You must pardon this expression but it is permissible to-day (... it was very hot on the day this lecture was given.) Everything is there in the astral body and if those who teach geometry, instead of using their wonted methods, could apply a pump in order to extract what is in the astral body, they would no longer need to teach—the knowledge would well up of itself. We add, then, the two distances from the foci and always get the same result. When an ellipse form seems beautiful, what does this really imply? It implies that the astral body is adding and the sum total is always the same. And now picture to yourselves that you are adding without knowing it and every time getting the same result. You feel pleased. Now you go to another point and carry out the same process. ... The same total again—oh! what joy! This is the living experience of the ellipse.
The lines between any point of the ellipse and the two foci will naturally differ, but the two lines together will come to the same length (a + b = c + d in diagram). You can add the distances of each point from these two foci and you will always get the same length. This is so simple in the case of the circle that there is no need for an mental process. In the case of the ellipse, however, we must make an addition. All lines to the centre of the circle are equal, but in the ellipse we have to make an addition. Now you will say: ‘Yes, but I do not add when I see an ellipse.’ You yourself do not, it is true, but your astral body does; what the geometrician does consciously the astral body does unconsciously. The astral body is a finished geometrician. You have no idea of all the knowledge that is contained in your astral bodies; in the astral body you are all the wisest of geometricians, only of course the geometry you know in the astral body can only be brought into consciousness by the ‘sweat of the brow.’ You must pardon this expression but it is permissible to-day (... it was very hot on the day this lecture was given.) Everything is there in the astral body and if those who teach geometry, instead of using their wonted methods, could apply a pump in order to extract what is in the astral body, they would no longer need to teach—the knowledge would well up of itself. We add, then, the two distances from the foci and always get the same result. When an ellipse form seems beautiful, what does this really imply? It implies that the astral body is adding and the sum total is always the same. And now picture to yourselves that you are adding without knowing it and every time getting the same result. You feel pleased. Now you go to another point and carry out the same process. ... The same total again—oh! what joy! This is the living experience of the ellipse. The hyperbola also has two foci which lie approximately here. Again we can draw lines to these two points. The strange thing here is that we do not add but subtract. We always get the same result by subtracting the lesser from the greater. Our astral body subtracts and is glad that the difference is always the same. In this inner feeling of equality the astral body experiences the source of the hyperbola.
The hyperbola also has two foci which lie approximately here. Again we can draw lines to these two points. The strange thing here is that we do not add but subtract. We always get the same result by subtracting the lesser from the greater. Our astral body subtracts and is glad that the difference is always the same. In this inner feeling of equality the astral body experiences the source of the hyperbola.
 There we must divide two distances instead of adding, subtracting or multiplying. That is to say, it must be possible for our astral body to determine two points—and also other points if it takes the larger line—and to divide the greater distance by the smaller. The astral body, then, must be able to divide and when it does this it gets a line (see diagram). All the points are so that their distances from two points are the same in the division.
There we must divide two distances instead of adding, subtracting or multiplying. That is to say, it must be possible for our astral body to determine two points—and also other points if it takes the larger line—and to divide the greater distance by the smaller. The astral body, then, must be able to divide and when it does this it gets a line (see diagram). All the points are so that their distances from two points are the same in the division. Let me try to make a diagrammatic sketch of this process. Underneath we have the Earth. Man is at first a horizontal being; then he stands upright—in the vertical position. It is an achievement of man's nature itself to attain the vertical position but he has the help of all the hierarchies as he passes through the course of his life. What is it that comes to his aid when he stands upright and walks? The forces that work from the Earth out into the expanses of cosmic space. These are the earthly forces. To-day physicists only speak of purely physical forces of the Earth—forces of attraction, of gravity and the like. The Earth, however, is not merely physical body but a being of spirit and soul and when, as little children, we raise ourselves to the upright position and walk, we are uniting ourselves with the forces of Will rising out of the Earth. The Earth-Will permeates our being; we allow the Earth -Will to flow into us and place ourselves in the upright position—the direction of the Earth-Will. This process is a union with the Earth-Will. But in opposition to the Earth-Will there is a will that works in from all sides of the cosmos. We have no knowledge of it, but yet it is the case that as we raise ourselves to the upright position, forces (from the cosmos) are working in from all sides and we come up against these forces that are pouring in from outside. This has no particular significance to-day, on the Earth, but during the ancient Moon period it had a tremendous significance. On the ancient Moon, conditions were such that from his earliest childhood man had a different orientation, in that he had to place himself in line with the direction of the Moon-Will. As the result of this he acquired the first germs of the skull formation. To-day we have inherited them, but on the Moon it was a question of acquiring them. In those times man worked in himself against the outer will-forces somewhat in the way a locomotive works when it has to push away snow. He pressed back the will-forces of the cosmos and his soft skull formation compressed itself into the hard skull covering. To-day this process is no longer necessary. The skull formation is inherited. It is no longer necessary to build up the skull bones. In the etheric body, however, we still build them, for as we rise to the upright position there is a densification in the head, representing the result of the fight between the forces streaming in from all sides of the cosmos. Thus, when we observe the etheric body, we may say that in his two legs, man builds up two lines of force and works against the forces that proceed from without. The etheric body is densified and this form arises (see next diagram). We raise ourselves upright. The physical legs have their junction above, but the etheric legs rise still higher.
Let me try to make a diagrammatic sketch of this process. Underneath we have the Earth. Man is at first a horizontal being; then he stands upright—in the vertical position. It is an achievement of man's nature itself to attain the vertical position but he has the help of all the hierarchies as he passes through the course of his life. What is it that comes to his aid when he stands upright and walks? The forces that work from the Earth out into the expanses of cosmic space. These are the earthly forces. To-day physicists only speak of purely physical forces of the Earth—forces of attraction, of gravity and the like. The Earth, however, is not merely physical body but a being of spirit and soul and when, as little children, we raise ourselves to the upright position and walk, we are uniting ourselves with the forces of Will rising out of the Earth. The Earth-Will permeates our being; we allow the Earth -Will to flow into us and place ourselves in the upright position—the direction of the Earth-Will. This process is a union with the Earth-Will. But in opposition to the Earth-Will there is a will that works in from all sides of the cosmos. We have no knowledge of it, but yet it is the case that as we raise ourselves to the upright position, forces (from the cosmos) are working in from all sides and we come up against these forces that are pouring in from outside. This has no particular significance to-day, on the Earth, but during the ancient Moon period it had a tremendous significance. On the ancient Moon, conditions were such that from his earliest childhood man had a different orientation, in that he had to place himself in line with the direction of the Moon-Will. As the result of this he acquired the first germs of the skull formation. To-day we have inherited them, but on the Moon it was a question of acquiring them. In those times man worked in himself against the outer will-forces somewhat in the way a locomotive works when it has to push away snow. He pressed back the will-forces of the cosmos and his soft skull formation compressed itself into the hard skull covering. To-day this process is no longer necessary. The skull formation is inherited. It is no longer necessary to build up the skull bones. In the etheric body, however, we still build them, for as we rise to the upright position there is a densification in the head, representing the result of the fight between the forces streaming in from all sides of the cosmos. Thus, when we observe the etheric body, we may say that in his two legs, man builds up two lines of force and works against the forces that proceed from without. The etheric body is densified and this form arises (see next diagram). We raise ourselves upright. The physical legs have their junction above, but the etheric legs rise still higher.  As a result of this the etheric head is densified and as a result of the formation of the brain there arises in the etheric body, in our age as well, the densified etheric body. This does not only take place in childhood but as man passes through seven life periods (from the first to the seventh year, from the seventh to the fourteenth year and so on) new lines are formed, lines of different forces which pass upwards. So that when we have reached the age of full and complete manhood—when we have passed the fiftieth year of life—we have added new pairs of pillars to that first strong pair formed during the first seven years of life. They appear in the etheric body in different colours. We strengthen our etheric sheath every time we develop these ‘life pillars’—for so indeed they may be called. After the first period of seven years the first pair of life pillars is completed, at the fourteenth year the second pair, at the twenty-first year the third pair, and finally, with the forty-ninth year, the seventh pair. Each pair of life pillars makes our etheric skull-covering more secure. Man passes through his life and after every seven years raises within himself different pillar formations which bear his skull. When we have understood this we shall have a living conception of the inner form of the larger section of our building. We enter at the West and say to ourselves: ‘Up to the first pair of pillars we see how man develops in the first seven years of his life; the second pair of pillars denotes his development to his fourteenth year, then on to the twenty-first year and so on.’ And the etheric sheath of the head is always around us. Man, the living being, is poured out into the forms as an etheric being.
As a result of this the etheric head is densified and as a result of the formation of the brain there arises in the etheric body, in our age as well, the densified etheric body. This does not only take place in childhood but as man passes through seven life periods (from the first to the seventh year, from the seventh to the fourteenth year and so on) new lines are formed, lines of different forces which pass upwards. So that when we have reached the age of full and complete manhood—when we have passed the fiftieth year of life—we have added new pairs of pillars to that first strong pair formed during the first seven years of life. They appear in the etheric body in different colours. We strengthen our etheric sheath every time we develop these ‘life pillars’—for so indeed they may be called. After the first period of seven years the first pair of life pillars is completed, at the fourteenth year the second pair, at the twenty-first year the third pair, and finally, with the forty-ninth year, the seventh pair. Each pair of life pillars makes our etheric skull-covering more secure. Man passes through his life and after every seven years raises within himself different pillar formations which bear his skull. When we have understood this we shall have a living conception of the inner form of the larger section of our building. We enter at the West and say to ourselves: ‘Up to the first pair of pillars we see how man develops in the first seven years of his life; the second pair of pillars denotes his development to his fourteenth year, then on to the twenty-first year and so on.’ And the etheric sheath of the head is always around us. Man, the living being, is poured out into the forms as an etheric being.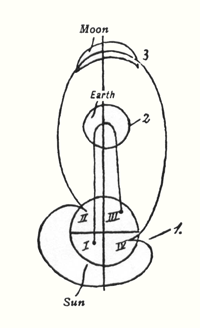 The drawing can of course only be diagrammatical. Let us suppose that this diagram represents, here the Sun, here the Earth and here the Moon. The sketch is only diagrammatical, for naturally I cannot express the dimensional proportions and distances of the heavenly bodies. That, however is not the point at issue. When the clairvoyant consciousness of the occult seer enters into a certain relationship with these three heavenly bodies, that is to say, with what they represent spiritually, the whole universe seems to be pervaded through and through with the interplay of the spiritual content of these various heavenly bodies. Beings have their home on all the heavenly bodies, as you have often heard; not only so, but they send forth their workings. Higher beings inhabit the heavenly bodies for long ages; subordinate beings are sent from one heavenly body to another and are the cause of currents being set in motion in the cosmos. These currents are often nothing less than the beings who are sent forth by certain elementary or higher beings from one cosmic body to the other. In the first place, therefore, clairvoyant consciousness perceives how magnetic or electric currents in the cosmos flow from one heavenly body to another; in more exact observation this resolves itself into a host, a stream, a swarm of spiritual beings passing from one heavenly body to another.
The drawing can of course only be diagrammatical. Let us suppose that this diagram represents, here the Sun, here the Earth and here the Moon. The sketch is only diagrammatical, for naturally I cannot express the dimensional proportions and distances of the heavenly bodies. That, however is not the point at issue. When the clairvoyant consciousness of the occult seer enters into a certain relationship with these three heavenly bodies, that is to say, with what they represent spiritually, the whole universe seems to be pervaded through and through with the interplay of the spiritual content of these various heavenly bodies. Beings have their home on all the heavenly bodies, as you have often heard; not only so, but they send forth their workings. Higher beings inhabit the heavenly bodies for long ages; subordinate beings are sent from one heavenly body to another and are the cause of currents being set in motion in the cosmos. These currents are often nothing less than the beings who are sent forth by certain elementary or higher beings from one cosmic body to the other. In the first place, therefore, clairvoyant consciousness perceives how magnetic or electric currents in the cosmos flow from one heavenly body to another; in more exact observation this resolves itself into a host, a stream, a swarm of spiritual beings passing from one heavenly body to another.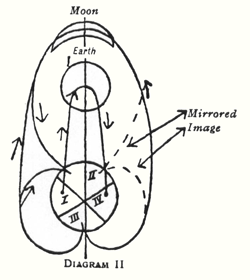 The line connecting with the Moon Moon must now be drawn differently. I am representing the same streams as in the first diagram only the Sun is turned a little. The lines are somewhat different but they arise within and flow into the same heavenly bodies.
The line connecting with the Moon Moon must now be drawn differently. I am representing the same streams as in the first diagram only the Sun is turned a little. The lines are somewhat different but they arise within and flow into the same heavenly bodies. Man is bound up with the cosmos; he is an actual expression of all the great cosmic connections. Now you need only think of the heart in man as the microcosm of the Sun, the lungs as the microcosm of the Earth (of this particular hierarchy of forces) and the brain as the microcosm of the Moon, and you have something both highly suggestive and significant.
Man is bound up with the cosmos; he is an actual expression of all the great cosmic connections. Now you need only think of the heart in man as the microcosm of the Sun, the lungs as the microcosm of the Earth (of this particular hierarchy of forces) and the brain as the microcosm of the Moon, and you have something both highly suggestive and significant.