| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: The Essence of Anthroposophy
03 Feb 1913, Berlin Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| – but it is certainly difficult to introduce into the modern life of the spirit enough understanding to enable people to feel Dante’s Beatrice and Philosophy as equally real and actual. Why is this? |
| In reality it is deeply symbolic when we take up Hegel’s philosophy, especially the Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences, and find as the last thing in this nineteenth-century book, a statement of the way in which philosophy interprets itself. It has understood everything else; finally, it grasps itself. What is there left for it to understand now? It is the symptomatic expression of the fact that philosophy has come to an end, even if there are still many questions to be answered since Hegel’s days. |
| This is the progress of the history of human evolution in relation to the spiritual facts under consideration. And now I leave it to all those, who wish to examine the matter very minutely, to see how it may also be shown in detail from the destiny of Sophia, Philosophia and Anthroposophia, how humanity evolves progressively through the soul principles which we designate the intellectual soul (the soul of the higher feelings), the self-conscious soul and the Spirit-Self. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: The Essence of Anthroposophy
03 Feb 1913, Berlin Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A lecture given during the first general meeting of the Anthroposophical Society in Berlin My dear theosophical friends! When in the year 1902, we were founding the German Section of the Theosophical Society, there were present, as most of our theosophical friends now assembled know, Annie Besant and other members of the Theosophical Society at that date – members who had been so for some time. Whilst the work of organization and the lectures were going on, I was obliged to be absent for a short time for a particular lecture of a course which I was at that time – more than ten years ago – delivering to an audience in no way belonging to the theosophical movement, and the members of which have, for the most part, not joined it. Side by side, so to say with the founding of the theosophical movement in Germany, I had during these days to deliver a particular lecture to a circle outside it; and because the course was a kind of beginning, I had used, in order to describe what I wished to say in it, a word which seemed to express this still better than the word ‘Theosophy’ – to be more in keeping with the whole circumstances and culture of our time. Thus, whilst we were founding the German Section, I said in my private lecture that what I had to impart could best be designated by the word ‘Anthroposophy’. This comes into my memory at the present moment, when all of us here assembled are going apart, and alongside of that which – justly of course – calls itself Theosophy are obliged to choose another name for our work, in the first place as an outer designation, but which at the same time may significantly express our aims, for we choose the name ‘Anthroposophy’. If through spiritual contemplation we have gained a little insight into the inner spiritual connection of things – a connection in which necessity is often present, even if to outer observation it appears to be a matter of mere ‘chance’ – feeling may perhaps be allowed to wander back to the transition I was then obliged to make from the business of founding the German Section to my anthroposophical lecture. This may be specially permissible today when we have before us the Anthroposophical Society as a movement going apart from the Theosophical Society. In spite of the new name no change will take place with regard to what has constituted the spirit of our work, ever since that time. Our work will go on in the same spirit, for we have not to do with a change of cause, but only with a change of name, which has become a necessity for us. But perhaps the name is for all that rather suitable to our cause, and the mention of feeling with regard to the fact of ten years ago, may remind us that the new name may really suit us very well. The spirit of our work – will remain the same. It is really that which at bottom we must call the essence of our cause. This spirit of our work is also that which claims our best powers as human beings, so far as we feel ourselves urged to belong to this spiritual movement of ours. I say, “ours best power as human beings” because people at the present time are not yet very easily inclined to accept that which – be it as Theosophy or Anthroposophy – has to be introduced into the spiritual and mental life of progressive humanity. We may say “has to be introduced” for the reason that one who knows the conditions of the progressive spiritual life of humanity, gains from the perception of them, the knowledge that this theosophical or anthroposophical spirit is necessary to healthy spiritual and mental life. But it is difficult to bring into men’s minds, in let us say a plain dry way, what the important point is. It is difficult and we can understand why. For people who come straight from the life of the present time, in which all their habits of thought are deeply connected with a more materialistic view of things, will at first naturally find it very difficult to feel themselves at home with the way in which the problems of the universe are grappled with by what may be called the theosophical or anthroposophical spirit. But it has always been the case that the majority of people have in a certain sense followed individuals who make themselves, in a very special way, vehicles of spiritual life. It is true the most various gradations are to be found within the conception of the world that now prevails; but one fact certainly stands out as the result of observing these ideas – that a large proportion of contemporary humanity follows – even when it does so unconsciously – on the one hand certain ideas engendered by the development of natural science in the last few centuries, or on the other hand a residuum of certain philosophical ideas. And on both sides – it may be called pride or may appear as something else – people think that there is something ‘certain’, something that seems to be built on good solid foundations, contained in what natural science has offered, or, if another kind of belief has been chosen, in what this or that philosophical school has imparted. In what flows from the anthroposophical or theosophical spirit, people are apt to find something more or less uncertain, wavering – something which cannot be proved. In this connection the most various experiences may be made. For instance, it is quite a common experience that a theosophical or anthroposophical lecture may be held somewhere on a given subject. Let us suppose the very propitious case (which is comparatively rare) of a scientific or philosophical professor listening to the lecture. It might very easily happen that after listening to it he formed an opinion. In by far the greatest number of cases he would certainly believe that it was a well founded, solid opinion, indeed to a certain degree an opinion which was a matter of course. Now in other fields of mental life it is certainly not possible, after hearing a lecture of one hour on a subject, to be able to form an opinion about that subject. But in relation to what theosophy or anthroposophy has to offer, people are very apt to arrive at such a swift judgment, which deviates from all the ordinary usages of life. That is to say, they will feel they are entitled to such an opinion after a monologue addressed to themselves, perhaps unconsciously, of this kind, “You are really a very able fellow. All your life you have been striving to assimilate philosophical – or scientific – conceptions; therefore you are qualified to form an opinion about questions in general, and you have now heard what the man who was standing there, knows.” And then this listener (it is a psychological fact, and one who can observe life knows it to be so) makes a comparison and arrives at the conclusion, “It is really fine, the amount you know, and the little he knows.” He actually forms an opinion, after a lecture of an hour’s length, not about what the lecturer knows, but very frequently about what the listener thinks he does not know, because it was not mentioned in the hour’s lecture. Innumerable objections would come to nothing, if this unconscious opinion were not formed. In the abstract, theoretically, it might seem quite absurd to say anything as foolish as I have just said – foolish not as an opinion, but as a fact. Yet although people do not know it, the fact is a very widely spread one with regard to what proceeds from theosophy or anthroposophy. In our time there is as yet little desire really to find out that what comes before the public as theosophy or anthroposophy, at least as far as it is described here, has nothing to fear from accurate, conscientious examination by all the learning of the age; but has everything to fear from science which is really only one-third science – I will not even say one-third – one-eighth, one-tenth, one-twelfth, and perhaps not even that. But it will take time before mankind is induced to judge that which is as wide as the world itself, by the knowledge which has been gained outwardly on the physical plane. In the course of time, it will be seen that the more it is tested with all the scientific means possible and by every individual science, the more fully will true theosophy, true anthroposophy be corroborated. And the fact will also be corroborated that anthroposophy comes into the world, not in any arbitrary way, but from the necessity of the historical consciousness. One who really wishes to serve the progressive evolution of humanity, must draw what he has to give from the sources from which the progressive life of mankind itself flows. He may not follow an ideal arbitrarily set up, and steer for it just because he likes it; but in any given period, he must follow the ideal of which he can say, “It belongs especially to this time.” The essence of Anthroposophy is intimately bound up with the nature of our time; of course not with that of our immediate little present, but with the whole age in which we live. The next four lectures,1 and all the lectures which I have to deliver in the next few days, will really deal with the ‘essence of Anthroposophy’. Everything which I shall have to say about the nature of the Eastern and Western Mysteries, will be an amplification of ‘essence of Anthroposophy’. At the present time I will point out the character of this ‘essence’, by speaking of the necessity through which Anthroposophy has to be established in our time. But once again I do not wish to start from definitions or abstractions, but from facts, and first of all from a very particular fact. I wish to start from the fact of a poem, once – at first I will only say ‘once’ – written by a poet. I will read this poem to you, at first only a few passages, so that I may lay stress on the point I wish to make.
After the poet has enlarged further on the difficulty of expressing what the god of love says to him, he describes the being he loves in the following words:
It appears to be quite obvious that the poet was writing a love-poem. And it is quite certain that if this poem were to be published somewhere anonymously now—it might easily be a modern poem by one of the better poets—people would say. “What a pearl he must have found, to describe his beloved in such wonderful verses”. For the beloved one might well congratulate herself on being addressed in the words:
The poem was not written in our time. If it had been and a critic came upon it, he would say: “How deeply felt is this direct, concrete living relation. How can a man, who writes poems as only the most modern poets can when they sing from the depths of their souls, how can such a man be able to say something in which no mere abstraction, but a direct, concrete presentment of the beloved being speaks to us, till she becomes almost a palpable reality.” A modern critic would perhaps say this. But the poem did not originate in our time, it was written by Dante.2 Now a modern critic who takes it up will perhaps say: “The poem must have been written by Dante when he was passionately in love with Beatrice (or someone else), and here we have another example of the way in which a great personality enters into the life of actuality urged by direct feeling, far removed from all intellectual conceptions and ideas.” Perhaps there might even be a modern critic who would say: “People should learn from Dante how it is possible to rise to the highest celestial spheres, as in the Divine Comedy, and nevertheless be able to feel such a direct living connection between one human being and another.” It seems a pity that Dante has himself given the explanation of this poem, and expressly says who the woman is of whom he writes the beautiful words:
Dante has told us – and I think no modern critic will deny that he knew what he wanted to say – that the ‘beloved one’, with whom he was in such direct personal relations, was none other than Philosophy. And Dante himself says that when he speaks of her eyes, that what they say is no untruth, he means by them the evidence for truth; and by the ‘smile’, he means the art of expressing what truth communicates to the soul; and by ‘love’ or ‘amor’, he means scientific study, the love of truth. And he expressly says that when the beloved personality, Beatrice, was taken away from him and he was obliged to forego a personal relation, the woman Philosophy drew near his soul, full of compassion, and more human than anything else that is human. And of this woman Philosophy he could use these words:
—feeling in the depths of his soul that the eyes represent the evidence for truth, the smile is that which imparts truth to the soul, and love is scientific study. One thing is obviously impossible in the present day. It is not possible that a modern poet should quite honestly and truly address philosophy in such directly human language. For if he did so, a critic would soon seize him by the collar and say. “You are giving us pedantic allegories.” Even Goethe had to endure having his allegories in the second part of Faust taken in very bad part in many quarters. People who do not know how times change, and that our souls grow into them with ever fresh vitality have no idea that Dante was just one of those who were able to feel as concrete, passionate, personal a relation, directly of a soul-nature, towards the lady Philosophy as a modern man can only feel towards a lady of flesh and blood. In this respect, Dante’s times are over, for the woman Philosophy no longer approaches the modern soul as a being of like nature with itself, as a being of flesh and blood, as Dante approached the lady Philosophy. Or would the whole honest truth be expressed (exceptions are of course out of the reckoning), if it were said today, deliberately that philosophy was something going about like a being of flesh and blood, to which such a relation was possible that its expression could really not be distinguished from ardent words of love addressed to a being of flesh and blood? One who enters into the whole relation in which Dante stood to philosophy, will know that that relation was a concrete one, such an one is only imagined nowadays as existing between man and woman. Philosophy in the age of Dante appears as a being whom Dante says he loves. If we look round a little, we certainly find the word ‘philosophy’ coming to the surface of the mental and spiritual life of the Greeks, but we do not find there what we now call definitions or representations of philosophy. When the Greeks represent something, it is Sophia not Philosophia. And they represent her in such a way, that we feel her to be literally a living being. We feel the Sophia to be as literally a living being as Dante feels philosophy to be. But we feel her everywhere in such a way – and I ask you to go through the descriptions which are still existing – that we, so to say, feel her as an elemental force, as a being who acts, a being who interposes in existence through action. Then from about the fifth century after the foundation of Christianity onwards, we find that Philosophia begins to be represented, at first described by poets in the most various guises, as a nurse, as a benefactress, as a guide, and so on. Then somewhat later painters etc. begin to represent her, and then we may go on to the time called, the age of scholasticism in which many a philosopher of the Middle Ages, really felt it to be a directly human relation when he was aware of the fair and lofty lady Philosophia actually approaching him from the clouds; and many a philosopher of the Middle Ages would have been able to send just the same kind of deep and ardent feelings to the lady Philosophia floating towards him on clouds, as the feelings of which we have just heard from Dante. And one who is able to feel such things even finds a direct connection between the Sistine Madonna, floating on the clouds, and the exalted lady, Philosophia. I have often described how in very ancient periods of human development, the spiritual conditions of the universe were still perceptible to the normal human faculty of cognition. I have tried to describe how there was a primeval clairvoyance, how in primeval times all normally developed people were able, owing to natural conditions, to look into the spiritual world. Slowly and gradually that primitive clairvoyance became lost to human evolution, and our present conditions of knowledge took their place. This happened by slow degrees, and the conditions in which we are now living – which as it were represent a temporary very deep entanglement in the material kind of perception – also come by slow degrees. For such a spirit as Dante, as we gather from the description he gives in the Divine Comedy, it was still possible to experience the last remnants of a direct relation of spiritual worlds – to experience them as it were in a natural way. To a man of the present day it is mere foolish nonsense to except him to believe that he might first, like Dante, be in love with a Beatrice, and might afterwards be involved in a second love-affair with Philosophy, and that these two were beings of quite similar nature, the Beatrice of flesh and blood, and Philosophy. It is true I have heard that it was said that Kant was once in love, and someone became jealous because he loved Metaphysics, and asked “Meta what?” – but it is certainly difficult to introduce into the modern life of the spirit enough understanding to enable people to feel Dante’s Beatrice and Philosophy as equally real and actual. Why is this? Just because the direct connection of the human soul with the spiritual world has gradually passed over into our present condition. Those who have often heard me speak, know how highly I estimate the philosophy of the nineteenth century; but I will not even mention it as possible, that anyone could pour forth his feelings about Hegel’s Logic in the words:
I think it would be difficult to say this about Hegel’s Logic. It would even be difficult, although more possible, with regard to the intellectual manner in which Schopenhauer contemplates the world. It would certainly be easier in this case, but even then it would still be difficult to gain any concrete idea or feeling that philosophy approaches man as a concrete being in the way in which Dante here speaks of it. Times have changed. For Dante, life within the philosophic element, within the spiritual world, was a direct personal relation – as personal as any other which has to do with what is today the actual or material. And strange though it seems, because Dante’s time is not very far removed from our own, it is nevertheless true, that for one who is able to observe the spiritual life of humanity, it follows quite as a matter of course for him to say: “People are trying nowadays to know the world; but when they assume that all that man is, has remained the same throughout the ages, their outlook does not really extend much further than the end of their noses.” For even as late as Dante’s time, life in general, the whole relation of the human soul to spiritual world, was different. And if any philosopher is of opinion that the relation which he may have with the spiritual world through Hegel’s or Schopenhauer’s philosophy, is the only possible one, it means nothing more than that a man may still be really very ignorant. Now let us consider what we have been describing – namely, that on the transition from the Graeco-Roman civilisation to our fifth period, that part of the collective being of man which we call the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, which was specially developed during the Graeco-Roman period, was evolved on into the self-conscious soul, during the development which has been going on up to the present. How then in this concrete case of philosophy does the transition from the Graeco-Roman to our modern period come before us – i.e., the transition from the period of the intellectual soul to that of the self-conscious soul? It appears in such a form that we clearly understand that during the development of the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, man obviously still stands in such a relation to the spiritual worlds connected with his origin, that a certain line of separation is still drawn between him and those spiritual worlds. Thus the Greek confronted his Sophia, i.e. pure wisdom, as if she were a being so to say standing in a particular place and he facing her. Two beings, Sophia and the Greek, facing each other, just as if she were quite an objective entity which he can look at, with all the objectivity of the Greek way of seeing things. But because he was still living in the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, he has to bring into expression the directly personal relation of his consciousness to that objective entity. This has to take place in order to prepare the way gradually for a new epoch, that of the self-conscious soul. How will the self-conscious soul confront Sophia? In such a way that it brings the ego into a direct relation with Sophia, and expresses, not so much the objective being of Sophia, as the position of the ego in relation to the self-conscious soul, to this Sophia. “I love Sophia” was the natural feeling of an age which still had to confront the concrete being designated as Philosophy; but yet was the age which was preparing the way for the self-conscious soul, and which, out of the relation of the ego to the self-conscious soul, on which the greatest value had to be placed, was working towards representing Sophia as simply as everything else was represented. It was so natural that the age which represented the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, and which was preparing the self-conscious soul, should bring into expression the relation to philosophy. And because things are expressed only by slow degrees, they were prepared during the Graeco-Roman period. But we also see this relation of man to Philosophia developed externally up to a certain point, when we have before us pictorial representations of philosophy floating down on clouds, and later, in Philosophia’s expression (even if she bears another name), a look showing kindly feeling, once again expressing the relation to the self-conscious soul. It is the plain truth that it was from a quite human personal relation, like that of a man to a woman, that the relation of man to philosophy started in the age when philosophy directly laid hold of the whole spiritual life of progressive human evolution. The relation has cooled: I must ask you not to take the words superficially, but to seek for the meaning behind what I am going to say. The relation has indeed cooled – sometimes it has grown icy cold. For if we take up many a book on philosophy at the present day, we can really say that the relation which was so ardent [passionate] in the days when people looked upon philosophy as a personal being, has grown quite cool, even in the case of those who are able to struggle through to the finest possible relation to philosophy. Philosophy is no longer the woman, as she was to Dante and other who lived in his times. Philosophy nowadays comes before us in a shape that we may say: “The very form in which it confronts us in the nineteenth century in its highest development, as a philosophy of ideas, conceptions, objects, shows us that part in the spiritual development of humanity has been played out.” In reality it is deeply symbolic when we take up Hegel’s philosophy, especially the Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences, and find as the last thing in this nineteenth-century book, a statement of the way in which philosophy interprets itself. It has understood everything else; finally, it grasps itself. What is there left for it to understand now? It is the symptomatic expression of the fact that philosophy has come to an end, even if there are still many questions to be answered since Hegel’s days. A thorough-going thinker, Richard Wahle,3 has brought this forward in his book, The Sum-Total of Philosophy and Its Ends, and has very ably worked out the thesis that everything achieved by philosophy may be divided up amongst the various separate departments of physiology, biology, aesthetics, etc., and that when this is done, there is nothing left of philosophy. It is true that such books overshoot the mark but they contain a deep truth, i.e., that certain spiritual movements, have their day and period, and that, just as a day has its morning and evening, they have their morning and evening in the history of human evolution. We know that we are living in an age when the Spirit-Self is being prepared, that although we are still deeply involved in the development of the self-conscious soul, the evolution of the Spirit-Self is preparing. We are living in the period of the self-conscious soul, and looking towards the preparation of the age of the Spirit-Self, in much the same way as the Greek lived in the epoch of the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, and looked towards the dawning of the self-conscious soul. And just as the Greek founded philosophy, which in spite of Paul Deussen4 and others first existed in Greeks, just as the Greek founded it during the unfolding of the intellectual soul, or soul of the higher feelings, when man was still directly experiencing the lingering influence of the objective Sophia, just as philosophy then arose and developed in such a way that Dante could look upon it as a real concrete, actual being, who brought him consolation after Beatrice had been torn from him by death, so we are living now in the midst of the age of the self-conscious soul, are looking for the dawn of the age of the Spirit-Self, and know that something is once more becoming objective to man, which however is carrying forward through the coming times that which man has won while passing through the epoch of the self-conscious soul. What is it that has to be evolved? What has to come to development is the presence of a new Sophia. But man has learnt to relate this Sophia to his self-conscious soul, and to experience her as directly related to man’s being. This is taking place during the age of the self-conscious soul. Thereby this Sophia has become the being who directly enlightens human beings. After she has entered into man, she must go outside him taking with her his being, and representing it to him objectively once more. In this way did Sophia once enter the human soul and arrive at the point of being so intimately bound up with it that a beautiful love-poem, like that of Dante’s could be made about her; Sophia will again become objective, but she will take with her that which man is, and represent herself objectively in this form – now not merely as Sophia, but as Anthroposophia – as the Sophia who, after passing through the human soul, through the being of man, henceforth bears that being within her, and thus stands before enlightened man as once the objective being Sophia stood before the Greeks. This is the progress of the history of human evolution in relation to the spiritual facts under consideration. And now I leave it to all those, who wish to examine the matter very minutely, to see how it may also be shown in detail from the destiny of Sophia, Philosophia and Anthroposophia, how humanity evolves progressively through the soul principles which we designate the intellectual soul (the soul of the higher feelings), the self-conscious soul and the Spirit-Self. People will learn how deeply established in the collective being of man is that which we have in view through our Anthroposophy. What we receive through anthroposophy is the essence of ourselves, which first floated towards man in the form of a celestial goddess with whom he was able to come into relation which lived on as Sophia and Philosophia, and which man will again bring forth out of himself, putting it before him as the fruit of true self-knowledge in Anthroposophy. We can wait patiently till the world is willing to prove how deeply founded down to the smallest details is what we have to say. For it is the essence of Theosophy or Anthroposophy that its own being consists of what is man’s being, and the nature of its efficacy is that man receives and discovers from Theosophy or Anthroposophy what he himself is, and has to put it before himself because he must exercise self-knowledge.
|
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: First General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society
03 Feb 1912, Mathilda Scholl |
|---|
| The leaders of our study group present in Berlin will be able to tell you that under the pressure of the difficult circumstances here, our life force is strengthened by looking up to him who guides us so wonderfully through writing and word. |
| They therefore fully support all the numerous protests by other domestic and foreign branches of the Theosophical Society against the attempts, which are incompatible with a love of truth and a theosophical attitude, to hinder and undermine Dr. Steiner's beneficial and self-sacrificing work, and consider membership of the Order of the Star in the East to be incompatible with membership of the Theosophical Society due to the unbrotherly antagonistic attitude towards the person and teachings of Dr. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: First General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society
03 Feb 1912, Mathilda Scholl |
|---|
Wilhelmstraße 92/93, Architektenhans report in the “Mitteilungen für die Mitglieder der Anthroposophischen Gesellschaft (theosophischen Gesellschaft), herausgegeben von Mathilde Scholl”, Nr. 1/1913 Dr. Steiner: Perhaps I may say that at the present time we are at the starting point of a significant, not new work; but at the starting point of a significant effort to consolidate and expand the old work. I have already brought into what I had to say yesterday all the feelings that I would like to place in your hearts and souls as a new color of our work. I hope that we will find ways and means to cultivate what we have cultivated in the old form, not in a new form, but in this new coming time, even more strongly, even more devotedly. That which has been saved from such difficulties must grow close to your hearts, and it would be a beautiful thing if each of us could truly feel this, that we can grow together with what we actually want. If we feel how what we call anthroposophy is a necessity for our time, and feel it in the way it must flow into our present cultural life, so that it wants to become a ferment in all individual fields; if we feel that all this wants to be and can be anthroposophy, then we will find the possibility of working in the right way. And the best contribution we can make today is not words, but our feelings and perceptions, our intentions, the principles we take within us to develop our individual powers. What is at stake is to find the right ways to allow everyone who wants to approach to find access to us. No one should or must be denied access to us, even if we must also carefully guard the sanctity and inviolability of our resolutions. Perhaps more than usual, it will be necessary for us to be able to fully rely on each other, for us to be sure that those who step onto our spiritual path will find the right thing from their hearts, and that those who do not want something for their soul will be deterred, so that all who come to us are really with us in some way. If we maintain a sense of seriousness and dignity in all our actions, we can be sure that we really have trust in each other, that we drop the personal everywhere, and that we look at people only from an objective point of view. It is not easy to let go of the personal. However, this should lead us not to be indulgent towards ourselves and others, but rather to examine ourselves again and again to see if this or that personal thing is not speaking after all. And we will find to a greater extent than we think how difficult it is for a person to go beyond what lives in his soul as personal. Many a person will be convinced that the judgment they had was based not so much on objective reasons as on sympathy and antipathy. Self-examination is part of it if you want to participate in a spiritual movement. I would like to emphasize not so much what these words mean literally, but what they can become if they are taken up by your hearts as they are meant to be. Perhaps they can serve as a starting point for the path, for the use of the means we need if we want to progress along the path we have once set for ourselves. Dr. Unger: As we are about to open the first General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society, we would like to express our heartfelt thanks for the words of welcome that have just been spoken. It is my duty to inform you that Dr. Steiner has accepted the honorary presidency of the Society at the request of the Central Committee and with the unanimous approval and enthusiasm of the large committee. If we now want to enter the General Assembly, it is only so that we can share some information about the current state of the Society. Today, I ask only to receive a few communications, and to see the value of this first meeting in the fact that, on the basis of these communications, we have proof that the work of the committee has since been applauded by our friends. It will now be my task to ask you at this opening whether you can give your approval to the actions of the Central Committee and the large committee. Fräulein von Sivers: Although not all the applications for membership have arrived yet, the number of our members is already quite large. The society already has 2557 members. How the individual groups are distributed will only become clear over time. I still have to read out a letter of welcome from the Anthroposophical Working Group in Sweden. The Scandinavian General Secretary, Lieutenant Colonel Kinell, has been forced to resign as a result of his experiences and has taken over the leadership of the Anthroposophical Society in Sweden.
The following telegram of greeting has arrived from France:
From Prague: The first General Assembly warmly welcomes the Prague Circle. Krkavec. From the remaining members of the Anglo-Belge branch in Brussels:
Weimar:
From the Bochum branch:
From the Paulus branch in Mulhouse:
Two friends sent us the following telegram: Budapest.
We have just received a letter from Moscow in which the working group there declares its affiliation with us. And, strangely enough, we received several warm letters of welcome from Spain, which had not previously been in contact with us, as a result of our “announcements”. Dr. Unger: It should be noted that many questions will probably still arise, but that these will resolve themselves over time. It would be good if the individual groups were to register with Fräulein von Sivers in the near future in order to be recognized as branches of our Society. The other provisions are, of course, contained in the 'Draft Principles of an Anthroposophical Society'. There will be no difficulties if we stick to the fact that working is the most important thing. The goals we have had so far remain our goals. It is planned to charter the individual groups so that, for the time being, we can have a full picture of the Society before us at the next General Assembly. We must all remember to ensure that messages about what has happened here, what the Anthroposophical Society wants and means, are disseminated as widely as possible. There are many people who are being deceived. Many have no idea where they are going when they pin on the asterisk, for example, out of good nature or other harmless considerations. Gradually, however, enlightenment must come. My question is therefore whether the assembly agrees with the results that are available so far; whether the printed preliminary statutes meet with your approval.
Mr. Günther Wagner: I just want to make an announcement about the library. At the board meeting in December of last year, the board of the former Theosophical Society transferred the library to me as my property, with the purpose of saving it for those whose dues created this library and for the movement to which we remain loyal. What is at issue today has already taken place once, and has a precedent. In the Minutes No. 4, January 1907, it says:
I would just like to say that this case has already occurred once. The Society has now reimbursed me for the library, and I hereby transfer the library to the Anthroposophical Society. Dr. Unger: We thank Mr. Wagner for his generous action. That was the only matter before me. Is there any other urgent matter? This is not the case. So we may close the first General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society with the expression of our wish and hope that we may make progress in our work. I hereby close the first General Assembly and hope that our anthroposophical affairs will flourish. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Discussion About the Founding of a Trading Company “Ceres”
06 Feb 1913, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| It would be a mistake to choose a commission. We have to develop understanding and act on the basis of the original initiative. We can only be understanding consumers as an Anthroposophical Society. |
| Measures of value are basically false, and if we want to gain understanding, we must gain this understanding by not basing ourselves on a foundation that has not fundamentally improved the social order. |
| To do that, we need to talk a little, so that understanding is gained and not just among the small circle of those present, which is a small circle for 2,500 members. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Discussion About the Founding of a Trading Company “Ceres”
06 Feb 1913, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[Architect Schmid: We want to create the daily bread in the broadest sense, not a caricature of what it is supposed to be. Just as each column on the Johannesbau is the only, correct, best expression of what it is supposed to represent, so it should be with our entire environment. The aim is not to create cheap coffee and so on, but the right coffee, cocoa and so on. The name you choose is Maja; we should offer the right thing for the same money. Many speakers spoke, then Mr. von Rainer: I had to ask the bread whether it wants to be sold like this. It told me: That's a sore point. - That doesn't suit the bread, the bread doesn't want to know anything about that either. The lowest possible prices, [that] doesn't suit the bread either. The bread is opposed to all these privileges because, in a sense, they violate the occult law under which it stands. That would just be another area of selfishness. Bread is very demanding and wants to be treated well and lovingly. It is against all modern business relationships and prefers a good wearer. Bread wants nothing to do with advertising. On the one hand, the matter must not take on fixed forms, but on the other hand, there is a desire to help others when the principle of altruism can be carried out in contrast to selfishness. Rudolf Steiner: We should definitely avoid bringing something into the world in an indefinite way. Above all, we must be clear that it is necessary for us to proceed practically, to bring something viable into the world. Of course, some of the general principles that are developed are useful, and it is a practical matter. If we don't want to talk at cross purposes, we have to take something important into account. As unlikely as it seems, this touches on the practical side of the matter: Mr. von Rainer has stated that the bread feels offended, and Mr. Schröder has apologized. The bread cannot excuse anything by its very nature. It is necessary that we absolutely take into account the real factors. In the moments after such a mistake as the one that has now been apologized for, but I think that when such a mistake is made later, it is important that it be translated into reality. In the moments when something like this is done, we are immediately dealing with the material consequences of it. We have to proceed practically; we talk about many points without any basis. What we should talk about would be: How can a trading company be established, how should it relate to those of our friends who produce something in some field or other and have something to sell, how can an understanding be reached with consumers? Basically, we cannot elect a commission; we cannot become a consumer association as an Anthroposophical Society. Things must develop in such a way that someone finds inspiration in their impulses and others go to them. It would be a mistake to choose a commission. We have to develop understanding and act on the basis of the original initiative. We can only be understanding consumers as an Anthroposophical Society. We can exchange our views. There are many things to consider. It is extremely important that this trade association does not take a purely materialistic point of view, but above all takes the point of view of offering support to good, appropriate production. The difficulties that arise from today's commercial nature, that those who are involved in material life cannot help but develop principles, however good a person they are, [that they] cannot help but develop the principles, as Mr. Schröder has described, that they apply in England, according to which a mistake would be worse than a crime. But I ask you, what should the merchant, the mediator do today in the face of the fact that he has to reckon with the cheapness of the goods and not with the quality. People want cheap bread without the bread being properly right and good. Measures of value are basically false, and if we want to gain understanding, we must gain this understanding by not basing ourselves on a foundation that has not fundamentally improved the social order. Anthroposophy must advance humanity, and we must base ourselves on a foundation that advances. We can, of course, do such a thing quite properly, but we have to approach it practically; it has to yield something fruitful. We have nothing to do with patterns. We have to work from what is properly at hand; if we work according to old patterns, the only thing that can happen is that we achieve something old. We cannot establish a company to market Rainer bread, but we can spread understanding that we eat this bread! The trade association should be a mediator in the most practical way possible. It would be completely impractical to proceed in the way we do for a purely idealistic cause, that we would organize collections. For a matter that is based on a material basis, it is not a matter of not having confidence in it from the outset, that would be an admission of failure from the outset, but rather of launching a matter that is actually well-founded, and it is a matter of the people who have an understanding of it participating with the prospect of interest and profitability. We did not want things to be based on material considerations that would fall apart after a few years, even though they had been justified several times. Capital should not be raised for an idealistic cause, but everything should be based on a practical foundation. These things must be taken into account; they are very beautiful when done right, but they should be understood in such a way that we stand vis-à-vis Mr. Schröder in such a way that we give him advice and he gives us advice, and should not talk about selfishness and altruism. After a few other [speakers], Dr. Steiner takes the floor again and says after a few introductory words: Of course, I take it for granted that everyone here is in favor of this trade association. We are in favor of everything good, and [it is also self-evident] that we consider Mr. Schröder to be a capable man for the job. It is very nice when there is such enthusiasm for the cause. However, I would like to emphasize right away: I am not here to but I have experienced exactly the opposite of what Ms. Wolfram has claimed: the teaching of Saturn, Sun and Moon is quite easy to explain; people accept it readily. But if you tell them to have their shoes made by the shoemaker or to have a whole sack of Rainer bread delivered, that is more difficult than getting the teaching of Saturn, Sun and Moon across. Above all, it is necessary for the Theosophists to start thinking rationally and not just to be enthusiastic about practical things, but to persevere in the long run. It is normal that everything is wrong at the beginning; it is usually very difficult to find understanding when this or that is wrong. The new thing about theosophists is that they should be aware that the good things are bound to appear with certain dark sides, which is self-evident. How often have we had to hear that what is based on an incorrect approach to the matter; some loaves of Rainer bread went moldy; that it is moldy is a sign that it is good, my dear theosophical friends, because vegetables only grow on good soil. It is only a matter of us working against such a thing. On the other hand, we must be clear that there are also difficulties inherent in the matter. I don't see why we can't look at the matter soberly. The story is nothing new, something we have always had in small circles. There have been many of us who said to others: Get your shoes made by this shoemaker, buy your bread here or there. There were also those who volunteered to get the necessities, to travel to cycles, order rooms and so on. All this has already been done. Mr. Schröder has realized that something should be organized, and the newspaper is also just an expression of systematization, where it is best to turn, systematization of the matter, so that one can work more rationally when organizing a matter than when it is left to chance. Because we have the belief that when anthroposophists do something right, it will be a beautiful and ideal thing; they will do things quite differently, namely, the anthroposophists. I mean a connection between those who have something to offer - be it food, be it something else - they should connect with the trade association, where the thing is offered. It will be seen that the thing will flourish. I will be blunt: the only possibility is that it pays off in a rational sense. If someone can do or provide something well, the trade association will come to help them make a living. It is understandable that some of us producers have certain difficulties as such. A producer cannot count on a purely anthroposophical clientele. There are many details to be considered. After further interjections, Dr. Steiner takes the floor again: It is only necessary that this point of view be put into practice immediately, starting with the fact that what is there can be sold; and then adding more and more. We need what has been said today to be understood as nothing other than a statement from consumers to producers. We do not need to postpone for the reason that the rest that needs to be done should come from the trade association itself. It should get in touch with our producers and get things moving. What we would like from our other friends is for them to get into the habit of taking things a little more seriously – the trade association can't do anything about that – and to be as well organized as possible when no one is buying from them. To do that, we need to talk a little, so that understanding is gained and not just among the small circle of those present, which is a small circle for 2,500 members. Try to spread understanding when you yourself agree with it, for this specific thing. Then we will actually make progress in this area, and then the matter is not so infinitely important, whether we say more or less: we take into account the other people or those who are among us. — Finally, it is quite true that we should carry anthroposophy out and not close ourselves off materially. But we shall also do what is necessary to support our materially productive friends; it is more important to accommodate a friend who is productive in some field and is part of society than to accommodate another who does everything he can to harm our movement just because it is more convenient for us. Altruism is not what moves us forward, but staying the course. After further interjections, Dr. Steiner says the following: Regarding Mr. Schröder's planned publication of a newspaper that is supposed to contain only an extract of the events of a certain period of time: It is not easy to publish such an extract. Just imagine: We were supposed to edit telegrams about the Balkan War that were supposed to be objectively true. One would have to proceed purely clairvoyantly – and that would be black magic in this case, [that] would not be a means of the physical plan to give a purely objective picture. The advertising story is a questionable thing. We have to take the view that it is being done practically, that will gradually come out. Paid advertisements are not practical. And even if it is tried today, it will be different in a year. The advertising system will have to be different. It will do the newspaper good if it takes the approach of other newspaper companies. The big newspapers live from advertising, but that is also what they are like. A newspaper cannot help but take on a certain configuration if it lives from advertising. Take a large newspaper company. I would like to know how many readers there are who read these advertisements. Do you think that those who spend money on advertisements are unaware of the situation I have just described? Those who place these advertisements and pay for them with hard-earned money have very specific reasons for placing them. And even if these advertisements are not successful the first time, they still have an effect in a variety of indirect ways. It is natural that newspapers should be dependent on advertisements. In short, it will not prove to be practical at all. Only a newspaper that does not depend on advertisements, that can live on subscribers, can be in a position as it should be. A newspaper that relies on only one advertisement cannot possibly stand on solid ground. You may say that we anthroposophists are reforming the advertising business. I would like you to start with practical principles. The impractical people consider themselves the most practical because they are familiar with this subject. If they set up something new, they are not at all practical. It must be borne in mind that things must be done in a truly practical way. It will then become clear that a great many things that we imagine are not possible in practice. Someone could easily say today: We are anthroposophists, we can easily organize things, everything should be put on a healthy basis. Certain things are in the nature of things. The advertising business cannot be reformed. If you base something on advertising, it cannot be reformed. Certain things are an inner necessity. So it is with many things that come into question in this matter, they cannot be reformed, they must be removed. Nothing can be reformed in the commercial sphere. The trade association would make no sense if it were to incorporate the principles of consumer associations and cooperatives. Our task is to ensure that what we receive is procured rationally and appropriately; commercial aspects must take a back seat. We must be sober and practical in our judgment. Our work must ensure that what is actually being implemented is that the paths of healthy, appropriate production are opened up to consumers. There is no reform in the commercial sphere. If you are dealing with a certain type of thing from the outset, you can only say: I don't want anything to do with the article, or I have to say that it is good. We must want to help healthy, appropriate production. [Mr. Selling: draws attention to “Lucifer-Gnosis”, issues 30-32, where you can find the basics of understanding. Dr. Steiner: The Rainer bread is just practical, that's what it's supposed to be eaten as. H. Klepran: If not everyone can enjoy it, it's because it's living bread, in contrast to the dead bread we are used to eating. Dr. Steiner: Found a very fine small handkerchief. Really nice! I believe it belongs to a lady.] |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Second Farewell Address to the General Assembly
08 Feb 1913, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| It is so that one must take it seriously, because it is a very strong accusation in the present, and effective if it were believed in relation to the inner, to the hateful motives. And with regard to the other underlying motives of Mrs. Besant, I find only a slight difference compared to another accusation that came across my eyes, from a letter that is one of a whole series of letters. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Second Farewell Address to the General Assembly
08 Feb 1913, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
So, my dear friends, we have finally come to the end of our meeting, but we can highlight one fact in all of this. You see, my dear Theosophical friends, something extraordinarily important seems to have taken place. One might ask: Was it a general assembly? What was it actually? When it is talked about later, it will be said, “Once upon a time...” — just as it is said in fairy tales. We were still members of the Theosophical Society in Adyar when we arrived here, but now we are no longer members. Something earth-shattering seems to have happened, but in terms of the matter, one has not actually noticed it. We are again diverging in terms of the matter, as we used to diverge, and precisely this fact, that we can do that, that we do that, is a very important one. Perhaps this does testify to how serious we were about the spiritual, about the cultivation of spiritual culture, about the content of our cause; and if we were serious about that, no form will break this content, but this content will seek its new form if the old one is challenged. As for myself, my dear Theosophical friends, I must confess that, with regard to the external events that have occurred, I have been so touched by the matter that I must say again: things actually only differ in degree. You see, Mrs. Besant has found it necessary to make the claim, which defies all facts, that I was educated in a Jesuit school. It is so that one must take it seriously, because it is a very strong accusation in the present, and effective if it were believed in relation to the inner, to the hateful motives. And with regard to the other underlying motives of Mrs. Besant, I find only a slight difference compared to another accusation that came across my eyes, from a letter that is one of a whole series of letters. I received a letter from Hamburg in which a lady writes that she had always been persuaded not to go to the lectures, but now she had seen for herself, because before she never went because a pastor had said that I was a Satan. I have not yet read the other letters, but there is one coming every day, sometimes two. Shortly before the lecture here in this hall, a letter was brought to me – I should definitely read it before the lecture. In the letter, a lady wrote to me that she had heard some of my lectures that she liked. But now she looked me up in the dictionary of writers to find out how old I actually am, and she discovered that I carefully dye my hair, because people my age don't have black hair anymore! So she can't come to my lectures anymore, because it would be outrageous and speak to the prevalence of such a thing. You hear all kinds of things and finally, the accusations are to be distinguished according to the motives for how they are made effective. The motives are human, all too human, whether one or the other makes them, whether one is accused by Mrs. Besant of having been educated in a Jesuit school or by another lady because of something else. That's how people act. There are many more stories I could tell. Something that really did meet with the enthusiastic support of our friends – the printing of the cycles – is also being made the target of attacks. I am being reproached for the fact that it says: “According to a postscript not checked by the speaker.” But there is a very simple reason for this; I don't have time to check the postscripts. They would never see the light of day if I had to read them first. The person concerned says: He – Dr. Steiner – has not looked at the matter, so he always leaves himself a back door open if he were to be caught making mistakes. In this way, one can suspect everything, while we have really only taken into account the energetic wishes of the members. We are dealing with serious, profound, and meaningful things, and so we must be able to fully distinguish between what is a serious and sacred matter and what is an external form, and we must not sleep and believe that we can always dream and talk about the content to get ahead. The worst things could happen to us if we were not on guard, if we did not take into account the need to remain vigilant. And in this respect, I was also able to tie in with what Dr. Peipers said today, the word about keeping watch. There is also a productive way of keeping watch. That is in our nature and not in that of our opponents. I hope that we will part peacefully, with the feeling that we will remain united intellectually. Goodbye! |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: The Obligation to Distinguish
20 May 1913, Stuttgart Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| But it happens time and again that these or those misunderstandings, these or those things open to misunderstanding, creep into our ranks. The one who can understand this best, the one who can really understand this well, is really myself. But if nothing were said at all, it would not work either. |
| That is why I would like to make a heartfelt request to you not to live too much by this need for peace. Misunderstandings arise easily, understandably. And if I had always been understood since 1907, many things would not have come about that quite understandably did come about. |
| I must keep emphasizing such things. It should be understood that it is not a license for anything if a person calls himself a Theosophist. The rejection of the Jesuit accusations that originated in Germany and which Mrs. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: The Obligation to Distinguish
20 May 1913, Stuttgart Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
My dear friends! Before I come to today's reflection, please allow me a few words. It may not have remained unknown among our friends that it would correspond to my inclination to speak most gladly about the factual theosophical things from the very beginning, namely about the objective matters of the spiritual world. But sometimes it turns out to be necessary to address a word to our friends that does not belong to the matter at hand, but to our affairs. Much as I dislike it, it sometimes has to be done. It had to be done in the most diverse ways during the period when the affairs that led to the free-standing Anthroposophical Society; and unfortunately it is necessary from time to time, again and again. Therefore, allow me today to say a few words to you before we come to the subject of our consideration. It is always the case, though, that you don't really know where to start. But it happens time and again that these or those misunderstandings, these or those things open to misunderstanding, creep into our ranks. The one who can understand this best, the one who can really understand this well, is really myself. But if nothing were said at all, it would not work either. I do not want to bother you with matters that have been discussed often enough. Because I feel, I would like to say, up to a kind of creepy feeling, I have been told more often by these or those lately: Thank God! Now that we have the Anthroposophical Society, we no longer have to worry about the matter, now we can have peace and quiet. It is a nice feeling to have peace and quiet. But it is creepy when there is this exaggerated need for peace and quiet if there is no peace from the other side. And there are enough other people around us to ensure that we do not give peace a chance! That is why I would like to make a heartfelt request to you not to live too much by this need for peace. Misunderstandings arise easily, understandably. And if I had always been understood since 1907, many things would not have come about that quite understandably did come about. If only they had had the will to represent what I tried to do with a certain clarity, to see it, to understand some of what was in what I tried to do, then they would have acquired a certain power of discernment since 1907, perhaps even earlier. Please forgive me for discussing these matters in such a dry, seemingly presumptuous way; but it has to be done because no one else is saying it. I would rather not say it. If we had acquired the ability to distinguish between things wherever work was considered important for the further progress of our cause, then the case could not always arise that, in addition to what we are trying to do, which, as our friends know, we are trying to do out of seriousness, out of real seriousness about occultism on the one hand and about the occult situation at the time, which I I tried to characterize in a general way the day before yesterday, if one had acquired a proper sense of the seriousness with which we should actually take the matter, it would gradually have become self-evident that much of the selfish stuff – if you will allow the expression – even such selfish stuff that came from Adyar in the years mentioned would simply have been viewed in the right way. It has caused me, I must say, a certain sadness - do not misunderstand the expression, the occultist in a sense knows no sadness - but yet I must say: It has caused me a certain sadness that in the way things are tried, the question could arise: How does the view presented here of the Christ problem or similar things square with what Miss Besant presents? It saddens me because it shows that the seriousness with which these matters are treated here is not appreciated in the right way, is not understood in the right way. Since no one else is saying it, I have to say this, although I would rather not because it could be misunderstood. I had hoped that people would not just look at the differences, but at the inferiority, the whole inferiority that is found in occult stuff, which has sometimes been taken up as if it were necessary to deal with it. I had hoped that discernment would arise for what one has discernment for in other fields! These are the words I would most like to avoid saying myself. If someone does something with seriousness and dignity and someone else does a botched job, you don't ask: How does what was done with seriousness and dignity deal with the botched job, with what openly bears its inability on its forehead! Thus it was necessary, at the starting point of our anthroposophical movement, to address a heartfelt request to you not to live too much in the need for calm and indifference in the face of what is sufficiently done in the world to throw dust in the eyes of our contemporaries about what is reality. It is not enough for us to acquire knowledge of these or those things with a certain curiosity – but it is necessary because there are other people living around us to whom we must gain access with what needs to be done in the spirit of the time mission. It is not enough to inform oneself with a certain curiosity about the monstrous things happening in the Theosophical Society and otherwise rest on the cushion of the Anthroposophical Society, but it is necessary to gain the appropriate attitude in one's soul. Because if this appropriate attitude is not gained, what must be done as a highly necessary defense will always be distorted in the most outrageous way. One should not believe that those people who are now trying to distort everything that must come from us as a necessary defense, or who are trying to simply accept such outrageous attacks in a seemingly noble way, one should not believe that either of these people are right. What is being done against us often comes from people whose actions show the kind of spirit behind it. Therefore, I would like to ask you not to let old comradely feelings prevail where the truth is concerned. In the course of my endeavors in developing the German Section, I have always had to come into conflict with the increasing inability to distinguish. And even if our friends had developed more and more discernment between the stuff that is spreading and what is being tried here – it is unpleasant for me to say this – and even if our friends had tried to apply discernment, it would not have been possible to come to me with every piece of nonsense that comes from the other side. Those who are familiar with the work that has been done by this side know that this is not based on intolerance, but on [painful] necessity. Inability has always had to be dealt with: examples can easily be given. For example, one should not have believed that so much was possible, as was expressed in the General Assembly, that something even more outrageous would be added to the outrageous! After the Jesuits were criticized from Adyar, one would have thought that these outrageous acts could not be surpassed. Miss Besant has made it possible to surpass these improprieties by managing, in her publication, which until recently was itself still being read in some of our lodges, not to retract the Jesuit accusation, but to reinforce it and justify it by referring to three people. The system is not to take back the untruths, but to refer to three others who have told the untruth. We must find it within ourselves to respond to these outrageous acts, and to subsequent ones. At the beginning of the German Section's work, a certain personage wrote me a card containing the following words, which were meant to sound friendly: “We are all pulling in the same direction, after all.” I could not for a moment think of pulling with this personality in one direction; because it would have been a violation of our serious work to pull with this personality in one direction. So such personalities had to be shaken off; because they did not want help to improve their incompetence, but they wanted to push themselves forward with their incompetence. This personality is one of those who now raise the Jesuit accusation, one of those on whom Mrs. Besant relies, a personality who, like Mrs. Besant, upholds this Jesuit accusation. As unpleasant as it is to talk about these things, it cannot be spared. The soul must find the opportunity to take a stand on these things. We cannot allow the belief that something is justified because it calls itself Theosophy to serve our contemporary world in this way. Another person, who had once been introduced to me by a Theosophist, sent me a writing of his that had nothing to do with what had to be done out of the seriousness of our movement. I also had to reject this person, which this personality wrote about a series of writings that are published by a certain publisher; anyone with discernment could see from this preface how incapable such a personality is of rational thought. There are many such personalities. The matter required that the personality discussed be rejected. That is the second of the personalities on which Mrs. Besant relies. I must keep emphasizing such things. It should be understood that it is not a license for anything if a person calls himself a Theosophist. The rejection of the Jesuit accusations that originated in Germany and which Mrs. Besant has recently allowed herself to be guilty of was easily seen through. What I said in Berlin was easily seen through. One could have found that it is not a matter of thinking about a matter in one way or another, but that the whole matter is not true, that the whole matter is untrue! The person who has been designated by Adyar as the General Secretary of the German Section finds the opportunity to have the following printed: Dr. Steiner and his followers reject this with indignation. Why this indignation, actually? Is it dishonorable to have dealings with Jesuits, or is it criminal to be dogmatic? So, my dear friends, the man who wrote this dares to write this to throw dust in people's eyes – I won't say he intends to, but it happens because of it. If someone says to me, “You broke stones in your youth,” and I say, “It's not true,” is it a retort when someone says, “Breaking stones is an honest occupation after all”? It doesn't matter if it's an honest occupation; what matters is that it's not true! We have to get into the habit of not engaging in such things. There are still people who say, “It's not meant to be so badly, he has justified himself.” It depends on the fact that it is not true! For this we must acquire a sense of discernment, so that we cannot see such stuff without inwardly taking a stand on it, without feeling how outrageous such things are. It is easy to carry out journalistic skirmishes over and over again if you leave what it is about undisturbed and write about something that has nothing to do with the matter, because people who do not feel the obligation to acquire discernment are deceived by it. There is another page that I would like to read to you, but the whole brochure is like that again! I have included in the “Mitteilungen” in the General Assembly report that I was written to by the man who then became the General Secretary in Germany: It would be incomprehensible to him how Krishnamurti could have gone through all that he was supposed to have gone through, but that is not the point; people in the West have no understanding of what an adept is. That is why Mrs. Besant chose the path of calling the one with whom she parades – those are his words – the Christ. In response to this account, one dares to write: “Something else, a fourth way of using the word ‘Christ’ – I can only ever serve you with one use of the word, though – was the [my writing of July 4, 1911, that Mrs. Besant uses the word “Christ” occasionally, based on the idea of Paul, but in a more exact sense, namely for an “adept” or “master who has already reached the goal of human perfection. Since the present-day cultural world knows no other model for this than Jesus, it is justified to use the term 'Christ' under certain circumstances also for the human being in whom the Christ-being reveals itself in its full abundance. But the present time is such that people read this without thinking. Much to my regret, I had to mention it here: because I must point out that it is part of the essence of the theosophical sentiment to feel that what is being done here under the flag of theosophy is actually the most outrageous thing! It would be the most outrageous thing if anyone harbored the belief that such people could still be converted! The question arises again and again: what could be done to teach this or that person a better opinion. The assumption arises again and again that it can be a matter of that at all! Those who have raised the Jesuit accusation in this way cannot be converted. It would be the most impossible undertaking to even want to negotiate with such a person! This is one of the theosophical misunderstandings. The real issue is that we should not allow our fellow human beings to be put off by things that are said because of human laziness! It was necessary for me to make these few remarks. I made them reluctantly. It never ceases to amaze me how even now, within the Anthroposophical Society, the belief can sometimes arise that some kind of work of initiation is to be developed on that side. I have learned many things about Adyar matters that I will not discuss here. The founding of the Anthroposophical Society began with such accusations being made from the other side. I understand the love for the cushion. But we also have the obligation to represent our cause without camaraderie, without regard to the person, if that person is dominated by such motives, as is the case here. We see how it begins; it is not yet complete. We will have many opportunities to sit on our pillow of rest if we close our eyes. It is right that we only take care of our own business, represent our cause positively and do not look to the right or left; it is right when we are the aggressors. But when it comes to our defense, I have to admit that it saddens me – now that it is about our sacred cause – that the days are filled with dealing with individual personalities, but that I have no time to defend our sacred cause against such outrageous attacks. And since this sorrow sometimes really has to befall me within the most necessary activity for our individual members, it was probably necessary to talk about these things here once. It will not happen too often that these things are spoken about, because I will wait and see if souls find the opportunity to truly confess themselves, which actually lies in the fact that today, in our time of crass materialism, in this time when there is so little sense of duty to examine the truth, that a matter that is so seriously meant may be attacked in such a way. For the sake of the cause and for the sake of the path that the cause must take into the hearts and souls of our contemporaries, it is necessary to write such things into our hearts. This is truly our holy cause! And I would not have spoken these unpleasant words if I had not been urged on by the whole assessment of the matter. I would feel obliged to continue to do what I have been doing for years within the movement, undeterred by what can happen in such a way. But if one feels such an obligation, one may still direct one's attention to it, so that souls may find the possibility to find the unheard of also unheard of, to find a position to the unheard of, not to allow that our present is approached with such things. My dear friends, with all my warmth, with the deepest friendship, I say to you: we will work, I will work with you on what needs to be done. When souls find the right position, the right thing happens in the outside world; all action develops out of the right attitude. I will wait. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Second General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society — Day One
18 Jan 1914, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| I don't know how widely this expression will be understood; but members who live further away and don't understand it can ask their friends in Berlin what a “Konzessions-Schulze in the disguise of a superman” is. |
| And how many are there who are able to bring the necessary interest and understanding to such endeavors? It is understandable that a pioneering undertaking like this one must meet with great resistance, especially from the partisans of the dualistic and monistic schools. |
| He then thought that since he is Polish, it would be nice if he could perhaps become Secretary General in Warsaw. But when he realized that under Besant's aegis the matter was becoming shaky, he thought he would do better if he could work under Dr. |
| 251. The History of the Anthroposophical Society 1913–1922: Second General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society — Day One
18 Jan 1914, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Wilhelmstraße 92/93, House of Architects Report in the “Mitteilungen für die Mitglieder der Anthroposophischen Gesellschaft (Theosophischen Gesellschaft), herausgegeben von Mathilde Scholl”, No. 6/1914
My dear friends! On behalf of the Executive Council, I warmly welcome you to the second General Assembly, the first ordinary General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society! For as long as we have held general meetings of the Theosophical Society, it has been customary for the General Secretary of the Theosophical Society to also chair the general meeting. However, it is the right of the general meeting to elect the chair. On behalf of the board, I propose that Dr. Steiner be elected to chair this general meeting. I ask you to vote on whether you agree to this.
Dr. Steiner: My dear Theosophical friends! We are gathered here for the first time in a regular General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society, and it is my duty to greet you most warmly and to express my joy at the large number of you who have come. I would also like to express the hope that this first General Assembly of our Society will be fruitful in all respects. My dear friends, you have surely brought with you hearts filled with an anthroposophical spirit for this day, hearts throbbing with the enthusiasm that is necessary if a spiritual current is to be brought into existence in the world, a spiritual current like ours, which can certainly, without being guilty of the slightest exaggeration, be said to have to be born in pain. And from the many antecedents that have befallen us in recent times, it will indeed become clear that we have a great need to approach our task with great seriousness and a certain urgency at this time. Before I try to continue the train of thought that I have stimulated with a few words, I would like to dedicate the word to those who have left the physical plane since we last gathered here and, as members of our movement, which is so close to our hearts, now look down on our work from the spiritual world. I would like to take this opportunity to emphasize once again that those who have passed away from the physical plane will continue to be considered our members in the most beautiful sense of the word, and that we will feel united with them as we did when we were still able to greet them on this or that occasion on the physical plane. First of all, we would like to remember an old theosophical personality, old in the sense that she was connected with what we call true, genuine theosophical life for the longest time of most of our ranks, Baroness Eveline von Hoffmann. She is one of those who have imbued their entire being and active will with what we call the theosophical attitude. Many have come to appreciate the deeply loving heart of this woman, if only because they have felt infinite strength flowing from this heart in times of suffering and adversity. Although little of this became known to the outside world, Mrs. von Hoffmann was a loyal and self-sacrificing helper to many. And we may consider it a particularly valuable thing that she, who had been involved in theosophical development for a long time, was last in our midst. And with her dear daughter, who is still with us, we will keep the memory of this loving, loyal, and helpful woman, who wants to be united with her in the spiritual world. I also have to remember some old members who left us for the physical plane this year. I have to mention our dear old friend Edmund Eggert in Düsseldorf. If some of us perhaps know the great inner difficulties that our friend had to struggle with, the heroic strength with which he became involved in what we call our spiritual current, then those who knew the good, dear man will certainly join me in making unceasing efforts to continue to be loyal friends of our dear Eggert in the spiritual worlds. And those of the dear friends who hear this, what I say from a troubled heart, will faithfully send their thoughts to the one who has passed from the physical plane. I also have to remember a dear, loyal member, a member who always gave us sincere, heartfelt joy when we were able to see her in our midst time and again, our dear Mrs. van Dam-Nieuwenhuisen from Nijmegen, who left the physical plane this last time, and who certainly was one of the most beloved personalities among those who were her close friends, who worked faithfully for our cause as long as we knew her, who in particular also did a great deal to ensure that our cause was appropriately represented among our Dutch friends. I must also mention a loyal, if perhaps quieter member, who always gave me great joy when I was able to see her in the circle of our dear Nuremberg friends, Fräulein Sophie Ifftner. She was much appreciated in the circle of our Nuremberg friends, who will ensure that the way is created through their feelings so that we will always find her when we seek her in the spiritual worlds. I would also like to mention another faithful friend who has been active within the circle of our worldview for many years. She has been tragically recalled from the physical plane to the spiritual worlds. I would like to mention one of those to whom she has become dear and precious, and who want to be and remain with her in their thoughts, Miss Frieda Kurze. I would also like to mention our Julius Bittmann, who was torn away from his dear family and from us, until his last difficult days, the fixed point of his inner life, despite difficult external circumstances, in what we call Theosophy. It was a deep joy for me to be able to spend the evening before the death of our dear Bittmann at his side once more, and I am sure that those of our friends who were closer to this man will not fail to form the path here as well, on which the theosophical thoughts unite us with the friend in the spiritual world. I must also mention Jakob Knotts in Munich, who was a man who, after all his various struggles in life, finally found his firm support and his definite point of reference in Theosophy, so that his friends will be his mediators in the same way. I must also mention another friend who left the physical plane during this period. Mr. Eduard Zalbin, who had come to us from Holland, was sadly mourned by his wife and children when we saw him depart from the physical plane through a quick death. Shortly before this occurred, Zalbin was still at our last general assembly, and his departure from the physical plane had to be pointed out there. I would like to remember an old friend of the Stuttgart Lodge, who had organized her innermost life in such a way that she associated everything she thought with Theosophy, and who will now certainly be surrounded by the thoughts of all those who knew her, Miss Duttenhofer. I must also mention Miss Oda Wallers, who we felt was connected to our cause with all her soul, for a long time. She was one of those souls who was as loyal to the cause as a human soul on earth can be, so loyal that we not only saw this soul depart from the physical plane with deep sorrow – a sorrow that does not need to be particularly emphasized in this case because all those who knew Miss Oda Waller knew her, felt it with the deepest sympathy – but at the same time we looked up to her in the spiritual world with the most beautiful hopes, with those hopes that are justified in the case of such a faithful soul, who, like Oda Waller, has firmly established in her heart to remain connected to the theosophical cause for all time. There will be more than a few who, united with their dear sister Mieta Waller, will be in heartfelt contact with our dear Miss Oda Waller. I have to remember our Munich friend Georg Kollnberger. Those who knew him will be our mediators when we reflect on him with our feelings and emotions. I have to remember a dear friend in Bonn who left the physical plane not so long ago, Miss Marie von Schmid. Those who knew her feel deeply how closely connected Miss von Schmid's soul was to the spiritual life. Those who felt a close connection with Miss von Schmid, a soul so open to the spiritual life, have lost a great deal, as have those who felt a close connection with an outwardly shy and withdrawn nature. It is so pleasant to meet such a nature in life. Precisely because she was so reserved, we got to know her so little. Those who knew her understand what I mean by these words. We have to remember a member who, in terms of his physical strength, was unfortunately taken from us all too soon, a man who was happy to put his physical strength at the service of our cause, but who will also be an esteemed member in the form in which he is now connected to us, Mr. Otto Flamme in Hannover. I must also remember our friend Fräulein Munch, who was found in the circle of our Nordic friends in our midst, and who, after a long, heroically endured illness, despite the most careful and loving care, finally had to leave the physical plane. Perhaps those who were closest to her will have the most understanding for what I would like to say about this soul, when we consider how she clung to the theosophical cause, I would say with inner strength, and passed through the gate of death with it. I would also like to mention a friend who had also become acquainted with our friends in Berlin and who, after long and severe suffering, has recently left the physical plane. She was fully aglow with the yearning to implement in practical life on the physical plane what shone so beautifully for her heart and soul. We are sure that she will now continue her work in other places in a way that we also assume for our dear friend Flamme from Hannover. All those who have passed away, as well as those who have become less well known in the circles of our members, we remember in this solemn hour: Mr. Brizio Aluigi from Milan, Mrs. Julie Neumann from Dresden, Mrs. Emmy Etwein from Cologne, Mrs. E. Harrold from Manchester, and we affirm that we sense, we want to live with them in thought – with these dear departed members, who, after all, have only changed the form of their way of life for us – that we want to surround them with the forces and thoughts with which we are accustomed to connecting with those friends who have left the physical plane; we affirm this will and remembrance by rising from our seats. Dr. Steiner continues: My dear friends! First of all, I have to read out some letters that have been sent to the General Assembly of the Anthroposophical Society.
I am sure that you will all accept these very warm greetings with thanks. My dear friends! Perhaps I may, in accordance with the custom of earlier years, say something in advance to this assembly; something that is really meant not otherwise than as a kind of greeting from the bottom of my heart to your hearts and souls, a greeting that I feel so deeply this year because we are united in this way for the first time within our Anthroposophical Society. For in a sense, the constituent assembly that we had to hold last year was what we had to hold. But only this year have we been able to see how many souls want to walk with us. And it shows itself to us through your extraordinarily large attendance. Perhaps it is right, at the very point of origin of our anthroposophical endeavors, to bring ourselves face to face with what we actually want to be with our goals and endeavors. When we turn to these goals and endeavors with our thoughts, two feelings must prevail in our souls, side by side, for they can hardly go hand in hand. One is a deep awareness of the necessity and importance of the spiritual life, to which we want to be devoted in our time with seriousness and loyalty, a feeling that must be connected with the earnest desire and the striving for sufficient energy to participate in what can deepen our time spiritually. The other sentiment that must go hand in hand with the first is what one would call, not wanting to be sentimental, but precisely in order to express something quite serious: the humblest modesty. Only in the humblest modesty and in the feeling of our inability to accomplish the great task can the necessary counter-image be created in our souls to what could so easily lead to an overestimation of ourselves and to pride. Because that is precisely the most important thing: the seriousness, the importance and the dignity of spiritual striving on the one hand; on the other hand, we can only advance in the right way on the path we have chosen in the most humble modesty towards our inability. And, my dear friends, if I may now pick up on the first thought that was expressed, we must never lose sight of the need for true and honest spiritual striving in our present time. What I would like to tell you, I must summarize here in a few words. But there are some things I do not want to leave unspoken. What is connected with the serious feelings is what must make us attentive to the whole course of the spiritual life of our time in the broadest sense. In particular, this makes it my task time and again to point out, in a way that I certainly do not seek from a different point of view, these or those other spiritual currents, which should truly not be fought in a superficial way, but only to show how little they are suited to meet the deep, serious longings of the souls of our time. But people do not yet know about most of the deep longings that are present in the souls. Unconsciously, they rest in the depths of the souls. But the spiritual scientist tries to dive down into these depths of the soul. He knows how necessary it is to make progress in this area and to integrate spiritual science into the currents of life as far as possible. People today do not always admit that there is something in the depths of the soul like the call for these spiritual necessities. But anyone who clearly sees in the eye of the mind what souls strive for without knowing it in their innermost being can find this silent, silent call for spiritual life everywhere. And this call becomes a duty in our soul: to work together on spiritual work in order to make progress in this area. One symptom is shown of how these or those personalities fight us, how they refute us and describe the things that come to our attention through our teaching as fantastic and unscientific. Sometimes, however, they give themselves away in the way they reject something, and by rejecting us they show that in fact they agree with us at the deepest level. Perhaps one of the most daring assertions that I have often made is that the materialism of our time, the monism in [contemporary] intellectual life, is based on fear. I have had to experience it that people from the audience, especially after such statements, approached me after the lecture and were horrified by such a grotesque assertion. I will not mention any names, I will only mention one man who has already achieved a great deal for our present intellectual life, who bears a revered name in connection with the name of our great Schiller, Alexander von Gleichen-Rußwurm, who belongs to the descendants of Friedrich Schiller, and who has already achieved a great deal. I will quote his words, which—one might perhaps call it “coincidence” if one were not a theosophist—yesterday “karma” delivered to my desk:
Please pay particular attention to these words: “We are all afraid.” Here you have expressed the opposite point of view to our own, which has been expressed again and again as a result of decades of research: that all clinging to materialism arises out of fear. So, sometimes people betray themselves by saying things that show how right we are with our views. We hear, when people betray themselves, especially when they put their hand on their heart, affirmations such as: “We are all afraid in this nocturnal darkness...”. One must look at what is going on between the lines of present life. Then one will feel the justification that is emphasized by the necessity of our spiritual work. And, my dear friends, however slowly it may proceed, we do see fruits that show us how what is sought in spiritual heights can be implemented in practical life. I would remind you of a saying that I have taken the liberty of saying and writing often in the course of the striving of our German Section: on the one hand, our task is to search for the secrets of the spiritual worlds, to make that which we can explore , to make it our spiritual heritage and to care for it among those who belong to us; on the other hand, our task is to make fruitful in the right way what we are exploring in the spiritual life in our lives, wherever we can. And we see fruits in this respect too - I would like to mention just one symptom. Souls are maturing in our midst who, we may say, are willing to carry into the place in life where they are placed, what can be won on our ground, even outside the circle of our Anthroposophical Society. Among many beautiful phenomena, let me mention one because it was deeply satisfying for me. Our young friend Karl Stockmeyer wrote a significant essay in a journal for the Baden school system about the impossibility and impracticality of what is being striven for from many sides: to use the cinematograph to teach mathematics in schools. It is wonderful to be able to guide the soul along such paths through the problems of life, where something can be gained if one engages with the way we have to approach the matter. This is exemplified by our dear young friend Karl Stockmeyer, who in such a modest way allows what has become his to be exemplary for what is meant when I have repeatedly said and written: In addition to cultivating the wisdom treasures, one should also make practical use in life of what we can gain in our souls from these wisdom treasures. I would like to sincerely request that as many of our friends as possible familiarize themselves with the unpretentious but very valuable essay. I always want to speak only symptomatically about such things, I want to speak so that it can be seen from the example how the things are meant. What we strive for from spiritual heights can be fruitfully applied in the particular. So when we try to bridge the gap between our spiritual values and the demands of practical life, we will gain the opportunity in many ways to let real theosophical-spiritual striving, anthroposophical spiritual life, flow into the life of the present. And such a task we have, we have a task! I would like to place all the emphasis I am capable of on this simple word: we have a task to carry into the world in a proper and correct way what we recognize as being right, what we are able to research. The mood in the world is not one that makes such a task easy. There are people who call themselves theosophists and who have done much to tarnish the reputation of the name “theosophy”. All the more reason for us to take on this task when people who believe they are at the height of spiritual culture repeatedly condemn us for giving a bad name to theosophy. For example, in a German journal, 'Die Tat', Giuseppe Prezollini uses strange words. In a lengthy essay, he describes what he means by theosophy. He starts by talking about all kinds of philosophical schools and characterizes them - one might say - wittily. Then we have the following sentence:
My dear friends! It is symptomatic that such things are written by people who are taken very seriously in their field. We must really bear in mind that what presents itself to our soul as a duty, that we have to regard a sacred belt in such a way that we have to stand up for it. The direct transition is made in this essay from philosophical education to the university. I would like to make the transition to the German university. All kinds of cheap books are appearing today. There is a collection; “Bildung der Gegenwart”; in it there is the following chapter on modern theosophy:
So now anyone can educate themselves about Theosophy for little money. But what is distressing is that this is in a treatise on the “History of German Philosophy from the Beginning of the Nineteenth Century to the Present”. What is distressing is that the man who writes this refers, for example, to something that I certainly never quoted as a source: a Buddhist catechism, a superficial compilation that no serious person can use. He goes on to quote the “Secret Doctrine”. But then he gives the sources from which he has informed himself; he mentions Hans Freimark's (!) “Moderne 'Theosophie” (1912). But that is not yet the distressing thing, because if an ordinary writer had done that, it would not have meant anything for our culture. But this is written by the full professor at the University of Giessen, Dr. Messer. We learn from it how official representatives of the highest intellectual life judge us. We must conclude: this is how men who teach our youth today write. With such conscientiousness, a licensed professor of philosophy, an official representative of science, teaches himself about things. Is one not entitled to conclude from this: if this man writes and teaches about Kant, Fichte, and Schelling, how is our youth taught today? I do not want to say anything against the views that Messer presents against Theosophy. It is not this opposing criticism that concerns me, but how the man who writes such things informs himself about the things. What value can his explanations of Fichte, Schelling, Hegel, etc. have if this is how the man informs himself? How, then, did that which is currently being disseminated as “science” and so accommodatingly believed by many come about? Can one not see the bleakest of circumstances here!? I am not talking about the fact that Messer is our opponent; I am talking, independently of that, about the nature of his “scientific conscience.” The final sentence in Messer's account reads:
Undoubtedly, there is sometimes good will and the belief that something is known associated with what today calls itself philosophy and the like. Nevertheless, it will take a great deal of serious and genuine spiritual striving to put the incredible arbitrariness and ignorance that is spreading today into the right perspective for our time. I do not wish to shrink from pointing this out in a fitting manner, in order to show how deeply significant what I understand by seriousness and dignity is, and how it must be taken if we want to help what we call our spiritual heritage today to find its appropriate place in the world. Those who know how I avoid saying such things on all other occasions will forgive me if I put these things in their proper light on this occasion, in order to show how things stand and what tasks we must take on. My dear friends! If, on the one hand, we link these considerations to the feeling of how serious and necessary our task is, then on the other hand, we should never forget how incapable we are, how modest we must be, how we must know how little we are actually capable of in the face of our great task. I am convinced that those who understand me will always adhere to this most humble modesty. So we must endeavor to bring our spiritual knowledge to people in such a way that we never lose the most humble modesty. If we were to take pleasure in the fact that we are compelled to speak such words, if we were to let ourselves be carried away by a feeling of superiority for a moment, it would be bad for us. We do not want to do that! We want to strive for our spiritual good in all seriousness and dignity, but we want to do so in such a way that this striving is carried by the most humble modesty, and that we carefully keep every trace of self-esteem, every trace of arrogance, away from our souls. Let this, what Karma has brought me, let this be kept in mind. I did not seek out the symptoms; they forced themselves on me. I was obliged to take Messer's book in my hands because I am obliged to inform myself about these things at the moment when I am working on a philosophical book myself. In the same way, the journal 'Die Tat' was also sent to me. This is a social monthly for German culture. I bought this, as they say, by chance from a newsagent. I really wasn't looking for these things. But I want to avoid telling you something else that I found in the farthest reaches of my mind that was similar to what I've been describing. I'll leave it at that. I wanted to address these words as a first greeting to your souls. I think it is the best greeting I can offer you, when I speak those words that also touch me deeply, and that can contribute to our being together in the right spirit in these days, and to give an impulse for what we decide in our souls for the Anthroposophical Society, if we all decide it in the right spirit. We come to the second item on our agenda, the report of the members of the Executive Council. Fräulein von Sivers: The membership movement is as follows: The total number of working groups and centers is 107; of these, 47 are in Germany and 60 in other countries. The number of new members is 3,702. Of these, 19 have died and 36 have left. The total number is therefore 3,647. Of these, 2,307 belong to the working groups in Germany. Dr. Steiner: Does anyone wish to comment on this report? Since this is not the case, we will move on to the third item on the agenda, the financial report. Mr. Seiler: The financial statements can be described as favorable, on the one hand because voluntary donations have been received, and on the other hand because two large items have ceased to apply, namely contributions to Adyar and contributions to congresses. Cash report The financial statements of the Anthroposophical Society from February 2, 1913 to August 31, 1913 are as follows [in Marks and Pfennigs]:  Dr. Steiner: Does anyone wish to comment on this financial report? Mr. Tessmar: The meeting has just heard the figures that make up the final result. The two auditors commissioned to audit the books have done so and dutifully checked the accounts. It is to be said that we found everything to be correct and in order, and we can testify that the sum of 5,340 Marks 32 Pfennigs is deposited at the savings bank; the proof of this was presented to us. I would like to emphasize that this cash report covers the period from February to August 1913, and that this year was particularly difficult because three financial statements had to be prepared. The accounts have been properly and correctly prepared. I therefore take the liberty of proposing that the treasurer be granted discharge for the period from February to August. Mr. Seiler: I would like to point out that a large number of members are unclear about the contributions. Each member has to pay five marks in entrance fees and at least six marks in annual dues. If a member belongs to a lodge or a group, they will be registered with us by the group. In this case, the group is then obliged to pay a contribution of three marks to the central fund. It is up to the individual lodges or groups to decide what contribution they charge their members. Members who do not belong to a group have to pay six marks to the central fund. The question has now arisen as to how much should be demanded from a regional group – foreign country, section. Basically, this issue is hardly acute, since the need for regional groups is hardly present. It only exists in one case. It has now been proposed to raise one mark from the members of such a regional group. At present, the dues for foreigners have been reduced to one mark to support the group. I would also like to mention that in previous years, the individual groups had to pay a fee for the charter diploma. A fee of ten marks was charged for these diplomas. Dr. Steiner: Does anyone wish to comment on the financial report? Fräulein Scholl: You have heard that it has been considered whether only one mark should be paid to the central fund by the individual lodges abroad for the member. However, as long as there are no national associations (no sections), there can be no reason for foreign lodges to pay only one mark in membership fees. This is simply for the reason of sending the “Mitteilungen”. In any case, it turned out that postage costs of around 80 to 100 marks had to be paid from Berlin for each issue. In 1913, seven issues were published, which resulted in additional postage costs of around 600 to 700 marks, a large portion of which was for shipments abroad. For the “Mitteilungen”, a standard rate, an annual contribution of at least two marks from each member, should also be levied. Relatively speaking, that is still very, very cheap, since a lot of the work is done for free. In other societies, much more is levied. I would like to propose levying two marks annually as a standard rate for the “Mitteilungen”. Mrs. Geelmuyden: If it should be necessary to translate the “Mitteilungen” into foreign languages, then it might be appropriate to set the contribution so low. As long as we enjoy the same rights, it is only fair that we foreigners also bear the costs. Mrs. von Ulrich: I would like to agree to change the membership fee and maybe make it an occult number, so that seven marks would have to be paid as a membership fee. Mrs. van Hoek: I would like to ask whether sending the “Mitteilungen” would not be simplified by sending the “Mitteilungen” only in one package abroad, and then having the respective lodges take over the mailing to the individual members themselves? Fräulein von Sivers: But in the future it will probably be even more necessary to address the mail personally to the individual members. The possibility has been created that a member belongs to several working groups: This also means a complication of the management. It will be necessary to start from a registry of personalities, not from branches, when sending messages and communications of any kind. Mr. von Rainer: If I understand Mr. Seiler correctly, there are two types of members. Those who belong to a working group and those who do not belong to a working group, the latter pay six marks to the central fund. If Fräulein Scholl's proposal is accepted, each member who is directly connected to the headquarters would have to pay eight marks. I would like to propose that we accept Ms. Scholl's proposal. Each member is managed by the working group in which they pay. Dr. Steiner: It would be a great help for the registry if each member were registered at the time of their registration and in all correspondence at the headquarters: “Member so-and-so, managed by working group so-and-so, belonging to working groups so-and-so.” Fräulein Stinde: If we could call the working groups that are dedicated to specific studies study groups, then there would be no confusion. Dr. Steiner: But groups could also be formed that are not dedicated to a specific study. Perhaps we could just say “group” to indicate the difference. So let's note this for once, that we say “group” and call the others “working groups” to distinguish them. Mr. Hubo: I would like to support Miss Scholl's proposal. Miss von Sivers: Even if this proposal is accepted, the clause can remain in place that a reduction could be granted if necessary and at the request of the student. Mr. Tessmar: Couldn't a conflict arise from the fact that it would be very difficult to account for the costs of sending the “Mitteilungen” in Mr. Seiler's account? Let's just drop the “Mitteilungen” and simply say: the contribution will be increased. That might be assumed. If the motion passes, then it must also be determined from when this increase should be introduced. Mr. Meebold: But if one group claims the right to a discount, difficulties will easily arise. Our group in London would have nothing against an increase in dues. But they are doing it with sacrifices, and it will be more difficult for them to continue if other groups have discounts. The “Mitteilungen” thing isn't really fair, because the foreign members receive it in German. Fräulein von Sivers: Perhaps the dues could just be increased by two marks for all German-speaking members. Mr. Baster: I would like to ask whether it is necessary to increase the contribution at all, since the cash balance was quite favorable. One must not forget that individual lodges already have a lot to pay for. Could not those members who receive the “Mitteilungen” directly from headquarters contribute to this? Fräulein von Sivers: I would like to point out that we are trying very hard to reduce expenses and that it would be necessary to enlarge the office space. We are forced to work under very uncomfortable external conditions at Motzstraße 17; our rooms there are quite inadequate in the long run. It is equally necessary to increase the number of employees as our society continues to grow. This year, we received a particularly large sum of voluntary contributions from the collection in Cologne before the Anthroposophical Society was founded, and we cannot count on this in the future. We have not touched them yet, in order to have something in the coffers for future cases, but we may soon be forced to make use of them because we do have to adapt external circumstances to the rapid growth of the movement. Mr. von Rainer: If in the future it should turn out that the contribution of two marks is too much, then that can be changed again at any general assembly. Mr. Bauer: It does not seem entirely practical to me that the two marks should be taken especially for the “Mitteilungen”; one could then do without the “Mitteilungen”. We may certainly make the request in the interest of simplifying the work: for German members, an annual contribution of five marks will be levied for the central fund; for foreigners, a contribution of three marks. If perhaps some fear that our current increase in contributions will not be met with entirely friendly feelings, I believe the matter can be smoothed over if we decide to introduce the increased contribution only for the year 1915. That is so far away that no one will be upset. Ms. Scholl: Mr. Bauer will excuse me if I do not agree with him on this. I find this last suggestion unjustified. I would consider it right to pay an additional two marks for the past year, for the “Mitteilungen” that have already appeared. After all, one can look back on work that has already been done. You know what had to be published in the interest of our movement, and how so many members abroad in particular were able to be informed about the true events within the Theosophical movement. When you look back on it, you have to say that it has a value that cannot be paid for with two marks today. That should encourage us to pay later rather than postpone it. I propose that we stick with the first motion to raise the dues by two marks. If individual members are unable to pay these dues, then there are certainly wealthier members in the individual lodges who could step in for them. This way, no one will be harmed. Fräulein von Sivers: Although I can understand Fräulein Scholl, who empathizes with the difficult external conditions under which work often has to be done in the cramped rooms on Motzstraße, I would still like to ask you to accept Mr. Bauer's proposal. 1915 is a normal point in time. The building in Dornach is standing, and the huge sacrifices that had to be made for the Johannesbau have been overcome. Of course, we have received proposals in which members propose an increase in contributions. Although they show a complete lack of knowledge of the situation, they are nevertheless very well intentioned. These proposals would now have to be read out. Dr. Steiner: My dear friends! It is sometimes in the nature of such discussions that they expand endlessly. But the whole matter can be simplified. Before deciding whether to accept the more rigorous approach of Miss Scholl or the more liberal approach of Mr. Bauer, and before voting on the Sivers motion – which would create the possibility that after some time members will be happy to pay again – we must first read two motions from our Tübingen friends. Fräulein von Sivers:
Dr. Steiner: You can now include these motions in the discussion. Mr. Schuler: The author of the motion is solely responsible for the wording of the two motions. The other signatories have only endorsed them in principle. The contributions alone should create a certain basis. We have had exceptionally low contributions so far. I take the view that the lower the contributions, the lower the efficiency. The dues would surely have to be increased bit by bit. In my experience, the truly needy and poor people are the ones most willing to pay all dues and increases. Regarding the opinion on increasing the dues, I would like to say: Those who can pay three marks can also pay five marks. The individual lodges would have the opportunity to demand higher dues on their own initiative. Dr. Unger: It was to be expected that Dr. Schuler would present a justification for these Tübingen proposals. These proposals are a serious matter. In the final analysis, it is not a question of payment here; after all, everything is moving towards the same goal. However, it is a different matter when it comes to creating clarity about the conditions that actually exist. It is not that the proposals contain truly strange things, but rather that these things are present due to a misunderstanding of the situation. We must pay particular attention to this at our Annual General Meeting, because such things are likely to cause confusion, which then proliferates again and again. These proposals speak of mistrust arising and so on. Furthermore, these Tübingen proposals show a tremendous confusion of the most diverse things. One should gradually start to distinguish between the Anthroposophical Society, the Theosophical Artistic Fund and the Johannesbau Association. In this proposal, the Theosophical Artistic Fund is placed in a kind of opposition to the Johannesbau Association and the Society itself. It is important to point this out because one should not actually base proposals on ambiguity. The matters of the Theosophical-Artistic Fund have been treated in this application out of complete ignorance of the facts. One really has no right to stick one's nose into such things. The point is that in recent years everyone has felt a sense of deepest gratitude, of deepest respect for all that is behind the Theosophical-Artistic Fund. We would never have had mystery plays today if these plays had been based on any kind of income. This is a pure gift that we accept in the appropriate way. Income and expenses do not and cannot play a role. It is a matter of course that an entrance fee is charged, but this should certainly not give anyone the right to interfere in these matters; we can only look up and accept this gift with the deepest gratitude. The Johannesbau Association is now endeavoring to create a framework for these mystery plays. So when people talk about the fact that funds are being withdrawn from the Johannesbau through the Theosophical-Artistic Fund, it is a gross distortion. We would not need a Johannesbau if we did not have the Mystery Plays, the gift from the spiritual worlds. It is deeply regrettable that these motions have been tabled with the best of intentions. That is precisely why they are completely unacceptable. Fräulein von Sivers: I would just like to add to what Dr. Unger said that it is one of the greatest ironies I have experienced in my working life within the Theosophical Society, which has been so rich in experiences, that what is being discussed here in this proposal has become possible. So a gift is made out of the purest, most unselfish motives, a personal, private gift. If two months of the year were not set aside for these performances, given the demands that the members place on Dr. Steiner's time, the mysteries would probably never be written at all. And it would never be possible to put on a performance in this short time if one had to ask society whether a worker could be given 50 pfennigs more or less in tips, or whether an artist could be compensated in this or that way. Anyone who knows just a little about everything that goes into a venture would give up from the outset under such conditions. The project was born out of personal initiative, and it was not even considered to ask society for contributions. How can one speak of a deficit when only expenses are calculated! How could such a low entrance fee even cover the expenses? Out of pure enthusiasm for art, to make possible something that is considered a gift, not only for society but for all humanity, the funds are given. The Mystery Plays have been enthusiastically received, and a worthy setting had to be created for them. The Johannesbau was created from this idea. So it cannot be said that it is the more enduring. Many of us are convinced that these dramas will live longer than a building made of wood and stone. Now it has proved expedient for the Theosophical Artistic Fund to provide an address for donations for the building. These will be receipted with the note “Theosophical Artistic Fund for the Johannesbau”. So they have nothing at all to do with the performances and are kept strictly separate from them. Fräulein Stinde: The Theosophical Artistic Fund was set up so that the mystery plays could be performed and only secondarily for the Johannesbau. Of course, we older members who set up the fund find it easier to understand all this than the younger members. That would be an excuse. But they could still know what it is about. Of course, most people don't appreciate the monetary value of art and performances; they don't realize that when a new play is performed in a theater, the costs amount to 60,000 to 80,000 marks. Thanks to the great willingness of our artists to make sacrifices, we are only able to make such performances possible; it would be impossible if we had to pay our artists. The entrance fee that is charged cannot be counted against the costs. Mr. Bauer: One more comment! It would be easy to say at first that a good opinion underlies the request, and therefore the rest could be overlooked. But we don't want to cloud the issue ourselves; we have to look at this opinion at its core. It may be well meant, but if we look closely, this good feeling has a heavy shadow. Otherwise this proposal would not be possible, because it could only come about from a bad opinion of others. One does not assume a sense of truthfulness in others. We must also be clear about this; specifically, he presents a good opinion based on mistrust. Dr. Steiner: My dear friends! We still have a great deal of work to do in the so-called business part of our General Assembly. Now, however, we must allow the time to come when some refreshment must be taken for the less intellectual organs. This point cannot be postponed any longer, because our stomachs would not be able to appear in such a way with the tea that is offered to us here at six o'clock that we would be able to achieve as much as possible. So we will now take a break and meet again here at four o'clock this afternoon to continue our negotiations. Adjourned at 1:30. The negotiations adjourned at 1:30 will resume at four o'clock. Fräulein von Sivers: The many arguments about the financial situation were perhaps quite useful in order to be able to know what the situation is. But since we have to make such strong demands on the willingness of the members of the Johannesbau this year, I hereby make the request that the assembly refrain from increasing the membership fee this year and break off negotiations on this point. The proposal is adopted. Mr. Walther: I propose that we also not enter into negotiations on the two Tübingen proposals, but rather assign them to the Executive Council of the Anthroposophical Society for resolution. Mr. Schuler: I have no objection to this, but I would like to emphasize that these are not “Tübingen proposals”. The proponent is responsible for the proposals. The others have only agreed to the increase in contributions. Dr. Steiner: The term “Tübingen motions” was not intended to refer to the Tübingen working group; it was meant only geographically, just so that the motions came from the city of Tübingen. The proposal is accepted. Dr. Steiner: We now come to the proposal of our auditor, Mr. Tessmar, to grant discharge to the treasurer and cashier. The assembly grants this discharge. Dr. Steiner: It will be necessary to deal with the Boldt proposal as the next proposal. I am obliged to present this Boldt proposal and to provide a little background information so that we are able to discuss this proposal in a reasonably objective manner. Mr. Ernst Boldt, a member of the Munich I working group, wrote a paper in 1911 that was published by Max Altmann in Leipzig at the time: “Sexual Problems in the Light of Natural and Spiritual Science”. I would like to explain Mr. Boldt's intentions with a few words from the brochure that was sent out by the publishing house at the time and from which I will read a few passages:
This is what is known in the book trade as a “blurb”, which is always added to books when they are first published. I don't know who wrote this particular blurb; sometimes authors write their own. But I don't want to claim that in this case, I just want to mention a very common usage in this instance, because not all of our members are informed about the practices of book distribution. If I were to tell the story of how I came to write this book, which culminates in my arguments, I would have to keep you waiting a very long time. I don't want to do that, but I would like to mention that Mr. Ernst Boldt originally intended to cover this subject, which was then condensed into his 1911 book of 148 pages, in a great many volumes. Then various things led him to make this short extract from his so-called “research”. I may well admit that long before this book was written, Mr. Boldt's various views and pretensions were brought to my attention by Mr. Boldt himself, according to various practices existing in our society, and that I was not in a position to Mr. Boldt made to me at the time – with the exception of the obvious, which is to tell a younger man: He should move in this or that direction in the field of thought so that he can move forward and also to give this or that piece of advice that you yourself consider good. Then, after this advice had been given, Mr. Boldt came to write this book. He also wrote me a letter of many pages, while the book was actually already in print. I am really not always able to respond to all such requests and to deal with all the details of what is in the literary intentions of our members. I also think it better if someone has the pretension to appear scientifically literary that he proves less in need of support in such a case. Now the book was published. Mr. Boldt had the obvious requirement that not only our various Theosophical working groups should display the brochure for this book – I have read it out so that you can judge it – in the lodge rooms in order to do their part for this book, but he also had the requirement, which is evident from his current behavior, that I should recommend the book in our circles; indeed, even assumes that the various measures or lack of measures that he criticized so sharply can be traced back to the fact that I did not recommend this book, and that I—despite Mr. Boldt's statement that I personally often asked how things were going with his book—never gave any information other than one that was “neither warm nor cold” when he asked me about it. You can understand that an author may easily feel that a piece of information is neither warm nor cold to him if it is not given to him exactly as he had imagined it. But not only did I have reasons not to deviate from a judgment that is “neither warm nor cold,” but I also had my good reasons, which I did not conceal from Mr. Boldt, in a gentle way, not to recommend the book. There will be more to say about some of this later, so I will mention the main reason I gave to Mr. Boldt first. I told him, roughly, that the book still has a very immature, amateurish character, and that this is especially evident from the fact that the whole execution is such that you can't do anything with it if you really want to get involved with the subject. Despite the cover, which says that it is a new publication that will change the whole of sex research over time, the book is actually such that, in my humble opinion, no one, even if they are responsive to the issues at hand, can really learn much from it. There would have been only one reason – I don't know if anyone of those who know me better could see this as a reason for me in this case – to recommend this book: it contains many praiseworthy and laudatory things about myself. But that is no reason for me to recommend the book just because Mr. Boldt praises me. And I must confess that I would have preferred it if what I have endeavored to produce over decades in various fields of knowledge had not been presented in such a way in a book. The fact that someone pays all kinds of adulation that refers to me will never be a reason for me to give a special recommendation about anything; the only reason for this can be the quality of the performance. So I did something for which, in addition to all the reasons I have given, there was another reason that could perhaps be appreciated: that it is my right to remain silent about something! I don't know if anyone doubts that I am entitled to do so? If one were to doubt that I am entitled to remain silent about anything, I would have to regard that as the worst kind of tyranny. If someone, as in this case, comes to me with the assumption that I am obliged to recommend this or that and would be acting incorrectly if I did not do so, I would have to regard that as the harshest and most terrible imposition that can possibly be placed on a human being. For I would like to know what would become of the freedom of mankind if a society were founded in which the person to whom some people adhere is obliged to recommend a book or other article by a member? You can imagine the tyranny that could result. So it happened that I could not give such a recommendation. I could give you many reasons for this; perhaps that could be done in the course of the negotiations. But our friends – perhaps with the exception of the 25 percent to which Mr. Boldt refers – did not particularly enjoy this work either. So it was left out of consideration. The great “injustice” has been done: this book has been ignored, let us say, has not been bought! My friends! In the past few days, a large number of us have received a brochure that now reads as follows:
Then, at the bottom, is the order form. A few days after the brochure appeared, I received the pamphlet “Theosophy or Antisophy? — A Free Word to Free Theosophists” from Ernst Boldt. The brochure contains the following words:
In the “preliminary remarks” of the brochure, I immediately read the words:
So, it is said, if the members are well-behaved and accommodating, it will be refrained from being carried out to the wider public; but if the members do not behave well, this printed “manuscript” may perhaps be presented to the wider public after all. However, it is very strange that this was only learned after the booklet had been purchased. I did not buy it, because it was sent to me for free. This booklet – which is not to be read out because it is not desired – contains many accusations against the backwardness and ignorance of the members of our “Anthroposophical Society”, who, in their developmental naivety, ignore such things that address the most important problems of the present. My dear friends, had the whole matter come to me before the program of our present General Assembly was sent out, I would have had – not exactly because of Boldt's proposal, which has more symptomatic significance, but for other reasons that could arise from the negotiations - I would have had reason enough not to give the four lectures announced, “The Human and the Cosmic Idea”, and instead to speak about the inferiority of some scientific work in the present day. For there is much that can be said about the subject that is called “sexology and related subjects”, which could one day provide an opportunity to say a few necessary words to those who hold many dubious views on this point at the present time, not to say it to our members, but so that our members can counter many of the corresponding pretensions in the present day by advancing the thought processes presented through their own research. In the brochure “Theosophy or Antisophy?” the author relies heavily on Nietzsche as a fighter against ascetic ideals, and Mr. Boldt finds that he needs to tell our members the truth quite bluntly. On page 28, he writes: It is entirely in the interest of keeping the Christian-Theosophical blood of life pure when we seriously warn against its parasites. However, Mr. Boldt does not look for these “parasites” among the 25 percent who are in favor of him, but among the other 75 percent.
here the printer was probably unaware that he should have used a z instead of a g; for Nietzsche writes “Wanzen” and not “Wangen”, and since I do not believe that Mr. Boldt wanted to speak of the “flirtatious cheeks” of our members, I assume that the printer stumbled here.
One cannot demand that the members of the Anthroposophical Society always be treated politely; nor can it be said that the least has been done here to be reasonably polite. There is not much politeness in the other sentence either:
So much for the tenor of how – and I am addressing the other 75 percent – you are addressed yourself. I myself am addressed in a peculiar way. If I put before me the figure in which I appear, then allow me to characterize it with an expression that is perhaps better understood in Berlin and the surrounding area than in the circles further outside this narrower country – that I say: the person who appears under the name “Dr. Steiner” seems to me like a “Konzessions-Schulze in the disguise of a superman”. That is more or less how I must appear after what I am portrayed as in this book. I don't know how widely this expression will be understood; but members who live further away and don't understand it can ask their friends in Berlin what a “Konzessions-Schulze in the disguise of a superman” is. Among other things, it is said that I have a right to do everything I do, but that because I have to make a pact with the 75 percent of the backward ones - those who are supposed to run away and who will contribute to the fact that infinity will one day smell of bugs - I am forced to say what my true opinion is. What I should actually have said about Mr. Boldt's book, I don't know; but in any case, I am the one who wears masks and has to rely not on telling the truth, but on saying what is pleasant for his 75 percent followers. So I appear in a very peculiar light:
Then it is said that it would indeed be necessary to gradually change tack, with the following words:
It's strange: what you have had to experience over the years! I must say: I do not want to expand the term “concessionary school in the disguise of the superman” any further, but only state a few things about how the 75 percent of the members who do not belong to Mr. Boldt are treated, and how I myself am treated, so that you may know a few things even if you have not been prompted by the brochure to read it. The brochure was sent to me together with the following letter: Munich, January 9, 1914,br> Adelheidstraße 15/III Dear Dr. Since summer 1911, I have repeatedly asked you for a factual statement about my book (“Sexual Problems in the Light of Natural Science and the Science of the Spirit”), which was published at the time. Since you have given me only inadequate, contradictory, evasive and confusing answers to my private questions and have repeatedly promised me “critical marginal notes” on my book but have repeatedly promised me, I saw myself compelled, for reasons of spiritual and intellectual self-preservation, to deal with this embarrassing and distressing subject in a pamphlet (“Theosophy or Anti-Theosophy? - A Free Word to Free Theosophists”) and to submit it to you as my contribution to the second General Assembly, with the urgent request that you take a stand on it in the next few days. I have announced the publication of my writing by sending 2,500 brochures to all branches of the Anthroposophical Society and have already sent out a number of copies; I may therefore assume that the content of the brochure is known at the General Assembly. Although the dam of cold objectivity may be breached here and there by the stream of feelings in my remarks, I know that you will have to call me to order strictly for this, but I would still ask you to always separate the factual content from the jagged form and not to give the latter too much weight. In any case, I ask for leniency as far as the form is concerned; not everything is meant as badly as it may appear in the rigid print on paper. I have not named any personalities and certainly did not want to offend anyone. It is in itself quite unimportant who said this or that, but the fact that it was said is what I could not get over. Should anyone feel offended, however, well, he may justify himself as best he can, or apologize and regret his behavior. I will certainly not be unreceptive to it. Whoever knows how much I have suffered from these things over these years will understand that I could not remain silent any longer. And you, dear Doctor, should know first that it was only pain that guided my pen. If freedom and independence, truth and truthfulness are not to remain empty phrases or abstractions in our circles, then these words, wherever they take on concrete life, must also be respected and duly appreciated; otherwise, the same applies to us as to what Lykophron of Phrygius says (pages 24-25): “You are all shadows without life, larvae without will” and so on. But we want to be free men indeed, over whom the sun of Christ can rejoice. I still remember exactly your wonderful words in Düsseldorf (1909) about the praise of the ability to make “first judgments”. At the time, you lamented finding this ability so undeveloped in our circles, where you would so much like to encounter it. Well, I did not wait to be shown the way to take a step – I did not need to be seduced or goaded – I had the strength, the courage and the good conscience for my “first judgment”! – I hope it is not misunderstood and held against me as a crime – I passed it with the best of intentions. Since it is financially and physically impossible for me to come to Berlin myself, I kindly request that this letter be read at the general assembly. With deepest admiration In the last few days, the explicit request has been made to discuss this letter first and to add the following:
On pages 25-26 of the brochure, the words can be read:
That is there, as required by “good human and intellectual law.” I continue to read the letter to you:
This “aspiration” is quoted from the messages no. X, page 3, where the sentence is: “We want to be praised less, but understood more diligently.” - Now Mr. Boldt continues:
There are the words that a great educator can tie up anything to people if they only believe in his honesty.
In addition, Ms. von Sivers will read a letter from Mr. Horst von Henning, because Mr. Horst von Henning is mentioned in the brochure “Theosophy or Antisophy?” in a special way that may be considered symptomatic. It says on page 10:
Fräulein von Sivers: Mr. Horst von Henning writes regarding the Boldt affair:
A second letter, which arrived on January 15, reads:
Fräulein von Sivers says: It would probably also turn out that Mr. Schure and Mr. Lienhard, like Mr. Deinhard, only gave Mr. Boldt a verbal assurance; after all, a well-meaning man like Mr. Schuré would hardly want to say anything other than, “Quite interesting!” to a young writer. Dr. Steiner: Ms. Wolfram has asked to speak first. Mrs. Wolfram: One could indeed just shrug off the Boldt case with a smile, and wave the application away with a hand gesture into the waste paper basket, and get on with the agenda. But since this “Boldt case” is a typical case, since there is not just one Boldt, but unfortunately many “Boldtes”, and it can happen to us again and again that our precious time is taken up and stolen in this truly unqualifiable way, I would like to present some of the facts of this case and conclude with an appeal to you, so that this Boldt case remains the only one of its kind and is not repeated. After all, we have better things to do than to waste our time on these matters, which are as tragic as they are comical. To avoid appearing to be concerned only with what Mr. Boldt said out of annoyance at the fact that his book was not accepted, and to avoid giving the impression that the book might not have been all that bad after all, and its author might have had some reason to write his pamphlet, then I would like to quote a few passages from the book to prove that we are dealing with a work that is as stupid as it is brazen and shamefully dishonest. From this it will be clear that if Mr. Boldt had read this book in 1911, he would no longer be with us today. Because if someone could write such a book, then he no longer belongs in our midst. We want to develop a sense of who belongs in our society and who does not. On page 2 of his book, Mr. Boldt says:
Yes, what impression do you get from that? The author is not a bit megalomaniac! He speaks of himself in the greatest conceivable modesty! I say this above all to show you that these accounts are teeming with examples of the impotence of consistent thinking. But the author does not notice any of this himself; on the one hand, he contradicts what he has said on the other. This only needs to be stated once. Because it is important to me to point out: we do not want to do it like our dear Mr. Horst von Henning, who may have read the book briefly. We want to approach the book with one thing in mind: whether it is sound or not. In this day and age, it is not difficult to publish a book teeming with mistakes – it is almost painful to listen to the chaos that it presents. And everyone who values logical thinking should get used to listening to this chaos. The young man continues (p. 4):
In his brochure, however, he says (p. 4):
In the book, however, he says “monistic-spiritualistic,” and then it continues:
Just think about this tangle of thoughts! And on this ground, Mr. Boldt now wants to graft everything that the seer gives in terms of spiritual science! This is now amalgamated by Mr. Boldt and the further ground is created from it, on which we - we “bugs” - can develop further. Furthermore: With its head in the sky, it seeks to gain a firm foothold on earth and vice versa: rooted in the physical world, it strives with its blossoms and fruits into the spiritual world. - For this reason, we too will not be able to please any of the contemporary parties, because our premises are also - since they are theosophical - “far beyond all party politics”. When it comes to the various issues of the day, there is no reason to ignore the gender issue in favor of the other cultural issues, for it asserts itself in all its harrowing scope. The theosophist must therefore not withdraw his attention from it. He must also allow the light of his spirit to fall on this area of life and fertilize it with the spiritual reform ideas of Theosophy. This has been admirably stimulated by Steiner's two lectures on 'Man and Woman' and 'Man, Woman and Child in the Light of Spiritual Science'. Our task was now to treat this subject in a broader developmental-historical sense and to bring together all occult knowledge about it. Where are the Theosophists, one might ask, who have so far dared to approach the reform of sexual life in the spirit of Theosophy? And how many are there who are able to bring the necessary interest and understanding to such endeavors? It is understandable that a pioneering undertaking like this one must meet with great resistance, especially from the partisans of the dualistic and monistic schools. But if such resistance also arises in part from the theosophical movement itself, this is merely due to the immaturity of the majority of its “followers”. But this movement is certainly not concerned with followers; it needs free spirits and big hearts that see through the life of the present with a bright, clear gaze and find the right points of attack for social action. It is really not that difficult to see that this is written by a young, rather self-confident man, in whose head it not only looks quite chaotic, but also hovers in a rather ominous way the spirit of megalomania. And it must be said that during the time this young man has been our member, he has not only forgotten nothing of his megalomania, but has also profited nothing from the teachings of spiritual science. What does the insistence that we must deal with sexual problems mean to anyone who reflects on the facts of developmental history that have been given us through spiritual scientific research? The frequent references to sexual problems are somewhat superfluous. If one has only studied and thought about what has been communicated to us, for example, about the development of the human being, about the course of development of the world and humanity, from the fact of the influence of the spirit into the world and so on, then everyone will have to say to themselves: How foolish it would be if we Theosophists were now to coin a very specific formula for how we wanted to deal with this sexual issue. After all, this is about the most personal area of each of us, and everyone will know that it is self-evident how a person should behave in their particular case. It is a different matter if we wanted to know what foolish views prevail in scientific circles. In the case of Mr. Boldt's book, however, one can only conclude that it is a stupid and brazen book; but it is also a shamefully dishonest book. And I will prove this to you. If one wanted to say that this Mr. Boldt was not aware of the terrible things he is saying and doing, that is no excuse. It only makes it much worse that in our circles, where enough can be learned, it is possible that a person writes, dares to write, that he lies and is not supposed to know it himself. So such things are growing in our circles. I still have to show you that there are other “Boldtes”, which is why I want to treat this case as a typical one. Mr. Boldt then talks about the “sources” of his book, cites works by Dr. Steiner and then says page [7-8]:
If you are not careful, you will not notice anything, not notice what the “ethical-aesthetic content of ideas” is. I must confess that I could not believe my eyes when I saw where Mr. Boldt finally ended up as a result of his interesting and valuable research, what he considers to be right for the sexual life of our time (p. 54 of his book). One can only describe it: that the ideal of asceticism should already be recognized, but that it should hover over people like a very distant ideal for the future. We humans are not yet so far that we could think of realizing such an ideal. When Mr. Boldt wants to think, he always quotes Nietzsche, and then he explains what is the only right thing for our time. It is remarkable that I, of all people, always have to say such things: the unrestricted freedom of the individual to experience lovingly sexually whatever he desires; and Mr. Boldt then presents the “Oneida practice” as something worthy of imitation. He says that what he quite openly proclaims as the conclusion of his ideal, his ethical-aesthetic idea, must be based on what Dr. Steiner himself says. In the remarks that follow $135 - as is the case with all profound works, there must be a commentary on them - things are said to explain why Dr. Steiner says the same thing as what Mr. Boldt proclaims as the ideological content of this book, which is his own soul property:
And now you shall see what it is capable of when we let all those into our circles who brutally and dirtyly exploit everything for themselves.
But all this is done in such a way that the reader thinks that Dr. Steiner said it.
And so on:
And what does Boldt make of it? He reinterprets everything in a sexual way!
There are still some passages that mean an increase. The assembly has expressed its will to refrain from further reading! Mrs. Wolfram, continuing: What do we have here? You cannot make even more unscrupulous use of another person's intellectual property! If Mr. Boldt had read the book thoroughly, he would no longer be in our ranks. And now I would like to make an appeal to you, after first adding something to what I said earlier: that there are many Boldtes, and that this one is just a typical case. Unfortunately, there is a view among far too many people that our movement is there to support all those who do not want to help themselves. Our society would be such a large aid institution, and one would be obliged, if one is the head of a branch, to support such and such a person in his outer life. In short, the greatest demands are placed on society. Those who now enter society with a state of mind like Mr. Boldt, for example, and who believe that they can do everything with their heads, although they can do nothing at all, these only form a choir of the discontented. It was people like that who could not play a role; they have now done what they could - which then led to their exclusion from our society. In order to give you a proper foundation, I would like to read a few words from No. 7/8, Volume IV, 1914 of Theosophy, edited by Dr. Vollrath, part of which is edited by Casimir Zawadzki. A year ago, he wrote me a letter asking me to do whatever I could to restore the old, good relationship between him, Dr. Steiner and the Society. This Zawadzki was a member of our Society for a while, and not a very comfortable member at that. I did what I could until he plagiarized Dr. Steiner's work in an outrageous manner, until he was expelled and threw himself into the arms of Dr. Vollrath, where he still is. He then thought that since he is Polish, it would be nice if he could perhaps become Secretary General in Warsaw. But when he realized that under Besant's aegis the matter was becoming shaky, he thought he would do better if he could work under Dr. Steiner again. And now I would like to point out how really not that much is needed to know whether someone fits into our society or not. Sometimes something like an impotence of logical thinking manifests itself in a single word. The letter reads:
Anyone who can write this has not just lost their marbles, they have lost several screws! It is completely hopeless to believe that someone who is capable of writing such a thing can deserve to be taught by us. He lacks any possibility of correct thinking when he writes this in a letter in which he wants to present himself in the best possible light. This gentleman then launched a sensational advertisement about a teaching course – again about sexual matters. I then wrote in reply to his letter that it was not acceptable, and the matter was dropped. Now Zawadzki is writing an article in No. 7/8 of Theosophy that is linked to No. III of the Mitteilungen für die Mitglieder der Anthroposophischen Gesellschaft (Communications for the Members of the Anthroposophical Society). So it is possible that a person like that could have had this No. III!
This is now attributed to Dr. Steiner because he published the letters of Dr. Hübbe-Schleiden.
Can you understand this? I can't! And I would like to point out that there must be no confusion where it is not possible to see at first glance what is important. It continues:
He goes on to discuss Dr. Steiner's “servant manner” and the complete lack of feeling for human dignity and reverence, talks about Dr. Unger and Mrs. von Reden, and then talks about the “Esoteric Section”:
Now he is slobbering again, something is going around in his mind, and so is Mr. Boldt.
There is no other way to say this about the Besant institutions. — Another gentleman also wrote to me, saying that I should do everything I could to help him meet Dr. Steiner again; but in the same issue of Vollrath's Theosophy, he is at it again. And now I would like to say the following. Everything must be done to counter the infiltration of certain elements by nurturing certain attitudes and feelings. There is a concept of tolerance within our society, of course we should be tolerant; but what do we mean by that? That we have recognized that there is an unspeakably valuable teaching material that can be handed down to us, and for which we feel a responsibility. We can still be tolerant of those who appear beautiful, but not of those for whom the sensation of what is true or untrue, what is beautiful or hypocritical, is no longer there in the brain. Observe what is first presented in the cases of Fidus, Hübbe-Schleiden, Prellwitz and others, and then how it is said, “That is not at all so,” and then they still write, “... with deepest reverence,” and so on. It is not true that we are a hospital. And by this I mean that we want to make a little front against the intrusion of such elements into us! Because that means being tolerant of what is most precious to us! The lodge boards could be granted more rights – which is only right and proper vis-à-vis a lodge board. There is so much debate about what a lodge board can and cannot do, but nothing is said about the rights it should have. I do not see a lodge committee as a “jack of all trades” who only has to ensure that the lodge rooms are clean, that lectures are available – and has nothing further to say. I think that a lodge committee should above all have the freedom for the waste paper basket once they have been trusted by being elected. The patronage of all possible products of the various Theosophical members must stop. In ordinary life, I am not legally obliged to read or buy something that someone sends me; and yet the lodge boards are supposed to be obliged to display something in the lodge rooms if someone has produced it, and you get a cold if you don't do it? In this regard, every lodge board must be able to ensure the most meticulous cleanliness of the atmosphere. If he can ensure the cleanliness of the lodge rooms, he must also be able to do the other. And it is really not that difficult to know who belongs to our ranks and who does not. If only we could get rid of the eternal judging according to emotional values, according to what someone “says”! A person is not what he says – he may believe it of himself; a person is what he does. And if he has done this or that on the physical plane as an expression of his being, then I judge by his deed. If a Hübbe-Schleiden, a Boldt and so on have done this or that, I know what they have done. And if he wants to be taken up again, he must bring forth a different deed as a metamorphosis of his being. The various lodge boards and the general board must at least have one resolution in the soul of each of them: from now on, everything must be done to ensure that the kind of people we have heard about today are the very last of their kind among us. If that were possible, then the matter could have been dealt with at our board meeting. If the Executive Council of the Anthroposophical Society is so sure of the trust that is so often mentioned, then it would be a matter of course that such documents as the Boldt case, when they arrive, are simply consigned to the wastepaper basket! I would like to propose that the board be given the right, on the basis of the trust placed in it by the election, to dispose of such matters as it sees fit, so that we do not waste our time on such things, as is the case now. Dr. Steiner: Perhaps something else would happen if the “concession Schulze in the disguise of the superman” would dare to stand up for Mr. Boldt's book. If I were to be as bold as Mr. Boldt wants me to be and recommend his book to the 75 percent of our members who are lagging behind, what would happen then? On page 14 of his brochure, Mr. Boldt says:
This is just an appetizer. And now I ask you to enjoy the other dishes as fully as possible! The meeting is suspended for tea; the negotiations will be continued on Monday, January 19, 1914. The continuation of the protocol will be published in the following issue of Mitteilungen. |
| 122. Genesis (1982): The Mystery of the Archetypal Word
17 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Whoever wishes to get an idea of what lived in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he used this word should clearly understand that in those days there was a lively comprehension of the fact that our earth evolution had a definite meaning and a definite goal. |
| We should have to go into very many things to get anywhere near an understanding of these Beings. To begin with, however, we can come to know one aspect of them, and that will suffice to bring us at least one step nearer to the potent meaning of the ancient Bible words. |
| One of them could do this, another that. But we understand the nature of these Beings best if we realise that at the time we are now considering they were working as a group towards a common goal; they were moved by a common aim. |
| 122. Genesis (1982): The Mystery of the Archetypal Word
17 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
For anyone who has a background of Spiritual Science, and has absorbed something of its teaching about the evolution of the world, then goes on to study those tremendous opening words of our Bible, an entirely new world should dawn upon him. There is probably no account of human evolution so open to misinterpretation as this record known as Genesis, the description of the creation of the world in six or seven days. When the man of today calls to life in his soul, in any language familiar to him, the words In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth, they convey to him scarcely a faint reflection of what lived in the soul of an ancient Hebrew who allowed the words to work upon him. It is not in the least a question of being able to replace the old words by modern ones; it is much more important that we should have been prepared by Anthroposophy to feel at least something of the mood which lived in the heart and mind of the Hebrew pupil of old when he brought to life within himself the words: B'reschit bara elohim et haschamayim v'et ha'aretz.1 A whole world lived while such words were vibrating through his soul. 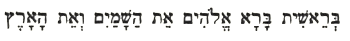 What was it like—this inner world which lived in the soul of the pupil? We can only compare it with what can take place in the soul of a man to whom a seer has described the pictures he experienced on looking into the spiritual world. For what in the last resort is Spiritual Science but the outcome of seership, of the living intuitions which the seer receives when, having freed himself from the conditions of sense-perception and of the intellect bound up with the physical body, he looks with spiritual organs into the spiritual worlds? If he wishes to translate what he sees there into the language of the physical world, he can only do so in pictures, but if his descriptive powers suffice, he will do it in pictures which are able to awaken in his hearers a mental image corresponding with what he himself sees in the spiritual worlds. Thereby something comes into existence which must not be mistaken for a description of things and events in the physical sense-world; something comes into existence which we must never forget belongs to an entirely different world—a world which does indeed underlie and maintain the ordinary sense-world of our ideas, impressions and perceptions, yet in no way coincides with that world. If we want to portray the origin of this our sense-world, including the origin of man himself, our ideas cannot be confined to that world itself. No science equipped only with ideas borrowed from the world of the senses can reach the origin of sense-existence. For sense-existence is rooted in the supersensible, and although we can go a long way back historically, or geologically, we must realise that, if we are to reach to actual origins, there is a certain point in the far distant past at which we must leave the field of the sense-perceptible and penetrate into regions that can only be grasped super-sensibly. What we call Genesis does not begin with the description of anything perceptible by the senses, anything which the eye could see in the physical world. In the course of these lectures we shall become thoroughly convinced that it would be quite wrong to take the opening words of Genesis as referring to events which can be seen with the outward eye. So long as one connects the words “heaven and earth” with any residue of the sensuously visible one has not reached the stage to which the first part of the Genesis account points us back. Today there is practically no way of obtaining light upon the world it describes except through Spiritual Science. Through Spiritual Science we may indeed hope to approach the mystery of the archetypal words with which the Bible opens, and to get some inkling of their content. Wherein lies their peculiar secret? It lies in the fact that they are written in the Hebrew tongue, a language which works upon the soul quite differently from any modern language. Although the Hebrew of these early chapters may not perhaps have the same effect today, at one time it did work in such a way that when a letter was sounded it called up in the soul a picture. Pictures arose in the soul of anyone who entered with lively sympathy into the words, and allowed them to work upon him—pictures harmoniously arranged, organic pictures, pictures which may be compared with what the seer can still see today when he rises from the sensible to the supersensible. The Hebrew language, or, better said, the language of the first chapters of the Bible, enabled the soul to call up imaginal pictures which were not wholly unlike those that are presented to the seer when, freed from his body, he is able to look into supersensible regions of existence. In order to realise in some measure the power of these archetypal words we must disregard the pale and shadowy impressions which any modern language makes upon the soul, and try to get some idea of the creative power inherent in sound-sequences in this ancient tongue. It is of immense importance that in the course of these lectures we too should seek to place before our souls the very pictures which arose in the Hebrew pupil of old when these sounds worked creatively in him. In fact we must find a method of penetrating the primeval record entirely different from those used by modern research. I have now given you an indication of our line of approach. We shall only slowly and gradually learn to comprehend what lived in the ancient Hebrew sage when he allowed those most powerful words to work upon him, words which we do at least still possess. So our next task will be to free ourselves as far as possible from the familiar, and from the ideas and images of “heaven and earth,” of “Gods,” of “creation,” of “in the beginning,” which we have hitherto held. The more thoroughly we can do this the better we shall be able to penetrate into the spirit of a document which arose out of psychic conditions quite different from those of today. First of all we must be quite clear as to the point of time in evolution we are speaking of, when we deal with the opening words of the Bible. You know of course that contemporary clairvoyant investigation makes it possible to describe to some extent the origin and development of our earth and of human existence. In my book Occult Science I tried to describe the gradual growth of our earth as the planetary scene of human existence, through the three preliminary stages of Saturn, Sun and Moon.2 Today you will have in mind, at least in broad outline, what I described there. At what point then in the spiritual scientific account should we place what draws near to our souls in the mighty word B'reschit? Where does it belong? If we look back for a moment to ancient Saturn, we picture it as a cosmic body having as yet nothing of the material existence to which we are accustomed. Of all that we find in our own environment it has nothing but heat. No air or water or solid earth is as yet to be found upon ancient Saturn; even where it is densest, there is only fire—living, weaving warmth. Then, to this living, weaving warmth, a kind of air or gaseous element is added; and we have a true picture of the Sun existence if we think of it as an interweaving, an interpenetration, of a gaseous, airy element and a warmth element. Then comes the third condition, which we call the Moon evolution. There the watery element is added to the warmth and the air. There is as yet nothing of what in our present earth we call solid. But the old Moon evolution has a peculiar characteristic. It divides into two parts. If we look back upon old Saturn, we see it as a single whole of weaving warmth; and the old Sun we still see as a mingling of gaseous and warmth elements. During the Moon existence there takes place this separation into a part which is Sun and a part which retains the Moon nature. It is only when we come to the fourth stage of our planetary evolution that the earth element is added to the earlier warmth, gaseous and watery elements. In order that this solid element could come into existence, the division which had taken place previously during the Moon evolution had first to repeat itself. Once again the sun had to withdraw. Thus there is a certain moment in the evolution of our planet when, out of the universal complication of fire and air and water, the denser, more earthy element separates from the finer, gaseous element of the sun; and it is only in this earthy element that what we today call solid is able to form. Let us concentrate on this moment, when the sun withdraws from its former state of union with the rest of the planet and begins to send its forces to the earth from without. Let us bear in mind that this was what made it possible, within the earth, for the solid element—what we today call matter—to begin to condense. If we fix this moment firmly in our minds we have the point of time at which Genesis, the creation story, begins. This is what it is describing. We should not associate with the opening words of Genesis the abstract, shadowy idea we get when we say “In the beginning,” which is something unspeakably poverty-stricken compared with what the ancient Hebrew sage felt. If we would bring the sound B'reschit before our souls in the right way, there must arise before us—in the only way it can do so, in mental images—all that happened through the severance of sun and earth, all that was to be found at the actual moment when the separation into two had just taken place. Furthermore we must be aware that throughout the whole of the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions, spiritual Beings were its leaders and its bearers; and that warmth, air, water are only the outer expressions, the outer garments of spiritual Beings who are the reality. Thus when we contemplate the condition which obtained at the moment of separation of sun and earth, and picture it to ourselves in thoughts full of material images, we must also be conscious that the elementary “water,” “air,” “fire,” which we have in our mind's eye, is still only the means of expression for moving, weaving spirit which, during the course of the preceding Saturn, Sun and Moon stages has advanced, has progressed, and at the time now being described has reached a certain stage in its evolution. Let us place before us the picture of an immense cosmic globe, composed of weaving elements of water, air or gas and fire, a globe which splits apart into a solar and a telluric element; but let us conceive too that this elementary substance is only the expression of a spiritual. Let us imagine that from this substantial habitation, woven of the elements of water, air and heat, the countenances of spiritual Beings, weaving within it, look out upon us, spiritual Beings who reveal themselves in this element which we have had to represent to ourselves through material images. Let us imagine that we have before us spiritual Beings, turning their countenances towards us, as it were, using their own soul-spiritual forces to organise cosmic bodies with the help of warmth, air and water. Let us try to imagine this! There we have a picture of an elementary sheath, which, to give a very rough sensuous image of it, we may perhaps liken to a snail-shell, but a shell woven not of solid matter, like the snail's, but from the forest elements of water, air and fire. Let us think of spirit, in the form of countenances, within this sheath, gazing upon us, using this sheath as a means of manifestation, a force of very revelation which, as it were, pricks outward into manifestation from what lies hidden in the supersensible. Call up before your souls this picture which I have just tried to paint for you, this image of the living weaving of spirit in a kind of matter; imagine too the inner soul-force which causes it to happen; concentrate for a moment on this to the exclusion of all else, and you will then have something approximating to what lived in an ancient Hebrew sage when the sounds B'reschit penetrated his soul. Bet the first letter, called forth the weaving of the habitation in substance; Resch the second sound, summoned up the countenances of the spiritual Beings who wove within this dwelling, and Schin the third sound, the prickly, stinging force which worked its way out from within to manifestation.  Now the underlying principle behind such a description is dawning upon us. And when we have grasped that, we are able to appreciate something of the spirit of this language; it had a creativeness of which the modern man with his abstract speech has no inkling. Now let us place ourselves at the moment immediately preceding the physical coagulation, the physical densification of our earth. Let us imagine it as vividly as possible. We shall have to admit that in describing what was taking place at that moment we cannot make use of any of the ideas which we use today to describe processes in the external sense-world. Hence you will see that it is utterly inadequate to associate any external deed with the second word we meet in Genesis—bara—however closely that deed might resemble what we understand today as creation. We do not thus get near to the meaning of that word. Where can we turn for help? The word implies something which lies very near the boundary where the sensible passes over directly into the supersensible, into pure spirit. And anyone who wishes to grasp the meaning of the word bara, which is usually translated “created” (In the beginning God created ...), must in no wise associate it with any productive activity which can be seen with physical eyes. Take a look into your own inner being! Imagine yourselves as having been asleep for a while, then waking up, and, without opening your eyes to things around you, calling up in your souls by inner activity certain images. Bring home vividly to yourselves this inner activity, this productive meditation, this cogitation, which calls forth a soul-content from the depths of the soul as if by magic. If you like you can use the word “excogitate” for this conjuring up of a soul-content out of the depths into the field of consciousness; think of this activity, which man can only perform with his mental images, but think of it now as a real, cosmic, creative activity. Instead of your own meditation, your own inward experience in thinking, try to imagine cosmic thinking-then you have the content of the second word of Genesis, bara. However spiritually you may think it, you can only liken it to the thought-life you are able to bring before yourselves in your own musing, you cannot get nearer to it than that! And now imagine that during your musing two kinds of images come before your souls. Suppose there is a man to whom on awakening two different kinds of thought occur, a man who muses about two different kinds of thing. Suppose that one kind of thought is the picture either of some activity, or of some external thing or of some being; it does not come about through external sight, through perception, but through reflection, through the creative activity of his soul in the field of his consciousness. Suppose that the second complex of ideas which arises in this awakening man is a desire, something which the man's whole disposition and constitution of soul can prompt him to will. We have elements both of thought and of desire coming up in our souls through inner reflection. Now imagine, instead of the human soul, the Beings called in Genesis the Elohim, reflecting within themselves. Instead of one human soul, think of a multiplicity of reflecting spiritual Beings, who, however, in a similar way—save that their musing is cosmic—call forth by reflection from within themselves two complexes which might be compared with what I have just been describing—a pure thought-element and an element of desire. Thus instead of thinking of the musing' human soul, we think of a group of cosmic Beings who awaken in themselves two complexes; one of the nature of thought or ideation, that is, one which manifests something, expresses itself outwardly, phenomenally; and another of the nature of desire, which lives in inner movement, inner stimulation, which is permeated with inner activity. Let us think of these cosmic Beings, who are called in Genesis the Elohim, musing in this way. The word bara, “created,” brings their musing home to us. Then let us think that through this creative musing two complexes arise, one tending towards external revelation, external manifestation, and another consisting of an inward stimulus, an inward life; then we have the two complexes which arose in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when the words haschamayim and ha'aretz—represented for the modern man by “heaven” and “earth”—sounded through his soul. Let us try to forget the modern man's conception of “heaven and earth.” Let us try to bring the two complexes before the soul, the one which tends more to disclose itself, tends to outward manifestation, is disposed to call forth some outside effect; and the other complex, the complex of inner stimulation, of something which would experience itself inwardly, something which quickens itself inwardly; then we have what expresses the meaning of the two words haschamayim and ha'aretz. As for the Elohim themselves, what kind of Beings are they? In the course of these lectures we shall learn to know them better, and to describe them in terms of Spiritual Science; but for the present let us try to reach in some measure the meaning of this archetypal word “Elohim.” Whoever wishes to get an idea of what lived in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he used this word should clearly understand that in those days there was a lively comprehension of the fact that our earth evolution had a definite meaning and a definite goal. What was this meaning and this goal? Our earth evolution can only have a meaning, if during its course something arises which was not there before. A perpetual repetition of what was already there would be a meaningless existence, and unless the Hebrew sage of old had known that our earth, after having passed through its preliminary stages, had to bring something new into existence, he would have regarded its genesis as meaningless. Through the coming into existence of the earth something new became possible, it became possible for man to become man as we know him. In none of the earlier stages of evolution was man present as the being he is today, the being that he will more and more become in the future; that was not possible in earlier stages. And those spiritual Beings who directed the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions were of a different nature from man—for the moment we will not enter into the question whether they were higher or lower. Those Beings who wove in the fiery, gaseous and watery stages of elementary existence, who wove a Saturn, Sun and Moon existence, who at the beginning of earth existence were weaving its fabric—how best do we come to know them? ... How can we draw near to them? We should have to go into very many things to get anywhere near an understanding of these Beings. To begin with, however, we can come to know one aspect of them, and that will suffice to bring us at least one step nearer to the potent meaning of the ancient Bible words. Let us consider those Beings for a moment—the Beings who stood nearest to man at the time when he was created from what had developed out of the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. Let us ask those Beings what they really wanted. Let us ask them what was their will, their purpose. Then we shall be able to get at least some idea of their nature. They had great ability; in the course of their evolution they had acquired capacities in various directions. One of them could do this, another that. But we understand the nature of these Beings best if we realise that at the time we are now considering they were working as a group towards a common goal; they were moved by a common aim. Although at a higher level, it is as if a group of men, each with his own special skill, were to co-operate today. Each of them can do something, and now they say to each other: “You can do this, I can do that, the third among us can do something else. We will unite our activities to produce a work in common in which each of our capacities can be used.” Let us then imagine such p. group of men, a group each of whom practises a different craft, but which is united by a common aim. What they intend to bring into existence is not yet there. The unit at which they are working lives to begin with only as an aim. What is there is a multiplicity. The unit lives, to begin with, only as an ideal. Now think of a group of spiritual Beings who have passed through the evolutions of Saturn, Sun and Moon, each one of whom has a specific ability, and who all at the moment I have indicated make the decision: “We will combine our activities for a common end, we will all work in the same direction.” And the picture of this goal arose before each of them. What was this goal? It was man, earthly man! Thus earthly man lived as the ultimate goal in a group of spiritual Beings who had resolved to combine their several skills in order to arrive at something which they themselves did not possess at all, something which did not belong to them, but which they were able to achieve by combined effort. If you accept all that I have described to you—the elementary sheath, the cosmic, meditative spiritual Beings working within it, the two complexes, one of desire quickening inwardly, and another manifesting outwardly—and then ascribe the common purpose I have just mentioned to those spiritual Beings whose countenances gaze out of the elementary sheath, then you have what lived in the heart of the Hebrew sage of old in the word Elohim. Now we have brought before us in picture form what lives in these all-powerful archetypal words. Then let us forget all that a man of today can think and feel when he utters the words: In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth. Bearing in mind all that I have told you today, try to put this picture before you. There is the sphere in which fiery, gaseous and watery elements weave. Within this active, weaving elementary sphere a group of pondering spiritual Beings live. They are engaged in productive pondering, their pondering is penetrated through and through by their intention to direct their whole operation towards the form of man. And the first-fruits of their musing is the idea of something manifesting itself outwardly, announcing itself, and something else inwardly active, inwardly animated. “In the elementary sheath the primeval Spirits pondered the outwardly manifesting and the inwardly mobile.” Try to bring before yourselves in these terms what is said in the first lines of the Bible, then you will have a foundation for all that is to come before our souls in the next few days as the true meaning of those all-powerful archetypal words which contain such a sublime revelation for mankind—the revelation of its own origin.
|
| 122. Genesis (1982): Ha'aretz and Haschamayim
18 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| How far has this brought us? We shall not understand the sublime process of the seven days of creation unless we bear these details in mind. If we do so, then the whole will seem a wonderful cosmic drama. |
| So we must not think of them as human, but we must certainly envisage that there is already in their nature a certain cleavage. When we speak of man today, we do not understand him at all unless we distinguish between body, soul and spirit. You know what great efforts we Anthroposophists have made to get a closer understanding of the activity and nature of this human trinity. |
| —a phrase which we must go into more closely if we would understand how the spirit of the Elohim permeated the other elements. We can only understand the verb racheph by praying in aid, so to speak, all the associations which it would have carried with it in those days. |
| 122. Genesis (1982): Ha'aretz and Haschamayim
18 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In a good many places in this course of lectures—as well as elsewhere in our Anthroposophical discussions—it may well sound as if I rather enjoyed having to set myself up in opposition, or apparent opposition, to “modern science.” I am thinking more of people in the outside world unacquainted with the kind of feeling that prevails in our circles, but it is a point on which I am particularly anxious to avoid any misunderstanding. You may take it as definite that it is a very real effort for me to do anything of the sort; and that I only do it precisely at those points where I myself am able to develop or carry further what science has to say. My sense of responsibility is such that it will not permit me to bring forward anything that conflicts with the opinions of modern science, unless I have first placed myself in a position to understand, and if necessary reproduce, its findings on the subject in hand. No one having such an attitude could possibly approach the all-important matters which are to occupy us in the next few days without the deepest sense of awe and of the responsibility that goes with it. Unfortunately, it just has to be said that, as regards the questions now to come before us, modern science breaks down altogether. The scientists are not even in a position to know why this should be so, or to perceive why their science must necessarily prove so hopelessly amateurish in face of the real and the great problems of existence. So, although in a short course of lectures it is naturally not possible to engage in controversy about every detail, please take it for granted that behind all I say I am fully aware of the modern scientific outlook on these subjects. Only, as far as possible, I must confine myself to what is positive, and trust that in a circle of Anthroposophists this will always be understood. In the last lecture I tried to show how those tremendous, archetypal words with which the Bible opens—words which are put before us in a language different in its very nature from modern tongues—can only be rightly interpreted if we try to forget the attitude of mind and feeling we have acquired as a result of the usual modern renderings. For the language in which these powerful words of creation were originally given to us has actually the peculiarity that the very character of its sounds directs the heart and mind towards those pictures which arise before the eye of the seer when he contemplates the moment of the welling-forth of the sense-perceptible part of our world out of the supersensible. Every single sound in which the immemorial origin of our earth existence is placed before us is full of active power. In the course of these lectures we shall often have to refer to the character of this language; today, however, let us confine ourselves to one of the first essentials. You know that in the Bible, after the words which yesterday I at least tried to put before your souls in picture form, there comes a description of one of the complexes which arose out of the divine meditation, out of the divine productive musing. I told you that we have to conceive that, as if out of a cosmic memory, two complexes arose. One was a complex which may be compared with the thoughts which can arise in us; the other is of the nature of desire or will. The one complex contains all that tends towards outer manifestation, tends to proclaim itself, tends, as it were, to force its way out—haschamayim. The other complex—ha'aretz—consists of an inner activity, a permeation with inward craving; it is something which inwardly vivifies, animates. Then we are told of certain qualities of this inner, vivifying, self-stimulating element, and these are indicated in the Bible by appropriate sounds. We are told that this self-stimulating element was in a state which is designated as tohu wabohu1—without form and void. To understand what is meant by tohu wabohu we must try to recapture a picture of what it expresses; and we only succeed in doing that if out of our spiritual scientific knowledge we call to mind what it was that, after its passage through the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions, emerged again and surged through space as our planetary earth existence.  I pointed out yesterday that what we call solidity, the state which offers a certain resistance to our senses, did not exist during the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions; only the elements of fire or warmth, gas or air, and water were to be found there. It was only with the emergence of the earth that the solid element was added. Thus at the moment when there happened what we were describing yesterday, when the tendency began for the sun to split off from the earth, there is a mutual interpenetration of the elements warmth, air and water—they surged through one another. That preliminary surging interpenetration which we have tried to picture to ourselves is thr meaning of the phrase inadequately translated as without form and void, but eloquently and effectively rendered by the succession of sounds tohu wabohu. What then does tohu wabohu signify? If we try to picture what can be aroused in our souls by these sounds it is something like this. The sound which resembles our own T calls up a picture of forces diverging from a central point in every direction. Thus the moment one utters the T sound one gets the picture of forces diverging from a centre in every direction to illimitable distances. So that we have to imagine the elements warmth, air and water permeating, interpenetrating each other, and within them a tendency to diverge, as from a centre in all directions. The sound tohu alone would suffice to express this tendency to push outwards, to separate. What then does the second part of the phrase signify? It expresses the very opposite of what I have just described. The character of the sound resembling our B, called forth by the letter Bet, expresses what you would get if you imagined an enormous sphere, a hollow sphere, with yourself inside it, and rays proceeding from every point inside this sphere towards its centre. Thus you imagine a point within space whence forces stream out in all directions—that is tohu; these forces are arrested at the extremities of the spherical enclosure, and turned back again on themselves from every direction of space—that is bohu. And if you have formed this idea, and think of all these streams of force as filled with the three elementary substances of warmth, air and water, then you know the character of this inner animation. The combination of these sounds indicates the way in which elementary existence is guided by the Elohim. How far has this brought us? We shall not understand the sublime process of the seven days of creation unless we bear these details in mind. If we do so, then the whole will seem a wonderful cosmic drama. Let us recall once more that in the word bara—“in the beginning the Gods created”—we are concerned with a soul-spiritual activity. I have likened it to the thoughts which are called up in our own souls. Thus we may think of the Elohim as arrayed in space, and bara as a cosmic soul-activity, a pondering. What the Elohim ponder is expressed by haschamayim and ha'aretz—the outward radiation and the inner, mobile energy. To make the comparison as close as possible picture yourselves in the moment of awakening; groups of ideas arise in your souls. This is how haschamayim and ha'aretz arise in the souls of the Elohim. Now you know that these Elohim came over to earth evolution at the stage to which they had evolved during the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. So that they are in a somewhat similar situation to your own when on awakening you call up thoughts in your souls. You can contemplate those thoughts, you can say what they are. You can say: “When I awake in the morning and recall what has previously been left in my mind, I can describe it.” It was something the same with the Elohim, when they said to themselves: “Let us now reflect upon what arises in our souls when we recall what took place during the ancient Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. Let us see how it looks in recollection.” What it looked like is expressed in the phrase tohu wabohu; it could be expressed by a picture such as I have given you, as streams radiating from a centre outwards into space and back again, in such a way that the elements are interwoven in this streaming of forces. Thus the Elohim could say to themselves: “At the stage to which you have so far brought things this is what they look like. This is how they are resumed.” Now in order to understand what comes next, usually rendered “darkness was above the fluid substances” or “above the waters”(above the abyss)—or darkness was upon the face of the waters (English A.V.)—we must take into consideration something else. We must once more turn our attention to the course of evolution before the earth came into existence. First we have the Saturn existence, inweaving in the fiery element. Then comes the Sun existence, with its addition of the airy element. But in my Occult Science you can read how with the addition of the air something else is associated. The fine warmth element of Saturn condenses to a gaseous element. But every such densification is accompanied by a counter-process of refinement. Condensation to the gaseous element is a descending process, but on the other side there is an ascent to the light element. Thus, speaking of the transition from Saturn to Sun, we must say that Saturn still weaves solely in the element of warmth, whereas during the Sun evolution something denser, the gaseous element, is added, but so also is light. The light element makes it possible for the warmth and the air to manifest themselves in outward radiance. Now let us take one of the two complexes—the one expressed as ha'aretz, usually translated as “earth”—and ask ourselves how the Elohim, turning their attention to this complex after their act of recollection, would have described it. They could not have said that what had already existed in the Sun evolution had now come to life again. For it was without light; light had separated from it. Ha'aretz had thus become one-sided. It had not brought with it the light, but only the coarser elements, the gaseous and the warmth elements. True, there was no lack of light in what is expressed by haschamayim, but haschamayim is the sunlike, issuing from the other complex. In ha'aretz there was no rarefaction, there was no light. We may then say that in one of the complexes warmth, air and water surged through one another in the way which is indicated by tohu wabohu. These elements were denuded, they lacked the light which had entered into evolution on the Sun. They remained dark, had nothing sunlike about them; for that had withdrawn with haschamayim. Thus the progress of earth evolution means that the light, which it still had so long as the sun remained united with it, had now withdrawn; and a dark fabric woven of the elements of warmth, air and water was left. We now have the content of the meditation of the Elohim before our souls in more detail. But we shall never be able to think of it in the right way unless we are conscious all the time that air, water and even warmth are external expressions of spiritual Beings. It would not be quite correct to call this elemental existence their “garment”; it should rather be regarded as making known their presence externally. Thus what we call air, water, warmth, are maya, illusion; they are only there for the outward aspect, and this is so even for the mind's eye. In reality this elemental existence is something psycho-spiritual, it is the external manifestation of the soul-spiritual of the Elohim. But we must not think of the Elohim as at all like man, for man is actually their goal. To fashion man, to call man, with his own peculiar organisation, into existence, that is the very matter of their cogitation. So we must not think of them as human, but we must certainly envisage that there is already in their nature a certain cleavage. When we speak of man today, we do not understand him at all unless we distinguish between body, soul and spirit. You know what great efforts we Anthroposophists have made to get a closer understanding of the activity and nature of this human trinity. To recognise this unity in trinity first becomes necessary in the case of man; and it would be a great mistake to think of Beings who existed before man, the Beings whom the Bible calls Elohim, as if they resembled man. Nevertheless in their case too we can rightly distinguish between a kind of body and a kind of spirit. Now when you distinguish between body and spirit in man, you are well aware that even his outer form bears testimony to the fact that his being lives in it in a variety of ways. For instance, we do not try to locate man's mind in his hand or his legs, but we say that his bodily functions are in his trunk and his limbs, and that the organ of his mind is the head, the brain; the brain is the instrument of mind. Thus we distinguish in the external human form certain parts as the expression of the physical, and certain other parts as the expression of the spiritual. We have to look upon the Elohim in somewhat the same way. All this surging elementary web of which I have spoken can only be correctly understood if it is looked upon as the bodily vehicle of the Elohim's psycho-spiritual. These elements of air, warmth and water are the external embodiment of the Elohim. But we have to make a further distinction; we have to look upon the watery and gaseous elements as more connected with the bodily, denser functions of the Elohim, and what permeates this tohu wabohu as warmth as being the element in which their spiritual part is at work. Just as in the case of man we say that the more bodily part functions in the trunk and the limbs, and the more spiritual part in the head, so if we look upon the entire cosmos as an embodiment of the Elohim, we can say that their more specifically bodily part lived in the air and the water, and their spiritual part moved in the warmth Now the Bible makes use of a remarkable phrase to express the relationship of this spiritual part of the Elohim to the elements: Ruach Elohim m'rachephet [See Figure 4, below.]—a phrase which we must go into more closely if we would understand how the spirit of the Elohim permeated the other elements. We can only understand the verb racheph by praying in aid, so to speak, all the associations which it would have carried with it in those days. If one simply says “And the spirit of the Gods moved upon the outspread substances—upon the waters” one has said almost nothing. We can only understand the word if we think of a hen sitting upon her eggs, and of her brooding warmth radiating out over the eggs beneath her. (I know it is a crude illustration, but it does help to bring out the meaning.) And if you think of the energy of this brooding warmth which streams from the hen into the eggs in order to bring the eggs to maturity, then you can have a notion of the meaning of the verb used here to convey what the spirit does in the element of warmth. It would of course be quite inaccurate to say that the spirit of the Elohim broods, because what the physical activity of brooding conveys today is not what is meant. What is meant to be conveyed is the activity of the outraying warmth. As warmth radiates from the hen, so the spirit of the Elohim radiates by means of the warmth element into the other elementary states. When you think of this, you have a picture of what is meant by the words: And the spirit of God (the Elohim) moved upon the face of the waters.  Now, up to a point, we have reconstructed the picture which hovered before the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he thought about this primeval condition. We have constructed a complex of spherically interwoven warmth, air, water, such as I have described the tohu wabohu to be, from which all the light had withdrawn with the haschamayim, and this interweaving of the three elementary states was inwardly permeated with darkness. In the one element, the warmth, there weaves or surges the spirituality of the Elohim, which itself expands with the expanding warmth, and brings to maturity what is at first immature in the darker elements. Thus when we come to the sentence And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters, we are dwelling on one characteristic of what in the first verse of the Bible is called ha'aretz—earth. We are expressing what is left after haschamayim has been withdrawn. Now let us recall once more the earlier conditions. From the earth we can look back to the Moon, Sun and Saturn conditions. Let us go back to the Sun. We know that at that time there was no separation of what we today call earth from the sun. Therefore the earthly part was not illumined by light from without. That its light comes from without is the essential characteristic of life on earth. At that time, however, you have to think of the earth-sphere as enclosed within the Sun, forming part of the Sun, not receiving light, but itself forming part of the Being that is radiating light into space. This condition can be summed up by saying simply that in it the earth element does not receive light, but is itself a source of light. Mark the difference! In the Sun evolution the earth itself participated in the radiation of light. In the earth evolution that is no longer the case. The earth has surrendered the radiant element, it has to receive light from without; light has to stream into it. That is the essential difference between the earth, as it has become in the course of evolution, and the Sun condition; with the separation of the sun, of the haschamayim, the light went out too. All that is now outside the earth. The elementary existence which surges in ha'aretz as tohu wabohu has no light of its own. The Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters, but that did not make the earth light; it left it in darkness. Let us take another look at this elementary existence as a whole. You know of course from earlier lectures that we are accustomed to enumerate what we call the elementary states within our earth existence, beginning with the solid, then coming to the watery, next to the gaseous or aeriform and then to the warmth. These four constitute the denser conditions of matter. But we have not yet finished. If we go further upwards we meet with finer conditions, of which we do not get a much better idea by calling them finer substances. The main thing is to recognise them as finer relatively to the denser ones, the gaseous, the warmth and so on. They are usually called etheric states, and we have always distinguished light as the first of these finer states. Thus, when we descend from warmth into the denser, we come to the gaseous condition; if we ascend, we come to light. Ascending still further, beyond the light we come to a yet finer etheric condition, we come to something which is not really recognisable in the ordinary sense-world. We only get a kind of external reflection of it. From the occult point of view one can say that the forces in this finer ether are those which govern the chemical affinities of matter, the chemical combinations, the organisation of substances such as we can observe if, for instance, we place a fine powder on a metal plate, and then draw the bow of a violin across the plate, getting as a result the “Chladni” sound-figures. What the coarse physical tone brings about in the powder also occurs throughout space. Space is differentiated, is permeated, by forces which are more rarefied than the forces of light, by forces which represent in the spiritual what tone is in the sense-world. So that when we ascend from warmth to light, and from light to this finer element, we can speak of a chemical of sound-ether, which has the power to decompose and to combine substances, but is in reality of the nature of sound, sound of which the sense-perceptible tone which the ear hears is only the outward expression, the expression made by its passage through air. That brings us somewhat nearer to this finer element which is above light. Thus when we say that what has the quality of manifesting itself externally withdrew from the ha'aretz with the haschamayim we must not think only of the light, but also of the finer etheric element of sound which permeates light. Just as we go downward from warmth to air, and thence to water, so we can go upward from warmth to light, and from light to what is of the nature of sound, of chemical combination. And from water we can descend lower to earth. When we mount from the sound-ether we come to a still higher etheric condition, which also withdrew with the haschamayim. We come to the finest etheric state of all, which weaves within the chemical or sound-ether we have just been describing. If you turn your spiritual ear in this direction, you do not of course hear a noise in the external air, but you hear the tone which vibrates through space, the tone which permeates space and organises matter just as the tone produced by the bow of a violin organises the Chladni sound-figures. But into this condition brought about by the sound-ether is poured a still higher etheric mode. And this higher ether permeates the sound-ether just as the meaning of our thought permeates the sound which our mouth utters, thereby transforming tone into word. Try to comprehend what it is that transforms tone into a word full of meaning; then you will have some idea of this finer etheric element permeating the organising sound-ether and giving meaning to it—the Word which vibrates through space. And this Word, which thrills through space and pours itself out into the sound-ether, is at the same time the source of life, it is really vibrant, weaving life! Thus what has withdrawn out of the ha'aretz with the haschamayim, what has gone into the sun, as distinct from the other, the lower, the earth part—as distinct from the tohu wabohu—announces itself externally as light. But behind the light is spiritual tone, and behind that is cosmic speech. Thus we may say that in the brooding warmth lives the lower spiritual part of the Elohim, somewhat as our own desire lives in the lower part of our soul. The higher spirituality of the Elohim, which went out with the haschamayim, lives in the light, in the spiritual sound, in the spiritual word, the cosmic Word. These can only stream into the tohu wabohu again from without. Let us now try to bring before us in a picture what hovered before the soul of the Hebrew sage as ha'aretz, as haschamayim. When what withdrew as spiritual light, as sound, as the uttering and formative Word-element, streams back again, how does it act? It works from the sun as articulate light, as light giving utterance to cosmic speech. Let us think of what we have called tohu wabohu in its darkness, in its surging interweaving of warmth, air and water; let us think of it in its light-forsaken darkness. And then let us think that out of the activity of the Elohim, through the creative Word, which as the highest etheric entity lies behind their activity, there rays in with the light all that streams out from the Word. How is one to describe what is taking place? One cannot more fittingly express it than by saying that the Beings who had withdrawn their highest into the etheric with haschamayim radiated answering light out of cosmic space into the tohu wabohu. There you have the substance of the memorable verse: And God said, Let there be light: and there was light. There you have the picture which hovered before the Hebrew sage. So we must think of the Beings of the Elohim as spread over the whole cosmos, we must think of this whole cosmos as their body, and the elementary existence in the tohu wabohu as the lowest form of this body; of the warmth as a somewhat higher form; and we must think of the haschamayim, the part which has withdrawn, as the highest spirituality, which now works creatively into the whole structure of the tohu wabohu. Now you see what I am leading up to—that it was the cosmic Word expressing radiant light which organised the surging of the elementary part, the tohu wabohu, and made it what it later became. Whence comes the power which organises the human form? There can be no human form such as we have, standing upright on two legs, making use of hands, unless it be organised by forces emanating from the brain. Our own form is organised by the highest spiritual forces streaming out from our own spiritual part. The lower is always organised by the higher. In the same way the ha'aretz, the body of the Elohim, their lower part, was organised by their higher bodily part, the haschamayim, and by the spiritual essence of the Elohim working within it. Thus the highest spirituality of the Elohim takes possession of what has been cast out, and organises it, and we can express this by saying that the light manifesting itself through the cosmic Word streams into the darkness. That is how the tohu wabohu was organised, raised out of the disorder of the elements. Thus, if you think of the haschamayim as the head of the Elohim, and the elementary part which is left behind as the trunk and limbs, organised through the power of the head, then you have the actual process. Then you have man expanded to cover the whole cosmos. And out of the spiritual organs in haschamayim he organises himself. When we think of all the streams of energy which pour out from the haschamayim to the ha'aretz we may venture to picture it as a macrocosmic man organising himself. Now in order to paint the picture more accurately, let us turn our attention to man as he is today. Let us ask ourselves how man has become what he is—I mean, what he is to the spiritual scientist, not to ordinary science. What is it that has given him the special structure which distinguishes him from all the rest of the living creatures around him? What is it which weaves throughout this human form? If one does not blind oneself it is very easy to say what makes him man; it is something he possesses which none of the beings around him has—speech, which expresses itself in its own proper sounds. That is what makes him man. Think of the form of the animal and ask yourselves how it could be raised to the level of the human form. What would have to permeate it for it to become human? Let us put the question in this way. Let us think of an animal form, and imagine that we have to make a breath enter into it—what would this breath have to contain, in order to make this form begin to speak? It would have to feel itself inwardly organised in such a way that it uttered the sounds of speech. It is the sounds of speech which make the animal structure human! How then can one picture the cosmos? Out of all that I have put before your souls, all that I have built up gradually out of this elementary existence, picture by picture, how can one come to feel the cosmos inwardly, how can one come inwardly to feel the structure of macrocosmic man? By beginning to feel how the sounds of speech flash into form. When the sound of A soughs through the air, learn to feel not merely its tone, learn to feel the form it makes, just as the tone of the violin bow, passed over the edge of a plate, makes a form in the powder. Learn to feel the A and the B in their transience through space; learn to experience them not merely as sound, but as form-making; then you will feel as the Hebrew sage felt when the sounds of speech stimulated in him the pictures which I have put before your mind's eye. That was the effect of the sounds of speech. That is why I had to say that Bet (B) aroused the idea of something enclosing, like a shell shutting something off and enclosing an inner content. Resch (R) stimulated a feeling such as one has when one feels one's head: and Schin (S) suggested what I might describe as a pricking or penetrating. That is a thoroughly objective language, a language which, if the soul is receptive, crystallises into pictures as the sounds are uttered. In the sounds themselves lies the lofty discipline which led the sage to the pictures which crowd upon the soul of the seer when he enters into the supersensible world. Sound is in this way transmuted into spiritual form, and conjures before the soul pictures which form a connected whole in the way I have described. What is so remarkable about this ancient record is that it has been preserved in a language the sounds of which create form, the sounds of which crystallise in the soul into form. And these forms are the very pictures which one gets when one penetrates to the supersensible out of which our material physical has evolved. When one comes to understand this, one feels a deep awe and reverence for the way in which the world has evolved; and one comes to realise that truly it is by no mere chance that this great document of human existence has been transmitted in this script—a script which by means of its very characters is capable of arousing pictures in the soul, and of guiding us to what in our own time the seer is to discover anew. That is the feeling which the Anthroposophist ought to cultivate when he approaches this ancient document.
|
| 122. Genesis (1959): Ha'aretz and Haschamayim
18 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| How far has this brought us? We shall not understand the sublime process of the seven days of creation unless we bear these details in mind. If we do so, then the whole will seem a wonderful cosmic drama. |
| This is how they are resumed.” Now in order to understand what comes next, usually rendered “darkness was above the fluid substances” or “above the waters”(above the abyss)—or darkness was upon the face of the waters (English A.V.) |
| So we must not think of them as human, but we must certainly envisage that there is already in their nature a certain cleavage. When we speak of man today, we do not understand him at all unless we distinguish between body, soul and spirit. You know what great efforts we Anthroposophists have made to get a closer understanding of the activity and nature of this human trinity. |
| 122. Genesis (1959): Ha'aretz and Haschamayim
18 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In a good many places in this course of lectures—as well as elsewhere in our Anthroposophical discussions—it may well sound as if I rather enjoyed having to set myself up in opposition, or apparent opposition, to “modern science.” I am thinking more of people in the outside world unacquainted with the kind of feeling that prevails in our circles, but it is a point on which I am particularly anxious to avoid any misunderstanding. You may take it as definite that it is a very real effort for me to do anything of the sort; and that I only do it precisely at those points where I myself am able to develop or carry further what science has to say. My sense of responsibility is such that it will not permit me to bring forward anything that conflicts with the opinions of modern science, unless I have first placed myself in a position to understand, and if necessary reproduce, its findings on the subject in hand. No one having such an attitude could possibly approach the all-important matters which are to occupy us in the next few days without the deepest sense of awe and of the responsibility that goes with it. Unfortunately, it just has to be said that, as regards the questions now to come before us, modern science breaks down altogether. The scientists are not even in a position to know why this should be so, or to perceive why their science must necessarily prove so hopelessly amateurish in face of the real and the great problems of existence. So, although in a short course of lectures it is naturally not possible to engage in controversy about every detail, please take it for granted that behind all I say I am fully aware of the modern scientific outlook on these subjects. Only, as far as possible, I must confine myself to what is positive, and trust that in a circle of Anthroposophists this will always be understood. In the last lecture I tried to show how those tremendous, archetypal words with which the Bible opens—words which are put before us in a language different in its very nature from modern tongues—can only be rightly interpreted if we try to forget the attitude of mind and feeling we have acquired as a result of the usual modern renderings. For the language in which these powerful words of creation were originally given to us has actually the peculiarity that the very character of its sounds directs the heart and mind towards those pictures which arise before the eye of the seer when he contemplates the moment of the welling-forth of the sense-perceptible part of our world out of the super-sensible. Every single sound in which the immemorial origin of our earth existence is placed before us is full of active power. In the course of these lectures we shall often have to refer to the character of this language; today, however, let us confine ourselves to one of the first essentials. You know that in the Bible, after the words which yesterday I at least tried to put before your souls in picture form, there comes a description of one of the complexes which arose out of the divine meditation, out of the divine productive musing. I told you that we have to conceive that, as if out of a cosmic memory, two complexes arose. One was a complex which may be compared with the thoughts which can arise in us; the other is of the nature of desire or will. The one complex contains all that tends towards outer manifestation, tends to proclaim itself, tends, as it were, to force its way out—haschamayim. The other complex—ha'aretz—consists of an inner activity, a permeation with inward craving; it is something which inwardly vivifies, animates. Then we are told of certain qualities of this inner, vivifying, self-stimulating element, and these are indicated in the Bible by appropriate sounds. We are told that this self-stimulating element was in a state which is designated as tohu wabohu—without form and void. To understand what is meant by tohu wabohu we must try to recapture a picture of what it expresses; and we only succeed in doing that if out of our spiritual scientific knowledge we call to mind what it was that, after its passage through the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions, emerged again and surged through space as our planetary earth existence.  I pointed out yesterday that what we call solidity, the state which offers a certain resistance to our senses, did not exist during the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions; only the elements of fire or warmth, gas or air, and water were to be found there. It was only with the emergence of the earth that the solid element was added. Thus at the moment when there happened what we were describing yesterday, when the tendency began for the sun to split off from the earth, there is a mutual interpenetration of the elements warmth, air and water—they surged through one another. That preliminary surging interpenetration which we have tried to picture to ourselves is the meaning of the phrase inadequately translated as without form and void, but eloquently and effectively rendered by the succession of sounds tohu wabohu. What then does tohu wabohu signify? If we try to picture what can be aroused in our souls by these sounds it is something like this. The sound which resembles our own T calls up a picture of forces diverging from a central point in every direction. Thus the moment one utters the T sound one gets the picture of forces diverging from a centre in every direction to illimitable distances. So that we have to imagine the elements warmth, air and water permeating, interpenetrating each other, and within them a tendency to diverge, as from a centre in all directions. The sound tohu alone would suffice to express this tendency to push outwards, to separate. What then does the second part of the phrase signify? It expresses the very opposite of what I have just described. The character of the sound resembling our B, called forth by the letter Bet, expresses what you would get if you imagined an enormous sphere, a hollow sphere, with yourself inside it, and rays proceeding from every point inside this sphere towards its centre. Thus you imagine a point within space whence forces stream out in all directions—that is tohu; these forces are arrested at the extremities of the spherical enclosure, and turned back again on themselves from every direction of space—that is bohu. And if you have formed this idea, and think of all these streams of force as filled with the three elementary substances of warmth, air and water, then you know the character of this inner animation. The combination of these sounds indicates the way in which elementary existence is guided by the Elohim. How far has this brought us? We shall not understand the sublime process of the seven days of creation unless we bear these details in mind. If we do so, then the whole will seem a wonderful cosmic drama. Let us recall once more that in the word bara—“in the beginning the Gods created”—we are concerned with a soul-spiritual activity. I have likened it to the thoughts which are called up in our own souls. Thus we may think of the Elohim as arrayed in space, and bara as a cosmic soul-activity, a pondering. What the Elohim ponder is expressed by haschamayim and ha'aretz—the outward radiation and the inner, mobile energy. To make the comparison as close as possible picture yourselves in the moment of awakening; groups of ideas arise in your souls. This is how haschamayim and ha'aretz arise in the souls of the Elohim. Now you know that these Elohim came over to earth evolution at the stage to which they had evolved during the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. So that they are in a somewhat similar situation to your own when on awakening you call up thoughts in your souls. You can contemplate those thoughts, you can say what they are. You can say: “When I awake in the morning and recall what has previously been left in my mind, I can describe it.” It was something the same with the Elohim, when they said to themselves: “Let us now reflect upon what arises in our souls when we recall what took place during the ancient Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. Let us see how it looks in recollection.” What it looked like is expressed in the phrase tohu wabohu; it could be expressed by a picture such as I have given you, as streams radiating from a centre outwards into space and back again, in such a way that the elements are interwoven in this streaming of forces. Thus the Elohim could say to themselves: “At the stage to which you have so far brought things this is what they look like. This is how they are resumed.” Now in order to understand what comes next, usually rendered “darkness was above the fluid substances” or “above the waters”(above the abyss)—or darkness was upon the face of the waters (English A.V.)—we must take into consideration something else. We must once more turn our attention to the course of evolution before the earth came into existence. First we have the Saturn existence, inweaving in the fiery element. Then comes the Sun existence, with its addition of the airy element. But in my Occult Science you can read how with the addition of the air something else is associated. The fine warmth element of Saturn condenses to a gaseous element. But every such densification is accompanied by a counter-process of refinement. Condensation to the gaseous element is a descending process, but on the other side there is an ascent to the light element. Thus, speaking of the transition from Saturn to Sun, we must say that Saturn still weaves solely in the element of warmth, whereas during the Sun evolution something denser, the gaseous element, is added, but so also is light. The light element makes it possible for the warmth and the air to manifest themselves in outward radiance. Now let us take one of the two complexes—the one expressed as ha'aretz, usually translated as “earth”—and ask ourselves how the Elohim, turning their attention to this complex after their act of recollection, would have described it. They could not have said that what had already existed in the Sun evolution had now come to life again. For it was without light; light had separated from it. ha'aretz had thus become one-sided. It had not brought with it the light, but only the coarser elements, the gaseous and the warmth elements. True, there was no lack of light in what is expressed by haschamayim, but haschamayim is the sunlike, issuing from the other complex. In ha'aretz there was no rarefaction, there was no light. We may then say that in one of the complexes warmth, air and water surged through one another in the way which is indicated by tohu wabohu. These elements were denuded, they lacked the light which had entered into evolution on the Sun. They remained dark, had nothing sunlike about them; for that had withdrawn with haschamayim. Thus the progress of earth evolution means that the light, which it still had so long as the sun remained united with it, had now withdrawn; and a dark fabric woven of the elements of warmth, air and water was left. We now have the content of the meditation of the Elohim before our souls in more detail. But we shall never be able to think of it in the right way unless we are conscious all the time that air, water and even warmth are external expressions of spiritual Beings. It would not be quite correct to call this elemental existence their “garment”; it should rather be regarded as making known their presence externally. Thus what we call air, water, warmth, are maya, illusion; they are only there for the outward aspect, and this is so even for the mind's eye. In reality this elemental existence is something psycho-spiritual, it is the external manifestation of the soul-spiritual of the Elohim. But we must not think of the Elohim as at all like man, for man is actually their goal. To fashion man, to call man, with his own peculiar organisation, into existence, that is the very matter of their cogitation. So we must not think of them as human, but we must certainly envisage that there is already in their nature a certain cleavage. When we speak of man today, we do not understand him at all unless we distinguish between body, soul and spirit. You know what great efforts we Anthroposophists have made to get a closer understanding of the activity and nature of this human trinity. To recognise this unity in trinity first becomes necessary in the case of man; and it would be a great mistake to think of Beings who existed before man, the Beings whom the Bible calls Elohim, as if they resembled man. Nevertheless in their case too we can rightly distinguish between a kind of body and a kind of spirit. Now when you distinguish between body and spirit in man, you are well aware that even his outer form bears testimony to the fact that his being lives in it in a variety of ways. For instance, we do not try to locate man's mind in his hand or his legs, but we say that his bodily functions are in his trunk and his limbs, and that the organ of his mind is the head, the brain; the brain is the instrument of mind. Thus we distinguish in the external human form certain parts as the expression of the physical, and certain other parts as the expression of the spiritual. We have to look upon the Elohim in somewhat the same way. All this surging elementary web of which I have spoken can only be correctly understood if it is looked upon as the bodily vehicle of the Elohim's psycho-spiritual. These elements of air, warmth and water are the external embodiment of the Elohim. But we have to make a further distinction; we have to look upon the watery and gaseous elements as more connected with the bodily, denser functions of the Elohim, and what permeates this tohu wabohu as warmth as being the element in which their spiritual part is at work. Just as in the case of man we say that the more bodily part functions in the trunk and the limbs, and the more spiritual part in the head, so if we look upon the entire cosmos as an embodiment of the Elohim, we can say that their more specifically bodily part lived in the air and the water, and their spiritual part moved in the warmth  Now the Bible makes use of a remarkable phrase to express the relationship of this spiritual part of the Elohim to the elements: Ruach Elohim m'rachephet—a phrase which we must go into more closely if we would understand how the spirit of the Elohim permeated the other elements. We can only understand the verb racheph by praying in aid, so to speak, all the associations which it would have carried with it in those days. If one simply says “And the spirit of the Gods moved upon the outspread substances—upon the waters” one has said almost nothing. We can only understand the word if we think of a hen sitting upon her eggs, and of her brooding warmth radiating out over the eggs beneath her. (I know it is a crude illustration, but it does help to bring out the meaning.) And if you think of the energy of this brooding warmth which streams from the hen into the eggs in order to bring the eggs to maturity, then you can have a notion of the meaning of the verb used here to convey what the spirit does in the element of warmth. It would of course be quite inaccurate to say that the spirit of the Elohim broods, because what the physical activity of brooding conveys today is not what is meant. What is meant to be conveyed is the activity of the outraying warmth. As warmth radiates from the hen, so the spirit of the Elohim radiates by means of the warmth element into the other elementary states. When you think of this, you have a picture of what is meant by the words: And the spirit of God (the Elohim) moved upon the face of the waters. Now, up to a point, we have reconstructed the picture which hovered before the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he thought about this primeval condition. We have constructed a complex of spherically interwoven warmth, air, water, such as I have described the tohu wabohu to be, from which all the light had withdrawn with the haschamayim, and this interweaving of the three elementary states was inwardly permeated with darkness. In the one element, the warmth, there weaves or surges the spirituality of the Elohim, which itself expands with the expanding warmth, and brings to maturity what is at first immature in the darker elements. Thus when we come to the sentence And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters, we are dwelling on one characteristic of what in the first verse of the Bible is called ha'aretz—earth. We are expressing what is left after haschamayim has been withdrawn. Now let us recall once more the earlier conditions. From the earth we can look back to the Moon, Sun and Saturn conditions. Let us go back to the Sun. We know that at that time there was no separation of what we today call earth from the sun. Therefore the earthly part was not illumined by light from without. That its light comes from without is the essential characteristic of life on earth. At that time, however, you have to think of the earth-sphere as enclosed within the Sun, forming part of the Sun, not receiving light, but itself forming part of the Being that is radiating light into space. This condition can be summed up by saying simply that in it the earth element does not receive light, but is itself a source of light. Mark the difference! In the Sun evolution the earth itself participated in the radiation of light. In the earth evolution that is no longer the case. The earth has surrendered the radiant element, it has to receive light from without; light has to stream into it. That is the essential difference between the earth, as it has become in the course of evolution, and the Sun condition; with the separation of the sun, of the haschamayim, the light went out too. All that is now outside the earth. The elementary existence which surges in ha'aretz as tohu wabohu has no light of its own. The Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters, but that did not make the earth light; it left it in darkness. Let us take another look at this elementary existence as a whole. You know of course from earlier lectures that we are accustomed to enumerate what we call the elementary states within our earth existence, beginning with the solid, then coming to the watery, next to the gaseous or aeriform and then to the warmth. These four constitute the denser conditions of matter. But we have not yet finished. If we go further upwards we meet with finer conditions, of which we do not get a much better idea by calling them finer substances. The main thing is to recognise them as finer relatively to the denser ones, the gaseous, the warmth and so on. They are usually called etheric states, and we have always distinguished light as the first of these finer states. Thus, when we descend from warmth into the denser, we come to the gaseous condition; if we ascend, we come to light. Ascending still further, beyond the light we come to a yet finer etheric condition, we come to something which is not really recognisable in the ordinary sense-world. We only get a kind of external reflection of it. From the occult point of view one can say that the forces in this finer ether are those which govern the chemical affinities of matter, the chemical combinations, the organisation of substances such as we can observe if, for instance, we place a fine powder on a metal plate, and then draw the bow of a violin across the plate, getting as a result the “Chladni” sound-figures. What the coarse physical tone brings about in the powder also occurs throughout space. Space is differentiated, is permeated, by forces which are more rarefied than the forces of light, by forces which represent in the spiritual what tone is in the sense-world. So that when we ascend from warmth to light, and from light to this finer element, we can speak of a chemical of sound-ether, which has the power to decompose and to combine substances, but is in reality of the nature of sound, sound of which the sense-perceptible tone which the ear hears is only the outward expression, the expression made by its passage through air. That brings us somewhat nearer to this finer element which is above light. Thus when we say that what has the quality of manifesting itself externally withdrew from the ha'aretz with the haschamayim we must not think only of the light, but also of the finer etheric element of sound which permeates light. Just as we go downward from warmth to air, and thence to water, so we can go upward from warmth to light, and from light to what is of the nature of sound, of chemical combination. And from water we can descend lower to earth. When we mount from the sound-ether we come to a still higher etheric condition, which also withdrew with the haschamayim. We come to the finest etheric state of all, which weaves within the chemical or sound-ether we have just been describing. If you turn your spiritual ear in this direction, you do not of course hear a noise in the external air, but you hear the tone which vibrates through space, the tone which permeates space and organises matter just as the tone produced by the bow of a violin organises the Chladni sound-figures. But into this condition brought about by the sound-ether is poured a still higher etheric mode. And this higher ether permeates the sound-ether just as the meaning of our thought permeates the sound which our mouth utters, thereby transforming tone into word. Try to comprehend what it is that transforms tone into a word full of meaning; then you will have some idea of this finer etheric element permeating the organising sound-ether and giving meaning to it—the Word which vibrates through space. And this Word, which thrills through space and pours itself out into the sound-ether, is at the same time the source of life, it is really vibrant, weaving life! Thus what has withdrawn out of the ha'aretz with the haschamayim, what has gone into the sun, as distinct from the other, the lower, the earth part—as distinct from the tohu wabohu—announces itself externally as light. But behind the light is spiritual tone, and behind that is cosmic speech. Thus we may say that in the brooding warmth lives the lower spiritual part of the Elohim, somewhat as our own desire lives in the lower part of our soul. The higher spirituality of the Elohim, which went out with the haschamayim, lives in the light, in the spiritual sound, in the spiritual word, the cosmic Word. These can only stream into the tohu wabohu again from without. Let us now try to bring before us in a picture what hovered before the soul of the Hebrew sage as ha'aretz, as haschamayim. When what withdrew as spiritual light, as sound, as the uttering and formative Word-element, streams back again, how does it act? It works from the sun as articulate light, as light giving utterance to cosmic speech. Let us think of what we have called tohu wabohu in its darkness, in its surging interweaving of warmth, air and water; let us think of it in its light-forsaken darkness. And then let us think that out of the activity of the Elohim, through the creative Word, which as the highest etheric entity lies behind their activity, there rays in with the light all that streams out from the Word. How is one to describe what is taking place? One cannot more fittingly express it than by saying that the Beings who had withdrawn their highest into the etheric with haschamayim radiated answering light out of cosmic space into the tohu wabohu. There you have the substance of the memorable verse: And God said, Let there be light: and there was light. There you have the picture which hovered before the Hebrew sage. So we must think of the Beings of the Elohim as spread over the whole cosmos, we must think of this whole cosmos as their body, and the elementary existence in the tohu wabohu as the lowest form of this body; of the warmth as a somewhat higher form; and we must think of the haschamayim, the part which has withdrawn, as the highest spirituality, which now works creatively into the whole structure of the tohu wabohu. Now you see what I am leading up to—that it was the cosmic Word expressing radiant light which organised the surging of the elementary part, the tohu wabohu, and made it what it later became. Whence comes the power which organises the human form? There can be no human form such as we have, standing upright on two legs, making use of hands, unless it be organised by forces emanating from the brain. Our own form is organised by the highest spiritual forces streaming out from our own spiritual part. The lower is always organised by the higher. In the same way the ha'aretz, the body of the Elohim, their lower part, was organised by their higher bodily part, the haschamayim, and by the spiritual essence of the Elohim working within it. Thus the highest spirituality of the Elohim takes possession of what has been cast out, and organises it, and we can express this by saying that the light manifesting itself through the cosmic Word streams into the darkness. That is how the tohu wabohu was organised, raised out of the disorder of the elements. Thus, if you think of the haschamayim as the head of the Elohim, and the elementary part which is left behind as the trunk and limbs, organised through the power of the head, then you have the actual process. Then you have man expanded to cover the whole cosmos. And out of the spiritual organs in haschamayim he organises himself. When we think of all the streams of energy which pour out from the haschamayim to the ha'aretz we may venture to picture it as a macrocosmic man organising himself. Now in order to paint the picture more accurately, let us turn our attention to man as he is today. Let us ask ourselves how man has become what he is—I mean, what he is to the spiritual scientist, not to ordinary science. What is it that has given him the special structure which distinguishes him from all the rest of the living creatures around him? What is it which weaves throughout this human form? If one does not blind oneself it is very easy to say what makes him man; it is something he possesses which none of the beings around him has—speech, which expresses itself in its own proper sounds. That is what makes him man. Think of the form of the animal and ask yourselves how it could be raised to the level of the human form. What would have to permeate it for it to become human? Let us put the question in this way. Let us think of an animal form, and imagine that we have to make a breath enter into it—what would this breath have to contain, in order to make this form begin to speak? It would have to feel itself inwardly organised in such a way that it uttered the sounds of speech. It is the sounds of speech which make the animal structure human! How then can one picture the cosmos? Out of all that I have put before your souls, all that I have built up gradually out of this elementary existence, picture by picture, how can one come to feel the cosmos inwardly, how can one come inwardly to feel the structure of macrocosmic man? By beginning to feel how the sounds of speech flash into form. When the sound of A soughs through the air, learn to feel not merely its tone, learn to feel the form it makes, just as the tone of the violin bow, passed over the edge of a plate, makes a form in the powder. Learn to feel the A and the B in their transience through space; learn to experience them not merely as sound, but as form-making; then you will feel as the Hebrew sage felt when the sounds of speech stimulated in him the pictures which I have put before your mind's eye. That was the effect of the sounds of speech. That is why I had to say that Bet (B) aroused the idea of something enclosing, like a shell shutting something off and enclosing an inner content. Resch (R) stimulated a feeling such as one has when one feels one's head: and Schin (S) suggested what I might describe as a pricking or penetrating. That is a thoroughly objective language, a language which, if the soul is receptive, crystallises into pictures as the sounds are uttered. In the sounds themselves lies the lofty discipline which led the sage to the pictures which crowd upon the soul of the seer when he enters into the super-sensible world. Sound is in this way transmuted into spiritual form, and conjures before the soul pictures which form a connected whole in the way I have described. What is so remarkable about this ancient record is that it has been preserved in a language the sounds of which create form, the sounds of which crystallise in the soul into form. And these forms are the very pictures which one gets when one penetrates to the super-sensible out of which our material physical has evolved. When one comes to understand this, one feels a deep awe and reverence for the way in which the world has evolved; and one comes to realise that truly it is by no mere chance that this great document of human existence has been transmitted in this script—a script which by means of its very characters is capable of arousing pictures in the soul, and of guiding us to what in our own time the seer is to discover anew. That is the feeling which the Anthroposophist ought to cultivate when he approaches this ancient document. |
| 122. Genesis (1959): The Mystery of the Archetypal Word
17 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Whoever wishes to get an idea of what lived in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he used this word should clearly understand that in those days there was a lively comprehension of the fact that our earth evolution had a definite meaning and a definite goal. |
| We should have to go into very many things to get anywhere near an understanding of these Beings. To begin with, however, we can come to know one aspect of them, and that will suffice to bring us at least one step nearer to the potent meaning of the ancient Bible words. |
| One of them could do this, another that. But we understand the nature of these Beings best if we realise that at the time we are now considering they were working as a group towards a common goal; they were moved by a common aim. |
| 122. Genesis (1959): The Mystery of the Archetypal Word
17 Aug 1910, Munich Translated by Dorothy Lenn, Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
If anyone who has a background of Spiritual Science, and has absorbed something of its teaching about the evolution of the world, then goes on to study those tremendous opening words of our Bible, an entirely new world should dawn upon him. There is probably no account of human evolution so open to misinterpretation as this record known as Genesis, the description of the creation of the world in six or seven days. When the man of today calls to life in his soul, in any language familiar to him, the words In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth, they convey to him scarcely a faint reflection of what lived in the soul of an ancient Hebrew who allowed the words to work upon him. It is not in the least a question of being able to replace the old words by modern ones; it is much more important that we should have been prepared by Anthroposophy to feel at least something of the mood which lived in the heart and mind of the Hebrew pupil of old when he brought to life within himself the words: B'reschit bara elohim et haschamayim v'et ha'aretz. A whole world lived while such words were vibrating through his soul. 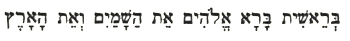 What was it like—this inner world which lived in the soul of the pupil? We can only compare it with what can take place in the soul of a man to whom a seer has described the pictures he experienced on looking into the spiritual world. For what in the last resort is Spiritual Science but the outcome of seership, of the living intuitions which the seer receives when, having freed himself from the conditions of sense-perception and of the intellect bound up with the physical body, he looks with spiritual organs into the spiritual worlds? If he wishes to translate what he sees there into the language of the physical world, he can only do so in pictures, but if his descriptive powers suffice, he will do it in pictures which are able to awaken in his hearers a mental image corresponding with what he himself sees in the spiritual worlds. Thereby something comes into existence which must not be mistaken for a description of things and events in the physical sense-world; something comes into existence which we must never forget belongs to an entirely different world—a world which does indeed underlie and maintain the ordinary sense-world of our ideas, impressions and perceptions, yet in no way coincides with that world. If we want to portray the origin of this our sense-world, including the origin of man himself, our ideas cannot be confined to that world itself. No science equipped only with ideas borrowed from the world of the senses can reach the origin of sense-existence. For sense-existence is rooted in the super-sensible, and although we can go a long way back historically, or geologically, we must realise that, if we are to reach to actual origins, there is a certain point in the far distant past at which we must leave the field of the sense-perceptible and penetrate into regions that can only be grasped super-sensibly. What we call Genesis does not begin with the description of anything perceptible by the senses, anything which the eye could see in the physical world. In the course of these lectures we shall become thoroughly convinced that it would be quite wrong to take the opening words of Genesis as referring to events which can be seen with the outward eye. So long as one connects the words “heaven and earth” with any residue of the sensuously visible one has not reached the stage to which the first part of the Genesis account points us back. Today there is practically no way of obtaining light upon the world it describes except through Spiritual Science. Through Spiritual Science we may indeed hope to approach the mystery of the archetypal words with which the Bible opens, and to get some inkling of their content. Wherein lies their peculiar secret? It lies in the fact that they are written in the Hebrew tongue, a language which works upon the soul quite differently from any modern language. Although the Hebrew of these early chapters may not perhaps have the same effect today, at one time it did work in such a way that when a letter was sounded it called up in the soul a picture. Pictures arose in the soul of anyone who entered with lively sympathy into the words, and allowed them to work upon him—pictures harmoniously arranged, organic pictures, pictures which may be compared with what the seer can still see today when he rises from the sensible to the super-sensible. The Hebrew language, or, better said, the language of the first chapters of the Bible, enabled the soul to call up imaginal pictures which were not wholly unlike those that are presented to the seer when, freed from his body, he is able to look into super-sensible regions of existence. In order to realise in some measure the power of these archetypal words we must disregard the pale and shadowy impressions which any modern language makes upon the soul, and try to get some idea of the creative power inherent in sound-sequences in this ancient tongue. It is of immense importance that in the course of these lectures we too should seek to place before our souls the very pictures which arose in the Hebrew pupil of old when these sounds worked creatively in him. In fact we must find a method of penetrating the primeval record entirely different from those used by modern research. I have now given you an indication of our line of approach. We shall only slowly and gradually learn to comprehend what lived in the ancient Hebrew sage when he allowed those most powerful words to work upon him, words which we do at least still possess. So our next task will be to free ourselves as far as possible from the familiar, and from the ideas and images of “heaven and earth,” of “Gods,” of “creation,” of “in the beginning,” which we have hitherto held. The more thoroughly we can do this the better we shall be able to penetrate into the spirit of a document which arose out of psychic conditions quite different from those of today. First of all we must be quite clear as to the point of time in evolution we are speaking of, when we deal with the opening words of the Bible. You know of course that contemporary clairvoyant investigation makes it possible to describe to some extent the origin and development of our earth and of human existence. In my book Occult Science, I tried to describe the gradual growth of our earth as the planetary scene of human existence, through the three preliminary stages of Saturn, Sun and Moon.1 Today you will have in mind, at least in broad outline, what I described there. At what point then in the spiritual scientific account should we place what draws near to our souls in the mighty word B'reschit? Where does it belong? If we look back for a moment to ancient Saturn, we picture it as a cosmic body having as yet nothing of the material existence to which we are accustomed. Of all that we find in our own environment it has nothing but heat. No air or water or solid earth is as yet to be found upon ancient Saturn; even where it is densest, there is only fire—living, weaving warmth. Then, to this living, weaving warmth, a kind of air or gaseous element is added; and we have a true picture of the Sun existence if we think of it as an interweaving, an interpenetration, of a gaseous, airy element and a warmth element. Then comes the third condition, which we call the Moon evolution. There the watery element is added to the warmth and the air. There is as yet nothing of what in our present earth we call solid. But the old Moon evolution has a peculiar characteristic. It divides into two parts. If we look back upon old Saturn, we see it as a single whole of weaving warmth; and the old Sun we still see as a mingling of gaseous and warmth elements. During the Moon existence there takes place this separation into a part which is Sun and a part which retains the Moon nature. It is only when we come to the fourth stage of our planetary evolution that the earth element is added to the earlier warmth, gaseous and watery elements. In order that this solid element could come into existence, the division which had taken place previously during the Moon evolution had first to repeat itself. Once again the sun had to withdraw. Thus there is a certain moment in the evolution of our planet when, out of the universal complication of fire and air and water, the denser, more earthy element separates from the finer, gaseous element of the sun; and it is only in this earthy element that what we today call solid is able to form. Let us concentrate on this moment, when the sun withdraws from its former state of union with the rest of the planet and begins to send its forces to the earth from without. Let us bear in mind that this was what made it possible, within the earth, for the solid element—what we today call matter—to begin to condense. If we fix this moment firmly in our minds we have the point of time at which Genesis, the creation story, begins. This is what it is describing. We should not associate with the opening words of Genesis the abstract, shadowy idea we get when we say “In the beginning,” which is something unspeakably poverty-stricken compared with what the ancient Hebrew sage felt. If we would bring the sound B'reschit before our souls in the right way, there must arise before us—in the only way it can do so, in mental images—all that happened through the severance of sun and earth, all that was to be found at the actual moment when the separation into two had just taken place. Furthermore we must be aware that throughout the whole of the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions, spiritual Beings were its leaders and its bearers; and that warmth, air, water are only the outer expressions, the outer garments of spiritual Beings who are the reality. Thus when we contemplate the condition which obtained at the moment of separation of sun and earth, and picture it to ourselves in thoughts full of material images, we must also be conscious that the elementary “water,” “air,” “fire,” which we have in our mind's eye, is still only the means of expression for moving, weaving spirit which, during the course of the preceding Saturn, Sun and Moon stages has advanced, has progressed, and at the time now being described has reached a certain stage in its evolution. Let us place before us the picture of an immense cosmic globe, composed of weaving elements of water, air or gas and fire, a globe which splits apart into a solar and a telluric element; but let us conceive too that this elementary substance is only the expression of a spiritual. Let us imagine that from this substantial habitation, woven of the elements of water, air and heat, the countenances of spiritual Beings, weaving within it, look out upon us, spiritual Beings who reveal themselves in this element which we have had to represent to ourselves through material images. Let us imagine that we have before us spiritual Beings, turning their countenances towards us, as it were, using their own soul-spiritual forces to organise cosmic bodies with the help of warmth, air and water. Let us try to imagine this! There we have a picture of an elementary sheath, which, to give a very rough sensuous image of it, we may perhaps liken to a snail-shell, but a shell woven not of solid matter, like the snail's, but from the forest elements of water, air and fire. Let us think of spirit, in the form of countenances, within this sheath, gazing upon us, using this sheath as a means of manifestation, a force of very revelation which, as it were, pricks outward into manifestation from what lies hidden in the super-sensible. Call up before your souls this picture which I have just tried to paint for you, this image of the living weaving of spirit in a kind of matter; imagine too the inner soul-force which causes it to happen; concentrate for a moment on this to the exclusion of all else, and you will then have something approximating to what lived in an ancient Hebrew sage when the sounds B'reschit penetrated his soul. Bet*, the first letter, called forth the weaving of the habitation in substance; Resch†, the second sound, summoned up the countenances of the spiritual Beings who wove within this dwelling, and Schin‡, the third sound, the prickly, stinging force which worked its way out from within to manifestation.  Now the underlying principle behind such a description is dawning upon us. And when we have grasped that, we are able to appreciate something of the spirit of this language; it had a creativeness of which the modern man with his abstract speech has no inkling. Now let us place ourselves at the moment immediately preceding the physical coagulation, the physical densification of our earth. Let us imagine it as vividly as possible. We shall have to admit that in describing what was taking place at that moment we cannot make use of any of the ideas which we use today to describe processes in the external sense-world. Hence you will see that it is utterly inadequate to associate any external deed with the second word we meet in Genesis—bara—however closely that deed might resemble what we understand today as creation. We do not thus get near to the meaning of that word. Where can we turn for help? The word implies something which lies very near the boundary where the sensible passes over directly into the super-sensible, into pure spirit. And anyone who wishes to grasp the meaning of the word bara, which is usually translated “created” (In the beginning God created ...), must in no wise associate it with any productive activity which can be seen with physical eyes. Take a look into your own inner being! Imagine yourselves as having been asleep for a while, then waking up, and, without opening your eyes to things around you, calling up in your souls by inner activity certain images. Bring home vividly to yourselves this inner activity, this productive meditation, this cogitation, which calls forth a soul-content from the depths of the soul as if by magic. If you like you can use the word “excogitate” for this conjuring up of a soul-content out of the depths into the field of consciousness; think of this activity, which man can only perform with his mental images, but think of it now as a real, cosmic, creative activity. Instead of your own meditation, your own inward experience in thinking, try to imagine cosmic thinking-then you have the content of the second word of Genesis, bara. However spiritually you may think it, you can only liken it to the thought-life you are able to bring before yourselves in your own musing, you cannot get nearer to it than that! And now imagine that during your musing two kinds of images come before your souls. Suppose there is a man to whom on awakening two different kinds of thought occur, a man who muses about two different kinds of thing. Suppose that one kind of thought is the picture either of some activity, or of some external thing or of some being; it does not come about through external sight, through perception, but through reflection, through the creative activity of his soul in the field of his consciousness. Suppose that the second complex of ideas which arises in this awakening man is a desire, something which the man's whole disposition and constitution of soul can prompt him to will. We have elements both of thought and of desire coming up in our souls through inner reflection. Now imagine, instead of the human soul, the Beings called in Genesis the Elohim, reflecting within themselves. Instead of one human soul, think of a multiplicity of reflecting spiritual Beings, who, however, in a similar way—save that their musing is cosmic—call forth by reflection from within themselves two complexes which might be compared with what I have just been describing—a pure thought-element and an element of desire. Thus instead of thinking of the musing' human soul, we think of a group of cosmic Beings who awaken in themselves two complexes; one of the nature of thought or ideation, that is, one which manifests something, expresses itself outwardly, phenomenally; and another of the nature of desire, which lives in inner movement, inner stimulation, which is permeated with inner activity. Let us think of these cosmic Beings, who are called in Genesis the Elohim, musing in this way. The word bara, “created,” brings their musing home to us. Then let us think that through this creative musing two complexes arise, one tending towards external revelation, external manifestation, and another consisting of an inward stimulus, an inward life; then we have the two complexes which arose in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when the words haschamayim and ha'aretz—represented for the modern man by “heaven” and “earth”—sounded through his soul. Let us try to forget the modern man's conception of “heaven and earth.” Let us try to bring the two complexes before the soul, the one which tends more to disclose itself, tends to outward manifestation, is disposed to call forth some outside effect; and the other complex, the complex of inner stimulation, of something which would experience itself inwardly, something which quickens itself inwardly; then we have what expresses the meaning of the two words haschamayim and ha'aretz. As for the Elohim themselves, what kind of Beings are they? In the course of these lectures we shall learn to know them better, and to describe them in terms of Spiritual Science; but for the present let us try to reach in some measure the meaning of this archetypal word “Elohim.” Whoever wishes to get an idea of what lived in the soul of the ancient Hebrew sage when he used this word should clearly understand that in those days there was a lively comprehension of the fact that our earth evolution had a definite meaning and a definite goal. What was this meaning and this goal? Our earth evolution can only have a meaning, if during its course something arises which was not there before. A perpetual repetition of what was already there would be a meaningless existence, and unless the Hebrew sage of old had known that our earth, after having passed through its preliminary stages, had to bring something new into existence, he would have regarded its genesis as meaningless. Through the coming into existence of the earth something new became possible, it became possible for man to become man as we know him. In none of the earlier stages of evolution was man present as the being he is today, the being that he will more and more become in the future; that was not possible in earlier stages. And those spiritual Beings who directed the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions were of a different nature from man—for the moment we will not enter into the question whether they were higher or lower. Those Beings who wove in the fiery, gaseous and watery stages of elementary existence, who wove a Saturn, Sun and Moon existence, who at the beginning of earth existence were weaving its fabric—how best do we come to know them? ... How can we draw near to them? We should have to go into very many things to get anywhere near an understanding of these Beings. To begin with, however, we can come to know one aspect of them, and that will suffice to bring us at least one step nearer to the potent meaning of the ancient Bible words. Let us consider those Beings for a moment—the Beings who stood nearest to man at the time when he was created from what had developed out of the Saturn, Sun and Moon evolutions. Let us ask those Beings what they really wanted. Let us ask them what was their will, their purpose. Then we shall be able to get at least some idea of their nature. They had great ability; in the course of their evolution they had acquired capacities in various directions. One of them could do this, another that. But we understand the nature of these Beings best if we realise that at the time we are now considering they were working as a group towards a common goal; they were moved by a common aim. Although at a higher level, it is as if a group of men, each with his own special skill, were to co-operate today. Each of them can do something, and now they say to each other: “You can do this, I can do that, the third among us can do something else. We will unite our activities to produce a work in common in which each of our capacities can be used.” Let us then imagine such a group of men, a group each of whom practises a different craft, but which is united by a common aim. What they intend to bring into existence is not yet there. The unit at which they are working lives to begin with only as an aim. What is there is a multiplicity. The unit lives, to begin with, only as an ideal. Now think of a group of spiritual Beings who have passed through the evolutions of Saturn, Sun and Moon, each one of whom has a specific ability, and who all at the moment I have indicated make the decision: “We will combine our activities for a common end, we will all work in the same direction.” And the picture of this goal arose before each of them. What was this goal? It was man, earthly man! Thus earthly man lived as the ultimate goal in a group of spiritual Beings who had resolved to combine their several skills in order to arrive at something which they themselves did not possess at all, something which did not belong to them, but which they were able to achieve by combined effort. If you accept all that I have described to you—the elementary sheath, the cosmic, meditative spiritual Beings working within it, the two complexes, one of desire quickening inwardly, and another manifesting outwardly—and then ascribe the common purpose I have just mentioned to those spiritual Beings whose countenances gaze out of the elementary sheath, then you have what lived in the heart of the Hebrew sage of old in the word Elohim. Now we have brought before us in picture form what lives in these all-powerful archetypal words. Then let us forget all that a man of today can think and feel when he utters the words: In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth. Bearing in mind all that I have told you today, try to put this picture before you. There is the sphere in which fiery, gaseous and watery elements weave. Within this active, weaving elementary sphere a group of pondering spiritual Beings live. They are engaged in productive pondering, their pondering is penetrated through and through by their intention to direct their whole operation towards the form of man. And the first-fruits of their musing is the idea of something manifesting itself outwardly, announcing itself, and something else inwardly active, inwardly animated. “In the elementary sheath the primeval Spirits pondered the outwardly manifesting and the inwardly mobile.” Try to bring before yourselves in these terms what is said in the first lines of the Bible, then you will have a foundation for all that is to come before our souls in the next few days as the true meaning of those all-powerful archetypal words which contain such a sublime revelation for mankind—the revelation of its own origin.
|

