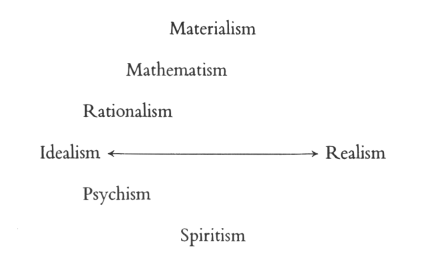
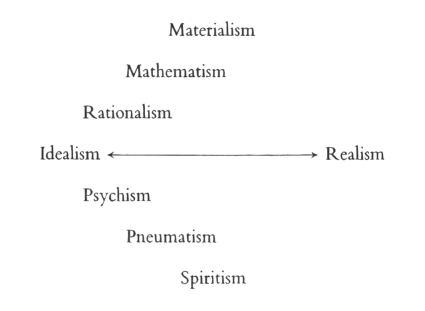
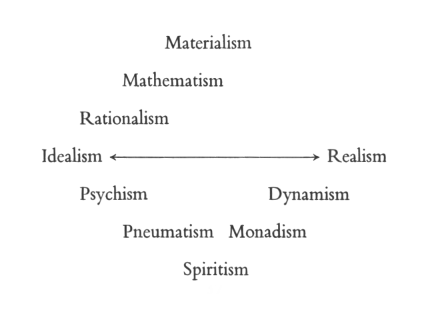
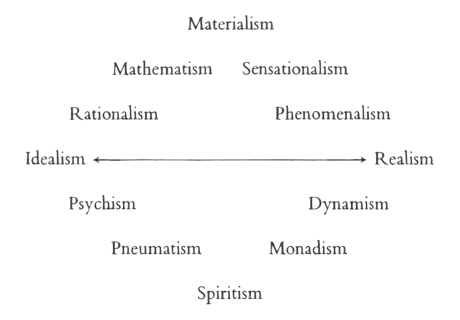
| 20. The Riddle of Man: Idealism as an Awakening of the Soul: Johann Gottlieb Fichte
Translated by William Lindemann |
|---|
| One can read in many places how he received Ws most direct impetus from the world views of Spinoza and Kant. But the way he finally acted in understanding the world through the essential nature of his personality becomes most visible when he is contrasted with the thinker who came forth just as much from the thinking of the Romance peoples as Fichte did from the German: Descartes (1596–1650). |
| And whoever has an ear for such things will also hear the power of this statement resounding in all subsequent thinkers until Kant. [ 6 ] Only with Fichte do its reverberations cease. If one enters deeply into his thought-world, if one seeks to experience with him his struggles for a world view, then one feels how he too is seeking world knowledge in self-knowledge; but one has the feeling that Descartes' statement, “I think, therefore I am” could not be the rock upon which Fichte, in his struggles, could believe himself secure against the waves of doubt that can turn man's mental pictures into an ocean of dreams. |
| 20. The Riddle of Man: Idealism as an Awakening of the Soul: Johann Gottlieb Fichte
Translated by William Lindemann |
|---|
[ 1 ] In his addresses on The Basic Characteristics of Our Present Age and To the German Nation, Johann Gottlieb Fichte seeks to portray the spiritual forces working in the evolution of mankind. Through the thoughts he brings to expression in these addresses, he imbues himself with the feeling that the motive force of his world view streams from the innermost being of the German people (Volksart). Fichte believes he is expressing the thoughts that the soul of the German people must express if it wants to reveal itself from the core of its spirituality. The way in which Fichte struggled for his world view shows how this feeling could live in his soul. It must seem important to someone observing a thinker to investigate the roots from which the fruit of his thoughts have sprung; these roots work in the depths of his soul and are not expressed directly in his thought-worlds, yet they live as the motive forces within these thought-worlds. [ 2 ] Fichte once expressed his conviction that the kind of world view one has depends upon the kind of person one is. He did so out of his awareness that all the life forces of his own personality had to bring forth—as its natural and obvious fruit—the conceptually strong heights of his world view. Not many people want to get to the heart of this world view because they consider what they find there to be thoughts—estranged from the world—into which only “professional” thinkers need penetrate. This feeling is understandable in someone without philosophical training who approaches Fichte's thoughts as they appear in his works. Still, for someone who has the possibility of entering into the full life of these thoughts, it is not strange to imagine that a time will come when one will be able to recast Fichte's ideas into a form comprehensible to anyone who wants, out of life itself, to think about the meaning of this life. These ideas could then be accessible even to the simplest human heart (Gemüt), however far removed from so-called “philosophical thinking.” For, these ideas have in fact received their philosophical form from the character assumed by the evolution of thought in thinking circles at the turn of the eighteenth into the nineteenth century; but these ideas get their life from experiences that are present in the soul of every human being, To be sure, the time has not yet arrived when it is fully possible to recast Fichte's thoughts from the language of the philosophy of his time into a universally human form of expression. Such things become possible only through the gradual progress made by certain ways of picturing things in man's spiritual life. Just as Fichte himself was obliged to carry his soul experiences to the heights of what one usually calls “abstract thinking”—and finds cold and estranged from life—so today also it is only possible to a very limited degree to carry these soul experiences down from those heights. [ 3 ] From his early youth until his sudden death while still in the prime of life, Fichte struggled for ever new forms of expression for these soul experiences. In all his struggles, one basic cognitive impulse is evident. Within man's own soul Fichte wishes to find a living element in which the human being grasps not only the basic force of his own existence, but in which there can also be known—in its essential being—what weaves and works in nature and in everything else outside him. In a drop of water, relative to the ocean, one has only a tiny sphere. But if one knows this little sphere in its character as water, then in this knowledge one also knows the whole ocean in its character as water. If something can be discovered in the being of man that can be experienced as a revelation of the innermost weaving of the world, then one may hope, through deepened self-knowledge, to advance to world knowledge. [ 4 ] Long before Fichte's time, the development of mankind's view of the world had already taken the path that proceeds from this feeling and this hope. But Fichte was placed at a significant point in this evolution. One can read in many places how he received Ws most direct impetus from the world views of Spinoza and Kant. But the way he finally acted in understanding the world through the essential nature of his personality becomes most visible when he is contrasted with the thinker who came forth just as much from the thinking of the Romance peoples as Fichte did from the German: Descartes (1596–1650). In Descartes there already comes to light—out of the feeling and hope described above—the way a thinker seeks certainty in world knowledge by discovering a solid point in self-knowledge. Descartes takes doubt in all world knowledge as his starting point. He says to himself: The world in which I live reveals itself within my soul, and from its phenomena I form mental pictures for myself about the course of things. But what is my guarantee that these mental pictures of mine really tell me anything about the working and weaving of the world in its course? Could it not be the case that my soul does indeed receive certain impressions from the things of the world, but that these impressions are so far removed from the things themselves that in these impressions nothing of the meaning of the world is revealed to me? In the face of this possibility can I say that I know this or that about the world? One sees how, for a thinker in this ocean of doubt, all knowledge can come to seem like a subjective dream, and how only one conviction can force itself upon him: that man can know nothing. But in the case of a person for whom the motive force of thinking has become as alive as the motive force of hunger is in the body: for him the conviction that man can know nothing means for the soul what starvation means for the body. All the innermost impressions about the health of one's soul, in a higher sense, right up to feeling the salvation of one's soul (Seelenheil) are connected with this. [ 5 ] It is within the soul itself that Descartes finds the point upon which he can base conviction: The mental pictures form for myself of the world's course are no dream; they live a life that is a part in the life of the whole world. Even though I can doubt everything, there is one thing I cannot doubt, for to express doubt in it would belie my own words. For is it not certain that when I give myself over to doubt I am thinking? I could not doubt if I did not think. Therefore I cannot possibly doubt my own experience in thinking. If I wanted, through doubt, to kill thinking: it would just rise up living again out of the doubt. My thinking lives, therefore; it does not stand in some dream world; it stands in the world of being (Sein). If I could believe that everything else, even my own body, gave me only the illusion of being, still my thinking does not deceive me. Just as true as it is that I think, it is true that I am, insofar as I think. It was from sentiments such as these that Descartes' “I think, therefore I am” (Cogito ergo sum) rang out into the world. And whoever has an ear for such things will also hear the power of this statement resounding in all subsequent thinkers until Kant. [ 6 ] Only with Fichte do its reverberations cease. If one enters deeply into his thought-world, if one seeks to experience with him his struggles for a world view, then one feels how he too is seeking world knowledge in self-knowledge; but one has the feeling that Descartes' statement, “I think, therefore I am” could not be the rock upon which Fichte, in his struggles, could believe himself secure against the waves of doubt that can turn man's mental pictures into an ocean of dreams. Looking at what Fichte wrote in his book The Vocation of Man (published in 1800), one feels how his ability to doubt lives in a very different part of the soul than with Descartes: “Nowhere is there anything enduring, neither outside me nor within me; there is only unceasing change. Nowhere do I know of any being, not even my own. There is no being. I myself do not know at all and do not exist. Pictures exist: they are all that there is, and they know about themselves in the manner of pictures—pictures that float past without anything there for them float past; pictures that relate to each other through pictures of pictures; pictures without anything pictured in them, without significance and purpose. I myself am one of these pictures; no, I am not even that; I am only a confused picture of the pictures.—All reality transforms itself into a strange dream, without a life that is dreamed about, and without a spirit who is dreaming; transforms itself into a dream that is connected with a dream about itself, My perceiving is the dream; my thinking—the source of all being and all reality that I imagine to myself, the source of my being, my power, my aims—is a dream about that dream,” These thoughts do not arise in Fichte's soul as the ultimate truth about existence, He does not wish, as one might suppose, really to regard the world as a dream configuration, He wants only to show that all the usual arguments for the certainty of knowledge cannot withstand penetrating examination, and that these arguments do not give one the right to regard the ideas one forms about the world as anything other than dream configurations. And Fichte cannot allow that any kind of certainty about being is present within thinking. Why should I say, “I think, therefore I am” since, after all, if I am living in an ocean of dreams, my thinking can be nothing more than “a dream about a dream”? For Fichte, what penetrates and gives reality to my thoughts about the world must come from a completely different source than mere thinking about the world. [ 7 ] Fichte claims that the distinctive spirit (Art) of the German people lives in his world view. This thought makes sense when one brings before one's soul precisely his picture of that path to self-knowledge which he seeks in contradistinction to Descartes. This path is what Fichte felt to be German; and as a traveler on this path, he differs from Descartes, who takes the spiritual path of the Romance peoples. Descartes seeks a sound basis for self-knowledge; he expects to find this sound basis somewhere. In thinking he believes he has found it. Fichte expects nothing from this kind of search. For, no matter what he might find, why should it afford a greater certainty than anything already found? No, along this path of investigation there is absolutely nothing to be found. For, this path can lead only from picture to picture; and no picture one encounters can guarantee, out of itself, its being. Therefore, to begin with, one must entirely abandon the path through pictures, and return to it again only after gaining certainty from some other direction. [ 8 ] With respect to the statement “I think, therefore I am,” one need only say something that seems quite simple if one wants to refute it. This is after all the way with so many thoughts a person incorporates into his world view: they are not dispelled by elaborate objections but rather by noting simple facts. One does not undervalue the thinking power of a personality like Descartes by confronting him with a simple fact. The fable of the egg of Columbus is true forever.1 And it is also true that the statement “I think, therefore I am” simply shatters upon the fact of human sleep. Every sleep, which interrupts thinking, shows—not, indeed, that there is no being in thinking—but that in any case “I am, even when I am not thinking.” Therefore, if only thinking is the source for being, then nothing could guarantee the being of soul states in which thinking has ceased. Although Fichte did not express this train of thought in this form, one can still definitely say: The power lying within these simple facts worked—unconsciously—in his soul and kept him from taking a path like that taken by Descartes. [ 9 ] Fichte was led onto a completely different path by the basic character of his sense of things. His life reveals this basic character from childhood on. One need only let some pictures from his life arise before one's soul to see that this is so. One significant picture that rises up vividly from his childhood is this. Johann Gottlieb is seven years old. Until this time he was a good student. In order to reward the boy's industriousness, his father gives him a book of legends, The Horned Siegfried. The boy is completely taken with this book. He neglects his duties somewhat. He becomes aware of this about himself. One day his father sees him throwing The Horned Siegfried into the brook. The boy is attached to the book with his whole heart; but how can the heart be allowed to keep something that diverts one from one's duty? Thus the feeling is already living unconsciously in the young Fichte that the human being is in the world as an expression of a higher order, which descends into his soul not through his interest in one thing or another, but through the path by which he acknowledges duty. Here one can see the impulse behind Fichte's stance toward certainty about reality. Perceptual experiences are not what is certain for man, but rather what rises up livingly in the soul in the same way that duty reveals itself. [ 10 ] Another picture from Fichte's life: The boy is nine years old. A landowner near his father's village comes into town one Sunday to hear the minister's sermon. He arrives too late. The sermon is over. People remember that nine-year-old Johann Gottlieb retains sermons in his soul so well that he can completely reproduce them. They fetch him. The boy, in his little farmer's smock, appears. He is awkward at first; but then presents the sermon in such a way that one can see that what lived in the sermon had utterly filled his soul; he does not merely repeat words; he speaks out of the spirit of the sermon that lives within him entirely as his own experience. This ability lived in the boy: to let light up in one's own self what approaches this self from the world. This was, after all, the ability to experience the spirit of the outer world in one's own self. This was the ability to find within the strengthened self the power to uphold a world view. A brightly-lit, evolving stream of personality leads from such boyhood experiences to a lecture by Fichte—then professor in Jena—heard and described by the gifted scientist Steffens. In the course of his lecture Fichte calls upon his listeners: “Think about the wall,” His listeners made every effort to think about the wall. After they had done this for a while, Fichte's next demand follows: “And now think about the one who thought about the wall,” What striving for a direct and living relationship between one's own soul life and that of one's listeners! What pointing toward an inner soul activity to be undertaken immediately—not merely to stimulate reflection on verbal communications, but rather to awaken a life element slumbering in the souls of his listeners so that these souls will attain a state that changes their previous relationship to the course of the world. [ 11 ] Such actions reflect Fichte's whole way of clearing the path for a world view. Unlike Descartes, he does not seek an experience of thinking that will establish certainty. He knows that in such seeking there is no finding. In such seeking one cannot know whether one's discovery is dream or reality. Therefore do not launch forth in such seeking. Strengthen yourself instead, by waking up. What the soul experiences when it wants to press forward out of the field of ordinary reality into that of true reality must be like an awakening. Thinking does not guarantee the being of the human “I.” But within this “I” there lies the power to awaken itself to being. Every time the soul senses itself as “I”—in full consciousness of the inner power that becomes active in doing so—a process occurs that presents itself as the soul awakening itself. This self-awakening is the fundamental being (Grundwesenheit) of the soul. And in this power to awaken itself there lies the certainty of the being (Sein) of the human soul. Let the soul go through dream states and states of sleep: one grasps the power of the soul to awaken itself out of every dream and every sleep by transforming the mental picture of its awakening into the image of the soul's fundamental power. Fichte felt that the eternity of the human soul lies in its becoming aware of its power to awaken itself. From this awareness came statements like these: “The world I was just marveling at disappears before my gaze and sinks away. In all the fullness of life, order, and growth that I see in it, this world is still only the curtain—by which an infinitely more perfect world is hidden from me—and the seed from which this more perfect world is to evolve. My belief goes behind this curtain and warms and enlivens this seed. My belief does not see anything definite, but expects more than it can grasp here below or will ever be able to grasp in the realm of time.—This is how I live and this is how I am; this is how I am unchangeably—firm and complete for all eternity; for, this being is not taken on from outside; it is my own one true being and existence.” (Vocation of Man) [ 12 ] When one looks at the whole way Fichte approaches life and at how permeated all his actions and thinking are with an attitude friendly to life and fostering of life, one will not be tempted to regard a passage like this as proof of a direction in thought hostile to life, that turns away from immediate and vigorous life on this earth. In a letter from the year 1790 there is a sentence that sheds significant light on Fichte's positive attitude toward life, precisely in relation to his thoughts about immortality: “The surest means of convincing oneself of a life after death is to lead one's present life in such a way that one can wish an afterlife:” [ 13 ] For Fichte, within the self-awakening inner activity of the human soul there lies the power of self-knowledge. And within this activity he also finds the place in the soul where the spirit of the world reveals itself in the spirit of the soul. In Fichte's world view the world-will weaves and works in all existence; and within the willing of its own being the soul can live this world-will within itself. The grasping of life's duties—which are experienced differently in the soul than are the perceptions of the senses and of one's thoughts—is the most immediate example of how the world-will pulses through the soul. True reality must be grasped in this way; and all other reality, even that of thinking, receives its certainty through the light shed upon it by the reality of the world-will revealing itself within the soul. This world-will drives the human being to his activity and deeds. As a sense-perceptible being, man must translate into reality in a sense-perceptible way what the world-will demands of him. But how could the deeds of one's will have a real existence if they had to seek this existence in a dream world? No, the world cannot be a dream, because in this world the deeds of one's will must not merely be dreamed; they must be translated into reality. Insofar as the “I” awakens itself in its experience of the world-will, it attains firm supports for certainty about its being. Fichte expressed himself on this point in his Vocation of Man: “Without any instrument weakening its expression, within a sphere completely similar in nature to itself, my will must work absolutely in and through itself: as reason it must work upon reason and as something spiritual upon something spiritual; it must work in a sphere for which my will nevertheless does not provide the laws of life, activity, and continuity; this sphere has them in itself; my will has therefore to work upon self-active reason. But self-active reason is will. The laws of the supersensible world, accordingly, would be a will ... That lofty will, accordingly, does not separated from the rest of the world of reason—take a path all its own. There is a spiritual bond between this will and all finite reasonable beings, and this will itself is the spiritual bond of the world of reason ... I hide my face before you and lay my hand on my mouth. I can never see how you are for yourself nor how you appear to yourself, just as certainly as I can never become yourself. After living through a thousand times a thousand spiritual worlds, I will still grasp you just as little as now, within this hut of the earth.—What I grasp, through my mere grasping of it, becomes something finite; and this, even through infinite intensification and enhancement, can never be transformed into something infinite. You are different from the finite not in degree but in kind. Through that intensification they make you only into a greater and ever great man; but never into God, the Infinite, Who cannot be measured.” [ 14 ] Fichte strove for a world view that pursues all being into the very roots of what lives in the world, and that learns to know the meaning of what lives in the world: learns to know it through the human soul's living with the world-will that pulses through everything and that creates nature for the purpose, in nature, of translating into reality a spiritually moral order as though in an outer body. Such a world view seemed to Fichte to spring from the character of the German people. To him a world view seemed un-German that did not “believe in spirituality and in the freedom of this spirituality,” and that did not “want the eternal further development of this spirituality and freedom.” In his view, “Whoever believes in a standstill, a regression, or a circle dance, or even sets a dead nature at the helm of world rulership” goes not only against any more deeply penetrating knowledge, but also against the essential nature of what is truly German.
|
| 51. Philosophy, History and Literature: The Unity of the World
31 Mar 1902, Berlin |
|---|
| Resolving this dualism into a monism is, however, a supreme urge in thinking itself; but epistemology is faced with a major problem here. Since Kant, dealing with it has been a duty for anyone who deals with questions of world view. Thus, in constructing a unified worldview, we have to perform two operations: on the one hand, to empirically trace the infinite multiplicity of the world down to its smallest differentiations, and on the other hand, to always form our thinking in an epistemological sense into a monism, into a unification of that multiplicity into a unity. |
| Today I am content with a simple 'Yes', while I still note: I also seek the monism in that, unlike Kant, I understand subject and object, spirit and nature as an inseparable unity and, like the medieval 'realists', see a real, not just nominal identity in the concept. |
| 51. Philosophy, History and Literature: The Unity of the World
31 Mar 1902, Berlin |
|---|
Discussion in the “Giordano Bruno League for a Unified World View” with a speech by Rudolf Steiner.
After these words of Kirchbach, Dr. Rudolf Steiner rose to give the following remarks: "I would like to stick closely to the question: What does a unified worldview mean in terms of its concept and values? In doing so, I am in direct opposition to the previous speaker. If I ask myself: From the standpoint of our modern natural science and spiritual science, are we justified in considering the world to be a unity? I have to say that we are, we are at least placed in the position of having to search for it. In the face of the manifold diversity into which the specialization of the sciences has undoubtedly led us, I ask: Where should we look for unity? To say from the outset that this or that must first be demonstrated as a unity seems to me to be the exaggerated demand of an extreme epistemology. For me, the pursuit of a unified worldview is justified by the simple fact that it is an indelible need of the human spirit that has existed at all times, perhaps more clearly in pre-Christian times, when it had not yet been suppressed by the dogmas and views of the church, which a union that seeks to build on Giordano Bruno's legacy has a particular duty to fight against. Meanwhile, I find that the results of the natural sciences also meet this need. Chemistry has found seventy elements and will perhaps increase this diversity; but at the same time it has found something very special: Between these elements, it has found certain relationships with regard to atomic weight, for example, according to which a scale of the elements can be constructed that is also a classification of these elements according to their acoustic, optical and other physical properties. From a gap in this scale, one has inferred missing elements, partially predicted their properties and actually discovered them afterwards. Thus the phenomenal elements, although different, nevertheless represent a great unity, which we can follow with the calculation. However, the chemist is forced to look for the unity elsewhere than in the brutal concept of a unified substance, namely in a system of lawful relationships. Professor Ostwald spoke out in this direction at a congress of natural scientists. Recently a journal has been founded to further develop the outdated materialism in this new natural philosophical sense. So we are standing in front of a new world view, which we cannot yet conclude, but to which a perspective has been opened up, and indeed a perspective on unity. The same applies to the uniformity of force. In terms of phenomena, we will probably never be able to trace electricity back to pure gravitation, but in the mathematical formula we use to calculate and convert it, we have something real and fundamental; and thus a perspective has been opened up for us regarding the unity of force. Without wanting to take the exact position of Goethe's metamorphosis theory, which was the first to seek a unifying principle in the organic realm, I do think, however, that it also represents an important step towards a unified world view. Added to this is the biogenetic law, according to which every being, in its embryonic development, once again passes through the forms of the species from which it originated. Since it has become possible to produce organic substances in the laboratory, we are offered a clear prospect of unity here as well. If one does not want to demand unity in the phenomenal, this perspective shows us where to look for the monon. And it is becoming increasingly clear to us what all great philosophers had no doubt about: that what we experience in the external world is equivalent to what we experience in the mind. If we proceed from external to internal experience, we will arrive at a unified world view. For those seeking unity, the last decades of science are quite comforting, for from all fields elements are flowing to them that open up a unified worldview. Its value lies in the fact that it satisfies a spiritual need, which, just as necessary as air and light, belongs to the happiness of a spirit that develops this need within itself.
|
| 53. Ibsen's Spiritual Art
23 Mar 1905, Berlin |
|---|
| The whole point of view of the modern times takes on this character. Have a look at the figure of Kant (1724-1804, German philosopher) how everything is put into the personality. What he says would be possible neither in mediaeval times, nor in antiquity. |
| He says: we cannot recognise, we have limits that we cannot overcome with our reason; it only feels something dark that urges and drives. Kant calls it the categorical imperative. The Greek, the medieval human being had sharply outlined ideals. |
| 53. Ibsen's Spiritual Art
23 Mar 1905, Berlin |
|---|
Before I close the lecture cycle of this winter with a picture of the human future and human ideals, I would like to talk of the present cultural life as it expresses itself in one of the most significant and most typical spiritual heroes of our time. Not from the literary, not from the aesthetic point of view, but from the world view I might speak of Ibsen's attitude; for really everything expresses itself just in Ibsen that the deepest and best spirits of the modern time feel and think. One has often said that every poet is the expression of his time. Indeed, this sentence holds good, but only if one gives it the quite special contents, it can be understood. Just as Homer, Sophocles, and Goethe were expressions of their time, it is undoubtedly Henrik Ibsen (1828-1906, Norwegian playwright and poet) for the present, and nevertheless how differently our time does leave its stamp on him as once on those personalities. In order to recognise how completely different the time was around the turn of the 18-th century, the time of Goethe, Schiller and Herder, and how differently our time expresses itself, one needs to put two things next to each other only. Goethe still rounds off the second part of his Faust, seals it and leaves it behind as a big will of his life. After his death he leaves a legacy behind to the human beings, shining into the future, full of forces in the confidence: “the traces of my days will survive into eternity” (Faust II, 11583-11584). A human being who is basically the representative of the whole humanity stands before us in Faust. We cling to him; he fulfils us with purpose in life, with life-force. Beyond his death Goethe points out that to us. Faust cannot become outdated; we find deeper and deeper truths in it. We feel it as something living on, something that we have not exhausted: this is an end of his life pointing to the future. Henrik Ibsen consciously finished his life work long before his death with his drama When We Dead Awaken (1899). What has fulfilled human beings for half a century, what existed in revolutionary and other ideas penetrated Henrik Ibsen's soul. He described what the hearts moves what separates them, fighting the struggle for existence in a way never seen before. This drama appears as a big review and stands there like a symbol of the artist himself. He was a hermit in the human life, a hermit in his own life. For half a century he looked for human happiness and truth, did not save any forces to get to light and truth, to the solution of the big riddles of life. Now he himself awakes, feels what lies behind him as something dead, and he decides to write nothing more. It is a review that points only to the transitory; what he longed for appears to him as something mysterious, something unreal the ideals collapse behind him. Because he awoke, he is at his wits' end. This is the poet who is the representative of our time, the poetically greatest one. This life balance is a criticism of everything that we have a give-up and at the same time an awakening from and at the criticism of our time. An immense overview of the modern life expresses itself in this drama; if we realise it, we understand the tragic in the personality of the poet. For Henrik Ibsen is a tragic personality. If one wants to understand him completely, one has to understand him as representative of our time. Hence, do not consider it as academic sophistry if I try at first to conceive the nerve of our time; for Henrik Ibsen is an expression of it. A word characterises our time and also the whole Ibsen, this is the word “personality.” Goethe also probably said: “personality is the highest happiness of the earth children only.” But, nevertheless, it happens with Ibsen quite differently. Ibsen is completely a child of our time, and from here we understand him best of all. Remember how differently the personality stands there in ancient Greece. How does Oedipus stand there? What moves the destiny of Oedipus goes far beyond his whole house. We have to make connections with quite different regions: his destiny extends beyond his individual personality, it is lifted out above personality however, the personal is not yet lifted out from the moral connection with the whole world. This is different from today: we have now to search for the centre in the personality that destiny relocated in the personality. Bit by bit we can pursue this. With the emergence of Christianity it happens that the urge of individuality wants to satisfy itself. The personality wants to be free, free before the highest, before the divine. The connections are torn, the personality shifts for itself. During the Middle Ages, personality tries to understand itself. How deeply the whole environment is yet connected with the personality in Greece! How the human being grows out of his surroundings! He is born out of the whole universe. The external configuration of the Greek life, however, is like a piece of art: Plato creates a state idea in which the single human being should adapt himself like a limb to the whole body. Christianity brings another ideal; but this new one is purchased by the price of the relationship with nature, one seeks above nature. The Christian searches what should release his personality in something that reaches beyond personality. Even the individual Roman felt as a member of the whole state: he is a citizen first, and then he is a human being. In mediaeval times, a tendency prevails that looks out over the environment, looks up to a yonder world which one clings to. This makes a big difference for the whole human thinking, feeling and willing. This continues that way up to modern times. The Greek, the Roman citizen lived and died for what surrounded him what lived in his outside world. In mediaeval times, something of a divine world order still lived, indeed, not in the environment, but in the “Gospel of the Good News,” and expressed it like in a mirror. In the best as in the simplest souls, in the mystic as in the people this divine world order was alive. It is something that is given from without, indeed, but that lives as something emerging in the soul. What happens in the world of stars as God's will fulfils the soul substantially: one knows what is beyond birth and death. Let us take the new time and look from the artistic point of view at Shakespeare. What finds expression in Shakespeare's dramas and lives in these dramas is the character first of all. Something like that does not exist in Greece and in mediaeval times. Shakespeare's dramas are character dramas; the main interest is directed to the human being, to that what happens in the depth of his soul, as he is put into the world. The Middle Ages had no real drama; the human beings were occupied with other interests. Now the personality emerges but with it all the uncertain, all the incomprehensible of personality emerges at the same time. Take Hamlet: one can hear so many different interpretations about that from so many scholars. About no work so many books were probably written. This is due to the fact that this character itself has something uncertain. It is no longer a mirror image of the outside world, also no longer a mirror of the Good News. The whole point of view of the modern times takes on this character. Have a look at the figure of Kant (1724-1804, German philosopher) how everything is put into the personality. What he says would be possible neither in mediaeval times, nor in antiquity. It is something quite uncertain that he represents: act in such a way that your action could become the guideline of the community. But this ideal remains something quite uncertain. He says: we cannot recognise, we have limits that we cannot overcome with our reason; it only feels something dark that urges and drives. Kant calls it the categorical imperative. The Greek, the medieval human being had sharply outlined ideals. He knew not only that he should live like the other human beings in their sense: they lived in his blood. This had changed: a categorical imperative which has no right contents positioned itself before the reason; nothing fills this soul with particular ideals. Thus it was in the 18th century. Something that asks for certain ideals awoke in our classical authors. It is interesting that Schiller who was a not less harsh critic of his time like Ibsen we take the Robbers: Karl Moor wants something certain, he wants to create human beings who change their time, do not practise only criticism , it is interesting that Schiller trusts in the ideal and says: whatever the world may be, I put human beings into it who set this world on fire. Even more significantly this comes to the fore with Goethe in his Faust. Goethe appears here as a spirit who looks into the new aurora. But now there came the 19th century with its demand for freedom, for personality. What is freedom? In which respect should the human being be free? One must want something certain. But it was freedom in itself, which one wanted. In addition to that, the 19-th century had become the most rationalistic one. The human beings see their surroundings; but no ideal pours out of them; the human beings are no longer borne by ideals. The human being stands on the peak of his personality, and the personality has become self purpose. Hence, humanity can no longer distinguish two concepts today: individuality and personality; it does no longer distinguish what must be separated. What is individuality? Individuality is that what appears full of contents in the world. If I have a future thought, full of contents, and imagine what I insert into the world, my personality may be powerful or weak, but it is the support of these ideals, the cover of my individuality. The sum of all these ideals is the individuality which shines from the personality. The 19th century does not make this differentiation; it considers the mere powerful personality, which should be, actually, a vessel, a self purpose. That is why the personality becomes something nebulous, and with it also that becomes nebulous which was as clear as ether once. Mysticism was called mathesis once because it was clear like two times two. The human being lived in such spiritual contents, he took stock of himself and found something that was higher than personality: he recognised his individuality. The 19-th century cannot understand mysticism, one talks of it as something unclear, something incomprehensible. This was necessary: the personality had to be felt once like a hollow skin. One speaks mostly of personality, however, the real personality exists least of all. Where the personality is fulfilled with individuality, one speaks of it least of all because it is a matter of course. One talks mostly of that what is not there. If, hence, the 19th century talks of mysticism, it speaks of something unclear. We understand why this happened that way. As a son of his time Henrik Ibsen deeply looked down into this personality and this time. Like an honest truth seeker he strives for the true contents of the personality, but as somebody who is completely born out of his time. “Oh my eye is dazzled by the light to which it turns.” How would have an old Roman spoken of the right? It was a matter of course to him; as little as he denied the light, he would have denied the law. With Ibsen one reads: “Right? Where is it valid as right?” Everything is determined by power to a greater or lesser degree. Thus we see Henrik Ibsen as a thoroughly revolutionary spirit. He looked into the human breast, and he found nothing there, everything that the 19th century offered was nothing to him. He expresses it: oh how have these old ideals of the French revolution lost their strength; we need a revolution of the whole human spirit today! This is the mood expressing itself in Ibsen's dramas. Once again let us consider the ancient times. The Greek felt well in his polis, the Roman in his state, the medieval human being felt as a child of God. How does the son of the modern time feel? He finds nothing around himself that can support him. The Greek and the medieval human being did not feel as lonesome human beings, with Ibsen the strongest man is the most lonesome one. This feeling of loneliness is something absolutely modern, and Ibsen's art arises from it. This concept, nevertheless, which speaks from Ibsen's dramas: we must appeal to the human personality, is nothing clear. These forces in the human being which must be uncovered are something uncertain, but we have to turn to them. Ibsen tries to understand the human beings around him in such a way. However, what else can one see in such a time than the struggle of the personality which is torn out from all social connections? Yes, there is the second possibility: if the human being is still connected with the state, with his surroundings, his personality bows to that, denies itself. However, what can these connections mean to the human being even today? They were true once, now the human being shifts only for himself and disharmonies originate between the personality and the surroundings. Ibsen has a decided sense of the untruth of these connections between the human being and his surroundings. The seeker of truth becomes the rigorous critic of the lie. Hence, his heroes become uprooted personalities, and those who want to produce the connection with their surroundings must become enslaved by the lie, can do it only by deception of their self-consciousness. In the dramas of the middle time this attitude can be found. We see this if we let pass by Brand (1866), Peer Gynt (1867), and Emperor and Galilean (1873) before our eyes. We find a tip to three ages in the latter drama. The first is that which we have characterised before, that of the past when the external form held good so much. Emperor Julian looks into the second, that of the Galilean, which shows an internalisation of the soul. But a third age is said to come when the human being has ideals again and coins them from within to the outside. Destiny once came from without. What must be longed for is the internal ideals which the strong human being can impress to the world; he should be an emissary not reproduce, but shape, create. The third world age in which the ideal comes into its own is not yet attained. In the loneliness, the human being finds it in his soul, but not in such a way that it had force and power to fashion the world. This unification of Christianity with the antique ideal is the reverse way. But Ibsen put this ideal on a weak soul which collapses; Julian is still the human being of the past. On the other hand, we have to do it with the human being who rests on the only formal, on the hollowed out personality. Nothing is more typical for Ibsen than the way he put the hard gnarled figure of his “Brand” into our time. He is not despotic and autocratic, but he is torn out of the connection with the environment. He stands there as a clergyman, surrounded by people to whom the connection with the divine had become a lie. Beside him a clergyman stands who only believes what he believes because he generally has no strong religious feeling. An ideal which is a higher one must be able to work on all human beings. The theosophical ideal of brotherliness immerses the human acting in mildness and benevolence and regards every human being as a human brother. As long as this ideal is not yet born and the human being must rest on the fragments and leftovers of the old ideals which mix personality and individuality, he appears as hard and sturdy. Who puts up the personality ideal in such a way becomes hard and sturdy like Brand, and it must be that way. Individuality connects, personality separates. Nevertheless, this passage through the personality uncovered forces which had to be developed and would not have emerged, otherwise. We had to lose the old ideals, to regain them once on a higher level. A poet like Ibsen had to reach into this personality and to describe it as a hollow one as he does it brilliantly in the League of Youth (1869). He explained what works on the personality, what it should only present in his later dramas in which he becomes the positive critic of the time like in the Pillars of Society (1877). He shows us the personality in conflict with its surroundings in the Ghosts (1881). During the conflict with her surroundings Mrs. Alving must lie where she seeks for truth to bring her son in a clean atmosphere. Thus fate befalls her like the ancient Greeks. Ibsen lives in the sign of Darwin, and this Oswald stands not in a spiritual, ethical connection with the past, but in that of heredity. The personality, as far as it is soul, can only be torn out from its surroundings; the corporeality is connected with the physical heredity, and thus a fate befalls Oswald Alving pouring out only from the physical laws like a moral, spiritual-divine fate befalls the antique hero. With it Ibsen is completely a son of his time. However, he also shows that way what of this personality is justified of the personality which should again become an individuality maybe later. In an especially typical way this problem faces us in the woman. Nora lives as it were at A Doll's House (1879) and grows out of it, seeking for the way to individuality. All old world views have stated an individual, natural difference between man and woman, and this reproduced till our time. The passage had just to be found by the personality to remove this. Only as personalities man and woman are opposing each other on the same level; not until they find the same in the personality, they are able to develop the same individual, so that they go once as companions toward future. As long as one got the ideals from without, they were connected with the natural, and the natural was rooted in the difference between man and woman which can be compensated only in the soul. From nature this contrast was brought into religion still in mediaeval times, while it yet had an echo of the natural in the divine. You find the male and female principles in the old religions side by side as something that flashes through the whole being, lives and works in nature. We find it in Osiris and Isis, in God Father and Mary. Only when one had cast off the nature basis, when one got to the soul and emancipated this soul, the personal in the human being finally managed to get to freedom by that which is not connected with the differentiation of man and woman. So only the contrast of male and female was overcome. And the poet of personality also had to find the typical word for it. Thus that differentiation grows up as a problem in him in such dramas like A Doll's House, Rosmersholm (1886) and The Lady from the Sea (1887). We see how Ibsen is connected with everything that constitutes the greatness, even if the emptiness of our time. The more Ibsen looked into the future, the more he felt how the emptiness must happen if the personality is emancipated, is detached from its divine-spiritual connections. Thus Ibsen himself faces the problem of personality in The Master Builder (1892) with the big question to the future: we have freed the personality to what end? Something uncertain remains with this search for the essential. As a real truth seeker he represents this unknown like in an allegory in The Lady from the Sea. She gets free for the old duties. However, one has to continue asking: to what end? This is shown in the drama symbolically in a marvellous way. When he tries to look even farther into the riddles of life in Little Eyolf (1894), in When We Dead Awaken, something deep disappears to him in the human heart in which he believed before. Desperation seizes the sculptor in When We Dead Awaken who tried to catch the ideal. He cannot yet form the free human being: animal grimaces rise before him. He tries to form something creatively that lifts him out of them, a resurrection however, always the grimaces push themselves to the fore, position themselves before the picture. When he realises that he cannot overcome them, he awakes and sees what is missing for our time, what it does not have. A tremendously tragic moment is put before us in When We Dead Awaken. Thus Henrik Ibsen is an intrepid prophet of our time: he still feels in the deepest heart, assured of a good future, that there must be something that reaches beyond personality; but he is quiet, and this silence has that tremendously tragic in itself. Who familiarised himself with what stands out in the personality beyond birth and death who made himself familiar with the big law of karma finds new contents also in the personal. He establishes a new ideal; he overcomes personality and makes himself the confessor and lord of this big law of retribution. The antique human being trusted in the reality around himself; he built up the supports of his soul on it. The Middle Ages experienced the ideal in the innermost soul. The modern human being has descended to isolation in the personality, to egotism. He still feels the categorical imperative but as something uncertain, dark. He strives for personal freedom, but the question imposes itself on him: to what end should the personality be freed? The old ideals say nothing more to our time; something new must arise. It is the purpose of the theosophical world view to bring freedom about which does no longer depend on personal arbitrariness, which combines again with divine ideals. It is the spiritual, theosophical life and world view to contribute to it, to build up this future. Only if the best of our time point to this theosophical, spiritual-scientific world view being rooted in the cosmic reality, it gets the significance which it must have. If a great man is quiet in tragic modesty, one like Henrik Ibsen who has aroused the minds, this is such a suggestion. In the days of the 19-th century drawing to an end he wrote his When We Dead Awaken. Now then, the time has come that to us dead human beings Goethe's saying comes true:
The time has come that we live again, that we become personalities again but emancipated personalities: individualities. |
| 69e. The Humanities and the Future of Humanity: Theosophy as a Lifelong Pursuit
04 Jan 1914, Leipzig |
|---|
| Perhaps some of you will see what I am about to say as a curiosity. In our time, Kant has found followers. And one of these followers has written Studies in a Psychology of Pessimism. |
| But this relationship can only be understood by going beyond what can be given in passive terms to what can be grasped in the spiritual world; which stands before us in such a way that Goethe can coin the words - he looked to Kant, who tried to set limits to human knowledge, who wanted to regard as mere belief that which is moral world order ; he called it an “adventure of reason” that should not be undertaken. Goethe, who had to reject the kind of world view that Kant represents; he said that if one could truly rise to the upper regions through virtue and faith in the moral order, then one should bravely endure the adventure of reason and also go up with the whole soul to a higher world. |
| 69e. The Humanities and the Future of Humanity: Theosophy as a Lifelong Pursuit
04 Jan 1914, Leipzig |
|---|
Dear attendees! After yesterday's lecture, which I was allowed to give here, some of the listeners may perhaps be astonished that one can speak of spiritual science or theosophy as a way of life. For what I tried to explain yesterday, as the fundamental, the basic principle of the study of the spiritual worlds, presupposes a vigorous, patient, long-lasting exercise of the human soul. Only through this can what was spoken of yesterday be achieved: that the soul becomes so strong and powerful within itself that it can feel itself to be a spiritual being and actually leave the physical body, thus living in such a way that, in the true sense of the word, the soul itself becomes a spiritual being among other spiritual beings in its experience, that it enters a new world in this spiritual world. That was the purpose of yesterday's paths. If we allow ourselves to be guided very briefly once more by the soul, what has emerged is that the human soul is capable of doing spiritual chemistry; that it is capable of extracting itself as a spiritual-soul being from the context in which it stands in everyday life with the body, just as one is capable of extracting hydrogen from water. And we have seen that by vigorously continuing the exercises we characterized yesterday, the soul really does come to know its physical body first as something external, like the other things, but to know itself as being lifted out and transferred into a spiritual world. And in the further progress of the soul's practice, it turns out that the soul also leaves what it experiences in a soul-like way in everyday life – which only brings back the memory of its life to the point where our ordinary memory, as at a point in our childhood, emerged before our self-awareness – but that then this inner content of the soul changes and that what comes out can be called the spiritual core of the human being , which, when it is experienced, contains the eternal part of the human being, which passes through the gate of death and of which one can then know from real knowledge that he [the human being] goes through repeated earthly lives, that he leads a life alternating between a life on earth that runs between birth and death, and a life in the spiritual world that runs between death and a new birth. Now it could be said: Is it not in the nature of things that this leaving of the physical body, this experiencing oneself as a spiritual-soul being in a completely different world, which can only be achieved after great efforts, that it is perhaps suitable for few people in the present, [that] therefore not everyone can become a soul researcher? Is it therefore not unnecessary to make that which only a few can really do, that which only a few can know, into common knowledge? One could object: How can someone who does not become a spiritual researcher themselves have any understanding of the messages that are given to them by the spiritual researcher about processes, conditions and entities in the spiritual world? For individuals, for a few people, one might say, the attainment of spiritual science may be a life asset; but for those who do not want to go this way, who do not reach a certain point on the path described yesterday, for them spiritual science cannot be a life asset. And yet! Even to the abstract thought it must appear as if that which can be attained in the indicated way must be a real inner good. In today's lecture, the term “theosophy” is used. One could say that spiritual science is a theosophical world view. For this has always been understood to mean a world view that gives the human soul certainty and knowledge that the deepest, innermost core of our being can be reached, and thus it turns out that in its essence we experience that as the root of our existence, is connected with the root of all existence in the world, with the divine-spiritual existence of the world. Through our essential core, we ourselves are rooted in the divine-spiritual. This is what is meant by the term theosophy. And a theosophical world view does not just want to say that one can sense and believe that the human being is connected in his nature to the divine spiritual world, but it wants to say that the human being can also recognize this connection, that he can penetrate to this point within himself where he is connected to the divine spiritual that permeates and interweaves the world. And from the consciousness of this cognizable connection, a theosophical world view wants to create strength and hope for life. Thus, a theosophical world view should actually be a true asset in life. But even if someone has gained the conviction through the path of the soul described yesterday that one can recognize how our soul is connected to its source, it might still seem as if only those who are able to undertake such research of the soul themselves can have a real awareness, a consciousness of this connection. But it is not so. This must be emphasized again and again: the conditions, processes and beings of the spiritual world can only be investigated by the method described yesterday. Only by going out of our physical body ourselves through the application of the described method and being among spirits, can we recognize the spiritual foundations of the world. But once they have been recognized by the spiritual researcher, the person to whom they are communicated need not be a spiritual researcher himself to find them understandable and comprehensible, to apply them in the fullest sense in life, to permeate life with them. To be able to research something in the spiritual world, one must be a spiritual researcher, just as one must be a painter to be able to paint a picture. But once the picture is there, it would be sad if only the painter could understand it. And so it is with what can be found through spiritual research. If it is presented in the right way, then the human soul is attuned to truth and not to error. And just as we can understand the picture that the painter, who can paint, has painted, so we can understand and grasp everything that the spiritual researcher has to say and put it at the service of life, without being a spiritual researcher ourselves. However, in our present time, it is still a long way before this can be achieved for a wider circle of people. For there is much that stands in the way of the modern soul if it wants to understand what the spiritual researcher has to say to the world. Today, people come from an admirable scientific culture. It has equipped him with habits of thought directed towards the external. Today, man is not accustomed to living in the very different concepts that the spiritual researcher brings out of the realm of the spiritual world. But this will change when people's habits of thought have recognized that what stands in the way of spiritual research is prejudice. Then people will find that the descriptions of spiritual science can be understood by everyone. Just as chemistry, physics and any other science cannot be used to benefit life, even though not everyone can become a chemist, physicist or whatever, and people use what comes from chemistry and physics without being chemists and physicists, it is certainly true that what the spiritual researcher has to say can be put into the service of life, can become part of our soul, can penetrate the soul. But then the concepts and ideas that the spiritual researcher has to give directly from the spiritual world have a different effect on the soul than the external concepts and ideas. And only when one has considered what spiritual research can be as a theosophical world view does one come to realize what a valuable asset this spiritual science is. Of course, one might say: When the spiritual researcher speaks of a vital good, this spiritual science cannot give bread and external goods at first. But what it has, it gives; and what it gives is food for the soul, but such food for the soul as it gives is more and more needed by souls due to the particular configuration that our life has taken on in our time. Now, in order to understand the essence of spiritual science, we must first think of one thing. That is, spiritual research differs from ordinary research in the sensory world in that the human being allows himself to be passively impressed by the truth through the other sciences; that the human being must devote himself and the world transmits the truth to him from the outside. In spiritual research, however, the soul must be active from the very beginning, developing inner energy. We have seen how the soul must ascend in three ways to the purely supersensible states, processes and entities. By placing itself in these states, it develops an inner facial expression, a purely spiritual mimicry. One cannot merely let what the states of the spiritual world are shine in from the outside. One must unite with it; one must become so one with it that one expresses it in oneself, but expresses it in one's soul, emancipated from the body. Thus, as a spiritual researcher, one enters the spiritual world. As long as one remains passive, it says nothing. Only when one expresses what it has to communicate, when the inner spiritual expression is an expression of what one experiences, only then does it speak. And the gesture, the movement of the soul, it enters into the spiritual world, but again actively, not by living into it as in the outer science, by speculating, but by letting thoughts live within you, you grasp the processes of the spiritual world. Only by imitating them with your own spiritual being can you become aware of them. And the third way was that the human being penetrates through spiritual physiognomy by immersing himself in the spiritual being and raising up the forces in himself from his depths that make him similar in his spiritual and mental state to the moments when he wants to immerse himself in a spiritual being, this spiritual being. Thus the spiritual researcher enters the spiritual world in three ways: through spiritual facial expressions, through spiritual gestures and postures, and through spiritual physiognomy, but always actively, always in activity. And what he brings forth from the spiritual world must be formulated in concepts. And here we arrive at the point where it turns out that it is actually more difficult to communicate the insights of the spiritual world than it is to communicate the insights of the physical world. A person in our time claims that spiritual science also expresses itself externally in exactly the same way as external science expresses itself. Now, external science expresses itself in such a way that it presupposes the object it wants to recognize. And only afterwards does it want to give the concepts about it. And it does right from its point of view. The spiritual researcher actively immerses himself in the spiritual world and he must himself become an expression of what he experiences in the threefold way as described; and his concepts are formed in such a way that they arise within him vividly, and testify to their truth not as an image, but through their content and their power. The external researcher communicates what he has seen, what he has observed. The spiritual researcher is different: He gives conceptual expression to that which he has experienced, that which has become a part of himself, that which he has struggled to understand; these concepts must be fluid and must illuminate each other so that the concepts are like living beings. But they are such that they arise out of what the deepest essence itself is. When the spiritual researcher forms his concepts and presents them to the public, these concepts contain information that he can only experience by bringing together the depths of the human soul with the foundations of the world, insofar as they are accessible to us, with the spiritual foundations of the world, so that his concepts are drawn from the depths of the soul. And these depths of the soul are present in every human soul. The spiritual researcher speaks of something that is present in every human soul. When he has researched it and expresses it, he expresses it in such a way that he lets a sound ring out with which the strings of the soul can resonate, to which it can bring full understanding because it is precisely the sound of one's own being. But these concepts, these ideas, these feelings, in which the spiritual researcher must clothe what he experiences, have the effect of impressing the innermost part of our soul so that it feels drawn to them, because the concepts are active and lead to activity. One cannot understand spiritual science with a casual mind that does not want to be alive within itself. It can only be understood by trying to follow it with the living life and activity of the concepts. Thus spiritual research arises from the activity of the soul and at the same time challenges it to be understood, the activity of the soul. From this we see that when we respond to spiritual research, we awaken the active power of the soul. It appeals to everything in our soul that wants to be active. The centuries-old scientific education of people has, however, pushed this active power of the soul into the background. But when a force is stretched to its highest degree, the counterforce asserts itself. And anyone who can look into the depths of today's souls knows that the souls long to get out of mere looking and observing, to do what calls for the innermost activity. In this way, the human being learns to feel and experience that he is in the midst of the spiritual world, but not as an understanding being that participates in its life. Thus, the concepts and ideas and feelings of spiritual science are themselves the educators of the soul, which they seek to guide to participate in the reasons for existence in which we are rooted. First of all, this is realized in the fact that our thinking is oriented – and we can truly speak of an inner soul-good that permeates us through the understanding we bring to the ideas of spiritual research – that our thinking habits, our way of understanding, our soul mood is seized. And while it is otherwise possible to experience that in our presence, especially with well-meaning thinkers, there is something about the orientation of thinking that leaves much to be desired, spiritual science, the messages of spiritual research, can really bring people to orient his thinking in such a way that he imbues this thinking with habits that have a certain natural tendency towards truthfulness; that have a tendency not to get involved in the contradictions of life; to notice how thinking must penetrate into external things. The education of our thinking, the sharpening of our thinking, is what will emerge first when spiritual science enters into our cultural life. I would like to give an example that can really show what the sharpness of thinking is like in our time. Let us assume that a very important thinker of the present day, who is regarded in the broadest circles today as an astute mind, has done many things that are noticed by those who have trained their thinking in what thinking must not do. There is a recent book by a thinker in which two assertions are found, separated by thirty or forty pages. The thinker in question wants to explain in what sense people today can still be Christians. And one approaches the soul of today's free-thinking people in a pleasing way when one says – and he says it –: Today we must go beyond the demon stories told in the Bible. All right, he may be of that opinion. Thirty pages later, however, one reads the remarkable sentence in the same book: When the spiritual and the physical touch in the soul, then demonic powers arise. You tell that to someone, and he can say: Well, the second time he didn't mean it like that, then he meant it figuratively. Yes, my dear audience, that is precisely the point: people are allowed to use such phrases and are not aware of the grotesque way in which they contradict all orderly thinking. But people do not notice this today. And we are only on the way to our thinking being corrupted by mere passivity in this direction. This is how it is for those who can see through and observe things. In another famous book, you can read today - there is talk of combating a certain philosophical school of thought - that an author uses the image: This philosophy moves like a clown who pulls up the ladder he has climbed up to him and falls down. The book is quite witty, but I would like to ask you how the clown is supposed to pull the ladder up to him. You only think and write something like that when your thinking is disoriented. But today we are only at the beginning; such books are full of impossible thinking. But since external culture is, as it were, the imprint of what people think, our culture must gradually be permeated by disordered thinking, unless this thinking is educated in such a way that it can respond with a fine feeling for what can and cannot be said. What can be said must be felt as connected with the essence and weaving of reality. Through orientated thinking, we can become familiar with reality, and this will be the fruit of spiritual science. Everyone will notice that this fruit of spiritual science harmonizes our lives; that it pours something into the soul that is able to bring this life into harmony with reality. In this way, spiritual science already has an educational and training effect on our thinking, making it inwardly active and alive. And something else results from this. Those who gradually absorb what educated thinking in spiritual science can form in them will feel within themselves the independence of their inner being, the wisdom, the spirituality of their actual core. And there would be no materialism and no monism if one were to really engage in truly trained, energetic, inwardly self-gathering thinking. The strengthening and invigoration of our soul is the fruit of what we have for our thinking from spiritual science. But spiritual science also brings forth as a second fruit of life that which belongs to the field of self-knowledge. Just as a diseased organism sometimes cannot endure the freshest air, but it can be seen from this that the organism is not healthy, so it can also be seen by some people in relation to spiritual science that they cannot tolerate it, that it makes an impression on them, this spiritual science, that it is fantasy, illusion. One will gradually come to realize that this is a form of self-knowledge; that from it one can see how one should struggle upwards in the soul in order to be able to understand what the spiritual researcher can obtain from the depths of the world. How far you are from self-knowledge can be recognized by measuring yourself against the demands that the spiritual researcher places on the soul. Therefore, no one should be deterred if they notice that, through spiritual science, their thinking is at first somewhat numbed, disturbed, or their memory no longer seems as coherent to them as it used to. All these are transitional phenomena. We must recognize ourselves in this and say to ourselves: We must struggle to bear the stronger demands in the soul. But then this spiritual science will communicate its healthy spiritual life to us all the more. And if we go further, we may find that perhaps even today spiritual science is not universally respected as a valuable possession because its value is not so immediately apparent. Nowadays, material goods are of course valued much more than spiritual goods because people do not really understand how material goods depend on spiritual goods. But if many a person could really ask himself out of a certain realization of things – and we can hear this question in our time from many souls who do not quite know how to begin with this or that, who lack a healthy direction in life, who lack the ability to give themselves direction and strength out of a powerful inner being – if many a person could ask himself: Where does all this come from? These things affect even our physical well-being. Today more than ever, we have to speak of the nervousness of our age, of how unbalanced people are, how they lack balance. Where does this lack of balance come from? Ultimately, it is rooted in the soul. An example of this: that which can most lead to an external feeling of unease, to all possible symptoms of nervousness, to everything else that makes our social life so difficult, what can lead to this is spiritual barrenness, emptiness of the soul, a non-connection of the soul with what spiritual research wants to give, what spiritual research wants to fill the soul with. Of course, there are some people today who say they have no need for the concepts of spiritual science. That is certainly true. But that is only in their conscious mind. In the depths of the soul there is always a longing for the sources of existence. And what we do not give to the soul asserts itself in it as emptiness, desolation, doubt. And, not overnight, but over decades, what is missing in the soul, what is present as chaos in the soul, pours out into the physical organization. We are no longer up to life. We can no longer pour the soul's strength into the physical because the soul is empty. Because people have become accustomed to paying attention to outward appearances in a natural way over the centuries, they have become estranged from that which can permeate the soul with spiritual content. A great many unhealthy symptoms, which go as far as the physical body and make people unable to cope with life, stem from this. And it will get worse and worse if spiritual science does not intervene and give the soul what it craves without knowing it with the higher consciousness. Have we not seen that in our time – I do not want to say that there is pessimism in general, but that it has been examined in a peculiar way? If one speaks of pessimism in general, one would have to mention all sorts of misunderstandings. One could mention that some older religions also contain pessimism. But that is not the point, but rather the way in which one tries to support pessimism in our time. This support shows something very peculiar. Perhaps some of you will see what I am about to say as a curiosity. In our time, Kant has found followers. And one of these followers has written Studies in a Psychology of Pessimism. He undertook a strange investigation that takes a completely objective, passive scientific approach to the human being and seeks to examine whether life contains more suffering, more unpleasantness than pleasure, happiness, etc. This professor [Kowalewski] first tried to determine whether this is really the case by asking schoolchildren. He had the children write down what they call happiness in life and what they call suffering in life. They wrote down the following as suffering: illness, death, flooding. As for pleasure, they wrote down: ice cream, playing, gifts. We should not be surprised at the quality of this zest for life. But for the positive researcher, it depends on numerical relationships, and Kowalewski did indeed not just come up with ordinary numbers, but difficult integral terms. His reasoning about pessimism is therefore not easy to read. He was able to determine that in 39 cases suffering was emphasized, in 25 to 27 cases pleasure. So one can conclude from the children's minds that life offers more of the painful than of the pleasurable. And he thought: That doesn't quite go into the positive, you have to do it differently. He also used the diary of a well-known contemporary philosopher. He always wrote down when he felt pleasure and when he felt suffering. And when Professor Kowalewski looked through this diary, he found that suffering outweighed pleasure. So he had the second piece of evidence. But he went further, he was looking for something more certain. He observed people who walk quickly and people who walk slowly. When you are sad, he says, you walk slowly; when you are happy, you walk quickly. That is the professor's premise. And lo and behold, it turns out that there is a far greater number of sad, slow walkers. And so a book has been written in which these numerical relationships have been expressed in mathematical integral forms, and one can say, so to speak, equipped with these: Well, if you examine the external life, the pessimistic world view turns out to be justified, because the external life contains much more of the fatal, the sorrowful, than of the beneficial, the pleasurable. Science has now proved that! Now there is no need to smile at such ideas. I am not going to talk about the value of such research, in what way it characterizes certain sciences. I just want to ask: What is actually being looked at here? Well, it is what touches man from the external world, what makes an impression on man, for nothing else can be investigated with such methods. No attention is paid to what man is capable of opposing to the impressions from outside, in the way of the unity and self-contained nature of his inner being. I would like to quote something else that Mechnikov said in his 'Contributions to Optimism'. He talks about someone who was a friend of his, a person who was very nervous, who experienced the disinclination of life in the deepest sense. He could no longer hear a carriage rattle. He could not hear that someone was ringing his bell. He could not see that many people were coming to meet him. And many other things as well. You can imagine what was unbearable for this person. In the end, he knew of no other way to save himself than through morphine, in order to have a sense of stability within himself. Often he was close to taking such a large morphine dose that he could find death. He was also close to death more often, but was saved again and again. Then Mechnikov continued: So that was the man, but it got better and better with his pessimism. And actually Mechnikov says quite rightly why this is so: his external perception, so to speak, became more and more dulled; the outside world no longer made such a strong impression on him as it had done before. Now we ask ourselves: What led to a greater balance of the soul in this person? That he became duller to the impressions of the outside world, that he was able to close himself off to these impressions. But throughout his life, his inner being was weak. But it can never be a matter of weakening us for everything beautiful and sublime that may come from the world, not to become nervous, but only for what I would like to express as follows: Could not man have had the same earlier, if a strong inner being, permeated with soul substance, had opposed the perceptions of the outer world? But that is precisely what spiritual science strives for: to make man strong within himself against the changing impressions of the outside world; so that we need not become dull to the world, and yet stand securely in the world. Then it will no longer be necessary to examine the questions of a better or worse life according to purely external things. Kowalewski has done an even more precise experiment and a careful analysis has shown that we have every reason to approach the outside world when we are confronted with it as being much richer in suffering than in pleasure. He did the following. He says: Let us assume that we are examining the sense of taste. Now he has established – in external science you need concepts; where the spirit is absent, you need concepts and words – he called what makes a taste impression in us in the smallest amount of any substance the 'gustie'; and so he established what the gustie is of quinine, which makes an unpleasant impression; sugar makes a pleasant impression. And so he had a number of people take quinine and sugar together to see how much of each was needed to balance it out. And lo and behold, he found that almost twice as much sugar gusti had to be used than quinine gusti if the sugar gusti was to balance the quinine gusti. That means that, in terms of taste, we have to double the pleasant if we want to eliminate the unpleasant. What I am reflecting on is that we cannot measure something that has an impact on our lives. And the mistake is that one does not take into account that one is actually not at all suited to assess the sugar level in the right way in relation to one's outer life. We take it for granted, but we estimate the quinine level quite strongly. As is well known, we are very much affected by the disease, but we rarely feel the full extent of our desire for health. And this is connected with the mistakes that are made in such investigations. But we can also fill our health, which must gradually become boring to us when the soul emptiness remains, with what comes to us from the spiritual world, and we can hold out, so to speak, what flows in from the spiritual world to us, which can always hold and carry us, against the obviousness of the disaffection of the outer world. One should not treat a pessimistic mood by asking: Is the world good or bad? but in such a way that one says to oneself: The person who does not find the strength to stand securely in the world has not drawn enough from the spiritual world. What the person of whom Mechnikov speaks acquires through the deadening of his outer organization flows into our soul as a true asset of life when we take up spiritual-scientific concepts and ideas. Just as the most important things for the development of the soul of the spiritual researcher himself flow from the soul's harmony, so the soul's harmony and balance flow out again as a vital asset from the communications of spiritual research. And we can cite another thing. We have now spoken of the influences of spiritual science on our thinking and imagining, on our minds. We can also speak of an influence on our will, on the initiative of our actions. The fact that we receive such concepts from the spiritual researcher, which are brought down from the spiritual worlds, means that these concepts also penetrate into our soul in such a way that they are suitable for pointing our soul to what is independent in it from the external sense world. But now, how much arises in our will as a result of external stimulation? I see something that stimulates me. Perhaps I see a flower, I pick it; I am stimulated by it. I do something in life in one way or another. Once the educators taught me something; as a result, the skill arose in me for this or that. If we examine our will, we find external stimuli everywhere. This is precisely what characterizes the will in everyday life: it is stimulated from the outside to a greater extent than is usually believed. Even people who believe themselves to be the freest are dependent on this or that stimulus. They believe they act freely, but they only act according to what has been exerted as a stimulus from the outside world. In particular, we can often see that when people resist this or that in the name of the freedom of their soul, they are in fact resisting because of their stubbornness, their lack of freedom, and not because of the freedom of their mind. In short, the will is rooted everywhere, so to speak, in the external world. When we take in spiritual science, what flows from its insights has a strengthening and invigorating effect on this will in particular. It works in such a way that this will in the soul becomes independent. But when it does that, we feel it as a force in the soul, as something that can only receive stimulation from within. We are enriched in our soul when we strengthen our will in this way. The external causes no longer affect that part of our inner being that we have acquired through our own will. We withdraw from external causes with our will. When someone becomes more and more deeply involved in spiritual science, they feel their will growing stronger. They can say: “I can now want more than I could before.” But this can only be achieved through devotion to spiritual science. But if there is no external stimulus for the will, where must impulses come from? Again, what arises as new will not remain in rest, in inactivity, if it receives impetus from within. There is only one thing that no longer compels: what we call love in the broadest sense. This means that the motives of our will must be warmed through by love through the influence of spiritual science. We learn to recognize more and more the deep meaning of the word:
where that which leads us to action leads us entirely through our love for the task at hand, and we strive to accomplish it with the strength of soul with which we strive to accomplish everything that arises from love. With this, we have gained a beautiful fruit of spiritual science as a treasure for life. We have achieved the transformation of our will into the will to love. The treasure of the will to love grows ever greater when spiritual science becomes our life's treasure. Again, it is not something that provides us with material goods. But this will to love is a strengthening, valuable good for our external security in life, which we will see grow and grow as we properly penetrate into spiritual science through the concepts and ideas of spiritual science. And again, a piece of self-knowledge can be linked to it. We often hear that people think highly of themselves when it comes to their will to love. But this is not the case. For when people, in wise self-observation, become aware of how the ideas and concepts of spiritual science make them aware of the selfishness and lack of love that still exists in them, spiritual science is once again the beautiful corrective, the genuine guide to self-knowledge. On the one hand, it gives us the will to love; on the other hand, it makes us aware of how much we still lack of this will to love. Thus, spiritual science is also the highest form of life, which can be described by the word self-education. And further, spiritual science leads us beyond what the concepts borrowed from the external world can give us. It leads us to what the spiritual researcher finds by going out of his body with his soul and connecting with the roots of the world from which he, spirit from spirit, is taken. It thus leads us to what is deepest in our soul. More and more one will see, as I also tried to explain yesterday - through the parable at the end - that science, which is built according to the pattern of external science, must stop at a certain point if it wants to become a worldview. I could explain this for many ideas that are important life ideas. I will explain it for only one idea now. Let us suppose that some philosopher, who at first wants nothing to do with spiritual science, Lotze, a man of spirit - I will stick to my habit of quoting those whom I consider worthy of opposition, those whom I regard as authorities - Lotze, who has written a book, 'Microcosm', which contains many significant works on philosophy, has also tried to present a philosophy of religion. But he arrives only at a conception of truth, at a recognition of such a conception of truth, which is won according to the pattern of those conceptions and ideas that are far removed from outer reality, that are won passively. Lotze therefore attempts to win a philosophy of religion by building it up in the sense of outer science. And, lo and behold, Lotze goes as far as is humanly possible. From his presuppositions he arrives at the assumption of a spiritual being, a divine being, that permeates and pervades the world, that is creatively active. He arrives at being able to conceive of the laws of nature as shaped and spiritualized by a unified divine essence. But every time a religious philosophy of this kind seeks to show how that which is shaped according to the pattern of external truth, like a natural law, is connected with the moral commandments, with that which, as inner impulses, inspires us in life, then it must come up against a duality for which it knows no connection. On the one hand, there are laws that operate with rigid, cold necessity. Where, in this whole system of natural laws, does that which lives in us as our moral impulses arise, as that which drives us to be noble in our human existence, that which permeates us with morality? Where does it spring from out there? If philosophy is to become a way of looking at life, then this question becomes relevant. It takes on significance. If philosophy is to become a regulator of our view of life, pointing out that on the one hand there is the world of necessity, and on the other the world of moral commandments, which, however, lives in us as if cut off from the world - how is it rooted in the world? As long as we remain with the passive concept of truth, we will never be able to bridge this gap, because there is a relationship between necessary truth and its legitimacy and moral truth and its legitimacy that cannot be seen in the external world, that cannot be passively grasped. The relationship between the natural order and the moral order cannot be grasped any more than the relationship between a mother and her child can be grasped through natural laws alone. The father could be there without the child being there. If the child is there, the child emerges from the father, but the father could be without a child. There is no necessity in the father, yet the father leads to the child. Perhaps one of the most significant conceptions and ideas of Christianity is that the relationship of the one God to the God who is to permeate our innermost being is presented in our morality as the relationship of the Father to the Son, the Christ. Theosophy or spiritual science shows us that there is a relationship between the moral world order and the natural-law necessity and world order, such as that of the Son to the Father. But this relationship can only be understood by going beyond what can be given in passive terms to what can be grasped in the spiritual world; which stands before us in such a way that Goethe can coin the words - he looked to Kant, who tried to set limits to human knowledge, who wanted to regard as mere belief that which is moral world order ; he called it an “adventure of reason” that should not be undertaken. Goethe, who had to reject the kind of world view that Kant represents; he said that if one could truly rise to the upper regions through virtue and faith in the moral order, then one should bravely endure the adventure of reason and also go up with the whole soul to a higher world. Then, at the same time, something is poured into the natural order as well as into the moral order that is as communal as that which exists between father and son, because nature, if we look at it as it is, could exist without morality, like the father without a son. Only when we look at what has really happened do we find the right relationship between father and son. So we have to go to what has really happened in the world, and there we come to the very core of Christianity. I wanted to give you an example of how religious concepts, which the human mind needs to feel its connection with what pulses through the world as divine-spiritual, how the human being can be strengthened in his religious life through spiritual science. For spiritual science shows him that one can really still grasp and understand that which, according to a great philosopher such as Kant, one should only assume and only be able to believe. Our time, however, is living into an epoch in which it is once again quite clear to the spiritual researcher how souls are increasingly longing not only to accept religious deepening based on the authority of faith, but also to be able to recognize as we recognize nature, that which binds people together with the Divine-Spiritual in the cosmos outside. Another asset for life will be that the newly awakening religious needs - for they will awaken, the religious needs appropriate to our time - will give these spiritual scientific concepts of inner support, of being set within, again. The spiritual researcher himself is familiar with all the objections that can be made. If someone wants to say, for example: Now you have presented spiritual science as a special bringer of love. Doesn't Christianity do that for itself? — Yes, of course. The person who says that is fully convinced of it, and perhaps from his point of view he is quite right. But one could give him an answer, which I once had to give to a clergyman who said to me: Yes, what spiritual science says about Christianity, at least in many respects one can certainly go along with that. But one thing strikes me. The way you speak, you only speak to a few educated people who fulfill certain conditions. But we speak to all people. And that must be a true teaching that speaks to all people. I replied, “Pastor, have you found that all people go to church with you?” He could not say that. You see, I said, I want to speak to those who do not go to church with you, because they also have a living yearning for an understanding of Christianity. The fact shows that you are not speaking for them. So you are not speaking correctly for all people. And we do not have the right to say: something is right because we like it; we have to observe the facts. You may think you can dress your teaching in words that will appeal to everyone, but what we think is not always right, the facts must speak. For those who do not go to church but still long for an understanding of Christianity, we must also speak. Of course, Christianity also speaks of love, but the point is not just to talk about the way to love; the point is to find the way that is the right way for a particular time. You must not be so selfish as to say: I want nothing to do with such a way to love, because the old way is good enough for me. That is egoism, which does not want to pay attention to the longings and tendencies of the souls that are touched by what will touch more and more souls in the future. But it is these souls that need the new paths, and the number of these souls will grow. The spiritual-scientific worldview wants to inspire them. It wants to give life goods of the kind that have been discussed here. I could speak about many other life goods that can flow from spiritual science, but the principle is how spiritual science creates life goods, how spiritual science brings forth that which is immortal in us. But through this, what consciousness evokes in us is awakened and activated: You are an independent being; within you is a source through which spiritual life can bubble, which empowers you, which can give you strength, which can give you everything you need for your life. Spiritual science is indeed gradually transformed into feelings and sensations. We not only experience immortality theoretically. From the whole structure of my lecture, you could see that the concepts of spiritual science bring to life and resonate within us what the spiritual researcher explores. This is particularly the case with one of the most important questions in life, the question of immortality. If you delve deeper into spiritual science, you will receive a spiritual doctrine of immortality, a teaching about the core of the human being that can be clothed in concepts and ideas so that we not only know about immortality, but feel within us what is immortal in us. We become like a plant that could feel how the germ grows within it into a new plant. We feel what passes through the gate of death; we learn to experience it. And the time will come when principles such as those set forth in my book 'The Education of the Child from the Point of View of Spiritual Science' will be applied to the education of the child, when the soul will be so stimulated that it will live on in us, that we will have acquired a feeling through the concepts we have absorbed, that we will know: by living towards death, you develop more and more what your eternal part is. In the second half of life, when we see wrinkles forming on our skin and our hair turning gray, we will feel how all this is like the fading blossoms of plants, but how there is something in us that is emerging ever stronger, overcoming what fades away in us. And as we live towards a new life, we will feel that life. Old age will not be filled with an empty hope, but with the experience of what is felt within as a reality, which will be carried through death into the realm of the spiritual. This, however, will give certainty in life. It will dispel all superficiality, all incoherence of the spirit, all chaos in life. Thus, in addition to the other possessions of life, there will be a particularly intimate possession for our soul. Just as I have pointed out that with the insights of spiritual science from the depths of human inner and outer perception, one can feel in harmony with all those who, in the right sense, have sensed the significance of human soul life and its relationship to the whole spiritual world through the whole development of humanity, so I would like to conclude by speaking of a thinker who is often forgotten today; a sincere, courageous thinker who, in a small booklet, which is really what is written on its title page, a “Dietetics of the Soul” - I would like to remind you of this dear connoisseur of the human soul, of Feuchtersleben. courageous thinker who, in a little book, which is really what it says on the title page, a “Dietetics of the Soul” - I would like to remind you of this dear connoisseur of the human soul, of Feuchtersleben, who tried to delve so intimately into the requirements and needs of human life, of the human soul; his “Dietetics of the Soul” was published more than 50 years ago. There is hardly a person with an inner life who could read it without something in them being touched that fills the soul with inner warmth; because Feuchtersleben was also one of those souls who, even if there was no spiritual science for them, sensed and felt what the soul longs for. And it is a beautiful saying in which I want to compress what I have spoken to you about, as if it were a feeling. He says:
Yes, the soul's true happiness and, we may add, the soul's true spiritual possessions consist in the expansion of the soul's inner being and possessions. And if spiritual science is what I tried to present yesterday and today, then it is indeed entirely that which, with all its impulses, strives for the expansion of the soul's inner being and possessions. And truly, with what spiritual science gives, one feels oneself standing within what the best minds of humanity have longed and thirsted for, because the soul needs it for its inner spiritual nourishment. Therefore, one is in harmony with such a fine, delicate soul as Feuchtersleben, one that nevertheless thinks and feels on a grand scale. And to sum up, if one wants to collect together in a general feeling what spiritual science can give as its best, one may say: spiritual science gives life's goods; it promotes the genuine, true happiness of the soul. It is held in the sense in which Feuchtersleben's saying is meant:
Question & Answer: Question: Can you slap children on the hand? Rudolf Steiner: That is not so easy to answer. Such questions take on a new significance and importance in our time. There is not always a simple answer to a simple question. Simplicity is convenient, but even a clock is not simple. The universe is even less simple, with less power in it than in a clock. Spiritual science does not make things more comfortable, but through it one sees into areas that are indispensable for shaping life. Then one finds that simple things are complicated. Spiritual science gets one used to taking things more precisely, taking things more seriously. Farm children are quite properly tapped on the knuckles, with proper taps, decorated with an iron ring, but they have not become nervous. City children, who have never been tapped on the knuckles, are often nervous. Life is complicated. What is achieved in one nature through something is not always achieved in the other nature through it. Goethe is right when he says, “One thing is not suitable for all”; we must take people as individuals and not judge abstractions. We cannot say that one thing or another is generally harmful or useful. Spiritual science will lead us from the abstract to the concrete, to an immediate understanding of immediate, concrete life. Then one will find that the question of nervousness will not have much to do with it; but much more important is the question of education from the spiritual-scientific point of view. Then one can completely dispense with what is indicated here. But this education requires much more of the activity of the soul of the educator, who is able to find his way into every soul. Beating is usually required by the nature of the educator, not the person being educated. In general, it can be said that corporal punishment is not particularly recommended as a means of education, regardless of whether it is on the fingers or elsewhere. Question: Is clairvoyance possible while awake? [...] Rudolf Steiner: As a rule, one cannot see the physical-sensory world and the spiritual world at the same time. The physical world is then like a sinking, and simultaneous seeing is usually caused by bringing something like a having [raising?] of the soul into the spiritual vision. What matters is not the state, but the fact that one is so present in the spiritual vision with one's ego, with one's consciousness, that one does not experience it as if in a trance, but consciously. Only then can one seek the connection between the two worlds. It is said that matter does not appear to be present when this state occurs. Yes, it was said yesterday that one has a picture in front of oneself and that one must first learn to read these pictures. You cannot relate them to reality as in the physical world, but must first learn to read them. Question: Is the concept of God actually set aside in Theosophy, or at least not emphasized as it is in the Christian religion? Rudolf Steiner: That is a strange question, because theosophy is named after the concept of “God” or “Theos”. It is as if one speaks of Selters water, from which the watery, liquid part has been completely removed. Such objections can only be made if one has not studied the subject. We do not have the immodesty to constrict God into a limited concept; in him we live and move and have our being, and so do our concepts. One can only gradually become familiar with the divine. Most of the time, such a question only wants to say: I do not want any other Christianity than I have always understood. Question: Should flawlessness be achieved? Rudolf Steiner: That is an abstraction. Questions are often asked about the beginning and end of the world and so on, but the human being can only gradually ascend to understanding. The concepts that are usually brought up are usually as unsuitable as possible. Spiritual science places us in life and keeps us from abstract speculation. Through theosophy, morality is also led into the concrete. Question: Is there not a danger for the theosophist of being withdrawn from his fellow human beings by the cult of the ego? Rudolf Steiner: Where there is strong light, there is also strong shadow. There must be a transformation into the will to love, so that the ego is sought much more outside than inside. Question: Christ's suffering and death is only an archetype for us, since we have to atone for our mistakes later anyway. Rudolf Steiner: I first have to familiarize myself with this question. It is based on a misunderstanding of the idea of karma. One then says: Why should I help a person who is in need and misery? One should help him first, that is written on his karmic account and has a further effect. How I can help one person, I can help two, three, five, fifty, a hundred, a thousand, and a mighty being like the Christ can help all people in karma. Question: How can I be released from a sin of thought that I cannot make amends for because the person concerned has since died? Rudolf Steiner: This must be balanced out in the further course of life. One must not judge this from a merely earthly point of view. We are not dissatisfied with our fate from a higher point of view. Between death and birth, we would be very dissatisfied if we did not have the suffering that flows from our deeds; we do not feel it as suffering at all, but as a relief to be able to balance it out; we strive to balance it out. There is a completely different state between birth and death than between death and a new birth. Question: What influence does anesthesia have on the finer bodies? Rudolf Steiner: Wherever it is possible to avoid anesthesia, it should be avoided. Normally, the soul and spirit leave the body during sleep; with anesthesia, they are forced out, that is, they are subjected to force. If it is necessary, it should be used, of course. Question: Does a stillborn child have an ego? Rudolf Steiner: No more than a corpse. It may have been an attempt at incarnation of the ego before it died in the mother's body. Question: We have often heard about the effects of karma. What about the cruel punishments in the Middle Ages? Rudolf Steiner: It is like an account book. The punishment is, so to speak, on the debit side and balances with the other side. There is no need for an absolute balance to be there immediately when a punishment occurs. The soul would not even be satisfied with that after death, because it wants to balance. Question: Some of the Theosophists look unusual in their hairstyles and clothing. A stranger can feel uncomfortably touched! Rudolf Steiner: This is certainly not a result of the spiritual current! One must be tolerant of the tastes of others; this is perhaps one of the assets of Theosophy. If you want to wear what you like, why shouldn't others be allowed to do the same? Hopefully it doesn't happen too often that Theosophists become Theosophists through hairstyles and clothing. And, ladies, wearing what you like is something that other women do too, and the Theosophists don't say anything, even if they don't always like it. Question: [Is there a] sense of self after death? Rudolf Steiner: Self-awareness is rooted in what remains after death. Only after death we have other tools for perception. Eyes and ears fall off. The soul produces other tools. [The] sense of self is preserved, indeed with a much more intense character. Other theosophists are said to have stated that after death there is only consciousness but no self-awareness? This may be stated in some books, but it has nothing to do with the spiritual science referred to here. Question: On the other hand, the seer of Prevorst: the people she speaks of still show remorse. Rudolf Steiner: This does not exclude self-awareness. The other questions are not of a nature that would be suitable for answering here. |
| 68c. Goethe and the Present: Weimar at the Center of German Intellectual Life
22 Feb 1892, Weimar |
|---|
| They developed an idealistic world view together; different in form but arising from the same core, it is set forth in Schiller's “Letters on the Aesthetic Education of Mankind” and in Goethe's “Fairy Tales”. From Kant's rigorous moral law, progress is made here to a free morality that creates good out of its own initiative, not compelled to do so by a categorical imperative. |
| 68c. Goethe and the Present: Weimar at the Center of German Intellectual Life
22 Feb 1892, Weimar |
|---|
Report in the “Weimarische Zeitung” of February 26, 1892 In a series of lectures dealing with the development of the main currents of German intellectual life, the lecture characterizing the high point of this development must naturally claim the main interest. This task was the fifth lecture of the cycle: “Weimar at the Center of German Intellectual Life,” and the lecturer, Dr. Rudolf Steiner, brilliantly fulfilled this task. In a speech that was as spirited and substantial as it was clear and vivid, he sketched out an image of the main period of German culture that took place on the soil of little Weimar. Goethe's appearance in Weimar, seemingly a coincidence in his life, has become a necessary factor in cultural history. Goethe and Karl August understood each other, and from the outset each of them appreciated the high human value of the other. When Goethe came to Weimar, he had already passed through a major period of his development. Works such as “Götz” and “Werther” show his gift for bringing to light the most profound source of life, which he had developed to perfection. He had had a teacher in Shakespeare, the poet of pure humanity, whose figures are not influenced by an external destiny, but create their own destinies from within themselves. In the Prometheus fragment, this overwhelming sense of power and individuality finds its most powerful expression. Artistically, the first ten years in Weimar were the least productive of Goethe's life; but they were significant for his personal development, to which the circle in which he lived contributed greatly: Wieland, the highly gifted Duchess Anna Amalia, the admirable Duchess Luise, the clear-minded, sensible Knebel. Charlotte von Stein replaced for him on earth what his Promethean belief had taken from him in the hereafter: the need for veneration. In view of this, the dispute about the limits of this relationship is simply laughable. Herder, too, was of the greatest value for his self-education. Both encountered each other at that time in the idea of the development of earthly things, each of which is a link in the great world harmony. For Goethe, this idea was the starting point of his scientific work. In place of the exclusively subjective world view of young Goethe, there now arises a more objective one that integrates man into the universe and its eternal laws. This world view and the corresponding ideal of art found their maturity in Italy. This change can already be seen in “Iphigenia”, in the figure of Orestes. Goethe is Orestes, Frau von Stein is Iphigenia. The man hunted by the Furies does not find redemption within himself, but it is given to him from the outside. The warning that we depend on the iron laws of the outside world, and that the urge for freedom within us has to contend with the forces of life, is also preached by “Tasso”, whose motif is the deep conflict between talent and life. With this objectivism, Goethe had distanced himself from all subjective partisan points of view. Therefore, when he returned from Italy, he was a stranger to Schiller; and it was only from the moment when Schiller, absorbed in the study of philosophy, also leaned towards the exclusive subjectivism of Goethe's clarified, non-partisan world view that the two men became friends. They developed an idealistic world view together; different in form but arising from the same core, it is set forth in Schiller's “Letters on the Aesthetic Education of Mankind” and in Goethe's “Fairy Tales”. From Kant's rigorous moral law, progress is made here to a free morality that creates good out of its own initiative, not compelled to do so by a categorical imperative. Schiller sought to lead man to freedom through beauty. Many researchers have already tried to find hidden wisdom in Goethe's Fairy Tale and have come to grief on the task. Dr. Steiner has for the first time revealed and explained the deeply symbolic nature of this difficult-to-understand poem in such a way that its great human and ethical content is fully revealed. The “Fairytale” proclaims in symbolic form the same thing that Schiller's letters proclaim in abstract form: only through the sacrifice of a limited ego does man achieve that higher self where he no longer has to obey the command of a moral law coming from outside, but can do out of himself what his personal judgment advises him. The educational ideal of the classical period was universal: Goethe and Schiller also made a scientific impact. Goethe's scientific outlook is a highly idealistic one, the value of which can only be fully realized again in an idealistic direction of science. At the same time, science, especially philosophy, reached an undreamt-of height in Jena: Fichte and Schelling, in the first place, also had a stimulating effect on Schiller and Goethe. Goethe and Schiller's correspondence is the perfect expression of this universality. It found its productive expression, on the one hand, in the Xenienkampf, and on the other, in Schiller's dramas and Goethe's epic and dramatic works of the following period. The lecturer then discussed, in broad strokes, but always picking out the essential with a sure hand, the structure and the accomplished poetic form of “Hermann and Dorothea”, where the demand of classical aesthetics that the material must be fully absorbed into the form is fulfilled in the most perfect way. The same is true of the “Natural Daughter”. The accusation that here not individuals but types have been created is rejected. The essence of this work of art is that individuality is only given to the extent that it is also a necessity within the framework of the work of art. Schiller's method of characterization is quite the opposite. It presents the individual as such for his own sake, but in contrast to his youth, now without bias. Schiller's approach to Goethe's style of poetry in The Bride of Messina is only apparent; for the idea of fate is opposed to Goethe's moral world order, and basically to modern and thus also to Schiller's view of the moral demand for human freedom. Schiller's dramas also gave the stage an inner momentum; a new idealistic acting style was also developed through them. Schiller was the link between Goethe and the public; when he died, Goethe was isolated. No one could follow him to the heights that he had reached through an unparalleled self-education. This self-education is most strongly reflected in “Faust,” which accompanied him from the wildest youth to the clarified maturity of old age. The material for Faust is based on the conflict in the human soul between the positive things it has and the only suspected things it would like to acquire. The ascent to the otherworldly realm does not happen here, as in the Theophilus saga, through the grace of the higher powers, but Faust wants to fight for everything through his own strength. From the very beginning, Goethe had in mind the glorification of the victory of this lofty aspiration. And it was not a unified external action that he was aiming at, but poetic transformation of his own experiences. But just as the subjective individual experience disappears in the clear, objective, general world view in the older Goethe, so in the second part of “Faust” the experience rises far above the visible, the real, it is transformed into images, into symbols and allegories; and it is from this point of view that the second part must be considered. The speaker also touched on the same phenomenon in Wilhelm Meister. Goethe's mission was to rejuvenate humanity in an aging age. Such a transformation is also taking place in our own day, for time has grown old again. The striving that rejuvenated Goethe's time, the striving for reality, also fulfills our youth. But what a difference! Goethe understood reality to mean the inner, the necessary, the divine in the earthly, while our present sees it in the external, the accidental. But a people with such a past can never forget it without at the same time descending from the height of its culture. And the generation that cannot say of itself: And Goethe's sun, behold, it smiles on us too! With this warm appeal to the present, the speaker concluded his interesting and thoroughly original remarks, through which he gave all his listeners an instructive and enjoyable hour. |
| 151. Human and Cosmic Thought (1991): Lecture II
21 Jan 1914, Berlin Translated by Charles Davy |
|---|
| How is it that people puzzle for centuries over questions such as that of the hundred possible and the hundred real thalers cited by Kant? Why is it that people fail to pursue the very simple reflections that are necessary to see that there cannot really be any such thing as a “pragmatic” account of history, according to which the course of events always follows directly from preceding events? |
| The crudest kind of materialism—one can observe it specially well in our day, although it is already on the wane—will consist in this, that people carry to an extreme the saying of Kant—Kant did not do this himself!—that in the individual sciences there is only so much real science as there is mathematics. |
| 151. Human and Cosmic Thought (1991): Lecture II
21 Jan 1914, Berlin Translated by Charles Davy |
|---|
THE STUDY of Spiritual Science should always go hand in hand with practical experience of how the mind works. It is impossible to get entirely clear about many things that we discussed in the last lecture unless one tries to get a kind of living grasp of what thinking involves in terms of actualities. For why is it that among the very persons whose profession it is to think about such questions, confusion reigns, for example, as to the relation between the general concept of the “triangle-in-general” and specific concepts of individual triangles? How is it that people puzzle for centuries over questions such as that of the hundred possible and the hundred real thalers cited by Kant? Why is it that people fail to pursue the very simple reflections that are necessary to see that there cannot really be any such thing as a “pragmatic” account of history, according to which the course of events always follows directly from preceding events? Why do people not reflect in such a way that they would be repelled by this impossible mode of regarding the history of man, so widely current nowadays? What is the cause of all these things? The reason is that far too little trouble is taken over learning to handle with precision the activities of thinking, even by people whose business this should be. Nowadays everyone wants to feel that he has a perfect claim to say: “Think? Well, one can obviously do that.” So they begin to think. Thus we have various conceptions of the world; there have been many philosophers—a great many. We find that one philosopher is after this and another is after that, and that many fairly clever people have drawn attention to many things. If someone comes upon contradictions in these findings, he does not ponder over them, but he is quite pleased with himself, fancying that now he can “think” indeed. He can think again what those other fellows have thought out, and feels quite sure that he will find the right answer himself. For no one nowadays must make any concession to authority! That would deny the dignity of human nature! Everyone must think for himself. That is the prevailing notion in the realm of thought. I do not know if people have reflected that this is not their attitude in other realms of life. No one feels committed to belief in authority or to a craving for authority when he has his coat made at the tailor's or his shoes at the shoemaker's. He does not say: “It would be beneath the dignity of man to let one's things be made by persons who are known to be thoroughly acquainted with their business.” He may perhaps even allow that it is necessary to learn these skills. But in practical life, with regard to thinking, it is not agreed that one must get one's conceptions of the world from quarters where thinking and much else has been learnt. Only rarely would this be conceded to-day. This is one tendency that dominates our life in the widest circles, and is the immediate reason why human thinking is not a very widespread product nowadays. I believe this can be quite easily grasped. For let us suppose that one day everybody were to say: “What!—learn to make boots? For a long time that has been unworthy of man; we can all make boots.” I don't know if only good boots would come from it. At all events, with regard to the coining of correct thoughts in their conception of the world, it is from this sort of reasoning that men mostly take their start at the present day. This is what gives its deeper meaning to my remark of yesterday—that although thought is something a man is completely within, so that he can contemplate it in its inner being, actual thinking is not as common as one might suppose. Besides this, there is to-day a quite special pretension which could gradually go so far as to throw a veil over all clear thinking. We must pay attention to this also; at least we must glance at it. Let us suppose the following. There was once in Görlitz a shoemaker named Jacob Boehme. He had learnt his craft well—how soles are cut, how the shoe is formed over the last, and how the nails are driven into the soles and leather. He knew all this down to the ground. Now supposing that this shoemaker, by name Jacob Boehme, had gone around and said: “I will now see how the world is constructed. I will suppose that there is a great last at the foundation of the world. Over this last the world-leather was once stretched; then the world-nails were added, and by means of them the world-sole was fastened to the world-upper. Then boot-blacking was brought into play, and the whole world-shoe was polished. In this way I can quite clearly explain to myself how in the morning it is bright, for then the shoe-polish of the world is shining, but in the evening it is soiled with all sorts of things; it shines no longer. Hence I imagine that every night someone has the duty of repolishing the world-boot. And thus arises the difference between day and night.” Let us suppose that Jacob Boehme had said this. Yes, you laugh, for of course Jacob Boehme did not say this; but still he made good shoes for the people of Görlitz, and for that he employed his knowledge of shoe-making. But he also developed his grand thoughts, through which he wanted to build up a conception of the world; and for that he resorted to something else. He said to himself: My shoe-making is not enough for that; I dare not apply to the structure of the world the thoughts I put into making shoes. And in due course he arrived at his sublime thoughts about the world. Thus there was no such Jacob Boehme as the hypothetical figure I first sketched, but there was another one who knew how to set about things. But the hypothetical “Jacob Boehmes”, like the one you laughed over—they exist everywhere to-day. For example, we find among them physicists and chemists who have learnt the laws governing the combination and separation of substances; there are zoologists who have learnt how one examines and describes animals; there are doctors who have learnt how to treat the physical human body, and what they themselves call the soul. What do they all do? They say: When a person wants to work out for himself a conception of the world, then he takes the laws that are learnt in chemistry, in physics, or in physiology—no others are admissible—and out of these he builds a conception of the world for himself. These people proceed exactly as the hypothetical shoemaker would have done if he had constructed the world-boot, only they do not notice that their world-conceptions come into existence by the very same method that produced the hypothetical world-boot. It does certainly seem rather grotesque if one imagines that the difference between day and night comes about through the soiling of shoe-leather and the repolishing of it in the night. But in terms of true logic it is in principle just the same if an attempt is made to build a world out of the laws of chemistry, physics, biology and physiology. Exactly the same principle! It is an immense presumption on the part of the physicist, the chemist, the physiologist, or the biologist, who do not wish to be anything else than physicist, chemist, physiologist, biologist, and yet want to have an opinion about the whole world. The point is that one should go to the root of things and not shirk the task of illuminating anything that is not so clear by tracing it back to its true place in the scheme of things. If you look at all this with method and logic, you will not need to be astonished that so many present-day conceptions of the world yield nothing but the “world-boot”. And this is something that can point us to the study of Spiritual Science and to the pursuit of practical trains of thought; something that can urge us to examine the question of how we must think in order to see where shortcomings exist in the world. There is something else I should like to mention in order to show where lies the root of countless misunderstandings with regard to the ideas people have about the world. When one concerns oneself with world-conceptions, does one not have over and over again the experience that someone thinks this and someone else that; one man upholds a certain view with many good reasons (one can find good reasons for everything), while another has equally good reasons for his view; the first man contradicts his opponent with just as good reasons as those with which the opponent contradicts him. Sects arise in the world not, in the first place, because one person or another is convinced about the right path by what is taught here or there. Only look at the paths which the disciples of great men have had to follow in order to come to this or that great man, and then you will see that herein lies something important for us with regard to karma. But if we examine the outlooks that exist in the world to-day, we must say that whether someone is a follower of Bergson, or of Haeckel, or of this or that (karma, as I have already said, does not recognise the current world-conception) depends on other things than on deep conviction. There is contention on all sides! Yesterday I said that once there were Nominalists, persons who maintained that general concepts had no reality, but were merely names. These Nominalists had opponents who were called Realists (the word had a different meaning then). The Realists maintained that general concepts are not mere words, but refer to quite definite realities. In the Middle Ages the question of Realism versus Nominalism was always a burning one, especially for theology, a sphere of thought with which present-day thinkers trouble themselves very little. For in the time when the question of Nominalism versus Realism arose (from the eleventh to the thirteenth centuries) there was something that belonged to the most important confessions of faith, the question about the three “Divine Persons”—Father, Son and Holy Ghost—who form One Divine Being, but are still Three real Persons. The Nominalists maintained that these three Divine Persons existed only individually, the “Father” for Himself, the “Son” for Himself, and the “Holy Ghost” for Himself; and if one spoke of a “Collective God” Who comprised these Three, that was only a name for the Three. Thus Nominalism did away with the unity of the Trinity. In opposition to the Realists, the Nominalists not only explained away the unity, but even regarded it as heretical to declare, as the Realists did, that the Three Persons formed not merely an imaginary unity, but an actual one. Thus Nominalism and Realism were opposites. And anyone who goes deeply into the literature of Realism and Nominalism during these centuries gets a deep insight into what human acumen can produce. For the most ingenious grounds were brought forward for Nominalism, just as much as for Realism. In those days it was more difficult to be reckoned as a thinker because there was no printing press, and it was not an easy thing to take part in such controversies as that between Nominalism and Realism. Anyone who ventured into this field had to be better prepared, according to the ideas of those times, than is required of people who engage in controversies nowadays. An immense amount of penetration was necessary in order to plead the cause of Realism, and it was equally so with Nominalism. How does this come about? It is grievous that things are so, and if one reflects more deeply on it, one is led to say: What use is it that you are so clever? You can be clever and plead the cause of Nominalism, and you can be just as clever and contradict Nominalism. One can get quite confused about the whole question of intelligence! It is distressing even to listen to what such characterisations are supposed to mean. Now, as a contrast to what we have been saying, we will bring forward something that is perhaps not nearly so discerning as much that has been advanced with regard to Nominalism or to Realism, but it has perhaps one merit—it goes straight to the point and indicates the direction in which one needs to think. Let us imagine the way in which one forms general concepts; the way in which one synthesizes a mass of details. We can do this in two ways: first as a man does in the course of his life through the world. He sees numerous examples of a certain kind of animal: they are silky or woolly, are of various colours, have whiskers, at certain times they go through movements that recall human “washing”, they eat mice, etc. One can call such creatures “cats”. Then one has formed a general concept. All these creatures have something to do with what we call “cats”. But now let us suppose that someone has had a long life, in the course of which he has encountered many cat-owners, men and women, and he has noticed that a great many of these people call their pets “Pussy”. Hence he classes all these creatures under the name of “Pussy”. Hence we now have the general concept “Cats” and the general concept “Pussy”, and a large number of individual creatures belonging in both cases to the general concept. And yet no one will maintain that the general concept “Pussy” has the same significance as the general concept “Cats”. Here the real difference comes out. In forming the general concept “Pussy” which is only a summary of names that must rank as individual names, we have taken the line, and rightly so, of Nominalism; and in forming the general concept “Cats” we have taken the line of Realism, and rightly so. In one case Nominalism is correct; in the other. Realism. Both are right. One must only apply these methods within their proper limits. And when both are right, it is not surprising that good reasons for both can be adduced. In taking the name “Pussy”, I have employed a somewhat grotesque example. But I can show you a much more significant example and I will do so at once. Within the scope of our objective experience there is a whole realm where Nominalism—the idea that the collective term is only a name—is fully justified. We have “one”, “two”, “three”, “four”, “five”, and so on, but it is impossible to find in the expression “number” anything that has a real existence. “Number” has no existence. “One”, “two”, “three”, “five”, “six”,—they exist. But what I said in the last lecture, that in order to find the general concept one must let that which corresponds to it pass over into movement—this cannot be done with the concept “Number”. One “one” does not pass over into “two”. It must always be taken as “one”. Not even in thought can we pass over into two, or from two into three. Only the individual numbers exist, not “number” in general. As applied to the nature of numbers, Nominalism is entirely correct; but when we come to the single animal in relation to its genus, Realism is entirely correct. For it is impossible for a deer to exist, and another deer, and yet another, without there being the genus “deer”. The figure “two” can exist for itself, “one”, “seven”, etc., can exist for themselves. But in so far as anything real appears in number, the number is a quality, and the concept “number” has no specific existence. External things are related to general concepts in two different ways: Nominalism is appropriate in one case, and Realism in the other. On these lines, if we simply give our thoughts the right direction, we begin to understand why there are so many disputes about conceptions of the world. People generally are not inclined, when they have grasped one standpoint, to grasp another as well. When in some realm of thought somebody has got hold of the idea “general concepts have no existence”, he proceeds to extend to it the whole make-up of the world. This sentence, “general concepts have no existence” is not false, for when applied to the particular realm which the person in question has considered, it is correct. It is only the universalising of it that is wrong. Thus it is essential, if one wants to form a correct idea of what thinking is, to understand clearly that the truth of a thought in the realm to which it belongs is no evidence for its general validity. Someone can offer me a perfectly correct proof of this or that and yet it will not hold good in a sphere to which it does not belong. Anyone, therefore, who intends to occupy himself seriously with the paths that lead to a conception of the world must recognise that the first essential is to avoid one-sidedness. That is what I specially want to bring out to-day. Now let us take a general look at some matters which will be explained in detail later on. There are people so constituted that it is not possible for them to find the way to the Sprit, and to give them any proof of the Spirit will always be hard. They stick to something they know about, in accordance with their nature. Let us say they stick at something that makes the crudest kind of impression on them—Materialism. We need not regard as foolish the arguments they advance as a defence or proof of Materialism, for an immense amount of ingenious writing has been devoted to the subject, and it holds good in the first place for material life, for the material world and its laws. Again, there are people who, owing to a certain inwardness, are naturally predisposed to see in all that is material only the revelation of the spiritual. Naturally, they know as well as the materialists do that, externally, the material world exists; but matter, they say, is only the revelation, the manifestation, of the underlying spiritual. Such persons may take no particular interest in the material world and its laws. As all their ideas of the spiritual come to them through their own inner activity, they may go through the world with the consciousness that the true, the lofty, in which one ought to interest oneself—all genuine reality—is found only in the Spirit; that matter is only illusion, only external phantasmagoria. This would be an extreme standpoint, but it can occur, and can lead to a complete denial of material life. We should have to say of such persons that they certainly do recognize what is most real, the Spirit, but they are one-sided; they deny the significance of the material world and its laws. Much acute thinking can be enlisted in support of the conception of the universe held by these persons. Let us call their conception of the universe: Spiritism. Can we say that the Spiritists are right? As regards the Spirit, their contentions could bring to light some exceptionally correct ideas, but concerning matter and its laws they might reveal very little of any significance. Can one say the Materialists are correct in what they maintain? Yes, concerning matter and its laws they may be able to discover some exceptionally useful and valuable facts; but in speaking of the Spirit they may utter nothing but foolishness. Hence we must say that both parties are correct in their respective spheres. There can also be persons who say: “Yes, but as to whether in truth the world contains only matter, or only spirit, I have no special knowledge; the powers of human cognition cannot cope with that. One thing is clear—there is a world spread out around us. Whether it is based upon what chemists and physicists, if they are materialists, call atoms, I know not. But I recognize the external world; that is something I see and can think about. I have no particular reason for supposing that it is or is not spiritual at root. I restrict myself to what I see around me.” From the explanations already given we can call such Realists, and their concept of the universe: Realism. Just as one can enlist endless ingenuity on behalf of Materialism or of Spiritism, and just as one can be clever about Spiritism and yet say the most foolish things on material matters, and vice versa, so one can advance the most ingenious reasons for Realism, which differs from both Spiritism and Materialism in the way I have just described. Again, there may be other persons who speak as follows. Around us are matter and the world of material phenomena. But this world of material phenomena is in itself devoid of meaning. It has no real meaning unless there is within it a progressive tendency; unless from this external world something can emerge towards which the human soul can direct itself, independently of the world. According to this outlook, there must be a realm of ideas and ideals within the world-process. Such people are not Realists, although they pay external life its due; their view is that life has meaning only if ideas work through it and give it purpose. It was under the influence of such a mood as this that Fichte once said: Our world is the sensualised material of our duty. [Note 2] The adherents of such a world-outlook as this, which takes everything as a vehicle for the ideas that permeate the world-process, may be called Idealists and their outlook: Idealism. Beautiful and grand and glorious things have been brought forward on behalf of this Idealism. And in this realm that I have just described—where the point is to show that the world would be purposeless and meaningless if ideas were only human inventions and were not rooted in the world-process—in this realm Idealism is fully justified. But by means of it one cannot, for example, explain external reality. Hence one can distinguish this Idealism from other world-outlooks: We now have side by side four justifiable world-outlooks, each with significance for its particular domain. Between Materialism and Idealism there is a certain transition. The crudest kind of materialism—one can observe it specially well in our day, although it is already on the wane—will consist in this, that people carry to an extreme the saying of Kant—Kant did not do this himself!—that in the individual sciences there is only so much real science as there is mathematics. This means that from being a materialist one can become a ready-reckoner of the universe, taking nothing as valid except a world composed of material atoms. They collide and gyrate, and then one calculates how they inter-gyrate. By this means one obtains very fine results, which show that this way of looking at things is fully justified. Thus you can get the vibration-rates for blue, red, etc.; you take the whole world as a kind of mechanical apparatus, and can reckon it up accurately. But one can become rather confused in this field. One can say to oneself: “Yes, but however complicated the machine may be, one can never get out of it anything like the perception of blue, red, etc. Thus if the brain is only a complicated machine, it can never give rise to what we know as soul-experiences.” But then one can say, as du Bois-Reymond once said: If we want to explain the world in strictly mathematical terms, we shall not be able to explain the simplest perception, but if we go outside a mathematical explanation, we shall be unscientific. The most uncompromising materialist would say, “No, I do not even calculate, for that would presuppose a superstition—it would imply that I assume that things are ordered by measure and number.” And anyone who raises himself above this crude materialism will become a mathematical thinker, and will recognize as valid only whatever can be treated mathematically. From this results a conception of the universe that really admits nothing beyond mathematical formulae. This may be called Mathematism. Someone, however, might think this over, and after becoming a Mathematist he might say to himself: “It cannot be a superstition that the colour blue has so and so many vibrations. The world is ordered mathematically. If mathematical ideas are found to be real in the world, why should not other ideas have equal reality?” Such a person accepts this—that ideas are active in the world. But he grants validity only to those ideas that he discovers outside himself—not to any ideas that he might grasp from his inner self by some sort of intuition or inspiration, but only to those he reads from external things that are real to the senses. Such a person becomes a Rationalist, and his outlook on the world is that of Rationalism. If, in addition to the ideas that are found in this way, someone grants validity also to those gained from the moral and the intellectual realms, then he is already an Idealist. Thus a path leads from crude Materialism, by way of Mathematism and Rationalism, to Idealism. But now Idealism can be enhanced. In our age there are some men who are trying to do this. They find ideas at work in the world, and this implies that there must also be in the world some sort of beings in whom the ideas can live. Ideas cannot live just as they are in any external object, nor can they hang as it were in the air. In the nineteenth century the belief existed that ideas rule history. But this was a confusion, for ideas as such have no power to work. Hence one cannot speak of ideas in history. Anyone who understands that ideas, if they are there are all, are bound up with some being capable of having ideas, will no longer be a mere Idealist; he will move on to the supposition that ideas are connected with beings. He becomes a Psychist and his world-outlook is that Psychism. The Psychist, who in his turn can uphold his outlook with an immense amount of ingenuity, reaches it only through a kind of one-sidedness, of which he can eventually become aware. Here I must add that there are adherents of all the world-outlooks above the horizontal stroke; for the most part they are stubborn fold who, owing to some fundamental element in themselves, take this or that world-outlook and abide by it, going no further. All the beliefs listed below the line have adherents who are more easily accessible to the knowledge that individual world-outlooks each have one special standpoint only, and they more easily reach the point where they pass from one world-outlook to another. When someone is a Psychist, and able as a thinking person to contemplate the world clearly, then he comes to the point of saying to himself that he must presuppose something actively psychic in the outside world. But directly he not only thinks, but feels sympathy for what is active and willing in man, then he says to himself: “It is not enough that there are beings who have ideas; these beings must also be active, they must be able also to do things.” But this is inconceivable unless these beings are individual beings. That is, a person of this type rises from accepting the ensoulment of the world to accepting the Spirit or the Spirits of the world. He is not yet clear whether he should accept one or a number of Spirits, but he advances from Psychism to Pneumatism to a doctrine of the Spirit. If he has become in truth a Pneumatist, then he may well grasp what I have said in this lecture about number—that with regard to figures it is somewhat doubtful to speak of a “unity”. Then he comes to the point of saying to himself: It must therefore be a confusion to talk of one undivided Spirit, of one undivided Pneuma. And he gradually becomes able to form for himself an idea of the Spirits of the different Hierarchies. Then he becomes in the true sense a Spiritist, so that on this side there is a direct transition from Pneumatism to Spiritism. These world-outlooks are all justified in their own field. For there are fields where Psychism acts illuminatingly, and others where Pneumatism does the same. Certainly, anyone who wishes to deliberate about an explanation of the universe as thoroughly as we have tried to do must come to Spiritism, to the acceptance of the Spirits of the Hierarchies. For to stop short at Pneumatism would in this case mean the following. If we are Spiritists, then it may happen that people will say to us: “Why so many spirits? Why bring numbers into it? Let there be One Undivided Spirit!” Anyone who goes more deeply into the matter knows that this objection is like saying: “You tell me there are two hundred midges over there. I don't see two hundred; I see only a single swarm.” Exactly so would an adherent of Pneumatism stand with regard to a Spiritist. The Spiritist sees the universe filled with the Spirits of the Hierarchies; the Pneumatist sees only the one “swarm”—only the Universal Spirit. But that comes from an inexact view. Now there is still another possibility: someone may not take the path we have tried to follow to the activities of the spiritual Hierarchies, but may still come to an acceptance of certain spiritual beings. The celebrated German philosopher, Leibnitz, was a man of this kind. Leibnitz had got beyond the prejudice that anything merely material can exist in the world. He found the actual, he sought the actual. (I have treated this more precisely in my book, Riddles of Philosophy.) His view was that a being—as, for example, the human soul—can build up existence in itself. But he formed no further ideas on the subject. He only said to himself that there is such a being that can build up existence in itself, and force concepts outwards from within itself. For Leibnitz, this being is a “Monad”. And he said to himself: “There must be many Monads, and Monads of the most varied capabilities. If I had here a bell, there would be many monads in it—as in a swarm of midges—but they would be monads that had never come even so far as to have sleep-consciousness, monads that are almost unconscious, but which nevertheless develop the dimmest of concepts within themselves. There are monads that dream; there are monads that develop waking ideas within themselves; in short, there are monads of the most varied grades.” A person with this outlook does not come so far as to picture to himself the individual spiritual beings in concrete terms, as the Spiritist does, but he reflects in the world upon the spiritual element in the world, allowing it to remain indefinite. He calls it “Monad”—that is, he conceives of it only as though one were to say: “Yes, there is spirit in the world and there are spirits, but I describe them only by saying, ‘They are entities having varying powers of perception.’ I pick out from them an abstract characteristic. So I form for myself this one-sided world-outlook, on behalf of which as much as can be said has been said by the highly intelligent Leibnitz. In this way I develop Monadism.” Monadism is an abstract Spiritism. But there can be persons who do not rise to the level of the Monads; they cannot concede that existence is made up of being with the most varied conceptual powers, but at the same time they are not content to allow reality only to external phenomena; they hold that “forces” are dominant everywhere. If, for example, a stone falls to the ground, they say, “That is gravitation!” When a magnet attracts bits of iron, they say: “That is magnetic force!” They are not content with saying simply, “There is the magnet,” but they say, “The magnet presupposes that supersensibly, invisibly, a magnetic force is present, extending in all directions.” A world-outlook of this kind—which looks everywhere for forces behind phenomena—can be called Dynamism. Then one may say: “No, to believe in ‘forces’ is superstition”—an example of this is Fritz Mauthner's Critique of Language, where you find a detailed argument to this effect. It amounts to taking your stand on the reality of the things around us. Thus by the path of Spiritism we come through Monadism and Dynamism to Realism again. But now one can do something else still. One can say: “Certainly I believe in the world that is spread out around me, but I do not maintain any right to claim that this world is the real one. I can say of it only that it ‘appears’ to me. I have no right to say more about it.” There you have again a difference. One can say of the world that is spread out around us. “This is the real world,” but one can also say, “I am clear that there is a world which appears to me; I cannot speak of anything more. I am not saying that this world of colours and sounds, which arises only because certain processes in my eyes present themselves to me as colours, while processes in my ears present themselves to me as sounds—I am not saying that this world is the true world. It is a world of phenomena.” This is the outlook called Phenomenalism. We can go further, and can say: “The world of phenomena we certainly have around us, but all that we believe we have in these phenomena is what we have ourselves added to them, what we have thought into them. Our own sense-impressions are all we can rightly accept. Anyone who says this—mark it well!—is not an adherent of Phenomenalism. He peels off from the phenomena everything which he thinks comes only from the understanding and the reason, and he allows validity only to sense-impressions, regarding them as some kind of message from reality.” This outlook may be called Sensationalism. A critic of this outlook can then say: “You may reflect as much as you like on what the senses tell us and bring forward ever so ingenious reasons for your view—and ingenious reasons can be given—I take my stand on the point that nothing real exists except that which manifests itself through sense-impressions; this I accept as something material.” This is rather like an atomist saying: “I hold that only atoms exist, and that however small they are, they have the attributes which we recognize in the physical world”—anyone who says this is a materialist. Thus, by another path, we arrive back at Materialism. All these conceptions of the world that I have described and written down for you really exist, and they can be maintained. And it is possible to bring forward the most ingenious reasons for each of them; it is possible to adopt any one of them and with ingenious reasons to refute the others. In between these conceptions of the world one can think out yet others, but they differ only in degree from the leading types I have described, and can be traced back to them. If one wishes to learn about the web and woof of the world, then one must know that the way to it is through these twelve points of entry. There is not merely one conception of the world that can be defended, or justified, but there are twelve. And one must admit that just as many good reasons can be adduced for each and all of them as for any particular one. The world cannot be rightly considered from the one-sided standpoint of one single conception, one single mode of thought; the world discloses itself only to someone who knows that one must look at it from all sides. Just as the sun—if we go by the Copernican conception of the universe—passes through the signs of the Zodiac in order to illuminate the earth from twelve different points, so we must not adopt one standpoint, the standpoint of Idealism, or Sensationalism, or Phenomenalism, or any other conception of the world with a name of this kind; we must be in a position to go all round the world and accustom ourselves to the twelve different standpoints from which it can be contemplated. In terms of thought, all twelve standpoints are fully justifiable. For a thinker who can penetrate into the nature of thought, there is not one single conception of the world, but twelve that can be equally justified—so far justified as to permit of equally good reasons being thought out for each of them. There are twelve such justified conceptions of the world. Tomorrow we will start from the points of view we have gained in this way, so that from the consideration of man in terms of thought we may rise to a consideration of the cosmic. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1916): The Idea of Freedom
Translated by R. F. Alfred Hoernlé |
|---|
| Whoever lacks the capacity to think out for himself the moral principles that apply in each particular case, will never rise to the level of genuine individual willing. Kant's principle of morality: Act so that the principle of your action may be valid for all men—is the exact opposite of ours. |
| For the free spirit transcends norms, in the sense that he is insensible to them as commands, but regulates his conduct in accordance with his impulses (intuitions). When Kant apostrophizes duty: “Duty! Thou sublime and mighty name, that dost embrace nothing charming or insinuating, but requirest submission,” thou that “holdest forth a law ... before which all inclinations are dumb, even though they secretly counter-work it,” [Translation by Abbott, Kant's Theory of Ethics, p. 180; Critique of Pure Practical Reason, chap. iii.] then the free spirit replies: “Freedom! |
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1916): The Idea of Freedom
Translated by R. F. Alfred Hoernlé |
|---|
The concept “tree” is conditioned for our knowledge by the percept “tree.” There is only one determinate concept which I can select from the general system of concepts and apply to a given percept. The connection of concept and percept is mediately and objectively determined by thought in conformity with the percept. The connection between a percept and its concept is recognized after the act of perception, but the relevance of the one to the other is determined by the character of each. In willing the situation is different. The percept is here the content of my existence as an individual, whereas the concept is the universal element in me. What is brought into ideal relation to the external world by means of the concept, is an immediate experience of my own, a percept of my Self. More precisely, it is a percept of my Self as active, as producing effects on the external world. In apprehending my own acts of will, I connect a concept with a corresponding percept, viz., with the particular volition. In other words, by an act of thought I link up my individual faculty (my will) with the universal world-process. The content of a concept corresponding to an external percept appearing within the field of my experience, is given through intuition. Intuition is the source for the content of my whole conceptual system. The percept shows me only which concept I have to apply, in any given instance, out of the aggregate of my intuitions. The content of a concept is, indeed, conditioned by the percept, but it is not produced by it. On the contrary, it is intuitively given and connected with the percept by an act of thought. The same is true of the conceptual content of an act of will which is just as little capable of being deduced from this act. It is got by intuition. If now the conceptual intuition (ideal content) of my act of will occurs before the corresponding percept, then the content of what I do is determined by my ideas. The reason why I select from the number of possible intuitions just this special one, cannot be sought in an object of perception, but is to be found rather in the purely ideal interdependence of the members of my system of concepts. In other words, the determining factors for my will are to be found, not in the perceptual, but only in the conceptual world. My will is determined by my idea. The conceptual system which corresponds to the external world is conditioned by this external world. We must determine from the percept itself what concept corresponds to it; and how, in turn, this concept will fit in with the rest of my system of ideas, depends on its intuitive content. The percept thus conditions directly its concept and, thereby, indirectly also its place in the conceptual system of my world. But the ideal content of an act of will, which is drawn from the conceptual system and which precedes the act of will, is determined only by the conceptual system itself. An act of will which depends on nothing but this ideal content must itself be regarded as ideal, that is, as determined by an idea. This does not imply, of course, that all acts of will are determined only by ideas. All factors which determine the human individual have an influence on his will. In a particular act of will we must distinguish two factors: the motive, and the spring of action. The motive is the conceptual factor, the spring of action is the perceptual factor in will. The conceptual factor, or motive, is the momentary determining cause of an act of will, the spring of action is the permanent determining factor in the individual. The motive of an act of will can be only a pure concept, or else a concept with a definite relation to perception, i.e., an idea. Universal and individual concepts (ideas) become motives of will by influencing the human individual and determining him to action in a particular direction. One and the same concept, however, or one and the same idea, influences different individuals differently. They determine different men to different actions. An act of will is, therefore, not merely the outcome of a concept or an idea, but also of the individual make-up of human beings. This individual make-up we will call, following Edward van Hartmann, the “characterological disposition.” The manner in which concept and idea act on the characterological disposition of a man gives to his life a definite moral or ethical stamp. The characterological disposition consists of the more or less permanent content of the individual's life, that is, of his habitual ideas and feelings. Whether an idea which enters my mind at this moment stimulates me to an act of will or not, depends on its relation to my other ideal contents, and also to my peculiar modes of feeling. My ideal content, in turn, is conditioned by the sum total of those concepts which have, in the course of my individual life, come in contact with percepts, that is, have become ideas. This, again, depends on my greater or lesser capacity for intuition, and on the range of my perception, that is, on the subjective and objective factors of my experiences, on the structure of my mind and on my environment. My affective life more especially determines my characterological disposition. Whether I shall make a certain idea or concept the motive for action will depend on whether it gives me pleasure or pain. These are the factors which we have to consider in an act of will. The immediately present idea or concept, which becomes the motive, determines the end or the purpose of my will; my characterological disposition determines me to direct my activity towards this end. The idea of taking a walk in the next half-hour determines the end of my action. But this idea is raised to the level of a motive only if it meets with a suitable characterological disposition, that is, if during my past life I have formed the ideas of the wholesomeness of walking and the value of health; and further, if the idea of walking is accompanied by a feeling of pleasure. We must, therefore, distinguish (1) the possible subjective dispositions which are likely to turn given ideas and concepts into motives, and (2) the possible ideas and concepts which are capable of so influencing my characterological disposition that an act of will results. The former are for morality the springs of action, the latter its ends. The springs of action in the moral life can be discovered by analyzing the elements of which individual life is composed. The first level of individual life is that of perception, more particularly sense-perception. This is the stage of our individual lives in which a percept translates itself into will immediately, without the intervention of either a feeling or a concept. The spring of action here involved may be called simply instinct. Our lower, purely animal, needs (hunger, sexual intercourse, etc.) find their satisfaction in this way. The main characteristic of instinctive life is the immediacy with which the percept starts off the act of will. This kind of determination of the will, which belongs originally only to the life of the lower senses, may however become extended also to the percepts of the higher senses. We may react to the percept of a certain event in the external world without reflecting on what we do, and without any special feeling connecting itself with the percept. We have examples of this especially in our ordinary conventional intercourse with men. The spring of this kind of action is called tact or moral good taste. The more often such immediate reactions to a percept occur, the more the agent will prove himself able to act purely under the guidance of tact; that is, tact becomes his characterological disposition. The second level of human life is feeling. Definite feelings accompany the percepts of the external world. These feelings may become springs of action. When I see a hungry man, my pity for him may become the spring of my action. Such feelings, for example, are modesty, pride, sense of honour, humility, remorse, pity, revenge, gratitude, piety, loyalty, love, and duty. [A complete catalogue of the principles of morality (from the point of view of Metaphysical Realism) may be found in Edouard von Hartmann's Phanomenologie des sittlichen Bewusstseins. ] The third and last level of life is to have thoughts and ideas. An idea or a concept may become the motive of an action through mere reflection. Ideas become motives because, in the course of my life, I regularly connect certain aims of my will with percepts which recur again and again in a more or less modified form. Hence it is, that with men who are not wholly without experience, the occurrence of certain percepts is always accompanied also by the consciousness of ideas of actions, which they have themselves carried out in similar cases or which they have seen others carry out. These ideas float before their minds as determining models in all subsequent decisions; they become parts of their characterological disposition. We may give the name of practical experience to the spring of action just described. Practical experience merges gradually into purely tactful behaviour. That happens, when definite typical pictures of actions have become so closely connected in our minds with ideas of certain situations in life, that, in any given instance, we omit all deliberation based on experience, and pass immediately from the percept to the action. The highest level of individual life is that of conceptual thought without reference to any definite perceptual content. We determine the content of a concept through pure intuition on the basis of an ideal system. Such a concept contains, at first, no reference to any definite percepts. When an act of will comes about under the influence of a concept which refers to a percept, i.e., under the influence of an idea, then it is the percept which determines our action indirectly by way of the concept. But when we act under the influence of pure intuitions, the spring of our action is pure thought. As it is the custom in philosophy to call pure thought “reason,” we may perhaps be justified in giving the name of practical reason to the spring of action characteristic of this level of life. The clearest account of this spring of action has been given by Kreyenbuhl (Philosophische Monatshefte, vol. xviii, No. 3). In my opinion his article on this subject is one of the most important contributions to present-day philosophy, more especially to Ethics. Kreyenbuhl calls the spring of action, of which we are treating, the practical a priori, i.e., a spring of action issuing immediately from my intuition. It is clear that such a spring of action can no longer be counted in the strictest sense as part of the characterological disposition. For what is here effective in me as a spring of action is no longer something purely individual, but the ideal, and hence universal, content of my intuition. As soon as I regard the content as the valid basis and starting-point of an action, I pass over into willing, irrespective of whether the concept was already in my mind beforehand, or whether it only occurs to me immediately before the action, that is, irrespective of whether it was present in the form of a disposition in me or not. A real act of will results only when a present impulse to action, in the form of a concept or idea, acts on the characterological disposition. Such an impulse thereupon becomes the motive of the will. The motives of moral conduct are ideas and concepts. There are Moralists who see in feeling also a motive of morality; they assert, e.g., that the end of moral conduct is to secure the greatest possible quantity of pleasure for the agent. Pleasure itself, however, can never be a motive; at best only the idea of pleasure can act as motive. The idea of a future pleasure, but not the feeling itself, can act on my characterological disposition. For the feeling does not yet exist in the moment of action; on the contrary, it has first to be produced by the action. The idea of one's own or another's well-being is, however, rightly regarded as a motive of the will. The principle of producing the greatest quantity of pleasure for oneself through one's action, that is, to attain individual happiness, is called Egoism. The attainment of this individual happiness is sought either by thinking ruthlessly only of one's own good, and striving to attain it even at the cost of the happiness of other individuals (Pure Egoism), or by promoting the good of others, either because one anticipates indirectly a favourable influence on one's own happiness through the happiness of others, or because one fears to endanger one's own interest by injuring others (Morality of Prudence). The special content of the egoistical principle of morality will depend on the ideas which we form of what constitutes our own, or others' good. A man will determine the content of his egoistical striving in accordance with what he regards as one of life's good things (luxury, hope of happiness, deliverance from different evils, etc.). Further, the purely conceptual content of an action is to be regarded as yet another kind of motive. This content has no reference, like the idea of one's own pleasure, solely to the particular action, but to the deduction of an action from a system of moral principles. These moral principles, in the form of abstract concepts, may guide the individual's moral life without his worrying himself about the origin of his concepts. In that case, we feel merely the moral necessity of submitting to a moral concept, which, in the form of law, controls our actions. The justification of this necessity we leave to those who demand from us moral subjection, that is, to those whose moral authority over us we acknowledge (the head of the family, the state, social custom, the authority of the church, divine revelation). We meet with a special kind of these moral principles when the law is not proclaimed to us by an external authority, but comes from our own selves (moral autonomy). In this case we believe that we hear the voice, to which we have to submit ourselves, in our own souls. The name for this voice is conscience. It is a great moral advance when a man no longer takes as the motive of his action the commands of an external or internal authority, but tries to understand the reason why a given maxim of action ought to be effective as a motive in him. This is the advance from morality based on authority to action from moral insight. At this level of morality, a man will try to discover the demands of the moral life, and will let his action be determined by this knowledge. Such demands are (1) the greatest possible happiness of humanity as a whole purely for its own sake, (2) the progress of civilization, or the moral development of mankind towards ever greater perfection, (3) the realization of individual moral ends conceived by an act of pure intuition. The greatest possible happiness of humanity as a whole will naturally be differently conceived by different people. The above mentioned maxim does not imply any definite idea of this happiness, but rather means that every one who acknowledges this principle strives to do all that, in his opinion, most promotes the good of the whole of humanity. The progress of civilization is seen to be a special application of the moral principle just mentioned, at any rate for those to whom the goods which civilization produces bring feelings of pleasure. However, they will have to pay the price of progress in the destruction and annihilation of many things which also contribute to the happiness of humanity. It is, however, also possible that some men look upon the progress of civilization as a moral necessity, quite apart from the feelings of pleasure which it brings. If so, the progress of civilization will be a new moral principle for them, different from the previous one. Both the principle of the public good, and that of the progress of civilization, alike depend on the way in which we apply the content of our moral ideas to particular experiences (percepts). The highest principle of morality which we can conceive, however, is that which contains to start with, no such reference to particular experiences, but which springs from the source of pure intuition and does not seek until later any connection with percepts, i.e., with life. The determination of what ought to be willed issues here from a point of view very different from that of the previous two principles. Whoever accepts the principle of the public good will in all his actions ask first what his ideals contribute to this public good. The upholder of the progress of civilization as the principle of morality will act similarly. There is, however, a still higher mode of conduct which, in a given case, does not start from any single limited moral ideal, but which sees a certain value in all moral principles, always asking whether this or that is more important in a particular case. It may happen that a man considers in certain circumstances the promotion of the public good, in others that of the progress of civilization, and in yet others the furthering of his own private good, to be the right course, and makes that the motive of his action. But when all other grounds of determination take second place, then we rely, in the first place, on conceptual intuition itself. All other motives now drop out of sight, and the ideal content of an action alone becomes its motive. Among the levels of characterological disposition, we have singled out as the highest that which manifests itself as pure thought, or practical reason. Among the motives, we have just singled out conceptual intuition as the highest. On nearer consideration, we now perceive that at this level of morality the spring of action and the motive coincide, i.e., that neither a predetermined characterological disposition, nor an external moral principle accepted on authority, influence our conduct. The action, therefore, is neither a merely stereotyped one which follows the rules of a moral code, nor is it automatically performed in response to an external impulse. Rather it is determined solely through its ideal content. For such an action to be possible, we must first be capable of moral intuitions. Whoever lacks the capacity to think out for himself the moral principles that apply in each particular case, will never rise to the level of genuine individual willing. Kant's principle of morality: Act so that the principle of your action may be valid for all men—is the exact opposite of ours. His principle would mean death to all individual action. The norm for me can never be what all men would do, but rather what it is right for me to do in each special case. A superficial criticism might urge against these arguments: How can an action be individually adapted to the special case and the special situation, and yet at the same time be ideally determined by pure intuition? This objection rests on a confusion of the moral motive with the perceptual content of an action. The latter, indeed, may be a motive, and is actually a motive when we act for the progress of culture, or from pure egoism, etc., but in action based on pure moral intuition it never is a motive. Of course, my Self takes notice of these perceptual contents, but it does not allow itself to be determined by them. The content is used only to construct a theoretical concept, but the corresponding moral concept is not derived from the object. The theoretical concept of a given situation which faces me, is a moral concept also, only if I adopt the standpoint of a particular moral principle. If I base all my conduct on the principle of the progress of civilization, then my way through life is tied down to a fixed route. From every occurrence which comes to my notice and attracts my interest, there springs a moral duty, viz., to do my tiny share towards using this occurrence in the service of the progress of civilization. In addition to the concept which reveals to me the connections of events or objects according to the laws of nature, there is also a moral label attached to them which contains for me, as a moral agent, ethical directions as to how I have to conduct myself. At a higher level these moral labels disappear, and my action is determined in each particular instance by my idea; and more particularly by the idea which is suggested to me by the concrete instance. Men vary greatly in their capacity for intuition. In some, ideas bubble up like a spring, others acquire them with much labour. The situations in which men live, and which are the scenes of their actions, are no less widely different. The conduct of a man will depend, therefore, on the manner in which his faculty of intuition reacts to a given situation. The aggregate of the ideas which are effective in us, the concrete content of our intuitions, constitute that which is individual in each of us, notwithstanding the universal character of our ideas. In so far as this intuitive content has reference to action, it constitutes the moral substance of the individual. To let this substance express itself in his life is the moral principle of the man who regards all other moral principles as subordinate. We may call this point of view Ethical Individualism. The determining factor of an action, in any concrete instance, is the discovery of the corresponding purely individual intuition. At this level of morality, there can be no question of general moral concepts (norms, laws). General norms always presuppose concrete facts from which they can be deduced. But facts have first to be created by human action. When we look for the regulating principles (the conceptual principles guiding the actions of individuals, peoples, epochs), we obtain a system of Ethics which is not a science of moral norms, but rather a science of morality as a natural fact. Only the laws discovered in this way are related to human action as the laws of nature are related to particular phenomena. These laws, however, are very far from being identical with the principles on which we base our actions. When I, or another, subsequently review my action we may discover what moral principles came into play in it. But so long as I am acting, I am influenced not by these moral principles but by my love for the object, which I want to realize through my action. I ask no man and no moral code, whether I shall perform this action or not. On the contrary, I carry it out as soon as I have formed the idea of it. This alone makes it my action. If a man acts because he accepts certain moral norms, his action is the outcome of the principles which compose his moral code. He merely carries out orders. He is a superior kind of automaton. Inject some stimulus to action into his mind, and at once the clock-work of his moral principles will begin to work and run its prescribed course, so as to issue in an action which is Christian, or humane, or unselfish, or calculated to promote the progress of culture. It is only when I follow solely my love for the object, that it is I, myself, who act. At this level of morality, I acknowledge no lord over me, neither an external authority, nor the so-called voice of my conscience. I acknowledge no external principle of my action, because I have found in myself the ground for my action, viz., my love of the action. I do not ask whether my action is good or bad; I perform it, because I am in love with it. Neither do I ask myself how another man would act in my position. On the contrary, I act as I, this unique individuality, will to act. No general usage, no common custom, no general maxim current among men, no moral norm guides me, but my love for the action. I feel no compulsion, neither the compulsion of nature which dominates me through my instincts, nor the compulsion of the moral commandments. My will is simply to realize what in me lies. Those who hold to general moral norms will reply to these arguments that, if every one has the right to live himself out and to do what he pleases, there can be no distinction between a good and a bad action, every fraudulent impulse in me has the same right to issue in action as the intention to serve the general good. It is not the mere fact of my having conceived the idea of an action which ought to determine me as a moral agent, but the further examination of whether it is a good or an evil action. Only if it is good ought I to carry it out. In reply I would say that I am not talking of children or of men who follow their animal or social instincts. I am talking of men who are capable of raising themselves to the level of the ideal content of the world. It is only in an age in which immature men regard the blind instincts as part of a man's individuality, that the act of a criminal can be described as living out one's individuality in the same sense in which the embodiment in action of a pure intuition can be so described. The animal instinct which drives a man to a criminal act does not belong to what is individual in him, but rather to that which is most general in him, to that which is equally present in all individuals. The individual element in me is not my organism with its instincts and feelings, but rather the unified world of ideas which reveals itself through this organism. My instincts, cravings, passions, justify no further assertion about me than that I belong to the general species man. The fact that something ideal expresses itself in its own unique way through these instincts, passions, and feelings, constitutes my individuality. My instincts and cravings make me the sort of man of whom there are twelve to the dozen. The unique character of the idea, by means of which I distinguish myself within the dozen as “I,” makes of me an individual. Only a being other than myself could distinguish me from others by the difference in my animal nature. By thought, i.e., by the active grasping of the ideal element working itself out through my organism, I distinguish myself from others. Hence it is impossible to say of the action of a criminal that it issues from the idea within him. Indeed, the characteristic feature of criminal actions is precisely that they spring from the non-ideal elements in man. An act the grounds for which lie in the ideal part of my individual nature is free. Every other act, whether done under the compulsion of nature or under the obligation imposed by a moral norm, is unfree. That man alone is free who in every moment of his life is able to obey only himself. A moral act is my act only when it can be called free in this sense. Action on the basis of freedom does not exclude, but include, the moral laws. It only shows that it stands on a higher level than actions which are dictated by these laws. Why should my act serve the general good less well when I do it from pure love of it, than when I perform it because it is a duty to serve the general good? The concept of duty excludes freedom, because it will not acknowledge the right of individuality, but demands the subjection of individuality to a general norm. Freedom of action is conceivable only from the standpoint of Ethical Individualism. But how about the possibility of social life for men, if each aims only at asserting his own individuality? This question expresses yet another objection on the part of Moralism. The Moralist believes that a social community is possible only if all men are held together by a common moral order. This shows that the Moralist does not understand the community of the world of ideas. He does not realize that the world of ideas which inspires me is no other than that which inspires my fellow-men. I differ from my neighbour, not at all because we are living in two entirely different mental worlds, but because from our common world of ideas we receive different intuitions. He desires to live out his intuitions, I mine. If we both draw our intuitions really from the world of ideas, and do not obey mere external impulses (physical or moral), then we can not but meet one another in striving for the same aims, in having the same intentions. A moral misunderstanding, a clash of aims, is impossible between men who are free. Only the morally unfree who blindly follow their natural instincts or the commands of duty, turn their backs on their neighbours, if these do not obey the same instincts and the same laws as themselves. Live and let live is the fundamental principle of the free man. He knows no “ought.” How he shall will in any given case will be determined for him by his faculty of ideas. If sociability were not deeply rooted in human nature, no external laws would be able to inoculate us with it. It is only because human individuals are akin in spirit that they can live out their lives side by side. The free man lives out his life in the full confidence that all other free men belong to one spiritual world with himself, and that their intentions will coincide with his. The free man does not demand agreement from his fellow-men, but he expects it none the less, believing that it is inherent in human nature. There are many who will say that the concept of the free man which I have here developed, is a chimera nowhere to be found realized, and that we have got to deal with actual human beings, from whom we can expect morality only if they obey some moral law, i.e., if they regard their moral task as a duty and do not simply follow their inclinations and loves. I do not deny this. Only a blind man could do that. But, if so, away with all this hypocrisy of morality! Let us say simply that human nature must be compelled to act as long as it is not free. Whether the compulsion of man's unfree nature is effected by physical force or through moral laws, whether man is unfree because he indulges his unmeasured sexual desire, or because he is bound tight in the bonds of conventional morality, is quite immaterial. Only let us not assert that such a man can rightly call his actions his own, seeing that he is driven to them by an external force. But in the midst of all this network of compulsion, there arise free spirits who in all the welter of customs, legal codes, religious observances, etc., learn to be true to themselves. They are free in so far as they obey only themselves; unfree in so far as they submit to control. Which of us can say that he is really free in all his actions? Yet in each of us there dwells something deeper in which the free man finds expression. Our life is made up of free and unfree actions. We cannot, however, form a final and adequate concept of human nature without coming upon the free spirit as its purest expression. After all, we are men in the fullest sense only in so far as we are free. This is an ideal, many will say. Doubtless; but it is an ideal which is a real element in us working up to the surface of our nature. It is no ideal born of mere imagination or dream, but one which has life, and which manifests itself clearly even in the least developed form of its existence. If men were nothing but natural objects, the search for ideals, that is, for ideas which as yet are not actual but the realization of which we demand, would be an impossibility. In dealing with external objects the idea is determined by the percept. We have done our share when we have recognized the connection between idea and percept. But with a human being the case is different. The content of his existence is not determined without him. His concept (free spirit) is not a priori united objectively with the perceptual content “man,” so that knowledge need only register the fact subsequently. Man must by his own act unite his concept with the percept “man.” Concept and percept coincide with one another in this instance, only in so far as the individual himself makes them coincide. This he can do only if he has found the concept of the free spirit, that is, if he has found the concept of his own Self. In the objective world a boundary-line is drawn by our organization between percept and concept. Knowledge breaks down this barrier. In our subjective nature this barrier is no less present. The individual overcomes it in the course of his development, by embodying his concept of himself in his outward existence. Hence man's moral life and his intellectual life lead him both alike to his twofold nature, perception (immediate experience) and thought. The intellectual life overcomes his twofold nature by means of knowledge, the moral life succeeds through the actual realization of the free spirit. Every being has its inborn concept (the laws of its being and action), but in external objects this concept is indissolubly bound up with the percept, and separated from it only in the organization of human minds. In human beings concept and percept are, at first, actually separated, to be just as actually reunited by them. Some one might object that to our percept of a man there corresponds at every moment of his life a definite concept, just as with external objects. I can construct for myself the concept of an average man, and I may also have given to me a percept to fit this pattern. Suppose now I add to this the concept of a free spirit, then I have two concepts for the same object. Such an objection is one-sided. As object of perception I am subject to perpetual change. As a child I was one thing, another as a youth, yet another as a man. Moreover, at every moment I am different, as percept, from what I was the moment before. These changes may take place in such a way that either it is always only the same (average) man who exhibits himself in them, or that they represent the expression of a free spirit. Such are the changes which my actions, as objects of perception, undergo. In the perceptual object “man” there is given the possibility of transformation, just as in the plant-seed there lies the possibility of growth into a fully developed plant. The plant transforms itself in growth, because of the objective law of nature which is inherent in it. The human being remains in his undeveloped state, unless he takes hold of the material for transformation within him and develops himself through his own energy. Nature makes of man merely a natural being; Society makes of him a being who acts in obedience to law; only he himself can make a free man of himself. At a definite stage in his development Nature releases man from her fetters; Society carries his development a step further; he alone can give himself the final polish. The theory of free morality, then, does not assert that the free spirit is the only form in which man can exist. It looks upon the freedom of the spirit only as the last stage in man's evolution. This is not to deny that conduct in obedience to norms has its legitimate place as a stage in development. The point is that we cannot acknowledge it to be the absolute standpoint in morality. For the free spirit transcends norms, in the sense that he is insensible to them as commands, but regulates his conduct in accordance with his impulses (intuitions). When Kant apostrophizes duty: “Duty! Thou sublime and mighty name, that dost embrace nothing charming or insinuating, but requirest submission,” thou that “holdest forth a law ... before which all inclinations are dumb, even though they secretly counter-work it,” [Translation by Abbott, Kant's Theory of Ethics, p. 180; Critique of Pure Practical Reason, chap. iii.] then the free spirit replies: “Freedom! thou kindly and humane name, which dost embrace within thyself all that is morally most charming, all that insinuates itself most into my humanity, and which makest me the servant of nobody, which holdest forth no law, but waitest what my inclination itself will proclaim as law, because it resists every law that is forced upon it.” This is the contrast of morality according to law and according to freedom. The Philistine who looks upon the state as embodied morality is sure to look upon the free spirit as a danger to the state. But that is only because his view is narrowly focused on a limited period of time. If he were able to look beyond, he would soon find that it is but on rare occasions that the free spirit needs to go beyond the laws of his state, and that it never needs to confront them with any real contradiction. For the laws of the state, one and all, have had their origin in the intuitions of free spirits, just like all other objective laws of morality. There is no traditional law enforced by the authority of a family, which was not, once upon a time, intuitively conceived and laid down by an ancestor. Similarly the conventional laws of morality are first of all established by particular men, and the laws of the state are always born in the brain of a statesman. These free spirits have set up laws over the rest of mankind, and only he is unfree who forgets this origin and makes them either divine commands, or objective moral duties, or the authoritative voice of his own conscience. He, on the other hand, who does not forget the origin of laws, but looks for it in man, will respect them as belonging to the same world of ideas which is the source also of his own moral intuitions. If he thinks his intuitions better than the existing laws, he will try to put them into the place of the latter. If he thinks the laws justified, he will act in accordance with them as if they were his own intuitions. Man does not exist in order to found a moral order of the world. Anyone who maintains that he does, stands in his theory of man still at that same point, at which natural science stood when it believed that a bull has horns in order that it may butt. Scientists, happily, have cast the concept of objective purposes in nature into the limbo of dead theories. For Ethics, it is more difficult to achieve the same emancipation. But just as horns do not exist for the sake of butting, but butting because of horns, so man does not exist for the sake of morality, but morality exists through man. The free man acts because he has a moral idea, he does not act in order to be moral. Human individuals are the presupposition of a moral world order. The human individual is the fountain of all morality and the centre of all life. State and society exist only because they have necessarily grown out of the life of individuals. That state and society, in turn, should react upon the lives of individuals, is no more difficult to comprehend, than that the butting which is the result of the existence of horns, reacts in turn upon the further development of the horns, which would become atrophied by prolonged disuse. Similarly the individual must degenerate, if he leads an isolated existence beyond the pale of human society. That is just the reason why the social order arises, viz., that it may react favourably upon the individual. |
| 31. Collected Essays on Cultural and Contemporary History 1887–1901: Discreet Anti-Semitism
13 Nov 1901, |
|---|
| IV Friedrich Paulsen once characterized the dark sides of our present day in treacherous words. In his essay "Kant, the philosopher of Protestantism", he says: "The signature of our century, which is drawing to a close, is: belief in power, disbelief in ideas. At the end of the last century, the hands of time stood the other way round: belief in ideas was dominant, Rousseau, Kant, Goethe, Schiller were the great powers of the time. Today, after the failure of the ideological revolutions of 1789 and 1848, after the successes of power politics, the keyword is the will to power." |
| 31. Collected Essays on Cultural and Contemporary History 1887–1901: Discreet Anti-Semitism
13 Nov 1901, |
|---|
IAntisemitism does not exactly have a great store of ideas, not even of witty phrases and catchphrases. One has to hear the same stale platitudes over and over again when the advocates of this "view of life" express the dull feelings of their breast. One experiences peculiar phenomena. You may think what you like about Eugen Dühring, but those who know him must be clear about one thing: he is a thinker who is thoroughly versed in many scientific fields, highly stimulating in mathematical and physical questions and original in many respects. As soon as he starts talking about things in which his anti-Semitism comes into play, he becomes as flat as a little anti-Semitic agitator in what he says. He differs from such a person only in the way he presents his platitudes, in the brilliance of his style. Having such paragon writers is of particular value to the anti-Semites. There is hardly any other party tendency where there is more constant reference to authorities than in this one. This or that person has said this or that derogatory word about the Jews; this is something that is always recurring in the publications of the anti-Semites. So it was particularly convenient for these people when they were able to track down some of the old glittering phrases of anti-Semitism in a book by a German university lecturer, and one who enjoys a certain reputation in the widest circles, in the "System der Ethik mit einem Umriß der Staats- und Gesellschaftslehre" by the Berlin professor Friedrich Paulsen. - Indeed, in the first chapter of the fourth book of the aforementioned ethics, one encounters sentences that could have been said - perhaps somewhat less elegantly - by an anti-Semitic agitator among beer philistines in a small town or written - albeit also less elegantly - by the corner editor of an anti-Semitic newspaper. And they can be read in a philosophical theory of morals, written by a German professor of philosophy and pedagogy who gives well-attended lectures, who writes books that are widely acclaimed, and who is even considered by many to be one of the best philosophers of our time. He writes what we have heard so often: "Different by descent, religion and historical past, they" (the Jews) "formed a foreign protective citizenship in the European states for centuries. Admission to citizenship was apparently based on equality not only of language and education, but above all of their political aspirations with those of the population group that had gained decisive influence on state life since 1848. With the change in the political constellation since 1866, the view of the position of the Jews in relation to the nation states has changed in wide circles of the population. If I am not mistaken, the mood of antipathy towards the Jews depends in no small measure on the instinctive feeling that the Jew does not see his future, the future of his family, as exclusively connected with the future of the state or people under which he lives, as other citizens do: If Hungary were to become Russian today, the hitherto Hungarian Jew would soon find himself in being a Russian Jew now, or he would shake the Hungarian soil from his feet and move to Vienna or Berlin or Paris, and be an Austrian, German or French Jew for the time being." If I happened to open Paulsen's "System of Ethics" at the place where these remarks appear, without knowing the whole context in which they are found, I would first be astonished that a contemporary philosopher would dare to write things of this kind in a serious book. For, first of all, there is something striking about these sentences that would suggest anything other than that they originate from a philosopher whose first and most necessary tool is supposed to be an uncontradictory logic. But to be logical means above all to examine the contradictions in real life more closely, to trace them back to their real causes. One may ask: may a philosopher do what Professor Paulsen does: simply register the change in two successive moods of the times, which contradict each other thoroughly, without uncovering the causes of this change or at least making an attempt to uncover them? The liberal views that came to the surface of historical development in 1848 brought with them the conviction that the Jews were "equal in language and education" and even in "political aspirations" with the Western peoples. A later period created a "mood averse to the Jews" in many circles. Paulsen makes it easy to understand this change. He attributes it to an "instinctive feeling", which he then describes in more detail. We will see in a sequel to this essay what this "instinctive feeling" is really all about. For now, let us just point out the inadmissibility of referring to "instinctive feelings" in a philosophical presentation of the "doctrine of morals", the basis and justification of which are not examined. After all, it is precisely the business of the philosopher to bring to clear conceptions what settles in other people's minds as unclear ideas. But Paulsen does not even attempt to do this. He simply makes the "instinctive feelings" that he thought he perceived his own and then says, quite worthy of the vague, unphilosophical pre-sentences: "Only when the Jews become completely settled... will the feeling of the abnormality of their citizenship disappear completely. Whether this can happen without the abandonment of the old national religious practice is, however, doubtful. After reading this sentence, I have only one question: whether it is not outrageous to say something so irrelevant in such a place, in a book that is intended for so many in an important matter? For one wonders what Professor Paulsen actually claimed. He has said nothing but that he believes he perceives "instinctive feelings" and that he cannot form an opinion about what is to become. If you want to take that as philosophical, you can. I think it is more philosophical to remain silent about things in which I have to confess so openly that I have no opinion. As I said, someone who only reads one passage in Paulsen's book would have to say that. And he would be right at first. In a second part of this article, we want to show how Paulsen's version appears in the light of the rest of his thought, and then how it appears in the light of German intellectual life in recent decades. I hope that in such an examination one will find a not uninteresting chapter on the "psychology of anti-Semitism". IIThose dull sentiments from which, among all other things, anti-Semitism springs, have the peculiarity that they undermine all straightforwardness and simplicity of judgment. Perhaps no social phenomenon in recent times has demonstrated this better than anti-Semitism itself. I was in a position to do so during my years as a student in Vienna some twenty years ago. It was the time when the Lower Austrian landowner Georg von Schönerer, who until then had mainly been a radical democrat, became a "national" anti-Semite. It will not be easy to explain this change in Sch6nerer himself. Anyone who has had the opportunity to observe this man in his public activities knows that he is a completely unpredictable character, for whom personal whim is more important than political thought, who is completely dominated by an unlimited vanity. It is not this man's own transformations, but rather the transformations of those who became his followers, that are a significant fact in the history of the development of the new anti-Semitism. Before Schönerer's appearance, it was easy to talk to young people in Vienna who had grown up under the influence of liberal sentiments. There was a genuine sense of freedom based on reason in this part of the youth. Anti-Semitic instincts also existed at that time. These instincts were not lacking in the more distinguished part of the German bourgeoisie either. But everywhere they were on the way to seeing such instincts as unjustified and overcoming them. It was clear that such things were remnants of a less advanced age that should not be indulged. In any case, it was clear that everything that was said with the claim to public validity should not have grown out of the kind of sentiment that anti-Semitism had, of which a person with a true claim to education would have been truly ashamed. Schönerer had an effect on the student youth and, moreover, initially on classes of the population that were not very intellectually advanced. The people who switched from freer views of life to his unclear manner suddenly began to speak in a completely different key. People who had previously been heard to declaim about "true human dignity", "humanity" and the "liberal achievements of the age" now began to speak unreservedly of feelings, of antipathies, which were like black and white to their earlier declamations and to which they would not have confessed shortly before without blushing with shame. A point had been reached in the spiritual life of such people which I would prefer to characterize by saying that strict logic has been removed from the ranks of the powers that rule man inwardly. You can see this for yourself at any moment. None of those who had just crossed over into the anti-Semitic camp dared to seriously argue against their former liberal principles. On the contrary, each of them claimed that in essence he was still committed to these principles, but as far as the application of these principles to the Jews was concerned, yes... And then came some kind of phrase that smacked every sane person in the face. Logic has been dethroned by anti-Semitism. For someone who, like me, has always been very sensitive to sins against logic, dealing with such people has now become particularly embarrassing. Lest one or the other think they can make bad jokes about this sentence, I would like to say that I am allowed to confess my nervousness about illogic without any immodesty. For I regard "logical thinking" as a general human duty and the particular nervousness in such matters as a disposition for which one can do as little as for one's muscular strength. But because of my nervousness, I myself was able to study the development of anti-Semitism using a particular example - I would say intimately. Every day I saw countless examples of the corruption of logical thinking by dull feelings. I know that I am only talking about one example here. Things have happened differently in many other places. But I believe that you can only truly understand something if you have experienced it intimately somewhere. And I am perhaps particularly well prepared to judge the "Paulsen case" through these "studies" of mine. All due respect to the professor. But there is a worrying logical conflict in his case. Not as blatant as with my peers who converted from liberalism to Schönererianism. That goes without saying. But I think: the milder case of Paulsen is put into perspective by the more blatant case. In the second book of his "System of Ethics", in the essay on the concepts of "good and evil", Paulsen writes: "A person's behavior is morally good if it objectively tends to promote the overall welfare, and subjectively if it is accompanied by a sense of duty or moral necessity." Shortly before this, Paulsen writes about the sentence "The end justifies the means": "If one understands the sentence in this way: not just any permitted end, but the end justifies the means; but there is only one end from which all determination of value proceeds, namely the highest good, the welfare or the most perfect organization of human life." Can there be a bridge from these two sentences to the views that the aversion to the Jews brings about? Should one not, in the truly logical progress of thought, energetically demand the purification of such aversion through reason? What does Paulsen do instead? He says: "With the change in the political constellation since 1866, the view of the position of the Jews in relation to the nation states has changed in wider circles of the population." Should he not now regard this change as a departure from his moral ideal, from devotion to the one end that truly justifies the means? Liberalism has taken the belief in the "most perfect organization of human life" as a moral ideal seriously. This seriousness, however, does not permit a change such as that which has occurred since 1866. It makes it impossible to arbitrarily limit humanity in any way. This is where Paulsen, in order not to become bitter against anti-Semitism, becomes lukewarm against logic. I will save further elaboration on this logical fissure for the end of this article. IIIThere must be deeper reasons in the intellectual culture of the present for the fact that a judgment such as that of Professor Paulsen on the Jews is possible within a work that claims to be at the height of contemporary philosophical education. Anyone who follows the course of intellectual development in the nineteenth century will, with some impartiality, easily be led to these reasons. There were always two currents in this development. One was in a straight line the successor to the "Enlightenment" of the eighteenth century; the other was a kind of counter-current to the results of the Enlightenment. The eternal merit of the latter will be to have held up the "pure, harmonious humanity" itself to man as the highest ideal. It is a moral demand of incomparable height to say that one should refrain from all accidental contexts in which man is placed and seek to emphasize the "pure human being" in everything, in the family, society, nation, and so on. Of course, those who say this know just as well as the wise philistines that ideals cannot be realized in direct life. But is it nonsensical to speak of the circle in geometry, because you can only draw a very imperfect circle on paper with a pencil? No, it is not absurd at all. Rather, it is extremely foolish to emphasize such a self-evident fact. It is equally foolish to speak in ethics of what cannot be because of the incompleteness of everything that is real. What is truly valuable here is only to state the goals that one wants to approach. This is what the Enlightenment did. This view was contrasted with the other, which sought its roots in the consideration of historical development. When one speaks of this, one touches on great errors in the education of the nineteenth century, which are connected with great virtues. One need only mention the names of Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm to recall the full meaning of the phrase: nineteenth-century man learned to understand his own past, he learned to understand what he is now through what he once was. The Brothers Grimm introduced us to our linguistic, our mythical past. Their conviction is contained in the beautiful words: "A good angel is given to man from his native land, who, when he sets out into life, accompanies him under the familiar guise of a fellow traveler; he who does not suspect what good will befall him as a result may feel it when he crosses the border of his fatherland, where he is left by that angel. This benevolent companionship is the inexhaustible wealth of fairy tales, legends and history." We know that in the nineteenth century such views were vigorously pursued. The arbitrary ideas that Rousseau's contemporaries had formed about the original states of mankind were replaced by observations of real conditions. Linguistics, religious studies, general cultural history and the history of peoples made the greatest progress. Research was carried out in all directions to find out how man had developed. Only a fool could underestimate all this. But it also revealed a deficiency in our views of life that must not be overlooked. Knowledge of the past should have merely enriched our knowledge; instead, it influenced the motives of our actions. Thinking about what happened to me yesterday becomes a stumbling block if it robs me of the impartiality of my decisions today. If I do not act today according to the circumstances that confront me, but according to what I did yesterday, then I am on the wrong track. If I want to act, I should not look at my diary, but at reality. The present can be seen from the perspective of the past, but it cannot be controlled from it. In one of his interesting writings, Friedrich Nietzsche's "Unzeitgemäßen Betrachtung" (Untimely Reflection) on the "benefits and harms of history for life" sheds light on the damage that occurs when the present is to be mastered through the past. Whoever has open eyes for the present knows that it is wrong to think that the solidarity of the Jews among themselves is greater than their solidarity with modern cultural endeavors. Even if this has been the case in recent years, anti-Semitism has made a significant contribution to this. Anyone who, like me, has seen with horror what anti-Semitism has done to the minds of noble Jews must have come to this conclusion. When Paulsen expresses a view such as that of the special interests of the Jews, he only shows that he does not know how to observe impartially. Let us not allow our judgment of how we should live together in the present to be clouded by our ideas that we have undergone separate developments in the past. Why do we encounter a certain bashful anti-Semitism within the educated world where the study of history is taken as a starting point? The future will certainly bring nothing other than the effects of the past; but where does the rule prevail in nature that the effects are equal to their causes? Whoever considers Paulsen's entire way of thinking will have to admit that he is an isolated phenomenon within the circles of so-called historical education. I will substantiate this in particular in a concluding statement. IVFriedrich Paulsen once characterized the dark sides of our present day in treacherous words. In his essay "Kant, the philosopher of Protestantism", he says: "The signature of our century, which is drawing to a close, is: belief in power, disbelief in ideas. At the end of the last century, the hands of time stood the other way round: belief in ideas was dominant, Rousseau, Kant, Goethe, Schiller were the great powers of the time. Today, after the failure of the ideological revolutions of 1789 and 1848, after the successes of power politics, the keyword is the will to power." There is no doubt that our time does not understand the mission of true idealism. Goethe once said that anyone who has really grasped the meaning of an idea will not allow any apparent contradiction with experience to rob him of his faith in it. Experience must submit to the idea once it has been recognized as correct. At present, such an idea has little appeal. Ideas have lost their power in our imagination. People point to "practical interests", to what "can prevail". One should consider that the history of intellectual progress itself, when seen from the right point of view, proves the power of ideas. Let me point to a striking example. When Copernicus put forward the great idea of the orbits of the planets around the sun, anything could be objected to it from the point of view of astronomical practice. Some of the facts about which people had experience contradicted the doctrine that Copernicus put forward. From the point of view of the practical astronomer, it was not Copernicus who was right at the time, but Tycho Brahe, who replied: "The earth is a coarse, heavy mass that is awkward to move, so how can Copernicus make a star out of it and guide it around in the skies?" Historical developments proved Copernicus right because, seeing through the correctness of the idea he had once conceived, he rose to the belief that later facts would eliminate the apparent contradiction. As it is with ideas in scientific progress, so it must be with them in moral life. Paulsen also admits this in theory by defending the above-mentioned proposition. He deviates from it in practice when he presents anti-Semitism as a partially justified phenomenon. Those who believe in the ideas cannot allow themselves to be distracted by the historical development of the last decades in the unconditional validity of these ideas. He would have to say to himself: things may be such for the time being that reality seems to contradict the absolutely liberal ideas; these ideas are independent of such contradiction. Anti-Semitism is a mockery of all faith in ideas. Above all, it makes a mockery of the idea that humanity is higher than any individual form (tribe, race, people) in which humanity lives itself out. But where are we heading if the philosophers, these bearers of the world of ideas, these appointed advocates of idealism, no longer have the proper trust in the ideas themselves? What will happen if they allow themselves to be robbed of this trust by the fact that, for a few decades, the instincts of a certain mass of people take a different path to that indicated by these ideas? A man like Paulsen can only be led to assertions such as those for which I have written these remarks by an excessive respect for historical reality. In the contradiction in which he sets himself to his own assertions, Paulsen shows quite clearly that he is under the spell of the false historical education I have characterized. He does not set out to criticize the historical development of popular instincts; on the contrary, he allows these popular instincts to have their say. That this is the case is also sufficiently expressed in the vague way in which Paulsen talks about antipathies towards the Jews. This way of speaking can certainly be recognized as "bashful anti-Semitism". Nowhere is it more necessary than in this area to document one's belief in the ideas through a decisive, unambiguous statement. One rightly complains that philosophy enjoys a low reputation in the present day. It would deserve this low esteem if it lost faith in what it has to guard above all, the ideas. The philosopher must understand his time. He does not understand it by making concessions to its perversities, but only by opposing these perversities with the criticism that comes to him from his world of ideas. The philosophical moral teacher should treat everything that the anti-Semites claim about the Jews in the same way as the mineralogist, who will also claim that salt forms cube-shaped crystals if someone shows him a salt crystal that has had its corners chipped off due to some circumstances. Antisemitism is not only a danger for Jews, it is also a danger for non-Jews. It stems from a mindset that is not serious about sound, straightforward judgment. It promotes such an attitude. And anyone who thinks philosophically should not stand by and watch. Belief in ideas will only come into its own again when we fight the unbelief that opposes it as vigorously as possible in all areas. It is painful to see a philosopher contradicting the very principles that he himself has clearly and excellently characterized. I do not believe that it is easy for a man like Paulsen to be intensely committed to anti-Semitism. Like so many others, the philosophical spirit protects him from this. But at present more is needed in this matter. Any vague attitude is evil. The anti-Semites will use the utterances of any personality as grist to their mill if that personality gives them cause to do so even by an indeterminate utterance. Now the philosopher can always say that he is not responsible for what others make of his teachings. That is undoubtedly to be admitted. But if a philosophical moral teacher intervenes in the current issues of the day, then in certain matters his position must be clear and unambiguous. And with anti-Semitism as a cultural disease, the situation today is such that no one who meditates in public matters should be in doubt as to how to interpret his statements about it. |
| 93a. Foundations of Esotericism: Lecture XXIII
25 Oct 1905, Berlin Translated by Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett |
|---|
| One part severed itself and the Earth emerged out of the Sun. It is at this point that the Kant-Laplace theory is relevant. The earth was in a nebulous condition coinciding with the Kant-Laplace theory. |
| 93a. Foundations of Esotericism: Lecture XXIII
25 Oct 1905, Berlin Translated by Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett |
|---|
Let us call to mind the point of time when, in the middle of the Lemurian Race, man raised himself up to spirituality. Now for the first time fructification with the Spirit, with the Monad became possible. Gradually, out of the chaotic Earth, through what had been separated off from man, the other beings had been formed which lived on the Earth as his companions. Man had developed a physical body, an etheric body and an astral body. The astral body had become purified and was just at that time adapted to receive Manas, Buddhi, Atma. On the Earth everything developed quite gradually, so that mankind, still without intellect or possibility of speech, arose out of the uncoordinated Earth mass. Now we ask: How did this come about? A plant too does not grow out of nothing. A seed must be planted into the Earth. This was also the case with the people who were there at that time. The human being too had grown up out of the Earth and for this a seed had to be there on the Earth. Once a similar being had already existed. This seed-man had arisen on the Old Moon. From there he passed over in the seed condition, went through a Pralaya and then appeared once more on the Earth. The development of the Earth had three preliminary stages: (Old Saturn, Sun and Moon). In the first three Earth Rounds these stages had a short recapitulation. In the First Earth Epoch the Saturn existence was repeated, in the Second Epoch the Sun existence and in the Third Epoch the Moon existence. It was only in the Fourth Round that the actual Earth existence emerged and then man had reached a somewhat higher stage than on the Old Moon. There he had not yet reached separate development, he had not yet become sufficiently purified to receive the Monad. On the Moon the astral body was still wild and passionate. On the Earth he had still to purify himself in order to be able to receive the higher principles. This purification was completed in the middle of the Lemurian Age. The last human beings during the Old Moon existence are our physical forefathers. On the Earth they now developed somewhat further. The Earth-men of the pre-Lemurian Age are the actual descendants of the inhabitants of the Moon. This is why we call the inhabitants of the Moon the Fathers or Pitris of Earth-Men. These Earth-Men were as yet unable to use their front limbs for work. They were of animal-like form having a certain great beauty. Their substance was much softer than the physical matter of today: it was very much softer than what we now find with the lower animals. They were irradiated and an inner fire shone through them. When human beings were going through an earlier stage of evolution, they were still more beautiful and nobler in their form. During the Age which preceded the Lemurian Age, we have the Hyperborean Age on the Earth, that of the Sun Men, of the Apollo-Men. They were formed out of a still nobler and even more delicate substance. Then we go still further back to the very first Race, to the Polarian men. At that time they lived in the tropical polar climate, a Race which was able to attain to special heights through the fact that a remarkable and great help had been granted them. The most beautiful of the Moon Pitris descended to the Earth. The Polarian human beings were very similar to four-footed animals, but they were formed out of a soft, pliant substance similar to a jellyfish, but much warmer. The human beings with the best forms, consisting of the noblest components, received at that time help of a special nature, for beings were still connected with the Earth who had earlier reached a higher stage. All esotericism recognises that the Sun was first a planet; it only later became a fixed star. The sequence of stages that the Earth has passed through is: Old Saturn, Old Sun, Old Moon, Earth. When the Sun was itself a planet, then everything which is now on the Moon and Earth was still in the Sun. Later Sun and Moon separated themselves from the Earth. Let us think back to the time of the Old Sun. Then everything which now lives on the Earth, dwelt on the Sun. The beings were then quite differently formed, having only a physical body, much less dense than it is now, and an etheric body. Man's whole way of life was plant-like. The beings lived in the light of the Sun. Light came to them from the centre of their own planet. They were totally different from present-day man. In comparison with present-day man the Sun-man stood upside down and the Sun shone upon his head. Everything connected with reproduction developed freely on the other side. Man at that time stretched his legs, so to say, into the air. The plant has remained at this stage, its roots are in the earth and it stretches its organs of reproduction, stamens and pistil, into the air (plant). This Sun-man developed in seven different stages. His direction on the planet is the same as the growth of the plant on the Earth. Then, with the third incarnation of the Earth he became a Moon-man. He bent over, the vertical becoming the horizontal (animal). The tendency towards a spine developed. The symbol for this is the Tau = T. On the Earth he turns completely round. For this the symbol is the Cross. The symbolism of the Cross depicts the development from the Sun, through the Moon to the Earth. On the Earth the symbol of the Cross was attained by the addition of the upper vertical member above the T. This developed further in the bearing of the Cross on the shoulders. The Sun-men too had attained a certain high development. There were also Sun Adepts, who had progressed further than the other Sun-men. They passed over to the Moon. There also they had the possibility of being on a higher level than the Moon-men, and they developed to quite special heights. They were the forefathers of the Earth-men, but had hastened much further ahead. When now in the second Epoch of the Fourth Round the Hyperboreans lived in their soft forms, these Sons of the Sun were in position to incarnate and they formed a particularly beautiful Race. They were the Solar Pitris. Already in the Hyperborean Epoch they created for themselves an upright form, completely transforming the Hyperborean bodies. This the other human beings were unable to do. In the Hyperborean Epoch the Solar Pitris became the beautiful Apollo-men, who in the Second Race had already attained the upright posture. In the Old Sun everything was contained which was later extrapolated as Moon and Earth. All life and all warmth streamed up from the centre of the Sun. Then, in the next Manvantara (the Old Moon) the following took place: Out of the darkness of Pralaya the Sun emerged. A part of the Sun substance had the urge to detach itself. At first a kind of biscuit formation developed. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] Then the one part severed itself completely and the two bodies continued side by side as Sun and Old Moon. The Sun retained the possibility of emitting light and warmth. The Old Moon retained the power of reproduction. It was able to bring forth again the beings who had been on the Sun, but they had to be dependent on the Sun for light and warmth. Because the Old Moon itself possessed no light, the beings had to orientate themselves towards the Sun. All plants therefore completely reversed their position on the Old Moon. The animals turned half round and human beings also only turned halfway; but to compensate for this they received on the Moon the astral body, Kama, and thereby, developed warmth from within outwards. The Kama was at that time still an essentially warming force. This is why the human beings did not already then turn themselves completely towards the Sun. Life was in the darkness. The Old Moon also circled round the Sun, but not as our Earth does today. The Moon rotated around the Sun, in such a way that only one side was turned towards it. A Moon-day therefore lasted as long as a half year does today. Thus on the one side there was an intense heat and on the other side an intense cold. On the Old Moon the predecessors of man again went through a certain normal development. But there were also Moon Adepts who hastened on in advance of the rest of mankind. At the end of the Old Moon evolution these Pitri beings were much more advanced than the rest of humanity, just as the Adepts are today. Now for the first time we reach the actual Earth evolution. In the next Pralaya which followed the Moon evolution, the Moon fell back into the Sun. As one body they went through Pralaya. When the Earth eventually emerged out of the darkness the whole Sun-mass was united with it. In that epoch the first or Polarian Race began. Then the previous Sun-Men, in accordance with conditions at that time, were able to form this specially favoured species, the Sons of the Sun, because the Sun was still united with the Earth. During the Hyperborean Period the whole again divided. One part severed itself and the Earth emerged out of the Sun. It is at this point that the Kant-Laplace theory is relevant. The earth was in a nebulous condition coinciding with the Kant-Laplace theory. The outer appearance seemed like the rings around Saturn. Now the second or Hyperborean Race evolved. Gradually the seeds of the Moon-Men appeared on the Earth, the Pitris in various degrees of perfection. They all still had the possibility of reproducing themselves through self-fertilisation. A second severance followed. With the Moon everything connected with self-reproduction departed from the Earth, so that there were now three bodies: Sun, Earth, Moon. Then the possibility of self-fertilisation ceased; the Moon had drawn out what made this possible. Then the Moon was outside and there were beings who were no longer able to reproduce themselves; thus in the Lemurian Age the two sexes originated. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] Such forms of evolution take their course only under the special guidance of higher beings, the Devas, in order to further evolution in a certain way. The leader of this whole progression is the God who in the Hebraic tradition is called Jahve; Jehovah. He was a Moon-God. He possessed in the highest sense of the word, the power that had developed on the Moon and accordingly he endeavoured to develop mankind further in this direction. In the earthly world Jahve represents that God who endows beings with the possibility of physical reproduction. Everything else (intellect) did not lie in the Jahve-Intention. If Jahve's intention alone had continued to develop, the human being would eventually have ceased to be able to reproduce himself, for the power of reproduction would have become exhausted. He would then only have been concerned with the creation of beautiful forms, for he was indifferent to what is inward, intellectual. Jehovah wished to produce beautifully formed human beings, like beautiful statues. His intention was that the power of reproduction should be continued until it had expended itself. He wanted to have a planet that only bore upon it beautiful but completely motionless forms. If the Earth had continued its evolution with the Moon within it, it would have developed into a completely rigid, frozen form. Jehovah would have immortalised his planet as a monument to his intention. This would doubtless have come about had not those Adepts, who had hastened beyond the Moon evolution now come forward. It was just at this time that they made their appearance. They had already developed on the Moon intelligence and the Spirit which we first developed on the Earth. They now took the rest of humanity into their charge and rescued them from the fate which otherwise would have befallen them. A new spark was kindled in the human astral body. Just at that time they gave to the human astral body the impetus to develop beyond this critical point. Jahve could now save the situation only by altering his manner of working. He created man and woman. What could no longer be contained in one sex was divided between the two sexes. Two streams now existed, that of Jahve and that of the Moon Adepts. The interest of the Moon Adepts lay in spiritualising mankind. Jahve, however, wished to make of them beautiful statues. At that time these two powers contested with one another. Thus on the Earth we have to do with a force having the power of self-reproduction; Kriya-shakti. This power is only present on the Earth today in the very highest Mysteries. At that time everyone possessed it. Through this power man could reproduce himself; he then became divided into two halves with the result that two sexes came into being on the Earth. Jehovah withdrew the entire power of self-reproduction from the Earth and placed it in the Moon side by side with the Earth. Through this arose the connection between the power of reproduction and the Moon beings. Now we have human beings with a weakened power of reproduction, but not yet having the possibility of spiritualising themselves. These were the predecessors of present-day man. The Moon Adepts came to them and said: You must not follow Jehovah. He will not allow you to attain to knowledge but you should. That is the Snake. The Snake approached the woman, because she had the power to produce offspring out of herself. Now Jehovah said: Man has become like unto ourselves, and brings death into the world and everything connected with it. ‘Lucifer’ is the name given to the Moon Adepts; they are the bestowers of human intellectuality. This they gave to the astral and physical bodies; had it been otherwise the Monads would not have been able to enter into them and the Earth would have become a planetary monument to Jehovah's greatness. By the intervention of the Luciferic principle human independence and spirituality were saved. Then Jehovah, so that man should not be completely spiritualised, divided the self-reproduction process into two parts. What would have been lost however if Jehovah had continued his work alone will reappear in the Sixth Root-Race, when man will have become so spiritualised that he will regain Kriya-shakti, the creative power of reproduction. He will be in the position to bring forth his own kind. In this way mankind was rescued from downfall. Through Jehovah's power man carries within himself the possibility of rigidifying. When one observes the three lower bodies we find that these bear within them the possibility of returning to the physical condition of the Earth. The upper parts: Atma, Buddhi, Manas, were only able to enter into human beings because the influence of the Snake was added. This gave man new life and the power to remain with the earthly planet. Reproduction however became bisexual and thereby birth and death entered into the world. Previously this had not happened. When man, by working out of the spirit, transmutes the physical body, he conquers death. The separate forces exhaust themselves when they take on special forms. The force enters into the form with ever increasing density and hence life in the Lemurian Age had to receive a new impulse, which was brought about by the turning around of the Earth Globe. The axis of the Earth was gradually turned. Previously there was a tropical climate at the North Pole; later through the turning around of the Earth axis the tropical climate came into the middle region. This change proceeded with comparative rapidity but lasted nevertheless for perhaps four million years. [Rudolf Steiner later revised his time scale of earthly evolution to much shorter periods. Ed.] Four million years were needed by the Moon Pitris in order to turn the axis of the Earth. At that time the Moon Pitris development was already much further on than that of present day man. Thus at that time the two sexes developed from the unisexual human being. In the beginning among the unisexual human beings there were very retarded individuals, but also those who were very far advanced. Only a small part of the Earth was a fitting dwelling place for the descending Monads. Then it was that human beings divided into two sexes. This had taken place earlier with the animals. Side by side with human beings there existed male and female animals. Very grotesque forms were able to live on the quite differently constituted Earth. They were also able to fly. They bore within them the future promise of what human beings possess today. Esoteric religions call human beings able to bring forth their own kind Bulls. (Certain animal symbols are related to this.) The Bull is a symbol of fertility; previously came the Lion, the symbol of courage, and before this the Eagle. In the vision of Ezekiel,61 referring to those earlier times, the animals have wings because they could raise themselves above the earth. Man only appeared later. Thus we have the human being as he evolved from the unisexual into the bisexual state, and together with him bisexual animals, male and female. It was only through the Lunar Pitris that man became mature enough to have a body capable of receiving the Monads. The latter however selected only the most highly developed examples and evolved a noble human form; only these had to be withdrawn completely from intercourse with anything around them, otherwise the beautiful bodies would have been lost. It was only then that the body formed itself in accordance with the Monad. The other forms which were less advanced failed to satisfy the descending Monad; hence they poured only a part of their spiritual force into the imperfect human bodies and the third stream utterly refused to incarnate. Because of this there existed very poorly endowed human bodies and also others quite devoid of spirit. In the middle of the Lemurian Age we find the first Sons of the Fire Mist; these incarnate in the fiery element, which at that time surrounded the Earth. The Sons of the Fire Mist were the first Arhats.62 Then there arose the other two kinds. In the first Lemurian human race those who had received only a small spark were little adapted to forming a civilisation and soon went under. On the other hand those who had received absolutely nothing found full expression for their lower nature. They mingled with the animals. From them proceeded the last Lemurian races. The wild, animal instincts lived in wild animal-like human forms. This brought about a degeneration of the entire human substance. Had all human beings been fructified with Monads, the whole human race would have greatly improved. The first evil arose through the fact that certain Monads refused to incarnate. From this, through intermingling, deterioration set in. In this way the human being suffered an essentially physical degradation. Only in the Atlantean Age did the Monads regret their previous refusal; they came down and populated all mankind. In this way arose the various Atlantean races. We have now reached a time when something happened to bring about the deterioration of the Earth. The wholesale deterioration of the races brought this about. It was then that the seed of Karma was planted. Everything that came later is the result of this original Karma; for had the Monads all entered into human forms at the right time, human beings would have possessed the certainty of animals, they could not have been subject to error, but they would not have been able to develop freedom. The original Arhats could not go astray; they are angels in human form. The Moon Adepts however had so brought things about that certain Monads waited before incarnating. Through this the principle of asceticism entered into the world—reluctance to inhabit the Earth. This discrepancy between higher and lower Nature arose at this time. Because of it man became uncertain; he must now try things out, oscillating from one experience to another, in an attempt to find his way in the world. Because he had original Karma, his own further Karma came about. Now he could fall into error. The intention was that man should attain knowledge. This could only be brought about through the original Karma. The Luciferic Principle, the Moon Adepts, wanted to develop freedom and independence to an ever-greater degree. This is very beautifully expressed in the saga of Prometheus:63 Zeus will not allow human beings to get fire. Prometheus however gives them fire, the faculty of developing ever higher and higher. By so doing he condemns man to suffering. Man must now wait for the coming of a Sun Hero, until the Principle of the Sun Hero in the Sixth Race will make him able to develop further without Luciferic knowledge. Those endowed with this higher degree of advancement are like Prometheus, they are Sun Heroes. We have thus learned to know a two-fold order of human beings: those who succumbed to the Jehovah Principle, the bringing of perfection to the physical Earth, and also spiritual human beings who were becoming more highly developed. Jehovah and Lucifer are engaged in an unceasing battle. It is the intention of Lucifer to develop everything upwards, towards knowledge, towards the light. In Devachan the human being can bring a certain degree of advancement to the Luciferic Principle. The longer he remains in Devachan the more of this can he develop. He must pass through as many incarnations as are necessary in order to bring this Principle fully to perfection. Thus there exists in the world a Jehovah Principle and a Lucifer Principle. If the Jehovah Principle alone were to be taught, man would succumb to the Earth. If the teaching of reincarnation and karma were allowed to disappear entirely from the Earth we should win back for Jehovah all the Monads and physical man would be given over to the Earth, to a petrified planet. If however one teaches reincarnation and karma, man is led upwards to spiritualisation. Christianity therefore made the absolutely right compromise, and for a period of time did not teach reincarnation and karma, but the importance of the single human existence, in order that man should learn to love the Earth, waiting until he is mature enough for a new Christianity, with the teaching of reincarnation and karma, which is the saving of the Earth and brings the whole of what has been sown into Devachan. As a result, in Christianity itself there is conflict between the two Principles: the one without reincarnation and karma, the other with this teaching. In the former case, everything which Lucifer could bring about would be taken from human beings. They would actually drop out of reincarnation and turn their backs on the Earth, becoming degenerate angels. In that case the Earth would be going towards its downfall. Were the hosts of Jehovah to be victorious on the Earth, the Earth would remain behind as a kind of Moon, as a rigidified body. The possibility of spiritualisation would then be a missed opportunity. The battle in the Bhagavad Gita64 describes the conflict between Jehovah and Lucifer and their hosts. It might still be possible today for the teaching of Christianity without reincarnation and karma to prevail. Then the Earth would be lost for the Principle of Lucifer. The whole earth is still a battlefield of these two principles. The principle that leads the earth towards spirituality is Lucifer. In order to live in accordance with this Principle one must first love the Earth, one must descend on to the Earth. Lucifer is the Prince who reigns in the kingdom of science and art, but he cannot descend altogether on to the Earth: for this, his power does not suffice. Quite alone, it would be impossible for Lucifer to lead upwards what is on the Earth. For this, not only is the power of a Moon Adept necessary, but of a Sun Adept, who embraces the universality of human life, not manifesting only in science and art. Lucifer is represented as the Winged Form of the Dragon; Ezekiel describes him as the Winged Bull. Now there came a Sun Hero, similar to those who appeared in the Hyperborean Epoch, represented by Ezekiel as the Winged Lion. This Hero, Who gave the second impulse, is the Christ, the Lion out of the tribe of Judah. The representative of the Eagle will come only later; he represents the Father Principle. Christ is a Solar Hero, a Lion-Nature, a Sun Pitri. The third impulse will be represented by an Adept who was already an Adept on Saturn. Such a one cannot as yet incarnate on the Earth. When man is not only able to develop his higher nature upwards, but working creatively is able to renounce completely his lower nature, then will this highest Adept, the Saturn Adept, the Father Principle, the Hidden God, be able to incarnate.
|
| 324. Anthroposophy and Science: Lecture II
17 Mar 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Walter Stuber, Mark Gardner |
|---|
| Kantianism speaks of the three dimensions being contained a priori in the human organization, and of the human organization transposing its subjective experience out into space. How is it that Kant came to this one-sided view? He arrived at this because he did not know that what is brought into consciousness in the delicate experience of the depth dimension, and otherwise abstractly, is experienced in its reality in our subconscious. |
| We don't have to remain on the abstract level—where, for example, Kant regards space and time as a priori—but we can progress to a discovery of the concrete aspects of the reality of the human being. |
| 324. Anthroposophy and Science: Lecture II
17 Mar 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Walter Stuber, Mark Gardner |
|---|
I pointed out yesterday in my introductory lecture that we can observe a transition from the ordinary knowledge of the world around us to mathematical knowledge, and that this is the beginning of a path of knowledge. This path when continued will lead to an understanding of the spiritual scientific method, as we mean it here, and ultimately to acceptance of it. It will be my special effort in these lectures to characterize the spiritual scientific method in such a way as to completely justify it. To accomplish this task will take the remaining seven lectures. Today, once again, I would like to consider in greater depth the first stage. I would like to place before you today something which as normal scientific thinking appears here and there in fragments. As these fragments are not always found in the same place and are not seen as a whole, we have the situation that it is not possible to rise in a methodical way from a science that is free of mathematics to one that includes it. We will also have difficultly following in an entirely methodical way the transition from a mathematical penetration of the objective world to a spiritual-scientific penetration into reality. I shall also, as I have already mentioned, try to reach this last phase in a methodical way. We will start today by observing the human being as he experiences himself when he looks at the outer world. You will know from my lectures, also my book Riddles of the Soul,1 that one cannot reach a comprehensive observation of man without splitting the entire human organization into three distinctly different members. Naturally we have eventually to deal with the complete human being. This complete man is however a most complicated organism and its members have a certain independence. Finally we will see how what is contained independently in these members combines into a whole. First we have to look at what I have named in Riddles of the Soul as the nerve-sense man: The member of the human organism that has its primary expression in the head, although from there it extends over the entire organism. Despite this extension we can clearly differentiate this member from the rest of the organism. This physical member is the mediator of our conceptual life. As human beings we make mental pictures and we are able to take the life of these mental pictures to ourselves through our sense organs. From the senses it flows toward our inner organism. The way we are connected with our life of feeling is similar to the way our mental pictures are related to our nervous system. The present-day psychological approach to these things is quite inexact. Our feeling life is not directly connected to our nerve-sense system, only indirectly. It is directly connected to what we call the rhythmic system in the human organism, consisting mainly of breathing, pulse, and blood circulation. The mistaken idea that the life of feeling, as part of the soul life, is directly connected to our nervous system originates from the fact that what we experience as feeling is always accompanied by mental pictures. The physical expression of this is that the rhythmic system is connected throughout the organism with the nerve-sense system. The fact that our life of feeling is always accompanied by a mental picture of some kind is related organically to the fact that the rhythmic system works back onto the nervous system. This can give the appearance that the life of feeling is directly connected to the nerve-sense system. I have pointed out in Riddles of the Soul that if one studies what occurs in us when we listen to music, one can see the relationship correctly between feeling and the forming of mental pictures. Besides these two systems, the nerve-sense system which provides the mental image, and the rhythmic System which mediates the life of feeling, we have the metabolic system. Every function of the human organism is contained in these three systems. The metabolic system is the expression of the will, and the real connection between willing and the human organism will become clear only if you study how a metabolic transformative action comes about in us when there is an act of will or even an impulse of will. Every metabolic activity is consciously or unconsciously the physical basis of some act of will or impulse of will. Our capacity for movement is also connected with our will activity and therefore is connected with some kind of metabolic activity. One must be clear about the fact that when we complete a movement in space, this is a primitive activity of the will. To use a saying of Goethe, the “ur-phenomenal” activity of the will can be seen as expressed by the physical transformations that occur in the organism. And, as in the case of feeling, the will activities are indirectly connected with the nerve-sense system through our following our will activities with mental pictures. So we can say, to start with, that our soul life and also our physical life can be divided in three ways organically as well as into three soul aspects. Let us try today to look at man from a certain point of view so that we may see how these three members of our physical organism and our soul organization relate to one another. We must also go into some detail to achieve our task of showing that spiritual science is a continuation of the familiar scientific way of considering things. First of all, let us consider what I have named the nerve-sense organism. This nerve-sense organism is contained mainly in the head, as I have already mentioned, but from there it extends over the rest of the organism, in a certain way impregnating it. This is not obvious if one looks at just the outer form of a human being, but it does in fact extend inwardly through the whole organism. Take the sense of warmth as an example, which extends over the entire organism. This can be seen as a part of our nerve-sense organization that for the most part is concentrated in the head, in the life of the senses, and yet is extended over the whole organism, making the whole human being into a kind of head in regard to this particular sense of warmth. For most people it is distasteful nowadays to try to understand this kind of problem. Because we have become so used to an outer way of considering things, the three members of the human organism are considered spatially, as separate from one another. There is a professor of anatomy who takes this view, who has asserted that anthroposophy separates the human organism spatially into head system, chest system, and abdominal system. This is clearly erroneous. It is of course not what we have said; we wish to approach these things precisely, not in dilettante fashion. One must know these things correctly, especially if one also wants to understand how three elements flow into one another and compose the threefold social organism. To begin with it is empirically evident that it is the head organization that has most to do with cognition, at least mathematical cognition, as it approaches man in the outer world. In relation to this head organizatiion we can now empirically establish that what we can call “dimensionality” confronts us initially as a kind of intimation. You will see best what I mean if we consider the three modes of human activity. The first of these I would like to call the total act of seeing, observation of the world with our own two eyes. Secondly, I would mention man's arms and hands. Even though they are attached to man's trunk and are therefore in a certain way connected with the metabolic system, they also have an inner relationship to the rhythmic system. Through their attachment near the rhythmic system, they are influenced by the life and functioning of this system. The fact that they are located beside the rhythmic system, which is more hidden, allows them to reveal the nature of what would normally be hidden. Please listen carefully; I repeat: The arms and hands, because of their specific location on the human body and through their life functions, can be seen as belonging to the rhythmic system. The most obvious demonstration of this connection is the way they are used freely in gestures to express feelings. When they are used in this way, they are lifted to a higher function than serving merely the body. In the case of animals, the corresponding members, the legs, are used only to serve the body, but in human beings the arms are freed for a higher function. Through the fact that they are used for gestures in connection with speech, they have the higher function of making the invisible aspects of speech visible. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] The third mode is the activity of walking, an activity primarily of the limb system. Let us consider the activities of seeing, arm movement, and walking from a scientific point of view. In general, what you see with both eyes presents itself to you in two dimensions and these dimensions are independent of any mental activity. I can represent these two dimensions by these perpendicular coordinates. I will draw these as dotted lines for the purpose of later references I wish to make. With these dotted lines representing two dimensions, I want to express the fact that our mental activity of comprehension is not really involved when we look only at these two dimensions. The third dimension is in sharp contrast to this. The third dimension of depth does not stand ready-made before our soul independent of any mental activity. It confronts us as something we undergo as an inner operation of the mind when we supplement what we normally see as the surface of things with the depth dimension and thus obtain a three-dimensional body. Roughly speaking, what we actually do in this case is not brought to consciousness. But when we enter into the activity more precisely, we see that one experiences the depth dimension in a different way from width and height dimensions. We can become aware, for instance, how we are able to guess how distant something is from us. In ordinary observation something is added to the mere observation of the eyes when we progress from a surface-picture consciousness to a full-bodied three-dimensional consciousness. So long as we remain within our consciousness, we cannot say how height perception and width perception are achieved. We simply have to accept the height and width dimensions; for the activity of seeing they are simply given. This is not true of the depth dimension. For this reason I will draw it in perspective; I will draw a solid line to represent the difference. In this third dimension of depth, we are able to have the act of perceiving enter our consciousness in a slightly conscious way. Thus we recognize when we examine the act of seeing, that the height and width dimensions are given to us purely in thought; that is, if we penetrate the act of seeing with our thoughts. The depth dimension, however, is based an an activation of consciousness, a kind of half-conscious mental operation. Therefore, what you may already have heard as the physiological and anatomical interpretation of the total act of seeing must be accepted only in reference to the physical components of the act of seeing, to that aspect which does not involve an operation of the mind; only the perception of surface can be attributed to the act of seeing. In contrast, when considering the depth dimension, it is not sufficient to merely consider the activity of the corpora quadrigemina, the organ in the human body upon which the visualizing activity of the eyes depends, the bodily aspect of seeing—here the cerebrum must serve a mediating function, the cerebrum being that part of the brain to which are attributed the anatomical-physiological aspects of the volitional operation of the intellect. Thus we can grasp this depth dimension when we examine it carefully, using both analytical and synthetic means. The matter of depth perception belongs into the realm of what I would like to call “conscious activation through the human head.” When we turn our attention from the act of seeing to that activity which may be seen externally through the movement of the arms and hands, we immerse ourselves in an element that is very difficult to grasp consciously. Even so, we can follow what takes place in our life of feeling when we gesture with our arms and hands, which are free for this kind of activity, and we can become aware of the way this action is related to depth perception with our two eyes. What is it really that depth perception mediates to us? It is the exact position of the left and the right eye. It is the convergence of the left axis and right axis of sight. The mental judgment of the distance of some object from us depends upon the distance at which the lines of sight cross each other. Very little of this convergence activity of the eyes lying at the basis of the judgment of depth is outwardly perceptible. When we turn to the activity of our arms and hands, we find we are able to distinguish more exactly, with little effort of consciousness, what is happening inwardly when we move our arms in the horizontal plane, in the dimension of right-left, in the width dimension. If we look carefully, our judgment in relation to the width dimension is connected with the feeling we have when we consciously move our arms in a horizontal gesture expressing how wide something is. We have a feeling experience of what we call symmetry. This experience takes place particularly in the width dimension, through the feeling that is mediated to us through our left and right arm movements. Through the corresponding movements of our left and right arms we can actually feel our own symmetry. Our grasping in feeling of the width dimension is translated for us chiefly through the medium of symmetry into mental pictures, and we then also evaluate symmetry in our mental life. But we must not overlook the fact that this judging of the symmetry of the width dimension is something secondary: If we only looked at the symmetry without having the accompanying feelings that correspond to the symmetrical aspects of left and right, our experience would be pale, dry and wanting in its full reality. You can understand all that symmetry shows us if you can feel the symmetry. But you can really only feel the symmetry through the delicate process of becoming conscious of the fact that the movements of the left and right arms belong together, and in the same way the movements of the hands belong together. What we experience in feeling thus supports everything we can experience in relation to the width dimension. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] But also what we have called the depth dimension in relation to the act of seeing enters our consciousness through something to be found in the activity of our arms. The way the axes of our vision intersect is similar to the way our arms can intersect. When our arms intersect, we have a certain equivalent to the act of seeing. When we cross our arms, first close to us and then farther away, if we follow the points of intersection we can get a sense of depth dimension by trying to experience what is going on in our arms. In these moments we don't experience the width dimension as fully as we do—with no effort on our part—in the act of seeing. But if I would represent symbolically what is expressed in relation to the dimensions by the arms and hands, I would have to sketch the width dimension and the depth dimension as full lines and the height dimension as a dotted line. That is all that I can experience through my arms. The height dimension remains unconscious to us when we make gestures, because we connect our gestures consciously with a surface which is made up of depth and width dimensions. When does the third dimension show itself in a distinct, conscious way? Actually, it only appears to our consciousness in the act of walking. When we move from one place to another, then the line which is this third, vertical dimension changes continually, and although our consciousness of this third dimension while we walk is almost imperceptible, we must not overlook it. In fact, the half-conscious intellectual awareness we can experience is related to this height dimension. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] Therefore, when we examine the act of seeing, which obviously belongs to the head organization, we realize that in the act of seeing there is given ready-made a two-dimensional activity, and in addition we must establish an activity that creates the third dimension—depth. In the action which we have described as representative of the rhythmic system, namely, the free movement of the arms and hands, we can have an inner experience of two spatial dimensions. The third spatial dimension—height—is given to our consciousness in the same way that width and breadth are given for the head organization in the act of seeing. Only in the metabolic-limb system (the connection between these two is only recognized when we study the metabolic activity in the act of walking) is everything open to our consciousness that gives us the full measure of three dimensions. If you consider the following, you will have something extraordinarily important. The only content of our fully alert consciousness is the life of mental pictures. In contrast to this, our life of feeling does not come into our consciousness with the same clarity. As we shall see later, our feelings by themselves have no greater intensity in our consciousness than our dreams. Dreams are rendered from the clear content of daily life, from the fully alert life of mental pictures; in this way they become distinct mental pictures in our consciousness. In the same way, our feelings in daily life are continually accompanied by the mental pictures representing them during our waking hours. In this way our feelings, which otherwise only possess the intensity of dream life, are brought to the distinct, fully conscious life of mental pictures. The will-movements remain completely in the subconscious. How do we know anything of the will? Basically, in our everyday consciousness we know nothing of the real nature of the will. This is made clear in the psychology of Theodor Ziehen, for instance, who in his Physiological Psychology speaks only of the life of mental pictures or the representational life of the mind. He says: As psychologists we can only follow the life of mental images, but we find certain mental images to be tinged with feeling. The fact that the life of feeling, as I explained to you just now, is bound up with the rhythmic system and only shines up into the life of mental pictures, this is unknown to Theodor Ziehen. In his view, feelings are only an aspect of the life of mental pictures. This psychologist simply has no insight into the actual organization of the human being, which I have now to describe to you. Because feelings are bound up with the rhythmic system, they remain in the half-conscious realm of dreaming. And the will activity remains completely unconscious. That's the reason why the average psychologist does not write about it. Just read Theodor Ziehen's strange explanations concerning the activity of the will, and you will see that its real nature is completely missed by such psychologists. When we observe the result of an act of will, this is only something we are able to look at externally. We do not know what has happened inwardly when a will impulse moves our arm. We only see the arm move; that is, we observe the outer happening afterward. Thus we accompany the manifestations of our will with mental images; they are mediated organically through the metabolic system and the limb system related to it. So it is only in part of the human organism, in the metabolic system—which is the bodily aspect of the soul's will activity—that we experience the reality of all three dimensions of space. In our ordinary process of knowing the reality of the three dimensions cannot be grasped. It cannot be grasped, as we will see, until we are able to look with the same clarity into our will activity as we normally do into our mental activity. It cannot come about in our ordinary way of knowing but only with spiritual-scientific knowledge. It is through the activation of the entire man, of the entire limb-and-metabolic system, that our subconscious experience of the three dimensions comes about. What happens is that what is contained in the metabolic-limb system is lifted into the rhythmic system. There it is experienced in its two-dimensional aspect, not in its total reality. When experienced in two dimensions, the height dimension has already become abstract. Only in the subconscious do we normally experience the height dimension. You can see how reality becomes an abstraction in the human organization through the human activity itself. In the working of the human organization, the height or vertical dimension already becomes an abstraction, appearing as a mere line, a mere thought in the region of the rhythmic system. Following this up into the nerve-sense system, what occurs? Both height and width become abstraction. We can no longer experience them; they can only be thought by the intellect as we approach the subject afterward. So in the head, the region of our ordinary knowledge, we only have the possibility of expressing the two dimensions abstractly. It is only the depth dimension for which we still have a faint consciousness in the head. So you can see, it is only due to a delicate perception of the depth dimension that we are able to know anything at all in our normal consciousness of the spatial dimensions. Please now consider: With our present constitution, what if depth perception should become equally abstract? Then we would be left with just three abstract lines—and it would never even occur to us to search for the realities represented by those abstract lines. In this way I have pointed you toward reality. In Kantianism this reality appears in an unreal form. Kantianism speaks of the three dimensions being contained a priori in the human organization, and of the human organization transposing its subjective experience out into space. How is it that Kant came to this one-sided view? He arrived at this because he did not know that what is brought into consciousness in the delicate experience of the depth dimension, and otherwise abstractly, is experienced in its reality in our subconscious. As it is pushed up into consciousness, it is made into an abstraction, with only a small remainder in the case of depth dimension. We experience the reality of the three dimensions through our individual human organization. The reality is present in actuality in the realm of the will, and physiologically in the metabolic-limb system. Initially in this system we are unconscious of reality in our ordinary mind, but we become conscious of it, at first in the thought abstractions of mathematical-geometrical space. With this subject of the three dimensions I wished to give an example of the ways and means by which spiritual science can penetrate human activity. We don't have to remain on the abstract level—where, for example, Kant regards space and time as a priori—but we can progress to a discovery of the concrete aspects of the reality of the human being. I wanted to use this particular example of the actual meaning of space because it will be useful in the future in leading us to an exact understanding of the mathematical facts from all sides. We will speak further of this tomorrow.
|