| 102. The Influence of Spiritual Beings on Man: Lecture III
15 Feb 1908, Berlin Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| In the numerous popular accounts of the origin of our planetary system one is first led back to a kind of original mist, to a vast fog-like structure, a nebula, out of which our sun and its planets have somehow agglomerated, although for the driving force in this process only physical forces, as a rule, are taken into account. This is called the “Kant-Laplace theory,” though it is somewhat modified today, and those who have arrived at an intellectual grasp of the gradual agglomeration of the different planets out of the original nebula up to the condition in which they and our earth now exist, are very proud of their intelligence. |
| However, the man who believes that this materialistic description is the only one naturally feels that his scientific eminence is vastly superior to everything put forward by spiritual research. The modified Kant-Laplace theory may definitely hold good as an external event, but within the whole forming of globes, within this whole crystallizing of the separate cosmic globes, spiritual forces and spiritual beings were at work. The experimenter shows us today in a beautiful way how this Kant-Laplace theory can proceed. One need only take a fairly small ball of oil that swims in water. Then one can very easily put a little cardboard disk in the plane of the equator through this ball and put a needle through the centre. |
| 102. The Influence of Spiritual Beings on Man: Lecture III
15 Feb 1908, Berlin Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The purpose of these lectures is to bring still loftier concepts to those more advanced students of theosophy who have been familiar for some time with its world-conception and—which is much more important—have become at home in its way of thinking and feeling. This will make it more difficult for the later-comers to follow; perhaps they are well able to follow with their understanding, but it will become increasingly difficult for them to regard as sound and reasonable what is brought forward from the higher sections of theosophy. Much goodwill, therefore, will be required of new-comers to follow these group-lectures with the understanding of feeling and perception. Yet we should make no progress if we had no opportunity of throwing light upon the higher realms of spiritual existence as well. That then is the purpose of these lectures. Now in the last lecture I gave you a picture of the evolution of our whole planetary system. Before that we had considered the planetary system itself in so far as the various planets are peopled by beings who have an influence on our human body. What is to be brought forward today will link on to these two previous studies. We will extend still further our picture of the planetary system and learn some of the mysteries of our cosmic existence from a spiritual aspect. In the numerous popular accounts of the origin of our planetary system one is first led back to a kind of original mist, to a vast fog-like structure, a nebula, out of which our sun and its planets have somehow agglomerated, although for the driving force in this process only physical forces, as a rule, are taken into account. This is called the “Kant-Laplace theory,” though it is somewhat modified today, and those who have arrived at an intellectual grasp of the gradual agglomeration of the different planets out of the original nebula up to the condition in which they and our earth now exist, are very proud of their intelligence. They continually emphasize that it is but little in keeping with the present important advance in science to speak of spiritual forces and spiritual beings in this separation of the heavenly bodies out of the nebula. Various popular books, too, describe such statements as completely backward and superstitious. Now the intelligence of a student of theosophy would suffice for an understanding of what is brought forward in this way. But he goes somewhat further. It is clear to him that the physical forces of attraction and repulsion were not enough. It is clear that all sorts of other things played a part. Theosophy has still to put up with being proclaimed thoroughly dense and stupid and a dreadful superstition by popular official science—which one could perhaps call “antisophy.” But we are living in an age which in a remarkable way is full of hope for the theosophist. It could he said that the theories, opinions and knowledge that modern popular science forms from its own facts look like tiny, gasping, dwarf-like creatures which run puffing and blowing at a considerable distance behind the facts. The facts of modern science are actually far, far ahead of the “belief” of modern science—only that is not recognized. I should only like to remind you of how we have often spoken here of the activity of the astral body during the night, of how the astral body at night works at upbuilding the physical and etheric bodies and ridding them of the fatigue substances they have acquired during the day. To express the sentence in this form would simply strike modern science as something not fit for polite society. But facts speak a plain language. When, for example, we can read in an American paper today that a researcher has established the theory that the sleep activity in man is an involving, constructive one, whereas on the other hand the waking activity is a destructive one, you have again a proof of how modern science runs after the facts like little dwarfs who cannot keep up. In the world-conception of theosophy you have the great illuminating views that are drawn out of a spiritual conception of the world. When we consider the origin of our present solar system theosophically we need in no wise—nor in other fields—directly contradict what is put forward by physical science. For theosophy has no objections to make in respect of what physical science strives to know—that is, what eyes could have seen in the successive phases of evolution. If at the time of the original nebula someone had placed a chair out in universal space, had sat on it for a sufficiently long life-time and had watched how the different globes had gathered themselves into balls and separated off, with physical eyes he would have seen nothing but what physical science has affirmed. But that would be just the same as if two observers reported that a man gave another a box on the ear and one of them should say: The man was furiously angry with the other and that made him shoot out his hand and give the other a box on the ear. The second observer might say: I saw nothing of anger or passion, I only saw the hand move and inflict the blow.—That is the external, materialistic description, the method employed by modern science; it does not contradict the spiritual examination of the facts. However, the man who believes that this materialistic description is the only one naturally feels that his scientific eminence is vastly superior to everything put forward by spiritual research. The modified Kant-Laplace theory may definitely hold good as an external event, but within the whole forming of globes, within this whole crystallizing of the separate cosmic globes, spiritual forces and spiritual beings were at work. The experimenter shows us today in a beautiful way how this Kant-Laplace theory can proceed. One need only take a fairly small ball of oil that swims in water. Then one can very easily put a little cardboard disk in the plane of the equator through this ball and put a needle through the centre. Now one rotates the needle very rapidly, little oil-balls split off, and it is easy to picture a cosmic system in miniature and to show how a cosmic system has separated itself off into globes in space. The experimenter has only forgotten one thing. He forgets that he himself was there, that he made the necessary preparation, that he then rotated the needle and that what cannot go of itself on a miniature scale cannot go of itself in the universe. Out there it is supposed to go of itself. Things are not in the least so very difficult to comprehend, but the right physical principles are so worn out that those who do not want to see them really need not see them. So, spiritual forces and spiritual beings were active in this whole process of planet formation and we will now learn something about it. I must remind you of the often-repeated fact that before our Earth became “Earth” it had gone through earlier embodiments, other planetary conditions—the Saturn, Sun, and Moon conditions, and only then advanced to its present Earth condition. Now picture vividly ancient Saturn, floating in space in the far-distant past, the first embodiment of our Earth. Within the whole being of Saturn there was as yet nothing at all of what we see round us today as our plants, minerals, animals. Saturn consisted in the beginning of nothing but the very first rudiments of humanity. We speak of ancient Saturn as of nothing but a sort of conglomeration of human beings. Man existed at that time only in the first rudiments of his physical body. Ancient Saturn was simply composed of individual physical human bodies—somewhat as a mulberry or blackberry is composed of nothing but single tiny berries. It was surrounded by an atmosphere, as today our Earth is surrounded by air, but in relation to what we know as atmosphere today it was spiritual. It was entirely of a spiritual nature and within the Saturn evolution man began his first development. Then came a time when Saturn went through a state similar to man's condition between death and rebirth in Devachan. One calls this state of a cosmic body, Pralaya. Thus Saturn went through a sort of devachanic state and when it entered again upon a kind of externally perceptible existence, it emerged as our Earth's second planetary stage, as Sun. This Sun-condition brought the human being again further. Certain beings which had remained behind now emerged at the side of the human kingdom, so that there were then two kingdoms on the Sun. Then came a Pralaya, a devachanic condition, after which the whole planet was transformed into the Moon-condition; and so it continued, again a Pralaya, until the Moon passed over into our Earth. When our Earth came forth from the purely spiritual devachanic state and received for the first time a kind of externally perceptible existence, it was not like it is today. In fact, seen externally, it could really be pictured as a kind of great primordial nebula, as our physical science describes. Only we must think of this primordial mist as immense, far greater than the present earth, extending far beyond the outermost planets now belonging to our solar system—far beyond Uranus. To spiritual science what is seen coming forth from a spiritual condition is not merely a kind of physical mist. To describe it as a kind of mist and nothing more is about as sensible as if a man who has seen another should reply to a question as to what he saw: I saw muscles which are attached to bones and blood—simply describing the physical aspect. For in the primordial mist there were a multitude of spiritual forces and spiritual beings. They belonged to it, and what happened in this primordial mist was a consequence of the deeds of spiritual beings. All that the physicist sees when he sets out a chair in cosmic space and watches the proceedings, he describes just as the observer who denied the passion and anger and described only the moving hand. In reality, what took place there—the separating off of cosmic bodies and globes—was the act of spiritual beings; in the primordial mist, therefore, we must see the garment, the outer manifestation, of a multitude of spiritual beings. They are spiritual beings at very varied stages of evolution. They do not arise out of a nothingness, they have a past behind them. They have the Saturn, Sun, Moon-past behind them. They have gone through all this and now they stand before the task of turning into deeds all that they have gone through. They have to “do” what they have learnt on Saturn, Sun, Moon, and they stand at most diverse heights of development. Among them are beings who were as advanced on ancient Saturn as man is on Earth today. These have already passed through their human stage on Saturn and thus stand far above man at the outset of the Earth's evolution. Other beings are there who went through their human stage on the Sun, others who did so on the Moon. The human being waited to go through his human stage on the Earth. Even if we consider only this fourfold hierarchy we have a series of different beings at different stages of evolution. We call the beings who went through their human stage on the Sun, the “Fire-Spirits,” but you must not imagine that they were externally like the men of today. They went through their human stage in a different external form. The ancient Sun planet had an extraordinarily fine light substance, far lighter than our present substance. At that time there was no kind of solid or fluid, nothing but the gaseous element existed, and the bodies of the Fire-Spirits in spite of their being of human rank were gaseous bodies. One can go through the human stage in cosmic evolution in the most varied forms. Only the Earth-man goes through it in the flesh on Earth. The beings who had human rank on the Moon and who were already at a higher stage than man went through it in a kind of watery condition. Thus these spirits and a whole host of others were united with the primordial mist that lay at the starting-point of our Solar system. Thus, for instance, you can readily understand that what began for man upon Saturn began in some way for other beings upon the Sun. As on Saturn the first rudiments of the physical body began, so on the Sun other beings followed, just as in schools different primary pupils are always following on. These beings have only advanced to the point of being physically incorporated in our contemporary animals. On the Moon followed beings who are present in our contemporary plants, and our present minerals have only been added on the Earth. These are our youngest companions in evolution whose pains and joys I described to you in a previous lecture. Thus in the original mist there were not only advanced beings but those too who had not yet reached the human stage. We must now add to those which I have enumerated, beings I have spoken of as lagging behind at certain stages of cosmic evolution. Let us take the Fire-Spirits. They had already attained their human stage on the Sun, and now, on the Earth, they are highly exalted beings, two stages above man. They are so advanced that not until man has ascended through the Jupiter and Venus existence to the Vulcan existence will he be mature for such an existence as that of the lofty Sun-Spirits at the beginning of the Earth's development. But now there were beings who had remained behind, who should have progressed on the Sun as far as the Fire-Spirits, but who for certain reasons stayed behind. They could not develop to the full height which the Fire-Spirits had reached when the Earth stood at the outset of its evolution. You will all remember that at the very beginning of its evolution the Earth was still one body with sun and moon—and this you can easily combine with the theory of the original mist or nebula. If you were, therefore, to stir together the three heavenly bodies, earth, sun, moon, in a gigantic cosmic cauldron you would get a body which at one time existed. Then came the time when the sun drew out and left earth and moon, to be followed by a time when the moon too drew out and left our earth as it is today with the sun on one side and the moon on the other. We now ask our-selves how it came about that three bodies arose out of the one. You will easily see why that happened when you re-member that highly-evolved beings, standing two stages above man, were present in the primordial mist—unified with its external existence. They would have had nothing directly to do on such a cosmic body as our present day earth, they needed a dwelling place with quite different characteristics. On the other hand the human being would have been consumed in an existence united with the sun. He needed a weakened, milder existence. It was essential then that through the action of the Fire-Spirits the sun should be withdrawn from the earth and made into their scene of action. It was not a merely physical event: we must under-stand it as the deed of the Fire-Spirits themselves. They drew out their dwelling place and all they needed as sub-stances from the earth and made their theatre the sun. By virtue of their nature they can endure that immense velocity of development. If the human being were exposed to such a velocity, then scarcely were he young when he would at once become old. All evolution went on at a furious tempo. Only such beings as stood two stages higher than man could bear the sun-existence. They drew away together with the sun and left behind the earth with the moon. Now we can answer the question too why the moon had to separate from the earth. If the moon had remained united with the earth then man could again not have sustained his existence. The moon had to be thrust out, for it would have mummified man's whole development. Men would not have undergone such a rapid development as they would had the sun remained, but they would have been carbonized, dried to mummies; their evolution would have been such a slow one that they would have become mummified. In order to produce just the degree of development useful to man, the moon with its forces and its subordinate beings had to be thrust out. And so likewise united with the moon are those beings which I have described as remaining at a time of life comparable to that reached today on earth by a seven-year-old child. As they only go through an existence such as a human existence up to the age of seven, when only the physical body is developed, they need a dwelling-place such as the moon. When you add the fact that not only these various beings were united with the original nebula, but a whole series more, standing at very varied stages of evolution, then you will understand that not only these cosmic bodies, earth, sun, moon, separated from the nebula, but other cosmic bodies too. Indeed they all agglomerated as separate globes because scenes of action had to be found for the varying stages of evolution of the different beings. Thus there were beings at the very beginning of our Earth who were scarcely fitted to take part in further development, who were still so young in their whole evolution that any further step would have destroyed them. They had to receive a sphere of action, so to speak, on which they could preserve their complete youthfulness. All other fields of action existed to give dwelling-places to those who were al-ready more advanced. For the beings who arose last of all during the Moon existence, and who therefore had stayed behind at a very early evolutionary stage, a field of action had to be separated out. This scene of action was the cosmic body which we call “Uranus,” and which therefore has but slight connection with our earthly existence. Uranus has become the theatre for beings which had to remain at a very backward stage. Then evolution proceeded. Apart from Uranus, all that forms our universe was contained in an original pap-like mass. Greek mythology calls this condition “Chaos.” Then Uranus separated out, the rest remaining still in the Chaos. Within it were beings who in their development stood precisely at the stage at which we human beings stood when our Earth passed through the Saturn condition. And for these beings a special theatre, “Saturn,” was created, since standing at that stage, only just beginning their existence, they could not share in all that came later. Thus a second cosmic body split off, Saturn, which you still see in the heavens today. It arose through the fact that there were beings who stood at the same stage as man at the Saturn-time of the Earth. Whereas Saturn arose as a separate cosmic body, everything else that belongs to our present planetary system, the earth with all its beings, was still in this original pap-like mass. Only Uranus and Saturn were outside. The next thing that took place was the separating of another planet which had to become the scene for a certain stage of development. That was the planet Jupiter, the third to split off from the misty mass which for us is actually the earth. At the time of Jupiter's separation, sun, moon, as well as all the other planets of our system, were still united with the earth. When Jupiter had split off there gradually arose the forerunners of contemporary humanity. That is to say, our present human beings emerged again just as a new plant comes out of the seed. The human seeds had gradually formed during the conditions of ancient Saturn, Sun and Moon, and now while the sun was still linked with the earth these human seeds came out again. But now the human beings would not have been able to evolve further, they could not support the tempo as long as the sun remained with the earth. Then something came about which we can well understand when we are clear that the beings we have called the Fire-Spirits took their scene of action away from the earth. The sun pressed out and we have now sun, with earth and moon together. During this time Mars—in a way which would take too much time to relate now in detail—had again formed a theatre for particular beings, and in its further advance Mars actually passed through the earth and moon and left behind what to-day we know as iron. Hence Mars was the cause of the iron particles deposited in living beings, that is, in the blood. Now someone could say: That is not so very remarkable, iron is everywhere. For just as other bodies were in the primordial mist, so too was Mars with the iron which it left behind. Iron is in all the other planets as well!—Science today, however, wonderfully confirms what is given here from the teaching of spiritual science. You will remember that I once showed you how one passes symbolically from the green sap of the plant, chlorophyll, to the blood of man. Plants arose at the period before this passage of Mars had taken place and have preserved their characteristic. Then the iron was deposited in the beings more highly organized than the plants, permeating the red blood. Thus what has recently been found in a Zurich laboratory is in complete accordance with these spiritual-scientific facts, namely, that blood can-not be compared with chlorophyll, simply because it was deposited later. We must not imagine that blood depends in any way on the substantiality of the chemical element “iron.” I say that especially, because someone might say that one can speak of no connection at all of chlorophyll with the blood. Today science makes the discovery that the blood is to be traced back to the element “iron”—whereas chlorophyll contains no iron. It is nevertheless in the fullest harmony with what Spiritual Science has to say, it is only a matter of looking at things in the right light. Then for reasons which we have already stated, the moon separated and we have the earth by itself and the present moon as its satellite. To the sun withdrew all the beings of an essentially higher order than man, whom we have called the Fire-Spirits. But there were certain beings which had not ascended high enough to be able really to endure the sun existence. You must be clear that they were beings exalted far above man, but still not so far advanced as to be able, like the Fire-Spirits, to live on the sun. Dwelling-places had to be created for them. None of the other theatres could have served them, for those were for beings of another nature, who had by no means attained the great age of the beings who, though belonging to the Fire-Spirits, had not quite kept up with them in cosmic evolution. In the main there were two species of beings who had remained behind, and two special arenas were therefore formed for them through the severing of Mercury and Venus from the sun. Mercury and Venus are two planets which have split off as the centres for those Fire-Spirits who are exalted far above human existence, yet who could not have supported the sun-existence. So you have Mercury in the neighbourhood of the sun as arena for those beings who had not been able to live with the Fire-Spirits on the sun, and Venus as arena for beings who in a certain respect had remained behind the Mercury beings but who yet stood far above man. Thus you have seen these various cosmic bodies originate out of the primoridal mist from inner causes, from spiritually-inspired activities. If one keeps to the physical alone, matters take their course in the way depicted by modern science, but the point is to learn to know the spiritual causes by which things have become what they are. Inside the primordial mist, the beings have themselves created the dwelling-places in which they could live. Now these various beings who were, so to say, harmoniously side by side before they had separated, did not remain without connection. On the contrary, they work through one another throughout. The influence of the Mercury and Venus beings on the earth is of a quite special interest. Put yourselves back into the time when the sun and then the moon released itself from the earth and man began his existence in his present form. He has acquired this existence in the present form through the fact that one of the Sun-Spirits forbore—if I may so express it—from continuing his existence on the sun, but united himself with the moon. In this way a lofty regent of the moon arose. Beings of a lower order existed on the moon, but one of the Sun-Spirits united himself with the moon-existence. This Sun-Spirit who is therefore really a displaced Sun-Spirit in the universe is, as divine, spiritual being, Yahve, Jehovah, the regent of the moon. We shall see why that came about if we consider the following. We have seen that if the sun had remained united to the earth man would have been consumed by the swift course of development, and if the moon and its forces alone had worked upon man he would have been mummified. Precisely through the harmony of sun and moon forces arose the equilibrium that keeps man in the present tempo of evolution. When the Earth had come over from the old Moon, man had his physical body from Saturn, his etheric body from the Sun and his astral body from the Moon. But be-cause he had the three bodies and the seed with the three bodies now began to develop, he had a very different form. You would open your eyes in amazement if I should de-scribe it to you, for the present human form has arisen quite slowly and gradually from the time of the moon-separation. But the base, inferior moon-forces could not have given man his present form. They could certainly have given him a form, but an inferior one. If the moon-forces had remained with the earth they would have held him fast in one form. Forces that give the form must proceed from the moon, while forces that continually alter the form proceed from the sun. But in order that the present human form should arise, a molder, a modeler of form, must work from the moon; it was not possible otherwise. At that time therefore began the development of the ego-man. The fourth member of the human entity arose and Yahve gave the human being the nucleus to a form which would enable him to become an ego-bearer. Now man was not yet capable of carrying out the work of which I have told you. I have explained that man's ego works upon his astral, etheric, and physical bodies. But he can only begin this work gradually. As a child needs teachers, so when man was already prepared to become an ego-bearer, he needed a stimulus on earth to enable him to advance, and there were two “stimulators.” You can think whence, from the whole cosmic evolution, they came. The beings who stood nearest to man were the Venus and Mercury beings. Until, at the end of the Atlantean Age, man could make the first feeble efforts to work independently with his ego upon the three bodies—for that was just possible at the end of the Atlantean Age—he had to have teachers. These teachers were beings of Venus and Mercury, and they went on working far beyond the Age of Atlantis. But they are not to be looked on as we look on our present teachers; the Venus beings must rather be thought of as those who endowed man with his intellectuality. Men knew nothing at all of this; just as the different human fluids work upon man, so did the forces of these beings influence him until he could work upon his bodies independently. What we find in man today as intelligence was mediated to him through the spirits who remained behind on Venus as Fire-Spirits of a lesser order. In addition to these were other teachers and they were in fact perceived consciously as teachers by men who attained clairvoyance—the teachers of the great Mysteries of ancient times. In the far past there was not only that all-embracing influence of the Venus-Spirits who worked more or less on mankind as a whole, there were also Mystery centres where the most advanced human beings received instruction spiritually from the Fire-Spirits. The exalted Fire-Spirits of Mercury instructed in the Mysteries; there they appeared—if we may say so—in a spiritual embodiment and were the teachers of the first initiates. Just as the first initiates became the teachers of the great masses of mankind, so did the beings of Mercury work as the teachers of the first initiates. From this you may realize that the beings of other stars have an influence upon man, but the very complicated nature of this influence can be seen from the following. You remember that in my Theosophy1 we roughly divide the human being by saying that he consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body, ego, spirit-self, life-spirit, spirit-man. The more correct division, as you know, is physical, etheric, astral bodies, then the three soul-forces in which the ego emerges—sentient soul, intellectual or mind soul, consciousness soul—and that only then we have spirit-self or Manas, life-spirit or Budhi, spirit-man or Atma. Thus the soul-element is inserted as sentient soul, intellectual soul, consciousness soul. If we follow man's evolution on the Earth we can say that to the three constituents brought over from the Moon, the first development to be added was the sentient soul, then arose the intellectual soul, and not till towards the end of Atlantean times, when man learnt for the first time to say “I” to himself, did the consciousness-soul arise. Since then man can begin to work consciously from within upon the members of his being. If we divide man thus into body, soul, spirit, then we have to divide the soul again into sentient soul, intellectual soul, consciousness soul. These evolved gradually, and the consciousness soul could as yet have no influence, for it arose only as the last. These members had therefore to be kindled from without, and beings from outside were active. Mars in fact worked on the sentient soul, the already-separated Mercury with its beings worked on the origin of the intellectual soul, and Jupiter, which had been in existence the longest, worked on the origin of the consciousness soul. Thus in the soul-nature of man we have the working of the three cosmic bodies, of Mars in the sentient soul, Mercury in the intellectual soul, Jupiter in the consciousness soul, and inasmuch as spirit-self presses into the consciousness soul, Venus with its beings is active. Mercury was also active with regard to the first initiates, so that the Mercury beings exercised a twofold activity, the one quite unconscious to man inasmuch as they developed his intellectual soul, and then as well they were the first teachers of the initiates when they worked in a fully-conscious way. The Mercury beings had thus a continuous double activity, rather as many country schoolmasters instruct the children and cultivate the land allotted to them. The Mercury beings had to develop the intellectual soul and besides that had to be the great schoolmasters of the great initiates. All these things can also be grasped by pure logic. Now you can perhaps ask why should just Jupiter work on the consciousness soul, since it is such a distant planet. But these things are not investigated on logical grounds, but by investigating the facts of the spiritual worlds. There you would perceive it as a fact that the consciousness soul is kindled by Jupiter beings, to whose help come, on the other hand, laggard Venus beings. Things cannot be fitted into an external scheme in the activity of the cosmos; one must realize that when a planet has already fulfilled a task, its beings can later fulfill another task as well. In the course of the second race of humanity Jupiter beings co-operated on the perfecting of the etheric body; then they themselves advanced a stage, and when the human being was far enough on for his consciousness soul to develop, they had to intervene again and help in its development. What is working in space enters into joint activity in most varied ways; one cannot pass from one activity to another in any sort of schematic way. So you see how the physicist when he looks out into the universe sees only the external bodies of spiritual organisms, and how spiritual science leads us to the spiritual foundations which bring about what the physicist sees. We have not been giving ourselves up to the illusion of the man who takes the little ball of oil and forgets that he himself turns it. We have sought for the beings who themselves drew out the globes of the planets which we perceive. We have not fallen into the illusion of thinking that if we are not there, the whole thing does not go on revolving. We have sought the “revolver,” the one who stands behind as the actual spiritually active being—so that one can always find full accord between what is said by Spiritual Science and discovered by official science. Only you can never derive what Spiritual Science says from the facts of science. You would then at most come to an analogy. If on the other hand the spiritual facts have been found by occult means, then, if you disregard what official science has yet to find, they will every time be in accord with what the physicist too has to say. So the theosophist can support the physicist. He knows very well that an occurrence in the physical realm may be just what the physicist describes, but in addition there is always the spiritual process. This does not prevent many scientists from feeling very superior and considering the theosophist a poor simpleton, or something worse. But the theosophist can look on quite calmly. It will be quite different in fifty years' time, for the continuation of merely materialistic science would do great harm to the health and well-being of man-kind if things were to remain as they are today, and if spiritual science were not to combat them.
|
| 181. Earthly Death and Cosmic Life: Confidence in Life and Rejuvenation of the Soul: A Bridge to the Dead
26 Mar 1918, Berlin Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| There is an abundance of literature by those who hold Kant as a great philosopher. That is due to the fact that they understand no other philosophers, and have to exercise much thought-force to understand Kant. |
| they can understand none of the others. It is only because Kant is so difficult to understand that he is regarded by them as a great philosopher. With this is connected the fact that man is afraid to regard the world as complicated, as requiring the power of thought for its comprehension. |
| 181. Earthly Death and Cosmic Life: Confidence in Life and Rejuvenation of the Soul: A Bridge to the Dead
26 Mar 1918, Berlin Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
To study the matter further we must refer to what has already been brought forward. When the subject under discussion is the relation of souls in human bodies to discarnate souls between death and rebirth, the chief thing is to direct the spiritual vision to the ‘psychic atmosphere’ in which they must meet in order to establish a relationship between them. We found that there must be a certain disposition of soul on the part of the living which, as it were, forms a bridge to the knowledge of the so-called dead. This disposition of soul always betokens the existence of a certain psychic element, and it may be said that when this element exists, when its presence shows the suitable feeling of the living, it is possible for these relations thus to come to pass. We had to show that this possibility of a blending in the psychic atmosphere is created by the living through two directions of feeling; the first of which may be called the feeling of universal gratitude to all life's experiences. The general relationship of the human soul to its environment falls into an unconscious part and a conscious part. Everyone knows the conscious part; it consists in man's following what meets him in life with sympathy and antipathy and with his general perception. The subconscious part consists in developing, below the threshold of consciousness, a better and more sublime feeling than any we can develop in ordinary consciousness. This feeling can only be described as the knowledge always in the hidden subconscious part of the soul that we must be thankful for every experience of life, even the smallest. Our difficult experiences may for the moment cause us pain, but to a wider view of existence, even painful experiences so present themselves that, not in the surface regions but in the subconscious soul, man can be thankful for them, thankful that life is unceasingly supplied with gifts from the universe. This exists as a real subconscious feeling in the soul. The other direction of feeling is that we must unite our own ego with every being with whom we have anything to do in life. Our actions extend to other beings, some, it may be, even inanimate; but wherever we have done anything, wherever our being has been united with another in action, something remains; and this remainder establishes a permanent relationship between our being and everything with which we have ever been connected. This feeling of kinship is the foundation for a deeper one, a feeling generally unrecognised by the higher soul; a feeling of oneness with the surrounding world. Those feelings—of gratitude and of union with the environment with which one is karmically united—can come to more and more conscious fruition. To a certain extent a man can awaken in his soul what lives in these feelings and perceptions; and to the degree in which this is done, he qualifies himself to build a bridge to souls living between death and rebirth. Their thoughts can only find the way to us when they are able to penetrate through the realm of the feeling of gratitude which we develop; and we can only find the way to them by fostering in our souls, at least to some extent, a feeling of communion. The fact that we are able to feel gratitude towards the universe enables such a mood to enter our souls. When we wish to enter into relation with the dead in any way, then because we have cultivated this disposition, because we are able to feel it, the way for the dead to reach us is opened; and because we can feel that our being lives in an organic community of which it forms a part, as our finger forms a part of our body, we become ripe to feel the same gratitude to the dead when they are no longer present in the physical body, so that by this means we can reach them with our thoughts. Only when we have acquired something of a disposition of gratitude, a feeling of communion, can we apply them in given cases. These experiences are not the only ones; subconscious perceptions and moods are of many kinds. All that we develop in the soul opens out the path to the world in which dwell the dead between death and rebirth. Thus there is a very definite feeling existing subconsciously, but which can be gradually brought into the consciousness, a feeling which we may put alongside of the feeling of gratitude; it becomes lost to man in proportion as he degenerates into materialism, although to a certain degree it always exists in the subconsciousness and is never rooted out, even by the strongest materialism. Enrichment, enhancement and an ennobling of life, however, depend on man's raising such things from his subconsciousness to his consciousness. The feeling here referred to can be called universal confidence in the life which flows through and past us;—confidence in life! In a materialistic view of life, this disposition to confidence in life is very difficult to find. It resembles gratitude to life, but is quite another feeling alongside of it; for confidence in life consists in a steadfast disposition of soul, so that life, however it may approach us, has under all circumstances something to give us, so that we can never degenerate to the thought that life could have nothing more to give us. True, we pass through difficult and sorrowful experiences, but in the greater life relations these present themselves as something that most enriches and strengthens us for life. The chief thing is that this enduring disposition existing in the lower soul should be raised to the higher—the feeling: ‘O Life! Thou raisest me and bearest me, thou providest for my progress.’ If such a disposition were fostered in educational systems a tremendous amount would be gained. It is even good to plan our teaching and education so as to show, by individual examples, that life deserves our confidence—just because it is often so hard to understand. When a man considers life from such a standpoint, asking: ‘Art thou worthy of confidence, O Life?’ he finds much that otherwise he would not find in life. Such a mood should not be considered superficially; it should not lead to finding everything in life brilliant and good. On the contrary, in particular cases this very ‘confidence’ in life may lead to a sharp criticism of evil and foolish things. When a man has not confidence in life, this often leads to his avoiding the exercise of criticism towards what is bad and foolish, because he wishes to pass by the things wherein he has no confidence. It is not a matter of having confidence in particular things; that belongs to another sphere. Man has confidence in one thing and not in another, according as the things and beings present themselves; but the point is for him to have confidence in the general life, as a whole, in the common relationships of life, for if he can draw up any of the confidence always present in the subconsciousness, a way is opened for the real observation of the spiritual guidance and wise disposition of life. Anyone who is observant, not in theory but with feeling, says again and again: ‘As the occurrences of life follow one another, they mean something to me when they take me into themselves, they have something to do with me in which I can have confidence.’ This prepares him for the real gradual perception of what spiritually lives and weaves in these things. Anyone who has not this confidence closes himself to this. Now to apply this to the relations between the living and the dead. When we develop this disposition of confidence, we make it possible for the dead to find his way to us with his thoughts; for thoughts can, as it were, sail on this mood of confidence from him to us. When we have confidence in life, faith in it, we are able to bring the soul into a condition in which the inspirations, which are thoughts sent to us by the dead, can appear;—gratitude towards life, confidence in life as described, belong in a sense together. If we have not this universal confidence in life as a whole, we cannot acquire sufficient confidence in anyone to extend beyond death; it is then simply a ‘memory’ of our confidence. We must realise that if this feeling is to meet with the discarnate dead, no longer incorporated in a physical body, it must be modified, and different from the perceptions and feelings which are extended to friends in the physical body. True, we have confidence in a man in the physical body and this will be useful for the conditions after death; but it is necessary that this confidence should be augmented by the universal, common confidence in life, for the relations of life after death are different. It is not only necessary to ‘remember’ the confidence we had in him in life, but we need to call forth freshly animated confidence in a being who can no longer waken confidence by his physical presence. For this it is necessary that we should ray something into the world, as it were, which has nothing to do with physical things; for the above-described universal confidence in life has nothing to do with physical things. Just as this confidence places itself side by side with the feeling of gratitude, so something else places itself beside the feeling of oneness which is ever present in the lower soul and can be raised to the higher. That again is something which should receive more consideration than it does. This can be done when the element of which I am about to speak is given consideration in the educational systems of our materialistic age. A great deal depends upon this. If man is to take his right place in the world in the present cycle of time, it is necessary for him to develop a faculty which must be cultivated from knowledge of the spiritual world, not from an undefined instinct;—we might even say he must draw up something from the lower soul which came of itself in earner times of atavistic clairvoyance without any need of cultivation and which, though a few scattered remains still exist, is now gradually disappearing, as is all else derived from olden times. What a man needs in this respect is the possibility through life itself to rejuvenate and refresh again and again his feelings towards what must be encountered in life. We can so squander life that after a certain age we begin to feel more or less ‘tired,’ because we have lost the living share in life and are not able to bring sufficient zest to it for its phenomena to give us joy. Just compare the two extremes: the grasp and acceptance of experience in early youth—and the weary acceptance of life's phenomena in later age. Just consider how many disappointments are connected with this. There is a difference in whether a man is able to make his soul forces take part in a continual resurrection so that each morning is new to his psychic experience, or whether, as it were, the course of his life has wearied him for the appreciation of its phenomena. It is specially important to consider this in our time, so that it should gain an influence in the systems of education. With respect to such things, we face a significant turning-point in human evolution. Our judgment of earlier epochs is framed under the influence of the modern science of ‘History,’ which is fiction of a strangely distorted kind. It is not even known how it has come about that training and education have been so directed that in later life man does not retain what he should. Under the influence of the present method the most that we produce in later years of life from the faculties exercised during our youthful education is a mere memory. We remember what we learnt, what was said to us, and as a rule we are contented if we do but remember. We do not, however, notice that many mysteries underlie human life, and in this connection one significant mystery. Reference has already been made to it in former lectures from another point of view. Man is a manifold being. We will first observe him as a twofold being. This twofold nature is expressed even in his outer bodily form, which shows us man as a head, and as the remaining part. Let us first divide man in this way. Were we to keep this difference in structure well in mind, we should be able to make very significant discoveries in natural science. If we observe the structure of the head purely physiologically, anatomically, it presents itself as that to which the more material history of evolution, known as the Darwinian theory, may be applied. In respect of his head, man is placed, as it were, in the stream of evolution; but only in respect of his head, not as regards the rest of his organism. In order to understand the descent of man, we must think of the head alone, disregarding the proportion in size, and consider all attached to it. Suppose evolution took such a course that in time to come man developed certain additional organs of still greater significance; this development, this metamorphosis, might go even further. This was actually the case in the past: man was, long ago, actually a head-being only, developing little by little and becoming what he is to-day. What is attached to the head, although physically larger, only grew there later. It is a younger structure. As regards his head, man is descended from the oldest organism, all the rest grew later. The reason why the head is so important to the present man is because it remembers former incarnations. The rest of his organisation is, on the other hand, a preliminary condition for later incarnations. In this respect man is a twofold being. The head is organised quite differently from the rest of the organism. The head is an ossified organ. The fact is that if man had not the rest of his organism, he would certainly be very spiritualised,—but a ‘spiritualised animal’ only. Unless the head were inspired thereto, it would never feel itself as ‘man.’ It points back to the old epochs of Saturn, Sun and Moon, the rest of the organism only to that of the Moon, and indeed to the later part of that period; it only grew on to the head-part and is really in this respect something like a parasite. We may well think of it in this way: the head was once the whole man; below, it had outlets and openings by which it fed. It was a very peculiar being. As it developed, the lower orifices closed to the environment, and therefore were no longer able either to serve for nourishment or to bring the head into connection with the influences streaming in from the environment; and because the head also ossified above, the remaining part of the body then became necessary. This part of the physical organism only came into being at a time when it was no longer possible for the rest of the animal creation to take form. It may be said that this is difficult to imagine. The only reply is that man must take the trouble to realise that the world is not so simple as some would like to believe, some who prefer not to think much in order to understand it. In this respect men experience a number of ideas by which they claim that the world is easy to understand, and they have very remarkable views. There is an abundance of literature by those who hold Kant as a great philosopher. That is due to the fact that they understand no other philosophers, and have to exercise much thought-force to understand Kant. As he was to them the greatest philosopher (in their own opinion men often consider themselves to be the greatest geniuses!) they can understand none of the others. It is only because Kant is so difficult to understand that he is regarded by them as a great philosopher. With this is connected the fact that man is afraid to regard the world as complicated, as requiring the power of thought for its comprehension. These things have been described from various points of view, and when some day my lectures on ‘Occult Physiology’ are published, men will be able to read how it can be proved by embryology, that it is foolish to say that the brain has developed from the spinal cord. The opposite is the case; the brain is a transformed spinal cord of former times, and the present spinal cord is only added to the brain as an appendage. We must learn to understand that what seems the simplest part of man has come into being later than what seems the more complicated; what is more primitive and at a more subordinate stage, has come into being later. This reference to the twofold nature of man is made here in order to explain the rest, which is the outcome of this duality. The consequence is, that as regards our soul life, which develops under the restrictions of the bodily nature, we ourselves are included in this duality. We have not only the organic development of the head and that of the rest of the organism, but also two different rates, two different velocities in the development of the soul. The development of the head is comparatively rapid, and that of the rest of the organism—we will call it the development of the heart—is about three or four times slower. The condition for the head is that as a rule it closes its development about the 20th year; as regards the head we are old at 20, it is only because we obtain refreshment from the rest of the organism, which develops three or four times as slowly, that we continue our life agreeably. The development of our head is quick, that of the heart, of the rest of the organism, three or four times slower; and in this duality we live our earthly life. In childhood and youth our headorganism can absorb a great deal, therefore we study during that time; but what we then received must be continually renewed and refreshed, must be constantly encompassed by the slower evolutionary progress of the rest of the organs, the progress of the heart. Now let us reflect that if education, as in our age, only takes into consideration the development of the head, it is because in training and education we only allow any rights to the head, the consequence is that the head is only articulated as a dead organism into the slower progress of the evolution of the rest; it holds this back. The phenomenon that at the present time man grows old early in his soul and inner nature, is chiefly due to the system of training and education. Of course we must not suppose that at the present time we can put the question: How shall we arrange education, so that this shall not happen? This is a very important matter which cannot be answered in a few words, for education would have to be altered in almost every respect, for it would not be a question of memory only, but of something with which man could refresh and revive himself. Let us ask ourselves how many to-day, when they look back to an achievement in childhood, upon all they experienced then, upon what their teachers and relations said, are able to remember more than: ‘You must do this,’ are able to plunge again into what was experienced in youth, looking lovingly back to the hand-clasp, to every single remark, to the sound of the voice, to the permeation with feeling of what was offered them in childhood, experiencing it as a continual fount of rejuvenation? It is connected with the rates of development we experience within us, that man must follow the quicker development of his head, which closes about the 20th year, and that the slower progress of the heart, the evolution of the rest of him, has to be nourished throughout his life. We must not only give the head what is prescribed for it, but also that from which the rest of the organism can again and again draw forth restorative force for the whole of our lives. For this it is necessary that every branch of education should be permeated by a certain artistic element. To-day, when people avoid the artistic element, thinking that to foster the life of fancy—and fancy carries man beyond mere everyday reality—might bring fantasy into education, there is no inclination whatever to pay attention to such mysteries of life. We need only look to certain spheres to see what is here meant—for it does, of course, still exist here and there—and we shall see that something can be realised in this way; but it must be realised by man's again becoming ‘man.’ This is necessary for many reasons; we shall draw attention to one of them. Those who wish to become teachers to-day are examined as to what they know, but what does this prove? As a rule only that the candidate has for the time of the examination, hammered into his head something which—if he is at all suited for that particular subject—he has been able to gather from many books, day after day acquiring what it is not in the least necessary to acquire in that way. What should be required above all in such examinations is to ascertain whether the candidate has the heart, mind and temperament for gradually establishing a relationship between himself and the children. Examination should not test the candidate's knowledge, but ascertain his power, and whether he is sufficiently a ‘man.’ To make such demands to-day would, I know, simply mean for the present time one of two things. Either it would be said that anyone who demands such tests is quite crazy, such a man does not live in the world of reality; or if reluctant to give such an answer, they would say: ‘Something of the kind does take place, we all want that.’ People suppose that results come about from this training, because they only understand the subject in so far as they bring their consideration to bear upon it. The foregoing is intended to throw light from a certain side upon something which the lower soul always feels, and which is so difficult to bring up into the higher soul at the present time; something which is desired by the human soul and will be desired more and more as the time goes on;—so that we may see in the right light the fact that the soul needs something wherewith continually to renew the power of its forces, so that we may not grow weary with our progressing life, but are always able to say, full of hope: ‘Each new day will be to us like the first one we consciously experienced.’ For this however we must, in a sense, not need to ‘grow old;’ it is urgently necessary that there should be no occasion to grow old in soul. When we observe how many comparatively young people there are who are dreadfully old and how few regard each day as a new experience given them, as to a lively child, we know what must be achieved and given by a spiritual culture in this domain. Ultimately the feeling here meant is the feeling which acquires the perennial hopefulness of life and enables us to experience the right relation between the living and the so-called dead. Otherwise the facts which should establish our relationship to one of the dead remain too strongly in the memory. A man can remember what he experienced with his dead during life. If, however, when the dead is physically absent we cannot have the feeling that we can always revivify what we experienced with him during life, our feeling and perception are not strong enough to experience this new relationship that the dead is still present as a spiritual being and can work as a spirit. If a man has grown so deadened that he can no longer revive anything of the hopefulness of life, he can no longer feel that a complete transformation has taken place. Formerly he could help himself by meeting his friend in life; now the spirit alone can come to his help. He can meet him, however, if he evolves this feeling of the ever-enduring stimulation of the life-forces, in order to keep the hopefulness of life fresh. It may seem strange to say so, but a healthy life, especially healthy in the directions which a man might develop here (unless he be in a clouded state of consciousness), never leads to the consideration of life as anything of which he can be tired; for even when he has grown old, a thoroughly sound life leads him to wish to accept each day as something new and fresh. Sound health does not lead a man to say when old: ‘Thank God my life is behind me;’ rather does he say to himself: ‘I should like to go back forty or fifty years and pass through the same circumstances again!’—This is the man who has learnt through wisdom to cheer himself with the thought that what he cannot carry through in this life, he will do more correctly in another. The sound man does not regret anything he has experienced, and if wisdom is needed for this, he does not long to have it in this life, but is able to wait for another. The right confidence in life is built on vigorously maintained life-hopes. These then, are the feelings which rightly inspire life and at the same time create the bridge between the living here and the dead yonder:—gratitude towards the life which greets us here; confidence in its experiences; an intimate feeling-in-common; the faculty of making hope active in life through ever fresh springing life-forces; these are the inner ethical impulses which, felt in the right way, can supply the highest external social ethics; for ethics, like history, can only be understood in the subconscious realm. Another question in regard to the relationship of the living to the dead frequently arises: What is the real difference in a relationship between man and man when incarnated in physical bodies, and between them when one is in a physical body and the other not, or when neither is in a physical body? In respect to one point of view I should here like to mention something of importance. When we observe the ego and actual soul life—also called the astral body—by means of spiritual science (the ego, as we have often heard, is the youngest, the baby among the principles of man's organisation, whereas the astral body is somewhat older, though only dating from the Moon evolution) we must say of these two highest principles that they are not as yet so far advanced for man to rely on them alone for power to maintain himself independently of other men. If we were here with one another—each only as ego and astral body—we should be together as though in a sort of primordial jelly. Our entities would merge into each other, we should not be separate and would not know how to distinguish ourselves one from the other. There could be no possibility of knowing whether a hand or leg were one's own or another's (the whole matter would then of course be quite different, we cannot really thus compare the circumstances). We could not even properly recognise our feelings as our own. To perceive ourselves as separated men depends on each one having been drawn out of the general fluid—as we must picture a very early period—like a drop; and in such a way that the individual souls did not flow together again, but each soul-drop was held together as though in a sponge. Something like that really occurred. Only because we as human beings are in etheric and physical bodies are we separated from one another, really separate. In sleep we are only separated by a strong longing for our physical body. This longing which draws us ardently to the physical body, divides us in sleep; otherwise we should drift through one another all night long. It would probably be much against the grain of sentimental minds if they knew how strongly they come into connection with other beings in their neighbourhood. This, however, is not so very bad in comparison with what might be if this ardent longing for the physical body did not exist as long as man is physically incorporated. We might now ask: What divides our souls from others in the time between death and rebirth? Well: as with our ego and astral body between birth and death we belong to a physical and etheric body, so after death, until rebirth, we are part of quite definite starry structures, in no way the same; each one of us belongs to quite a distinct structure. From out [of] this instinct we speak of ‘man's star.’ This starry structure, taking its physical projection first, is periphically globular, but we can divide it in many ways. The regions overlap each other, but each belongs to another. Expressed spiritually, we might say that each belongs to a different rank of Archangels and Angels. Just as people here are drawn together through their souls, so between death and rebirth, each belongs to a particular starry structure, to a particular rank of Angels and Archangels; their souls all meet together there. The reason this is so, but only apparently (for we must not now go further into the mystery) is because on earth each one has his own physical body. I say ‘apparently’ and you will wonder; but it is surprising when investigated how each has his own starry structure and how these overlap. Let us think of a particular group of Angels and Archangels. In the life between death and rebirth, thousands of Angels and Archangels belong to one soul; imagine only one of all these thousands, taken away and replaced by another, and we have the region of the next soul. 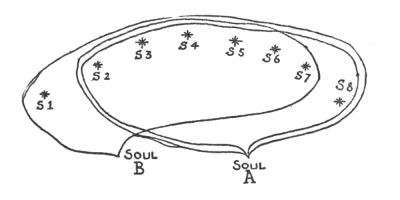 In this diagram two souls have, with one exception, which they have from another realm, the same stars; but no two souls have absolutely similar starry structures. Thus men are individualised between death and rebirth, by having each his special starry structure. From this we see upon what the separation of souls between death and rebirth is based. In the physical world, as we know, this division is effected by the physical body. Man has his physical body as a shell as it were; he observes the world from it, and everything must come to the physical body. All that comes into the soul of man between death and rebirth stands, as regards the relation between his astral body and ego, in a similar way in regard to a starry structure, as here the soul and the ego stand with regard to the physical body. Thus the question as to how this severance comes about is also answered as above. From these considerations we have seen to-day how we can work upon our souls in forming certain feelings and perceptions, so that the bridge of communication may be formed between the so-called dead and the living. What has just been said can also attract thoughts, perceptive thoughts and thoughtful perceptions, which can in their turn have a share in the creation of this bridge. This takes place by our seeking more and more to form a kind of perception with regard to some particular dead friend which when we have experienced something in the soul, can bring up the impulse to ask ourselves: How would the dead experience what I experience at this moment? By creating the imagination that the dead experienced the event side by side with us and making this really a living feeling, man gauges in a certain respect, either how the dead has intercourse with the living, or the dead with the dead, when we consider the various starry realms given, in relation to our own souls or to each other. We can here surmise what interplays between soul and soul through their assignment to the starry realm. If we concentrate through the presence of the dead upon a directly present interest, if in this way we feel the dead living immediately beside us, then from such things as are discussed to-day we become more and more conscious that the dead really do approach us. The soul will develop a consciousness of this. In this connection we must have confidence in life that these things are so; for if we do not have confidence but are impatient with life, the other truth obtains. What confidence brings is drawn away by impatience; what man might learn through confidence, is made dark by impatience. Nothing is worse, than if by our impatience we conjure up a mist before the soul. |
| 235. Karmic Relationships I: Lecture IV
24 Feb 1924, Dornach Translated by George Adams, Mabel Cotterell, Charles Davy, Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| How often have I indicated the great contrast in this regard, as between Kant and Schiller. Kant, both in life and in knowledge, “kantified” everything (“Kante,” in German, means a hard edge or angle.—Note by translator.) In science, through Kant, all became hard and angular; and so it is in human action. “Duty, thou great and sublime name, thou who containest nothing of comfort or ease ... ”—this passage I quoted in my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity to the pretended anger (not the sincere, but the pretended, hypocritical anger) of many opponents, while over against it I set what I must establish as my view: “Love, thou who speakest with warmth to the soul ...” |
| 235. Karmic Relationships I: Lecture IV
24 Feb 1924, Dornach Translated by George Adams, Mabel Cotterell, Charles Davy, Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I wish to bring before you certain broader aspects concerning the development of karma, for we shall presently enter more and more into those matters which can only be illustrated—shall we say—by particular assumptions. To gain a true insight into the progress of karma we must be able to imagine how man gathers his whole organisation together when he descends out of the spiritual world into the physical. You will understand that in the language of today there are no suitable forms of expression for these events which are practically unknown to our present civilisation. Therefore the terms we employ cannot but be inexact. When we descend out of the spiritual into the physical world, for a new life on earth, we have our physical body prepared for us, to begin with, by the stream of inheritance. This physical body is none the less connected in a certain sense, as we shall see, with the experiences we undergo between death and a new birth. Today, however, it will suffice us to bear in mind that the physical body is given to us from the earthly side, whereas those members which we may describe as the higher members of the human being—the ether-body, astral body and Ego—come down out of the spiritual world. Take first the ether-body. Man draws it together from the whole universal ether, before he unites himself with the physical body which is given to him by heredity. The union of the soul-spiritual man as Ego, astral body, and ether-body, with the physical human embryo, can only take place inasmuch as the ether-body of the mother-organism gradually withdraws itself from the physical embryo. Man therefore unites himself with the physical germ after having drawn together his ether-body from the universal ether. The more precise description of these events will occupy us at a later stage. For the moment we are mainly interested in the general question, whence come the several members which the human being has in earthly life between birth and death? The physical organism comes, as we have seen, from the stream of inheritance, and the ether-organism from the universal ether from which it is first drawn together. As to the astral organism, we may truly say that the human being remains in all respects unconscious of it, or only subconsciously aware of it, during his earthly life. This astral body contains all the results of his life between death and a new birth. For between death and a new birth—according to what he has become through his preceding lives on earth, man enters into manifold relations with other human souls who are in the life between death and a new birth, and also with the spiritual Beings of a higher cosmic order who do not descend to earth in a human body, but have their being in the spiritual world. All that a man brings over from his former lives on earth—precisely according to how he was and what he did—meets with the sympathy or antipathy of the beings whom he learns to know during his passage through the world between death and a new birth. Not only is it of great significance for karma, what sympathies and antipathies he meets among the higher Beings according to the things he did in his preceding earthly life. Not only so; it is also of deep significance that he now comes into relation to those human souls to whom he was related on the earth, and there takes place a wonderful “reflection” as between his being and the being of the souls to whom on earth he was related. Let us assume he had a good relation to a soul whom he now meets again between death and a new birth. All that the good relationship implies, was living in him during his former life, or lives on earth; and this good relationship will now be mirrored in the other soul when he encounters him between death and a new birth. Yes, it is really so. As he goes through the life between death and a new birth, man sees himself reflected everywhere in the souls with whom he is now living, because in effect he was living with them on the earth. If he did good to another human being, something is mirrored to him from the other's soul. If he did evil, something is mirrored likewise ... And he now has the feeling—if I may use the word “feeling” with the reservations I made at the beginning—he has the feeling: “This human soul, you helped. All you experienced in helping him, all that you felt for this soul, the feelings that led you on to act thus helpfully towards him, your own inner experiences during the deed that helped him, are coming back to you now from his soul.” Yes, they are actually mirrored to you from the other's soul. Or again, you did harm to a human soul. That which was living in you while you did him harm, is mirrored back. And so you have your former earthly lives (and notably your last life) before you as though in a far and wide-spread reflector, mirrored by the souls with whom you were together. Especially with respect to your life of action, you have the impression that it is receding from you. Between death and a new birth you lose the Ego-feeling—the sense of “I” which was yours when in the body on earth. Indeed, you have lost it long ago. But you now get the feeling of “I” from this far-spread reflection. You come to life in the mirroring of your deeds, in the souls with whom you were during your earthly life. On earth, your “I,” your Ego, was in the body—as it were, a point. Between death and a new birth, it is mirrored to you from the surrounding circumference. This life is an intimate being-together with the other human souls—according to the relations you have entered into with them. And this is a reality in the spiritual world. When we go through a room hung with many mirrors, we see ourselves reflected in each one. But—in ordinary human parlance—we know that the reflections are “not there.” They do not remain when we go away; we are reflected no longer. But that which is reflected here in human souls remains; stays in existence. And there comes a time in the last third of the life between death and a new birth when we form our astral body out of these mirrored pictures. We draw all this into our astral body. In deed and truth, when we descend from the spiritual world into the physical, we carry in our astral body what we have re-absorbed into ourselves, according to the way our actions of the former life on earth were mirrored in other souls between death and a new birth. This gives us the impulses which impel us towards or away from the human souls with whom we are born again in the physical body. In this way the impulse to karma in a new earthly life is formed between death and a new birth—though I shall have to describe it more in detail in the near future; for we must take the Ego also into account. Now we can trace how an impulse from one life works on into other lives. Take, for example, the impulse of love. We can do our deeds, in relation to other men, out of the impulse which we call love. It makes a great difference whether we do them out of a mere sense of duty, convention, respectability and so on, or whether we do them out of a greater or lesser degree of love. Assume that in one earthly life a man is able to perform actions sustained by love, warmed through and through by love. It remains as a real force in his soul. What he takes with him as an outcome of his deeds, what is now mirrored in the other souls, comes back to him as a reflected image. And as he forms from this his astral body, with which he descends on to the earth, the love of the former earthly life, the love which he poured out and which was now returned to him from other souls, is changed to joy and gladness. Such is the metamorphosis—if so we may describe it. A man does something for his fellow-men, something sustained by love. Love pouring out from him accompanies the actions which help his fellow-men. In the passage through life between death and a new birth, this outpouring love of the one life on earth is transmuted, metamorphosed, into joy that streams in towards him. If you experience joy through a human being in one earthly life, you may be sure it is the outcome of the love you unfolded towards him in a former life. This joy flows back again into your soul during your life on earth. You know the inner warmth which comes with joy, you know what joy can mean to one in life—especially that joy which comes from other human beings. It warms life and sustains it—as it were, gives it wings. It is the karmic result of love that has been expended. But in our joy we again experience a relation to the human being who gives us joy. Thus, in our former life on earth, we had something within us that made the love flow out from us. In our succeeding life, already we have the outcome of it, the warmth of joy, which we experience inwardly once more. And this again flows out from us. A man who can experience joy in life, is again something for his fellow-men—something that warms them. He who has cause to go through life without joy is different to his fellow-men from one to whom it is granted to go through life with joyfulness. Then, in the life between death and a new birth once more, what we thus experienced in joy between birth and death is reflected again in the many souls with whom we were on earth and with whom we are again in yonder life. And the manifold reflected image which thus comes back to us from the souls of those we knew on earth, works back again once more. We carry it into our astral body when we come down again into the next life on earth—that is the third in succession. Once more it is instilled, imprinted into our astral body. What is it in its outcome now? Now it becomes the underlying basis, the impulse for a quick and ready understanding of man and the world. It becomes the basis for that attunement of the soul which bears us along inasmuch as we have understanding of the world. If we find interest and take delight in the conduct of other men, if we understand their conduct and find it interesting in a given earthly life, it is a sure indication of the joy in our last incarnation and of the love in our incarnation before that. Men who go through the world with a free mind and an open sense, letting the world flow into them, so that they understand it well—they have attained through love and joy this relation to the world. What we do in our deeds out of love is altogether different from what we do out of a dry and rigid sense of duty. You will remember that I have always emphasised in my books: it is the deeds that spring from love which we must recognise as truly ethical; they are the truly moral deeds. How often have I indicated the great contrast in this regard, as between Kant and Schiller. Kant, both in life and in knowledge, “kantified” everything (“Kante,” in German, means a hard edge or angle.—Note by translator.) In science, through Kant, all became hard and angular; and so it is in human action. “Duty, thou great and sublime name, thou who containest nothing of comfort or ease ... ”—this passage I quoted in my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity to the pretended anger (not the sincere, but the pretended, hypocritical anger) of many opponents, while over against it I set what I must establish as my view: “Love, thou who speakest with warmth to the soul ...” Over against the dry and rigid Kantian concept of duty Schiller himself found the words: “Gern dien' ich dem Freunde, doch tue ich es leider mit Neigung, drum wurmt es mich oft, dass ich nicht tugenhaft bin.” (Gladly I serve my friends, yet alas, I do it with pleasure, wherefore it oftentimes gnaws me, I am not virtuous.) For in the Kantian ethic, that is not virtuous which we do out of real inclination, but only that which we do out of the rigid concept of duty. Well, there are human beings who, to begin with, do not attain to love. Because they cannot tell their fellow-man the truth out of love (for if you love a man, you will tell him the truth, and not lies), because they cannot love, they tell the truth out of a sense of duty. Because they cannot love, out of a sense of duty they refrain from thrashing their fellow-man or from boxing his ears or otherwise offending him, the moment he does a thing they do not like. There is indeed a difference between acting out of a rigid sense of duty—necessary as it is in social life, necessary for many things—there is all the difference between this and the deeds of love. Now the deeds that are done out of a rigid concept of duty, or by convention or propriety, do not call forth joy in the next life on earth. They too undergo that mirroring in other souls of which I spoke before; and, having done so, in the next life on earth they call forth what we may thus describe: “You feel that people are more or less indifferent to you.” How many a person carries this through life. He is a matter of indifference to others, and he suffers from it. Rightly he suffers from it, for men are there for one another; man is dependent on not being a matter of indifference to his fellows. What he thus suffers is simply the outcome of a lack of love in a former life on earth, when he behaved as a decent man because of rigid duty hanging over him like a sword of Damocles. I will not say a sword of steel; that would be disquieting, no doubt, for most dutiful people; so let us say, a wooden sword of Damocles. Now then, we are in the second earthly life. That which proceeds as joy from love, in the third life becomes as we have seen, a free and open heart, bringing the world near to us, giving us open-minded insight into all things beautiful and good and true. While as to that which comes to us as the indifference of other men—what we experience in this way in one earthly life, will make us in the next life (that is, in the third) a person who does not know what to do with himself. Such a person, already in school, has no particular use for the things the teachers are doing with him. Then, when he grows a little older, he does not know what to become—mechanic or Privy Councilor, or whatever it may be. He does not know what to do with his life; he drifts through life without direction. In observation of the outer world, he is not exactly dull. Music, for instance—he understands it well enough, but it gives him no pleasure. After all, it is a matter of indifference whether the music is more or less good, or bad. He feels the beauty of a painting or other work of art; but there is always something in his soul that vexes: “What is the good of it anyhow? What's it all for?” Such are the things that emerge in the third earthly life in karmic sequence. Now let us assume, on the other hand, that a man does positive harm to another, out of hatred or antipathy. We can imagine every conceivable degree. A man may harm his fellows out of a positively criminal sense of hatred. Or—to omit the intermediate stages—he may merely be a critic. To be a critic, you must always hate a little—unless you are one who praises; and such critics are few nowadays. It is uninteresting to show recognition of other people's work; it only becomes interesting when you can be witty at their expense. Now there are all manner of intermediate stages. But it is a matter here of all those human deeds which proceed from a cold antipathy—antipathy of which people are often not at all clearly aware—or, at the other extreme, from positive hatred. All that is thus brought about by men against their fellows, or against sub-human creatures—all this finds vent in conditions of soul which in their turn are mirrored in the life between death and a new birth. Then, in the next earthly life, out of the hatred is born what comes to us from the outer world as pain, distress, unhappiness caused from outside—in a word, the opposite of joy. You will reply: we experience so much of suffering and pain; is it all really due to hatred—greater or lesser hatred—in our preceding life? “I cannot possibly imagine,” man will be prone to say, “that I was such a bad lot, that I must experience so much sorrow because I hated so much.” Well, if you want to think open-mindedly of these things, you must be aware how great is the illusion which lulls you to sleep (and to which you therefore readily give yourself up) at this point. You suggest-away from your conscious mind the antipathies you are feeling against others. People go through the world with far more hatred than they think—far more antipathy, at least. It is a fact of life: hatred gives satisfaction to the soul, and for this reason, as a rule, it is not at first experienced in consciousness. It is eclipsed by the satisfaction it gives. But when it returns as pain and suffering that comes to us from outside, it is no longer so; we notice the suffering quickly enough. Well, my dear friends, to picture, if I may, in homely and familiar fashion, the possibilities there are in this respect, think of an afternoon-tea, a real, genuine, gossiping party where half-a-dozen (half-a-dozen is quite enough) aunts or uncles—yes, uncles, too—are sitting together expatiating on their fellows. Think of it. How many antipathies are given vent to, what volumes of antipathy are poured out over other men and women, say in the course of an hour and a half—sometimes it lasts longer. In pouring out the antipathy they do not notice it; but when it comes back in the next earthly life, they notice it soon enough. And it does come back, inexorably. Thus, in effect, a portion (not all, for we shall still learn to know other karmic connections) of what we experience as suffering that comes to us from outside in one earthly life, may very well be due to our own feelings of antipathy in former lives on earth. But with all this, we must never forget that karma—whatsoever karmic stream it may be—must always begin somewhere. If these are a succession of earthly lives: a b c (d) e f g h and this one, (d), is the present life, it does not follow that all pain which comes to us from without, is due to our former life on earth. It may also be an original sorrow, the karma of which will work itself out only in the next life on earth. Therefore I say, a part—even a considerable part—of the suffering that comes to us from outside is a result of the hatred we conceived in former lives. And now, as we go on again into the third life, the outcome of the suffering which came to us (though only of that suffering which came, as it were, out of our own stored-up hatred), the outcome of the pain which was thus spent in our soul is a kind of mental dullness—dullness as compared with quick, open-minded insight into the world. There may be a man who meets the world with a phlegmatic indifference. He does not confront the things of the world, or other men with an open heart. The fact is, very often, that he acquired this obtuseness of spirit by his sufferings in a former life on earth, the cause of which lay in his own karma. For the suffering which subsequently finds expression in this way, in dullness of soul, is sure to have been the result of feelings of hatred, at least in the last earthly life but one. You can be absolutely sure of it: stupidity in any one life is always the outcome of hatred in this or that preceding life. Yet, my dear friends, the true concept of karma must not only be based on this; it is not only to enable us to understand life. No, we must also conceive it as an impulse in life. We must be conscious that there is not only an a b c d, but an e f g h. That is to say, there are the coming earthly lives and what we develop as the content of our soul in this life will have its outcome and effect in the next life. If anyone wants to be extra stupid in his next earthly life but one, he need only hate very much in this life. But the converse is also true: if he wants to have free and open insight in the next earthly life but one, he need only love extra much in this life. The insight into and knowledge of karma only gains real value when it flows into our will for the future, plays its part in our will for the future. And the moment has now come in human evolution when the unconscious cannot go on working as it did when our souls were passing through their former lives on earth. Men are becoming increasingly free and conscious. Since the first third of the 15th century we are in the age when men are becoming ever more free and conscious. And so for those men who are men of the present time, a next earthly life will already contain a dim feeling of preceding lives on earth. A man of today, if it occurs to him that he is not very bright, does not ascribe it to himself, but to his native limitations; following the current theories of materialism, he will generally ascribe it to his physical nature. Not so the men who return as the reincarnation of those of today. They will already possess at least a dim, disquieting feeling: if they are not very bright, somewhere or other there must have been something connected with feelings of antipathy or hatred. And, if we now speak of a Waldorf School educational method, naturally for the present we must take account of the prevailing earthly civilisation. We cannot yet educate frankly towards a consciousness of life in terms of reincarnation, so to speak. For the people of today have not yet a feeling—not even a dim feeling—of their repeated earthly lives. Nevertheless, the beginnings that have been made with the Waldorf School method will go on developing, if they are truly received. They will develop in the coming centuries, in this direction. This principle will be consciously applied in moral education. If a child has little talent, if a child is dull, It is somehow due to former lives in which he developed much hatred. With the help of spiritual science, you will try to find against whom the hatred may have been directed. For the men and women who were hated then, against whom the deeds inspired by hatred were done, must be there again somewhere or other in the child's environment. Education in coming centuries will have to be placed far more definitely into life. When you see what is coming to expression in such a child, in the metamorphosis of unintelligence in this life, you will then have to recognise from what quarters it is mirrored or rather was mirrored in the life between death and new birth. Then you will do something as educator so that this child will develop an especial love towards those for whom he felt specific hatred in former lives on earth. You will soon see the beneficial result of a love thus specifically roused and directed. The child's intelligence, nay, the whole life of his soul, will brighten. It is not the general theories about karma which will help us in education, but this concrete way of looking into life, to see where the karmic connections lie. You will soon notice it; after all, the fact that destiny has brought these children together in one class is not a mere matter of indifference. People will get beyond the hideous carelessness that prevails in these things nowadays, when the “human material”—for so they often call it—which is thrown together in a class, is actually conceived as though it were bundled together by mere chance; not as though destiny had brought these human beings together. People will get beyond this appalling indifference. Then they will gain a new outlook as educators; they will be able to perceive the wonderful karmic threads that are woven between the one child and the other, as a result of their former lives. Then they will bring consciously into the children's development that which can create a balance. For karma is, in a certain sense, inexorable. Out of an iron necessity we may write down the unquestioned sequence: Love—Joy—an open heart. These are necessary connections. Nevertheless, we also stand face to face with a necessity when we see a river run its course; yet rivers have been regulated, their, course has been known to be altered. So likewise it is possible, as it were, to regulate the karmic stream, to work into it, to affect its course. Yes, it is possible. If therefore in childhood you notice there is a tendency to dullness and stupidity and you perceive the connections, if now you guide the child to develop love in its heart, if you discover (which would be possible already today for people with a delicate observation of life), if you discover which are the other children to whom the child is karmically related, and you now bring the child to love them especially, to do deeds of love towards these other children—then you will give, to the antipathy that was, a counter-weight in the love: and in a next earthly life the dullness will have been improved. There are educators, trained, as it were, by their own instinct who often do these things instinctively. Instinctively they will bring dull-witted children to the point where they develop love, thus educating them by degrees into more intelligent and perceptive beings. It is only when we come to these things that our insight into the karmic connections becomes of real service to life. Before we go on to pursue the detailed questions of karma, one other general question will naturally come before our souls. What sort of person is it—generally speaking—whom you may confront so as to know that you are karmically related to one another? I must reply with a word which is sometimes used in a rather off-hand way nowadays: such a person is a “contemporary”; he is with us simultaneously on the earth. Bearing this in mind, you will say to yourself: If you are with certain human beings in a life on earth, then you were with them in a former life (generally speaking, at least; there may of course, be displacements). And you were with them again in a life before it. Now what of those who live fifty years later than you? They again were with other human beings in their former lives on earth. As a general rule, according to this line of thought, the human beings of the B series—shall I call it—will not come together with human beings of the A series.  It is an oppressive thought, but it is true. I shall afterwards speak of other doubts and questions, such as arise, for instance, when people say—as they so often do—“Humanity goes on increasing and increasing on the earth,” and other things of that kind. Today, however, I want to put this thought before you; perhaps it is an oppressive thought, but it is none the less true. It is a fact that the continued life of mankind on earth takes place in rhythms. One shift of human beings—if I may put it so—goes on, as a general rule, from one life to the next; so does another shift, and they are in a certain sense separated from one another. They do not find their way together in the earthly life, but only in the long intervening life between death and a new birth. There, indeed, they find their way together, but not in the earthly life. We come down again and again with a limited circle of people. Precisely from the point of view of reincarnation, to be contemporaries is a thing of inner importance, inner significance. Why is it so? I can assure you, on the basis of spiritual science, this question, which may well occupy one intellectually to begin with, has caused me the greatest imaginable pain. For it is necessary to bring out the truth, the inner nature of the fact. Thus you may ask: Why was I not a contemporary of Goethe's? Not having been a contemporary of Goethe's in this life, generally speaking—according to these truths—you can more or less conclude that you have never lived with him on earth. Goethe belongs to another shift. What lies behind this? You must reverse the question; but to do so, you must have a real feeling, a perception of what the life of men together really is. You must be able to ask yourself a question on which I shall have very much to say in the near future: What is it really to be another man's contemporary? What is it, on the other hand, only to be able to know of him from history, as far as earthly life is concerned? What is it like? We must indeed have a free mind, a sensitive heart, to answer these intimate questions: What is it like—with all the accompanying inner experiences of the soul—when a contemporary man is speaking to you, or doing any actions that come near you? What is it like? And having gained the necessary perception of this, you must then be able to compare it with what it would be like if you encountered a person who is not your contemporary, and probably has never been so in any life on earth, whom you may none the less revere—more, perhaps, than any of your contemporaries. What would it be like if you met him as a contemporary? In a word—forgive the personal note—what would it be like if I were a contemporary of Goethe? If you are not an insensitive, indifferent kind of person ... Needless to say, if you are insensitive and have no feeling for what a contemporary can be, you are scarcely in a position to answer such a question. What would it be like if I, walking down the Schillergasse, let us say, towards the Frauenplan in Weimar, had suddenly encountered “the fat Privy Councilor,” say in the year 1826 or 1827? One knows quite well, one could not have borne it. You can stand your contemporary; you cannot bear a man who, in the nature of the case, cannot be your contemporary. In a sense, he acts like a poison on your inner life. You can only bear him inasmuch as he is not your contemporary, but your predecessor or successor. Of course, if you have no feeling for such things, they remain in the unconscious; but you can well imagine a man who has an intimate feeling for spiritual things ... if he knew that as he went down the Schillergasse towards the Frauenplan in Weimar, he would encounter the “fat Privy Councilor”—Goethe, with the double chin—he would feel himself inwardly impossible. A man who has no feeling for such things—he no doubt would just have taken off his hat! These things are not to be explained out of the earthly life. The reasons why we cannot be contemporary with a man are in fact, not contained within the earthly life. To see them, we must penetrate into the spiritual facts. Therefore, for earthly life, such things appear paradoxical. Nevertheless, they are as I have said. I can assure you, with genuine love I wrote the introduction to Jean Paul's works, published in the Cotta'sche Bibliothek der Weltliteratur. Yet, if I had ever had to sit side by side with Jean Paul at Bayreuth, it would have given me a stomach-ache, without doubt! That does not hinder one's having the highest reverence. And it is so for every human being—only with most people it remains in the sub-conscious, in the astral or in the ether-body; it does not affect the physical. The experience of the soul which affects the physical body must also become conscious. You must be well aware of this, my dear friends. If you want to gain knowledge of the spiritual world, you cannot escape hearing of things which will seem grotesque and paradoxical. The spiritual world is different from the physical. Of course, it is easy enough for anyone to turn to ridicule the statement that if I had been a contemporary of Jean Paul's, it would have given me a stomach-ache to have to sit beside him. That is quite true—it goes without saying for the everyday, banal, Philistine world of earthly life. But the laws of the banal and Philistine world do not determine the spiritual facts. You must accustom yourselves to think in other forms of thought, if you wish to understand the spiritual world; you must be prepared to experience many surprising things. When the everyday consciousness reads about Goethe, it may naturally feel impelled to say: “How I should like to have known him personally, to have shaken him by the hand!” and so on. It is a piece of thoughtlessness; for there are laws according to which we are predestined for a given epoch of the earth. In this epoch we can live. It is just as in our physical body we are predestined for a certain pressure of air; we cannot rise above the earth to a height where the pressure no longer suits us. Nor can a man who is destined for the 20th century live in the time of Goethe. These were the things I wanted to bring forward about karma, to begin with. |
| 324. Anthroposophy and Science: Lecture I
16 Mar 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Walter Stuber, Mark Gardner Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Along with this methodology, one can see the tendency of this newer scientific thinking to observe the entire field of natural science through mathematics, and with these mathematical thoughts, arrive at mathematical results. You all know the saying by Kant: In every individual science there is only so much real knowledge as there is mathematics. It is thought that in observation, as well as in experimentation, mathematics must be introduced. |
| Now a further question arises which the scientist can answer himself, out of his own experience with scientific work. I have already mentioned what Kant called our attention to, that in every science there is only so much knowledge as there is mathematics contained in it. And, I repeat, this is a one-sidedness, because it is only applicable to a certain field. Kant's error lies in the fact that he takes a specialized truth and tries to make it into a universal law. |
| 324. Anthroposophy and Science: Lecture I
16 Mar 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Walter Stuber, Mark Gardner Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The spiritual science that underlies this course in anthroposophy, must fight for its validity in the truest sense of the word. This can seem strange to one who has become familiar with the motivating forces of this anthroposophically-oriented spiritual science, for it stands solidly on a common ground with scientific and other cultural demands of our time. It deals with all that is necessary and basic for spiritual life in these times. One can see, however, that spiritual science must fight, if one takes into consideration the many prejudices that exist at present. Spiritual science is in some ways a natural adversary of certain reactionary forces that remain and can be observed in the souls of human beings of our time. In these lectures it will be my task to present to you in a direct and scientific manner the significance of what we understand here as spiritual science. I will gradually proceed from relatively elementary things to a real knowledge of man from the point of view of this anthroposophically-oriented spiritual science. I will take pains to introduce some chapters and some special questions by speaking of the methodology, and by the choice of special examples indicate their significance. Today in this first lecture I would like to point out how present-day scientific thinking has increasingly come to rely on the experiment for its main support. In this regard present-day scientific thinking stands in a certain polarity to older kinds of knowledge acquisition, especially to those which start from simply observing nature and the world as it presents itself. One can start by observing the established facts of nature and the world, or—as we often do today—by first creating the conditions of an event and then, with the knowledge of these conditions, observing a fact and being led by this to certain scientific results. Along with this methodology, one can see the tendency of this newer scientific thinking to observe the entire field of natural science through mathematics, and with these mathematical thoughts, arrive at mathematical results. You all know the saying by Kant: In every individual science there is only so much real knowledge as there is mathematics. It is thought that in observation, as well as in experimentation, mathematics must be introduced. Through this, one feels oneself in a secure element, one feels in a position to have an overview of a series of facts with the use of mathematical formulas. This is a totally different relationship to knowledge than when such facts are simply described in their natural state. This feeling of certainty which one has in treating knowledge mathematically, has been characteristic of scientific thinking for a long time. One cannot say we have today a really clear idea of the reasons why one feels so certain and safe with the mathematical handling of the natural world. A clear knowledge of the feeling of certainty accompanying the use of mathematics will lead us to acknowledge the necessity that a spiritual science must come about with an equivalent degree of certainty. This spiritual science does not have to beg for acceptance from natural science or any other special field. This spiritual science will conform in every discipline to the scientific conscientiousness of modern times; it will, in addition, oppose all that is brought forward by modern science that is suspect, and it will answer questions that often go unanswered. Spiritual science will be on a very sure mathematical foundation. I only have to ask a very simple question for you to see that this feeling of certainty derived from the mathematical treatment of certain subjects leads quickly to uncertainty. What would we do with a science like history if in every science there were only so much real knowledge as there is mathematics? How shall we understand and get the facts straight in matters of the human soul if we have to struggle to understand what modern psychology, by the use of mathematics, has developed in order also to secure certainty of understanding? One must come to recognize that in this field it is not possible to introduce mathematics into actual knowledge. One of the first questions that must occupy us is this: What is the significance of this mathematical certainty in the context of human cognition? It is in approaching an answer to this question that we will be led to the justification for spiritual-scientific investigation. I have also said that the newer science prefers the experiment, where one knows the conditions of a process exactly, to outer observation where the determining conditions are more hidden; even in the case of psychology and also the field of education, attempts are made to go over from mere observation to experiment. In saying this, I must emphasize that spiritual science has nothing against the correct use of experimentation in psychology and education. The point I wish to call attention to is this: What draws the scientists in these fields to obtain knowledge by the use of experiment? In these areas we can actually find reasons for the inclination toward the use of experimentation. Let us therefore explore the transition to experimentation in the fields of psychology and education. We can see how until recently investigators in psychology and education have carefully observed the details of the daily life of man, be it fully mature men and women or the transitional developmental life. We might ask: What is fundamentally necessary for an observation of the soul life of the grownup or the developing child? It is to acquire a certain inner relationship to what one observes. Try to put yourselves into the observational methods of olden times, in the fields of psychology and education. You will find that the inner relationship that once existed between human beings has diminished in recent times. We are not so intimately connected in an objective way with the soul life of another human being as was the case in the past. We are no longer aware when our own soul vibrates in sympathetic reverberation with what lives in the soul of another. We are more removed from the objective soul life of the other; formerly it could be directly observed. We are becoming more and more estranged from any really intimate contact with the soul of the other, where in a directly intuitive way one takes part with one's own inner nature in the inner nature of the other soul. Now an effort is made to approach the human soul from the outside through the use of instruments. There is an effort to explore the human soul through the use of apparatus in an external way. This effort is in the character of our time and must be acknowledged as being partially justified. If one has become estranged from a direct perception of the inner activity, then one must accept the outer expression of the inner activity, and at the same time be content with the outer use of experimentation. It is especially true that when we are estranged from the spirit and soul elements of our fellow man, and yet our experiments are the material expression of this soul-spiritual element, these experiments must be explained in a spiritual sense. They should be wrought throughout with the results of spiritual research. I do not want to speak against experiments as such, but there is a need (I will speak today only in an introductory way) to illuminate the results of these experiments spiritually from within. To explain this properly, I will give you the following example. Investigations have established that the rate of growth differs between boys and girls. In the development of a boy, it has been shown that in certain phases he grows more slowly, while in the same time period the girl grows faster. One can take notice of these facts even if one only looks at the outer expression of the soul life. But to explain such facts one must know how the soul motivates the growing process, how the soul of the boy is inwardly different, and how the force of the soul expresses itself in different phases of life. Then one will be able to see how the difference of growth rates between boys and girls permits a comprehension of what goes on in the soul of a boy and what goes on in the soul of a girl. It is just here that one can know that a human being who develops very rapidly during the period of 14 to 17 years, develops different forces than those of a human being who grows rapidly in a somewhat earlier period of life. Especially in our age, in which there is real proficiency in the handling of facts in an outer experimental way, especially now if we are not to be drawn into superficiality, into externalities, what is investigated experimentally must be permeated with the results of spiritual research. This consciousness is opposed to the more mathematical type of consciousness that gives the researcher such a feeling of extraordinary sureness. If one wishes to examine the different ways of research, one might ask oneself the question: How does one actually know things mathematically when one applies mathematics to the facts of the outer sense-accessible world? And what distinguishes this mathematical approach from other modes of dealing with the facts given to us? Let us start with the fact that the outer objects and events of the world are given to man through his senses. From childhood on, the outer factual world presents itself to us as a kind of chaos. But as time passes we strengthen ourselves inwardly with all kinds of mental images and concepts. (I have set this forth in detail in my booklet Truth and Science.) Through the process of making mental pictures of the outwardly perceived world, we take what may lie far apart in observation and we bring the mental pictures of these observations close together within us. Through this activity we thus create, in our mental life, a certain order in what otherwise is chaotic in the purely sense-perceptible. We must, however, look very exactly at how we treat the perceptual facts of the world when we do not use our mathematical knowledge. We might ask what happens when we simply observe the outer world and make mental pictures about the connections between the observable facts—for instance, when we use the familiar law of cause and effect. We must acquire some thoughts about what we are doing when we simply observe the facts of the outer world. What do we really do when we bring order into the sense-perceptible chaos? It appears to me that in relation to this question David Hume has spoken quite correctly; however, his fault lies in that he has taken to apply to the universal field of human cognition what is meant only for this particular field, namely, the “observation of outer nature free of mathematics.” Most errors and one-sidednesses are based an the application of very correct thinking in one field to the totality of human cognition. This makes it so difficult to take the assertions considered to be universally true. Arguments can be raised for the universal truth being applicable to specific areas, and arguments can also be raised for the opposite point of view. David Hume says: We observe the outer world and we arrange it in a lawful way through our own mental pictures. However, what we then have in our soul as law is not directly representative of something in the objective world. We cannot say that the outer world is always going to follow the course predicted by such a law. We can only say, according to David Hume, that until today we have been able to see the sun rise every morning. That is a statement that fits the facts. We can put these facts into the form of a general law. But in doing so we have no guarantee that we have anything other than a series of events that have happened in the past, of which we made a comprehensive mental picture. What is it really in us that brings about these lawful connections between the sense-perceptible occurrences? What kind of significance do these lawful connections have for the field which we are considering? Is David Hume correct when he says: It lies in the habit of our souls to gather together in a lawful manner the facts as they present themselves to us and, because we respond to this soul habit, we create for ourselves various natural laws? These natural laws are nothing else than what has been gathered together from individual facts through habit of our souls. Thus one can say: Above all, man develops a practical life by bringing order and harmony into the otherwise chaotic stream of everyday facts; and the more one advances in this knowledge, in this special kind of knowledge, the more one inclines to this characteristic soul habit. This being the situation, one is not inclined to preserve individual phenomena as such; one wants to respond to the soul habit of bringing into uniformity what faces one as sense-perceptible, empirical manifoldness. If one is honest, one has to admit that all the knowledge obtained in this way stands as a closed door to the outer world in that it does not allow the essence of this outer world to enter our cognition. In this kind of cognition we must say: Out there are the material facts; we arrange them habitually into our system of mental pictures, and thus have a comprehensive view of them. We know when a series of facts have happened, that this series will happen a second time in a similar way when the same facts appear again before us. But as long as we remain in this field of knowledge, we cannot see through the outer appearances; we also, of course, do not claim to do so. When we want to present rash metaphysical hypotheses concerning matter, that it consists of this or that, we are attempting to change the state of affairs in which we do not deal with the material itself. We say to ourselves: We cannot see through matter to find out what it really is in its inner being, so what we are inclined to do is to arrange sequences of mental pictures and put these in the form of laws. By doing so, we remain outside what appears as outer reality; we only create pictures of the external material happenings. Basically, we need this kind of knowledge to maintain our normal human consciousness, and to this end, we concern ourselves with these pictures. Try to think for a moment what it would mean for human consciousness if we were not able to give ourselves up to the kind of knowledge consisting only of pictures of the external world—if every time we wished to know something of the outer world, this world had to flow into us, as it does when we eat or drink, if it had to become part of our soul's apprehension before we could know anything. Just imagine how incompatible such a uniting of the material existence and our inner life would be with what our soul-constitution must be in acquiring knowledge of the outer world! We are in the position where we must tell ourselves: In our activity of knowing, nothing flows into our soul life from the outer world; we form pictures of what we experience in the outer world and these pictures really have nothing to do with the outer world. Permit me to make an analogy out of the field of art to explain what I have been saying. Suppose I am painting something. The outer world is completely unconcerned about anything I might paint on a canvas. Take, for example, a couple of trees we see out there of which, let's say, I have painted a likeness on a canvas: the trees are completely indifferent as to how I have painted them, or if I do paint them. My picture is added to what is out there as something foreign, something that has nothing directly to do with that outer reality. In the field of theoretical and psychological knowledge it is basically the same as I have just described with the example of painting. If we were not separated from the world as just described, and were to take the content of the world into our soul in a way similar to when we eat or drink, our soul would grow together with, be one with, the world around us, and we would be unable to distinguish ourselves from our surroundings. We will take up the subject of human freedom at a later time and show that it can only be understood if the way of knowing the material world is as I have characterized it. This, however, is not so when I know something mathematically. Let's start by imagining how you know something of a mathematical nature, whether it is in the field of arithmetic, algebra, higher mathematics, or in the field of analytical or synthetic geometry. There we are not confronted by an outer world, we live directly and immediately in the objects of our mathematical knowledge. We form mathematical objects inwardly with all their interconnections and relationships, and when at times we sketch these forms, it is only for our own ease and comfort. What we refer to as mathematical is never some part of the outer world which we perceive with the senses, it is always something inwardly constructed. It is something that only lives in the part of our soul life that is not concerned with the senses as such. We build up, we inwardly construct, the mathematical content of our soul. There is a radical difference between the field of knowledge concerned with the empirical outer world presenting itself to the senses and that of the mathematical. In the external given world the objects of our knowledge remain strictly outside of us. In mathematical knowledge we stand with our whole soul within the objects of our knowledge, and what is observed as substance is the result of an experience in our soul of what we ourselves constructed. Here we have a significant problem which forms, as it were, the first stage to what will be the next higher stage of considerations: How does one arrive at the anthroposophical spiritual science when starting from the familiar science of the present day? I don't believe anyone will be able to answer this question in a truly scientific way who cannot first answer the question: How is our knowledge of a purely observational kind raised to the kind of knowledge of nature that is permeated with mathematics?—how is this knowledge related to mathematical knowledge as such? Now a further question arises which the scientist can answer himself, out of his own experience with scientific work. I have already mentioned what Kant called our attention to, that in every science there is only so much knowledge as there is mathematics contained in it. And, I repeat, this is a one-sidedness, because it is only applicable to a certain field. Kant's error lies in the fact that he takes a specialized truth and tries to make it into a universal law. We have a tendency not to want to leave the facts alone as they are presented to us, but rather to color them with what we have created as mathematical formula, so that we may measure and compare them. What really lives in us when we strive in this direction, when we don't want to remain standing still, habitually combining the outer facts with general rules, when we permeate the given facts with what we have formulated in full consciousness mathematically as objects in our soul life? It is clear that anyone who has experience in the field of objective observation will admit that the whole of nature surrounding his own being is felt, in regard to its materiality, as something foreign. Please notice that, in a sense, we can submerge ourselves into what we feel as a foreign material element, with the help of what we have ourselves inwardly constructed as mathematical formulas. What we describe in a mathematical way actually seems as if what happens in nature has occurred according to the mathematical formula that we have constructed. What is at the basis of this perception? It is the fact that we desire above all else to become one with what we perceive at first as foreign surroundings. We group what is presented to us externally in order to be able to reconstruct it in the same way that we construct something in the purely mathematical realm. We strive to experience what presents itself to us externally in an inwardly exact manner. This internalization of the outer world with the wish to experience exactness is what motivates a mathematical explanation of nature. This is especially characteristic of our present-day scientific efforts in the direction of technology. Today's science has an intense longing to penetrate outer occurrences with mathematical concepts. This means that we bring something we have created in our own soul out into what presents itself to us in raw perception. We do this so that we may understand what is perceived, but in doing so we can have the impression that the outer occurrence actually proceeds in the way we portray it mathematically. When we have gone so far that we have achieved this ideal, as we have in the field of optics and light theory, where every phenomenon is represented in terms of a formula, what really have we done? What really is the content of our soul when instead of plain external appearances a sum of mathematical formulas seem to present themselves? What does our soul receive from this? We look at this edifice, the world portrayed as mathematical relationships, and then we turn our gaze to the actual outer world and we find something strange. We find that all that we look at, all that we consider outer material world, appears inwardly dark until it is brightened by the introduction of mathematical concepts. But at the same time we cannot deny the fact that the picture we have created of the outer world no longer contains reality, no longer the reality which presented itself to us originally. Take, for example, optical appearances, the whole field as it presents itself to our eyes; contrast this with what we have, to a certain extent, correctly constructed as mathematical geometric optics, full of rules. If one uses just a little objectivity, it is clear that in what is constructed as a mathematical picture there is nothing left of the abundance of color. Everything that our senses first offered us, namely, actual outer reality, has been pressed out of the picture. The picture of the outer world is in sharp contrast to what is really out there; it lacks reality, it lacks the tremendous abundance that actually exists in the world. In the coming lectures I will be speaking of a comparison, that to begin with I would like you to consider as an analogy. When we permeate empirical facts with mathematics, our activity consists of two stages: First we must look at the empirical facts, let's say the facts of the eye. The second is the arrangement of these percepts into mathematical formulas. In a certain way, as a result of this we have essentially an experience of mathematical formulating. We no longer view the empirical world of phenomena. This process can be compared to our inhaling life-sustaining oxygen; we saturate our whole organism with it. The oxygen then combines with carbon and we exhale carbon dioxide, which is no longer the life-sustaining air. But the combined process was necessary for our inner life. We had to inhale the life-strengthening oxygen and combine it with something in us. What is produced in this way is something killing; we can contrast it with what was inhaled, which was life-sustaining. For the time being, this should only be considered as a picture of the way in which we pursue the knowledge of nature. We take something into ourselves that is presented to the senses and try to unite it intimately with something we produce only in ourselves, with mathematical construction. We feel that something is created by this union. Nature is not contained in what we have created; the living quality is not there, just as the life force is no longer in the air we exhale. We can say that our perception of the outer world is like an inhaling by the soul of what then is changed into the opposite. If one looks closely at this process of striving for mathematical knowledge of nature, it is proof of the fact that mathematical knowledge is something completely different from the merely perceptual knowledge of nature. This mere perceptual knowledge of nature contrasts with the habitual state of our soul, which consists of a feeling of competence derived from the use of inwardly formed mathematical knowledge. This state of soul wishes to have something that will explain the outer world in accordance with our own being, to unite something inner with something outer. When one realizes how the longing for mathematical explanations of nature are based on this soul habit of longing to take inner possession of the outer world, then it will also be clear that what one attains by this is completely different from the content of sense experience. One goes more deeply into human inner life with mathematical knowledge. One believes that one gets correspondingly closer to the outer world through an inner representation of the nature of the outer world. One has an inner experience of what has been changed into mathematical formulas; at the same time, one has basically lost the fullness of the outer world. One must, however, be conscious of the fact that what the outer world has given has been connected with something constructed purely inwardly. One must really experience what goes on in one's soul when one makes mathematical formulas; one must experience this correctly. One must see that a mathematical formula actually is constructed within us. One must realize that this inner human construction has been achieved apart from the outer world, and yet in a sense it has brought one closer to the outer world. Even so, this inner mathematical construction cannot be regarded as inner reality as compared to what we find in the outer world. If this were not true, we would have the feeling that this mathematical construction contained true reality instead of a bland version of the outer world which it does actually present to us. Think what the situation would be if in our spiritual contemplation of a mathematical construction we had the whole content of the eyes' original experience in all its color intensity. If this were the case, we would experience in the formula itself the lighting up, the intensity of colors, when considering the wave theory, or “interference phenomena,” in mathematical form. This we certainly do not see. The fact that we do not see this proves that with our mathematical formulas we penetrate only to some degree into the outer world. We do come closer to it, but at the same time we no longer have the full reality of it. We have shown a progression from an ordinary sense-based knowledge to a knowledge of inner mathematical construction. The question then arises: Can this progression be continued further in human soul life? First, we have an outer world before us; then we confront it in such a way that the laws which we create, based on observation, are entirely different from it in form. We go through this and we can do so because we become inwardly separated from the outer world. We are inwardly completely separated from the outer world while experiencing these mathematical formulas. We do gain a certain penetration through these mathematical formulas, but it is obvious that they are not filled with reality or we would see the whole outer reality recreated in the formulas. When we take a closer look we see that not only are they not real in themselves but in fact they have the effect of destroying reality. The question now arises: would it be possible to strengthen our capacity to make these inner mathematical constructions by which we then penetrate the sense-perceptible world? Is it possible that what is first experienced mathematically as pale abstractions can be made stronger? In other words, could the force which we have to use to attain a mathematical knowledge of nature be used more effectively?—with the result not just a mathematical abstraction, but something inwardly, spiritually concrete? In that case, we would not just see a re-created version of the outer world or an abstract mathematical picture, but we would have something formed in an entirely different manner. We would have gained something with the full character of reality, but obtained similarly to the way we obtain mathematical pictures. We would then have before us spiritually a reality that shines out toward us in the same way that the outer sense-perceptible world streams toward us. But we would have this from pictures filled with reality, not from mathematically abstract pictures. We would have lifted ourselves, through strengthening our mathematical capacity, to a higher level, and in doing so we would reveal more of our own inner reality. This we can see as a third step in our attainment of knowledge. The first step would be the familiar grasping of the real outer world. The second step would be the mathematical penetration of the outer world, after we have first learned inwardly to construct the purely mathematical aspect. The third would be the entirely inner experience, like the mathematical experience but with the character of spiritual reality. So we have before us: The ordinary outer empirical knowledge of nature, then mathematical knowledge, and finally, spiritual knowledge. We have, as the last step, through an inwardly creative activity, spiritual worlds before us . As preparation for viewing these worlds as real, we start by creating mathematical, pictorially-abstract elements. We use this mathematics in relation to the outer world, but if we are honest we must say: What we construct mathematically is still not a reality in itself; it does not bring reality up out of the depths of our souls, rather it is a picture of reality. In spiritual science we gain the ability to bring out of the depths of our souls what is not just a picture of the outer existence, but reality itself, true reality. The three levels of human knowledge are: Knowledge of physical nature, mathematical knowledge, and spiritual knowledge. This is not just taking spiritual science out of thin air with the purpose of constructing a spiritual science method; rather, it arises naturally. Starting from merely empirical research we come to a mathematical approach, and the continuation of this leads us to study an anthroposophically-oriented spiritual science. This, my dear friends, is what I wanted to say today as an introduction to this course of lectures. I wanted to show you that this anthroposophical spiritual science knows where its place is in the whole system of sciences. It is not born out of some kind of subjective caprice, some kind of dilettantism; it is born out of an exact theory of knowledge. It is born out of the knowledge that must be used even to understand the correct use of mathematics. It was not for nothing that Plato demanded of his pupils that they must first of all have a good grounding in the knowledge of geometry and mathematics. Plato did not require an arithmetical or geometric knowledge of some particular kind, but rather a sound understanding of what really happens in a man when he does mathematics or geometry. This is based an a seemingly paradoxical but deeply meaningful saying of Plato: “God geometrizes.” He did not mean by this that God just created with mathematics, or with five- or six-sided figures; rather, He creates with the force of which we can only make pictures to ourselves, in our mathematical abstract thinking. Therefore I believe that he who understands the place of mathematics in the whole field of the sciences, will also understand the correct place of spiritual science. Spiritual science will battle for its right to exist, no matter what adversaries it may have, for it builds on an exact foundation thoroughly in accord with historical necessity. Therefore I can say: We welcome any and all opponents who will seriously enter into what spiritual science has to say; we welcome any serious dialogue. Spiritual science has no fear of opposition because it is well supplied with all the scientific weapons of ordinary science and it knows how to use them. It would only not like to be continuously interrupted by those who don't understand it, due to their dilettantism and uninformed opinions. Spiritual science as we mean it here is actually a necessity for the other special sciences. The borders of these other special sciences must be crossed over with the help of spiritual science. We must inwardly resolve at least to confront those who, without reason, oppose this spiritual science, and sometimes even be a bit rude with them. There is a fundamental need for humanity to adopt this spiritual science as quickly as possible, and in all seriousness. This can really happen if only we bring good will to the understanding of it. |
| 343. The Foundation Course: Theory and Living Spirit
27 Sep 1921, Dornach Translated by Hanna von Maltitz Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| One takes for instance the example of the development of the earth according to geology and so on, spanning only a certain time in history and then according to these impressions arrive at the origin of the earth as coming out of the ancient mists, or like the modified hypotheses in the sense of the Kant-Laplace theories which are no more valid these days; then out of this comes the imagining of the earth's origin and out of the second main statement of the mechanical heat theory, the theory of entropy, the imagining how everything is heading for death through heat (Wärmetod). |
| For example, Herman Grimm said a rotting and decaying carcass bone would be an appetizing piece compared to what the Kant-Laplace theory made of the earth.—What Herman Grimm added is true, future generations of scholars will be able to make astute treatises to explain the nonsense which the Kant-Laplace theory introduced into people's heads, to their detriment. |
| 343. The Foundation Course: Theory and Living Spirit
27 Sep 1921, Dornach Translated by Hanna von Maltitz Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] Emil Bock: I would like to open the hour of our discussion with my immediate task in asking Dr Steiner to give answers regarding the letter of Dr Rittelmeyer. This letter has indeed grown out of various wishes for guidelines regarding possible answers to those who made these objections. [ 2 ] Rudolf Steiner: If we have to start with it, please permit me to make a few points. I ask you however, to link your remarks to those comments I will be making, because obviously some of you here can approach what Dr Rittelmeyer has formulated, from another point of view. [ 3 ] Firstly, I think there is a feeling for many today that some kind of impact is needed in religious life, that religious life needs a kind of renewal in the most diverse areas. Dr Rittelmeyer has formulated the experience which he indicates is present with those familiar with it and I have to admit, something similar has at times confronted me. Already in relation to his first point presented here, one expects unified thoughts, a soul-powerful feeling—and this is summarised in the words "one thing is necessary"—while one finds in Anthroposophy a sum, even perhaps a very large sum of declarations regarding the world content and so for a person, who knows no sure approach, has to say: it appears to me through this experience that in many respects it has already been there for such a long time and has now contributed a lot to the fact that we in our current western civilisation have entered into a dead end. [ 4 ] Just think how vague, how uncertain an experience would be to presume it could perhaps be more succinctly formulated in order to solve the problem. One could even make references to this in our domain. In our domain another kind of domain has arisen out of Anthroposophic foundations where something similar has happened as what is meant with this point, if I understand it correctly. This is in the domain of social thinking. Something like a unified thought has come about, I could say, in the domain of the Threefold social organism. Firstly, I only want to make characteristic comparisons. I must confess this example doesn't show anything significant when it appears publicly in such a short formulation. In life such short formulations don't prove to be really effective; having a decisive importance. I always encounter an objection for instance when someone says: You want to tell me something about the human organism, and instead of giving me a uniform idea, you present an entire physiology.—One must try and understand how the doubt-free comfortable thoughts of modern time have contributed largely to our unhappiness and inner and outer relationships, and what we are suffering from is based on the vague manner of our desire to understand everything in a summary. One has to say to oneself: precisely because such ideas arise, proves that something must change when things happen, which many expect in a vague way. In particular, when it is then said, instead of such "uniform ideas." instead of "mighty soul feelings," a number of exercises are given, some of them could be of a moral nature—and others—they are called "occult" in the letter, which makes an unusual, thoughtful impression on others—yes, it must even be said: What can one then actually expect?—One can expect that there will simply be a debate about what current humanity is missing. I'm speaking firstly in this way, how in the anthroposophical domain it is by all means necessary; we will soon address the particular religious questions given in the letter itself. [ 5 ] You see, the moral exercises, which are mentioned here as familiar, are such that according to their wording, they certainly would be known if they were moral instructions. Firstly, according to the anthroposophic context, this is not what they are. In an anthroposophic context they are indications for the attainment of higher knowledge. It is certainly presented in such a way that it must be clear: they are indication for the attainment of a higher, supersensible knowledge. One must after all admit: If I would say a person necessarily longs for the attainment of supersensible knowledge, as opposed to if I say, that a kind of tranquillity in relation to "exulting to the skies, grieving to death" provides humanity with a moral stand, there is certainly a more radical difference between them. By me expressing something like the demand for serenity, I'm expressing something which could perhaps be quite well known, and which could initially sound like an obvious moral instruction, but which is not a discussion based on the demand for serenity. Is it said in my book 'Knowledge of the higher Worlds and its attainment' that for the purpose of morality, for the purpose of obtaining moral support it is necessary to develop serenity? No! Something quite different is said. It is said that an exercise needs to be done, it is said that this exercise needs to be repeated, in this way the exercise should be done in a certain rhythm in such a way that one could describe it as done in tranquillity. To repeat a certain exercise is quite different to a moral action. Above all you need to consider what is given in my book Knowledge of the higher Worlds and its attainment. You see, it is actually the most natural thing that one person can say to another: you need to make an effort to search for the truth. That is a self-evident fact. Here the important thing is that within the rhythmic sequence of thoughts, thoughts are rendered to the truth, in relation of human beings to the truth. This exercise, this making-oneself-conscious-in-the-present within such a content, this repeated rhythmic making-oneself-conscious-in-the-present is what is involved. It is about applying quite a particular mood for spiritual knowledge. I want to explain this attitude to you in more detail. I will deviate from the strict formulation of the letter but maybe this will make some things much clearer. [ 6 ] Let's see, take for example a professor, lecturer or some scholar who gives lectures. Very often it happens that he prepares his lecture, then memorises it and then delivers it. This is indeed not possible if one really allows spiritual science to live within it. If you lived within spiritual science, this would be unworthy of you. Preparation can only be that a certain inner accumulation regarding the subject matter comes about. As a result of this inner assembly you do indeed step—even though you have a been connecting with the subject matter a thousand times—each time again with a new approach regarding the subject matter, so that you gradually grasp it clearly and speak out of the direct observation of it once again. You see, when you learn about something, for example a chapter in geography—good, you learn it, you have it, and then you retain in your thoughts. This doesn't happen in spiritual science at all if it is to be alive. Whoever wants to be a spiritual scientist in reality, must just again and again allow the most elementary things to draw through the soul. What I have written for example in my book Theosophy doesn't have a conclusive meaning. What it contains, I had to repeatedly allow to be drawn through my soul for it to have meaning. It can't be said: The book Theosophy is there, I know its contents.—It would, on the basis of spiritual science, be the same if one would say: I don't believe that there is a person who could say: I have eaten for 8 days so now I don't need to repeat it.—Every day we sit down to eat and do the same thing. Why? Because it is Life, it is not something which can be merely stored in thought form. The life in spiritual science is Life, and it declines if it is not ever and again lived through. This is what needs to be considered. [ 7 ] If you have through spiritual science approached life you would have become acquainted with the possibility for instance, that you can help those who have passed through the gate of death, by giving them a kind of meditative content based on the spiritual world which they have entered through the gate of death. This doesn't mean that one, for example, reads something to them once and now recon: now they understand it—no, it involves repeating it ever and again, this living-yourself-into the content, each time, as something new. This is far too seldom respected. People are used to observe everything as theory. Spiritual science is no theory, it is Life; but if one treats it by thinking one can learn it, like you learn about other things, then you make it into a theory. Obviously one can make it into a theory but then if you take it up this way, it is only a theory. Every serious spiritual scientist knows that one must live in it; the exercises are not exhausted by knowing their contents. [ 8 ] These are things which have disappeared from Western consciousness. What this Western consciousness is, shows also in other things. People have come to me who say: There's something awful about the Buddha speeches, they contain mere repetitions; one should surely produce a publication with only the contents of the speeches and leave out the repetitions.—Yet, no one really understands the Buddha-speeches who can make such a statement because the essence of the Buddha speeches depend upon following the rhythmic sequence in very small slots, always repeating the same one. This is an oriental method which does not coincide with our work here and in order to clarify this, I will make some comments. [ 9 ] Continuing with the letter, there is further mentioned about the exercises, that some are strange and questionable. Yes, we must look at the kind of judgement or the basis upon which this assessment is made today. If one speaks about the desire present today for something new, then one must acquaint oneself with why such a desire exists; and what exists must really be characterised. I could, in order to make myself clear, perhaps bring to mind the book of Oswald Spengler The Decline of the West. Spengler followed up with a small brochure entitled Pessimism? I will quote a sentence from Pessimism. He says: It is not important to recognise truth, but to make facts matter.—Now a discussion follows regarding this statement, regarding what he understands as "truth" and as "facts". In one place he says: "Truths are the greats of thought ... what stands in a dissertation is truth, that a candidate fails his dissertation is a fact."—Now one must imagine that with such a sentence something must somehow be said, but it is complete nonsense. Yet people read over something like this, they take it all in, which says something, and they don't notice anything strange and consider it as something outlandish. One can't possibly have a discussion about such a statement, it is total nonsense. Something like this is not even discussed when it is such nonsense; you don't even notice it. It can't fail that in a time in which such a judgment prevails, many strange and questionable things are found. However, we can imagine where we have actually arrived—in any case in another connection than meant by Spengler. We graduate today, so to say without a fuss, up to the highest levels of our study; here in our knowledge itself there are actually no disasters or turning points. You could say that a disaster happens when a student fails, but not knowledge itself. This involvement of the whole person, so that you are able to live with a problem in such an inner way as you have any other outer experience, is something which is rarely found. When you have written a book or if you are a private tutor you may feel very satisfied, but you don't experience disasters or turning points because of the material. This is something which has, one could say, spread over the entire scientific life. [ 10 ] It is necessary that we come to live within the spirit once again, that the spirit becomes a reality in whose processes we participate. This is no contradiction against tranquility. Precisely though cultivating tranquility you acquire the right way to participate more strongly and concretely towards what happens objectively; finally, it is no contradiction against tranquility when one observes all the horror of a volcanic eruption or some similar events this way. [ 11 ] I would like to say that in our modern time there is hardly any receptivity necessary for the particular way to spiritual science, simply the entire way of thinking, the quite different way of experiencing truth, is first necessary. You see, when someone says: Yes, we don't need thinking, we don't need intellectualism, we need feelings!—it is because he doesn't get the feeling that he's being moved inwardly; what should be given is what is lacking. [ 12 ] You see, is it really enough today, to adhere to ancient religious rules? When one gives a single lecture—and I speak from experience—when one gives a single lecture, let's say, from certain details regarding the social question, then there are many listeners who could say or write: Sure, this is all possible but in this lecture the name of Christ is not mentioned even once.—Yes, my dear friends, there is still a divine commandment which says: You should not pronounce the name of God in vain—and there is the commandment: You should not continuously say, God, God. It can be something very Christian, no not continuously say the name of Christ; perhaps it is even Christian for this reason, because the name of Christ is not misused. It is not through the use of Christ's name in every third line that something becomes Christian. [ 13 ] All these things should stop in the old thinking's comfortable way. Those who don't drop this comfortable thinking—they would also have the vague feeling that something must change—they can't be informed about the demands of the time because everything which exists in the demands of the time is something which they are unable to experience; they can't, because they are merely taught that these demands must be experienced basically as they have always been, and not commit to actually moving to solutions which must be investigated to really meet the demands of the time. Often the enormous difference between theoretical thought and immersed-in-spirit-living, is not considered. However, already during the first step into spiritual science there must be a living-within-the-spirit. I'm not saying you need to be clairvoyant or something of the kind, but that there needs to be a living-in-spirit; there must be another form of experience of truth, of content, than what one is accustomed to these days. [ 14 ] Another objection which Dr Rittelmeyer expressed took me quite by surprise, I must admit, but this is the way it's going to happen. The objection is that people feel insulted when, instead of something being pointed out as within them, they are made aware of what individuals perhaps know, what individuals have seen. People feel, they expressed it as "their human kingdoms having been stolen", they had felt great and now they must feel small.—Yes, I must admit, this objection surprised me because I don't really understand its content. Isn't it true, what is said consequently in the letter, that people expect something to happen from above, but now they feel thrown back on to themselves, on to exercises they need to do, on to efforts needed to understand something.—I initially feel an extraordinary contradiction between both these allegations. Secondly, I must add this: my whole life I have been—and it has been already quite long—extremely glad if a truth appears somewhere, and I actually find it disturbing when someone rejects the truth, because it has not grown out of their own soil. This is quite an egotistical subjective judgment, but we are stuck in such egotistical subjective judgments, and as a result we need a renewal of thinking in our current time, because it exists. [ 15 ] Here we have a bunch of judgements which indicates how necessary it is that a shift takes place. If these judgemental directions, which have been created by our time, continue to exist, then we will get nowhere. It is already necessary to say, even though it may sound rough, it is above all necessary to mention that the objectors must think about their objections, to what a degree they should not be making them, in order for the entry of the renewal not to be disturbed by the most ancient judgments. This is what has to be said above all things. [ 16 ] Another objection which is of course often made is that Anthroposophy appears in the form of a science and the inference is made that the realm of belief and the realm of knowledge must metamorphose. Actually, the objection depends, when it is made, on the inexact understanding of the context in Anthroposophy. In Anthroposophy the claim is never made that a belief must be transformed into knowledge or something similar, but in Anthroposophy this first positive element appears: it is shown that through knowledge not only can one have something in the sensory world of appearance, but also in the spiritual world. The question can at least be: Are the methods which are applied directed to the real, safe and equivalent?—This can then be examined and re-examined. When the issue is expressed in a way of objecting to imagination, objecting to inspiration and so on, then there is nothing to be discussed. However, no judgment can be made when one says: I feel uncomfortable if something is to be known about it.—It isn't important if something is unpleasant, but it is important that a certain method regarding the super-sensory can be known, just as in the sensory world something can be known. What can be known can't be judged in a way so that one can say the objects of faith were based on the free recognition of inner truths because Anthroposophy is a knowledge forced through "hallucination and proof."—Anthroposophy is just a science and is established as a science, it can't get involved with such an objection because it is a science. One could have the same objection against mathematics; one could say it would be detestable if mathematical truths were actual truths. Such an objection can't actually be made, because it is basically pointless. [ 17 ] An objection which I have heard with the most diverse nuances, is this, that something is expected, which could be something shocking, which you accept and get away with by listening to such things as "Christ is the ruler of the sun" or the issue about the "Two Jesus children." which are equally indifferent to you. My dear friends, I must admit I don't really understand how these things can be indifferent, when they are understood. The unbelievably important question of the present day is: How can the realm of morality be founded in the realm of natural necessities? We live today on the one side within a scientifically acknowledged realm of natural necessities and one allows that within this realm of necessities, hypotheses are made which are not supported by direct observation. One takes for instance the example of the development of the earth according to geology and so on, spanning only a certain time in history and then according to these impressions arrive at the origin of the earth as coming out of the ancient mists, or like the modified hypotheses in the sense of the Kant-Laplace theories which are no more valid these days; then out of this comes the imagining of the earth's origin and out of the second main statement of the mechanical heat theory, the theory of entropy, the imagining how everything is heading for death through heat (Wärmetod). Who constructs this hypothesis regarding the earth's origin and evolution must say to himself—because according to the scientific point of view on which it is based, it can't be assumed otherwise—that this ancient mist was there as the sovereign entity with laws of aerodynamics and laws of aerostatics, and out of this the laws of hydrodynamics and hydrostatics were created, and then luckily such conditions arose through which connections were created as we find in the simplest cells, the amoebas, and then all that turned into complicated organisms, also humans, and in humans moral ideals rose through which human worth could be felt. [ 18 ] What would we be as humans if we hadn't had our moral ideals, and if through these moral ideals we didn't, through the acceptance of a divine world order in the entire global context, become ennobled? It is useless to just let it go; to say we will separate the realm of the certainty of faith which we have in moral ideals, from what we have as the natural order. Such a separation can only happen with those who aren't really inwardly serious about what they see presented in the natural order. [ 19 ] My dear friends, I once became acquainted with someone who at the time was involved with the great problem of death in the world, explored from Haeckel's point of view. With an earnest attitude, an inner enthusiasm to understand such a point of view, he approached this view which is quite honestly based on the foundation of science. What did he have to say about moral-religious ideals? He said: "Those are religious foam bubbles rising in human life, it is something people put in front of themselves, it is something on which the human race lives, from which they take their dignity; but one day the great graveyard of the heat death will arrive, and then all outer forms of organisms, everything which appeared as moral-religious foam bubbles will be buried, and in the world's space a sloop will be circling in some curve that can be said to be something which people once created according to mechanistic or dynamic laws, these people allowed bubbles to rise and from this the people derived their worth; and all of that has turned out to be a cosmic cemetery." [ 20 ] You see, out of this person's honesty, because he couldn't unhook himself from it, he returned to the blissful womb of the Catholic Church for some years. This is only one example out of many. [ 21 ] This abyss has opened up between the moral-religious world order and the scientific-mechanic world order. There are only a few people capable of enough sensitivity, who doesn't tolerate the entire world view regarding the earth's origin or demise according to science. For example, Herman Grimm said a rotting and decaying carcass bone would be an appetizing piece compared to what the Kant-Laplace theory made of the earth.—What Herman Grimm added is true, future generations of scholars will be able to make astute treatises to explain the nonsense which the Kant-Laplace theory introduced into people's heads, to their detriment. [ 22 ] My dear friends, if with your deepest insight you want to look at what such a point of view has caused for the doom of the human soul, starting in the lowest classes in school, then in order to do what needs to be done today, you must search much deeper than is normally done. You can't get stuck half way and say: We must withdraw religious content from the general view of the world, we must have our own religious certainty and beside it, science may exist.—For then, at most, man's moral-religious view of the world will help him return to the bosom of the blessed Roman Catholic Church to numb himself if he still comes under such an anesthetic. [ 23 ] In the course of evolution, we have reached the point where we no longer know that the spiritual lives in all-natural laws, that for example what happens within man himself, where there is actually a hearth within him, is accomplished outside in nature. My dear friends, the people from the 19th century quite correctly were strongly affected by for example what Julius Robert Mayer expressed as a law of conservation of energy and of matter. (Erhaltungssatz der Kraft.) It has really come to the fore that the law of the conservation of power and of matter in the 19th century dominates our physics today. However, this is valid for outer nature only and there only within certain boundaries which become more limited as time goes by; but in terms of time it doesn't apply to human beings. It is simply true that within man there is a hearth where all material things which he takes into himself, is transformed into nothing, where matter is destroyed, matter is dissolved. By letting our pure thoughts be assimilated by our etheric body and letting these thoughts work on our physical body through the etheric, matter is destroyed in our physical body. (During the next explanation drawings were made on the blackboard. The originals are no longer available.) I'm sketching diagrammatically, it is intensively spread over the entire human being, I draw it in such a way as if it is only a part. This place in a person where matter becomes destroyed is at the same time the place where matter is created again, when morality, when religious perceptions glows through us. What is created here simply by our perceptions through moral and religious ideals, this is like a seed for future worlds. If the material world perishes, when the material world has been destroyed in the heat death then this earth will be transformed into another world body, and this body of a world will be made from the moral ideals created into material forms. Because our science is not capable of penetrating deeply enough into matter, it is not capable of grasping the thought that matter itself is an abstraction. We may speak about the thermal death of the earth, but at the same time we have to speak of what is cast off from plants, in wilting and drying out, and about the seed surviving into the next year; even as we can speak in relation to the heat death, we can speak about the seed which remains to us and survives the world death. [ 24 ] There is a sphere where scientific truths end; mere scientific truths in the sense of today, where moral ideals end being bubbles of foam, when the earth will expire in the heat death. There is an accessible region for man, where moral ideals are received when physical matter is destroyed, a sphere where the Word becomes a natural scientific truth: "Heaven and Earth will pass away but My words will not pass away!"—There is a sphere where the Bible becomes science; and before this—it needs to be acknowledged in the background of today's aspirations—no healing can occur, before we have the opportunity to advance to a science, not a one-sided science like today, nor one which is a one-sided abstract spiritual science. [ 25 ] Today the term "spiritual science" is applied only to the science of ideas. For Anthroposophy spiritual science is not only what can be grasped on the other side of materiality, but it is something whose processes penetrate matter. [ 26 ] With results of this research it is then possible, certainly by applying diligent spiritual scientific methods, to consider everything regarding the relationship between the sun and Christ. These things must be considered in the right light. With a certain authority we have during the course of the last three centuries come to see something regarding the stars, sun and moon, which can be calculated. What has brought us misfortune is that we only calculate. We need to once again observe that by looking at the arithmetic of the world's structure, we are in fact investigating a corpse. We need to learn to investigate the spirit of the cosmic whole. Everything depends on this. We won't find the spirit, if we allow matter to violate us in such a way that it presents itself in the universe as something which can only be calculated, or at most be judged according to basic mechanical laws. For this reason, it can already be said that it depends entirely on the individual human being who says: "For me it is not important that the Christ is the ruler of the sun".—This sentence must be understood in the correct way: "For me it is a matter of indifference". [ 27 ] My dear friends, I've heard a few people say they are indifferent to what the Christ has to do with the sun, but they were not indifferent when their taxes increase by fifty percent. Yet it is more necessary for the overall salvation of mankind that Christ and the sun are seen to be related than the rising tax of fifty percent is. [ 28 ] How we think in detail about the two Jesus children may be discussed again. However, what would one say to an objection which claims we should practice something that, yes, I don't know what it is, and then the issue about the two Jesus children is put on the table, which leaves us indifferent. I open the Gospel and read a great deal which is presented there, similar to the issue about the two Jesus children mentioned in Anthroposophy. Then again, you don't say: We want religion, but we are quite indifferent whether Jesus was the son of Joseph and Mary or something similar, every single Gospel truth leaves us completely indifferent.—I don't know to what else you don't care about. One doesn't want to enter into something which is of no interest to you, but an objection is not the same, it is definitely not. [ 29 ] Now I would still like to enter into point eight which I've written down for myself, because time is marching on. It is said that a certain progress is expected in people's internalizing; yet through the way culture has been created, people have come to hate culture, they don't want to hear anything more about culture, and now (with Anthroposophy) something arrives which doesn't only speak about internalization, but even what strives to have an effect on architecture and the art of movement. [ 30 ] Yes, my dear friends, if you take life seriously you won't want anything other than what appears in Anthroposophy, what appears to you as spiritual foundations penetrating everything in outer life. I'm still talking about Anthroposophy; we will still touch on what religion has to say about it. That's just the trouble, we are no longer in the position to bring what we experience in the spiritual into our outer life, and finally this happens just in those areas where it is the most noticeable. Just imagine you had said to a Greek that he couldn't express his spiritual experiences in outer life. Just as the Greek thought about his Apollo, as he thought about Zeus, he created his Zeus temple accordingly, his colonnaded temple. We no longer create, we imitate what is old; we don't have the possibility of taking those areas relating to the spirit and also create an external physiognomy of life. The only thing we can create is a department store. The department store is the grandiose creation of the materialistic spirit of the present day. However, if we wanted a home for the spirit and turn to a builder, then he would build it in a Romantic, Gothic or some or other style, and we would have no feeling, when we stand there within the walls, of anything being expressed of what we had inwardly lived through spiritually. [ 31 ] You see, when the thought was created—not through me but through others—to build a house for Anthroposophy, not for an instant would an idea exist to approach a builder and let him erect a Renaissance or Baroque building and then to move in there, but the idea could come about in the following way. In this building this and that would be spoken about and the forms which would be visible all around should say exactly the same as what is being spoken within it. If this is not only theoretical but life, if the forms are creative, then they are presented—as living—in the world. It is impossible to measure what is created here as a matter of course in comparison with the dishonest cultural activity of the times which has brought us into all this trouble. [ 32 ] This is what I wanted to present primarily, my dear friends. There are too many questions to deal with in one stroke; I will continue with them tomorrow. I've limited myself today by entering into what has been raised against Anthroposophy in general. I will however expand on what in particular will be raised against the service which Anthroposophy will bring towards religious renewal. I would like to stress the following: if somehow an idea develops that it equally represents an existing religious confession, or a creed, which one thinks to justify only through Anthroposophy as its basis, then you do Anthroposophy a wrong because it has never claimed to be a religious education nor is it a religion or wants to establish a religion. This Anthroposophy will not do. Anthroposophy follows impulses to knowledge, goals to knowledge; and whoever says that Anthroposophy is not a religion because it doesn't have the characteristics of religion—say something which Anthroposophy must say about itself from the outset. You can't accuse someone of being something he doesn't even want to be! The objections which are actually made from a religious side, appear to me as if, let's say, someone is active in a field and is accused of not doing what he could in another field. The objections raised by Dr Rittelmeyer, as far as I have taken into account, certainly involve the relationship people have to Anthroposophy. For this reason, I approached it from this side and will enter into it from the religious side, tomorrow. |
| 7. Mysticism at the Dawn of the Modern Age: Valentin Weigel and Jacob Boehme
Translated by Karl E. Zimmer Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| A detailed elaboration of this train of thought is presented in the views of Immanuel Kant (1724–1804). (I have shown the erroneous aspect of this train of thought in my book,Die Philosophie der Freiheit, Philosophy of Spiritual Activity. Here I must confine myself to saying that with this simple, straightforward way of thinking Valentin Weigel stands on a much higher level than Kant.)—Weigel says to himself, Although perception flows from man yet it is only the nature of the counterpart which emerges from the latter by way of man. |
| 7. Mysticism at the Dawn of the Modern Age: Valentin Weigel and Jacob Boehme
Translated by Karl E. Zimmer Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] Paracelsus was primarily concerned with developing ideas about nature that breathe the spirit of the higher cognition he advocated. A kindred thinker who applied the same way of thinking to man's own nature in particular is Valentin Weigel (1533–1588). He grew out of Protestant theology as Eckhart, Tauler, and Suso grew out of Catholic theology. He had precursors in Sebastian Frank and Caspar Schwenckfeldt. They emphasized the deepening of the inner life, in contrast to the church dogma with its attachment to an external creed. For them it is not the Jesus whom the Gospels preach who is of value, but the Christ who can be born in every man out of his deeper nature, and who is to be his deliverer from the lower life and his leader in the ascent to the ideal. Weigel quietly and modestly administered his incumbency in Zschopau. It is only from his posthumous writings printed in the seventeenth century that one discovers something about the significant ideas he had developed concerning the nature of man. (Of his writings we shall mention here: Der güldene Griff, Alle Ding ohne Irrthumb zu erkennen, vielen Hochgelährten unbekannt, und doch allen Menschen nothwendig zu wissen, The Golden art of Knowing Everything without Error, unknown to Many of the Learned, and yet Necessary for all Men to Know.—Erkenne dich selber, Know Thyself.—Vom Ort der Welt, Of the Place of the World.) Weigel is anxious to come to a clear idea of his relationship to the teachings of the Church. This leads him to investigate the foundations of all cognition. Man can only decide whether he can know something through a creed if he understands how he knows. Weigel takes his departure from the lowest kind of cognition. He asks himself, How do I apprehend a sensory thing when it confronts me? From there he hopes to be able to ascend to the point where he can give an account of the highest cognition.—In sensory apprehension the instrument (sense organ) and the thing, the “counterpart,” confront each other. “Since in natural perception there must be two things, namely the object or counterpart, which is to be perceived and seen by the eye, and the eye, or the perceiver, which sees and perceives the object, therefore, consider the question, Does the perception come from the object into the eye, or does the judgment, and the perception, flow from the eye into the object.” (Der güldene Griff, chap. 9) Now Weigel says to himself, If the perception flowed from the counterpart (thing) into the eye, then, of one and the same thing, the same complete perception would of necessity have to arise in all eyes. But this is not the case; rather, everyone sees according to his eyes. Only the eyes, not the counterpart, can be responsible for the fact that many different conceptions of one and the same thing are possible. In order to make the matter clear, Weigel compares seeing with reading. If the book did not exist of course I could not read it; but it could be there, and I would still not be able to read anything in it if I did not know the art of reading. Thus the book must be there, but of itself it cannot give me anything at all; everything that I read I must bring forth out of myself. That is also the nature of natural (sensory) perception. Color exists as a “counterpart;” but out of itself it cannot give the eye anything. On its own, the eye must perceive what color is. The color is no more in the eye than the content of the book is in the reader. If the content of the book were in the reader, he would not have to read it. Nevertheless, in reading, this content does not flow out of the book, but out of the reader. It is the same with the sensory object. What this sensory object is outside, does not flow into man from the outside, but rather from the inside.—On the basis of these ideas one could say, If all perception flows from man into the object, then one does not perceive what is in the object, but only what is in man himself. A detailed elaboration of this train of thought is presented in the views of Immanuel Kant (1724–1804). (I have shown the erroneous aspect of this train of thought in my book,Die Philosophie der Freiheit, Philosophy of Spiritual Activity. Here I must confine myself to saying that with this simple, straightforward way of thinking Valentin Weigel stands on a much higher level than Kant.)—Weigel says to himself, Although perception flows from man yet it is only the nature of the counterpart which emerges from the latter by way of man. As it is the content of the book which I discover by reading and not my own, so it is the color of the counterpart which I discover through the eye, not the color which is in the eye, or in me. On his own path Weigel thus comes to a conclusion which we have already encountered in the thinking of Nicolas of Cusa. In his way Weigel has elucidated the nature of sensory perception for himself. He has attained the conviction that everything external things have to tell us can only flow out from within ourselves. Man cannot remain passive if he wants to perceive the things of the senses, and be content with letting them act upon him; he must be active, and bring this perception out of himself. The counterpart alone awakens the perception in the spirit. Man ascends to higher cognition when the spirit becomes its own object. In considering sensory perception, one can see that no cognition can flow into man from the outside. Therefore the higher cognition cannot come from the outside, but can only be awakened within man. Hence there can be no external revelation, but only an inner awakening. And as the external counterpart waits until man confronts it, in whom it can express its nature, so must man wait, when he wants to be his own counterpart, until the cognition of his nature is awakened in him. While in the sensory perception man must be active in order to present the counterpart with its nature, in the higher cognition he must remain passive, because now he is the counterpart. He must receive his nature within himself. Because of this the cognition of the spirit appears to him as an illumination from on high. In contrast with the sensory perception, Weigel therefore calls the higher cognition the “light of grace.” This “light of grace” is in reality nothing but the self-cognition of the spirit in man, or the rebirth of knowledge on the higher level of seeing.—As Nicolas of Cusa, in pursuing his road from knowing to seeing, does not really let the knowledge acquired by him be reborn on a higher level, but is deceived into regarding the church creed, in which he had been educated, as this rebirth, so is this the case with Weigel too. He finds his way to the right road, and loses it again at the moment he enters upon it. One who wants to walk the road which Weigel indicates can regard the latter as a leader only up to its starting-point. [ 2 ] What we encounter in the works of the master shoemaker of Görlitz, Jacob Boehme (1575–1624), is like the jubilation of nature, which, at the peak of its development, admires its essence. Before us appears a man whose words have wings, woven out of the blissful feeling that he sees the knowledge in himself shining as higher wisdom. Jacob Boehme describes his condition as a devotion which only desires to be wisdom, and as a wisdom which desires to live in devotion alone: “When I wrestled and fought, with God's assistance, there arose a wondrous light in my soul which was altogether foreign to wild nature, and by which I first understood what God and man are, and what God has to do with man.” Jacob Boehme no longer feels himself to be a separate personality which utters its insights; he feels himself to be an organ of the great universal spirit which speaks in him. The limits of his personality do not appear to him as limits of the spirit which speaks out of him. For him this spirit is omnipresent. He knows that “the sophist will censure him” when he speaks of the beginning of the world and of its creation, “since I was not there and did not see it myself. Let him be told that in the essence of my soul and body, when I was not yet the I, but Adam's essence, I was indeed there, and that I myself have forfeited my felicity in Adam.” It is only in external similes that Boehme can intimate how the light broke forth within himself. When as a boy he once is on the summit of a mountain, above where great red stones seem to close the mountain off, he sees an open entrance, and in its depths a vessel containing gold. He is overcome with awe, and goes his way without touching the treasure. Later he is serving his apprenticeship with a shoemaker in Görlitz. A stranger walks into the store and asks for a pair of shoes. Boehme is not allowed to sell them to him in the master's absence. The stranger leaves, but after a while calls the apprentice outside and says to him, Jacob, you are little, but one day you will become an altogether different man, at whom the world will be filled with astonishment. At a more mature period of his life Jacob Boehme sees the sunshine reflected in a burnished pewter vessel; the sight which confronts him seems to him to reveal a profound mystery. From the time he experiences this manifestation he believes himself to be in possession of the key to the mysterious language of nature.—He lives as a spiritual hermit, supporting himself modestly by his trade, and at the same time setting down, as if for his own memory, the notes which sound in him when he feels the spirit within himself. The zealotry of priestly fanaticism makes his life difficult. He wants to read only that scripture which the light within himself illuminates for him, but is pursued and tormented by those to whom only the external scripture, the rigid, dogmatic creed, is accessible. [ 3 ] Jacob Boehme is filled with a restlessness which impels him toward cognition, because a universal mystery lives in his soul. He feels himself to be immersed in a divine harmony with his spirit, but when he looks around him he sees disharmony everywhere in the divine works. To man belongs the light of wisdom, yet he is exposed to error; there lives in him the impulse toward the good, and yet the dissonance of evil can be heard throughout the course of human development. Nature is governed by great natural laws, and yet its harmony is disturbed by superfluities and by the wild struggle of the elements. How is the disharmony in the harmonious, universal whole to be understood? This question torments Jacob Boehme. It comes to occupy the center of his world of ideas. He wants to attain a conception of the universal whole which includes the inharmonious too. For how can a conception explain the world which leaves the existing inharmonious elements aside, unexplained? Disharmony must be explained through harmony, evil through good itself. In speaking of these things, let us limit ourselves to good and evil; in the latter, disharmony in the narrower sense finds its expression in human life. For this is what Jacob Boehme basically limits himself to. He can do this, for to him nature and man appear as one essence. He sees similar laws and processes in both. The non-functional is for him an evil in nature, just as the evil is for him something non-functional in human destiny. Here and there it is the same basic forces which are at work. To one who has understood the origin of evil in man, the origin of evil in nature is also plain.—How is it possible for evil as well as for good to flow out of the same primordial essence? If one speaks in the spirit of Jacob Boehme, one gives the following answer: The primordial essence does not exist in itself alone. The diversity of the world participates in this existence. As the human body does not live its life as a single part, but as a multiplicity of parts, so too does the primordial essence. And as human life is poured into this multiplicity of parts, so is the primordial essence poured into the diversity of the things of this world. Just as it is true that the whole man has one life, so is it true that each part has its own life. And it no more contradicts the whole harmonious life of man that his hand should turn against his own body and wound it, than it is impossible that the things of the world, which live the life of the primordial essence in their own way, should turn against one another. Thus the primordial life, in distributing itself over different lives, bestows upon each life the capacity of turning itself against the whole. It is not out of the good that the evil flows, but out of the manner in which the good lives. As the light can only shine when it penetrates the darkness, so the good can only come to life when it permeates its opposite. Out of the “abyss” of darkness shines the light; out of the “abyss” of the indifferent, the good brings itself forth. And as in the shadow it is only brightness which requires a reference to light, while the darkness is felt to be self-evident, as something that weakens the light, so too in the world it is only the lawfulness in all things which is sought, and the evil, the non-functional, which is accepted as the self-evident. Hence, although for Jacob Boehme the primordial essence is the All, nothing in the world can be understood unless one keeps in sight both the primordial essence and its opposite. “The good has swallowed the evil or the repugnant into itself ... Every being has good and evil within itself; and in its development, having to decide between them, it becomes an opposition of qualities, since one of them seeks to overcome the other.” It is therefore entirely in the spirit of Jacob Boehme to see both good and evil in every object and process of the world; but it is not in his spirit to seek the primordial essence without further ado in the mixture of the good with the evil. The primordial essence had to swallow the evil, but the evil is not a part of the primordial essence. Jacob Boehme seeks the primordial foundation of the world, but the world itself arose out of the abyss by means of the primordial foundation. “The external world is not God, and in eternity is not to be called God, but is only a being in which God reveals Himself ... When one says, God is everything, God is heaven and earth and also the external world, then this is true; for everything has its origin from Him and in Him. But what am I to do with such a saying that is not a religion?”—With this conception as a background, his ideas about the nature of the world developed in Jacob Boehme's spirit in such a way that he lets the lawful world arise out of the abyss in a succession of stages. This world is built up in seven natural forms. The primordial essence receives a form in dark acerbity, silently enclosed within itself and motionless. It is under the symbol of salt that Boehme conceives this acerbity. With such designations he leans upon Paracelsus, who has borrowed the names for the process of nature from the chemical processes (>cf. above). By swallowing its opposite, the first natural form takes on the shape of the second; the harsh and motionless takes on motion; energy and life enter into it. Mercury is the symbol for this second form. In the struggle of stillness with motion, of death with life, the third natural form (sulphur) appears. This life, with its internal struggle, is revealed to itself; henceforth it does not live in an external struggle of its parts; like a uniformly shining lightning, illuminating itself, it thrills through its own being (fire). This fourth natural form ascends to the fifth, the living struggle of the parts reposing within itself (water). On this level exists an inner acerbity and silence as on the first, only it is not an absolute quiet, a silence of the inner contrasts, but an inner movement of the contrasts. It is not the quiet which reposes within itself, but which has motion, which was kindled by the fiery lightning of the fourth stage. On the sixth level, the primordial essence itself becomes aware of itself as such an inner life; it perceives itself through sense organs. It is the living organisms, endowed with senses, which represent this natural form. Jacob Boehme calls it sound or resonance, and thus sets up the sensory impression of hearing as a symbol for sensory perception in general. The seventh natural form is the spirit elevating itself by virtue of its sensory perceptions (wisdom). It finds itself again as itself, as the primordial foundation, within the world which has grown out of the abyss and shaped itself out of harmonious and inharmonious elements. “The Holy Ghost brings the splendor of majesty into the entity in which the Divinity stands revealed.”—With such conceptions Jacob Boehme seeks to fathom that world which, in accordance with the knowledge of his time, appears to him as the real one. For him facts are what the natural science of his time and the Bible regard as such. His way of thinking is one thing, his world of facts another. One can imagine the former as applied to a quite different factual knowledge. And thus there appears before our mind a Jacob Boehme who could also be living at the turn of the nineteenth to the twentieth century. Such a man would not penetrate with his thinking the biblical story of the Creation and the struggle of the angels with the devils, but rather Lyell's geological insights and the “natural history of creation” of Haeckel. One who penetrates to the spirit of Jacob Boehme's writings must come to this conviction.1 (We shall mention the most important of these writings: Die Morgenröthe im Aufgang, The Coming of the Dawn. Die drei Prinzipien göttlichen Wesens, The Three Principles of the Divine Essence. Vom dreifachen Leben des Menschen, Of the Threefold Life of Man. Das umgewandte Auge, The Eye Turned Upon Itself. Signatura rerum oder von der Geburt und Bezeichnung aller Wesen, Signatura rerum or of the birth and designation of all beings. Mysterium magnum.)
|
| 3. Truth and Science: The Starting Point of Epistemology
Translated by John Riedel Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Only what we call concepts and ideas have been given to us in a form we call “the intellectual view”. Kant and the more recent philosophers who follow him completely deny that people have this ability, because all thinking is supposed to incorporate only objects standing in the vicinity (Gegenstände) and brings forth absolutely nothing out of itself. |
| We must look for causes and effects in the world (Ursachen und Wirkungen, primal circumstances and how they work themselves out), but we ourselves must produce causality as thought-form before we can find it in the world. But if one wanted to hold on to Kant's assertion that concepts without intuitions are empty, it would be unthinkable to demonstrate the possibility of characterizing the given world through concepts. |
| 3. Truth and Science: The Starting Point of Epistemology
Translated by John Riedel Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] According to everything we have seen, investigations at the beginning of a theory of knowing (epistemology), everything that already belongs to the arena of knowing must be excluded. Knowing itself is something that comes with the human condition, something arising through daily activity. If a theory of knowing is really to extend to illuminating the entire field of becoming familiar with, of knowing concepts and ideas (Erkennens), then it must take as its starting point something that has remained completely untouched by this activity, from which the latter itself receives its impetus. What to begin with lies outside of knowing cannot be knowing itself. Therefore, we must look for it immediately before the familiarity of knowing (cognition, Erkennens), so that the very next step that the human being takes from this precursor is an activity of knowing. The way in which this absolute first is to be determined must be such that nothing that already comes from knowing, from cognition, flows into it. [ 2 ] But such a beginning can only be made with the immediately given picture of the world, the world picture that is available to man before he has subjected it in any way to the cognitive process, before he has made even the slightest statement about it, before he has made the slightest mental judgement about it. What passes before us, and what we pass by, which is a disconnected world view, not separated into individual components,61 in which nothing is separated, nor related to, or determined by anything else, that is what is immediately given. At this stage of existence-awareness (des Daseins), if we may use the expression, no object, no event is more important, more meaningful than any other. The rudimentary animal-organ, devoid of meaning for development and for life itself, has the right, perhaps for a later stage of recognition-illuminated existence-awareness, to be considered the noblest most essential part of the organism. Before all cognitive activity, nothing presents itself in the world picture as substance, nothing as accident, nothing as cause or effect; the opposites matter-spirit, body-soul, have not yet been created. But we must also keep away any other predicate from the worldview held at this stage. It can be understood neither as reality nor as appearance, neither as subjective nor as objective, neither as accidental nor as necessary. Whether it is a “thing in itself” or a mere idea cannot be decided at this stage. We have already seen that the findings of physics and physiology, which lead to subsuming “the given” under one of the above categories, must not be placed at the forefront of epistemology. [ 3 ] If a being with fully developed human intelligence were suddenly created from nothing and confronted the world, the first impression that the world would make on its senses and thinking would be something like what we call the immediately given world view. However, the same thing is not present to a person in this form at any moment of his life. There is nowhere in his development a boundary between pure, passive turning towards what is immediately given and the thinking recognition of it. This circumstance could raise concerns about our positing a beginning of epistemology. About this Hartmann says, “We do not ask what is the content of consciousness of the child who is awakening to consciousness, or of the animal standing at the lowest stage of living creatures, because the philosophizing person has no experience of this. He cannot infer or reconstruct the content of consciousness of primitive biologic organisms at any stage from fertilization to death, as such attempts must always be based on personal experience. We must therefore first determine what is the content of consciousness found by the philosophizing person at the beginning of philosophical reflections”.62 The objection to this, however, is that the world view that we have at the beginning of philosophical reflection already contains predicates that are only conveyed through cognition. These must not be accepted uncritically, but must be carefully peeled out of the world picture so that it appears completely pure of everything that has been added through the cognitive process. The boundary between what is given and what is known will not coincide with any moment of human development, but must be drawn artificially. But this can happen at any stage of development if we only correctly draw the line between what comes to us without mental determination, before recognition, and what is made from it through determination and recognition. [ 4 ] Now one can accuse me of having already accumulated a whole series of mental characterizations, so that I may separate that supposedly immediate world view from the one that people have completed through cognitive processing. But the following must be said against this: the thoughts we have brought up should not characterize that world view, should not indicate any properties of it, should not say anything at all about it, but should only guide our consideration, in such a way that it is taken to the boundary where recognition is placed at its beginning. There can therefore be no talk of the truth or error, the accuracy or falsity of those statements, which in our opinion precede the moment in which we stand at the beginning of the theory of knowledge. They only have the task of leading appropriately to this beginning. No one who is about to deal with epistemological problems is at the same time confronted with what is rightly called the beginning of knowing, for he has already developed knowledge to a certain extent. To remove from this everything that has been gained by cognition, and to establish a pre-cognitive beginning can only be done conceptually. But concepts have no cognitive value at this stage; they have the purely negative task of removing everything from the field of vision that belongs to knowledge and leading it to where knowing begins. These considerations are signposts pointing to the beginning of the act of knowing, but do not yet belong to it. In everything that the epistemologist puts forward before establishing the beginning, there is only expediency or inexpediency, not truth or error. But even in this starting point itself, all error is excluded, because the error can only begin with recognition, with knowing (Erkennen), and cannot therefore lie before it. [ 5 ] The last sentence cannot be claimed by any epistemologist not proceeding from these considerations. Where the starting point is made by mentally evaluating an object (or subject), an error is possible at the very beginning, namely right at this evaluation. The justification of this depends on the laws on which the act of knowing is based. However, this can only emerge during epistemological investigations. Only if one says that I separate all mental determinations acquired through knowing from my picture of the world and only hold on to everything that comes into the horizon of my observation without my intervention, then all error is excluded. Since I fundamentally abstain from making any statements, I cannot make any mistakes. [ 6 ] Insofar as error comes into consideration epistemologically, it can only lie within the act of cognition. An illusion is not an error, so if the moon appears larger to us at its rising point than at its zenith, we are not dealing with an error, but with a fact well founded in the laws of nature. An error in knowing would only arise if we incorrectly interpreted “bigger” and “smaller” when combining given perceptions in thinking, but this interpretation lies within the act of knowing. [ 7 ] If one really wants to understand cognition in its entire essence, then one must undoubtedly first grasp it where it begins, where it sits in the world. It is also clear that what lies before this beginning must not be included in the explanation of cognition, but rather must be assumed. Penetrating the essence of our assumptions is the task of scientific work (wissenschaftlichen Erkenntnis) in its individual branches, where we do not want to gain special knowledge about this or that, but rather we want to examine knowing itself. Only when we have understood the act of cognition can we come to a judgment about the significance of statements about world-contents that are made with cognition. [ 8 ] That is why we refrain from making any attribution, any characterization about what is immediately given, so long as we do not know how such an attribution relates to what is determined. Even with the concept of the “immediately given” we say nothing about what lies before cognition. Its only purpose is to point out the same thing, to focus attention on it. The conceptual formation is here, at the beginning of the theory of knowing, only the first connection in which knowing sits in relation to world-content. This designation itself provides for the eventuality that the entire content of the world is only a web of our own "I", and that exclusive subjectivism therefore rightly exists, because there can be no question of this first connection (dieser Tatsache) being “given”. It could only be the result of cognitive consideration. In other words, it could only turn out to be correct through epistemology, but could not serve as a prerequisite for it. [ 9 ] Everything that can arise within the horizon of our experiences in the broadest sense is now included in this immediately given world content: sensations, perceptions, views, feelings, acts of will, dream and fantasy images, images, concepts, and ideas. [ 10 ] At this level, illusions and hallucinations are also on an equal footing with other parts of the world content. For what relationship these perceptions have to other perceptions can only be learned by cognitive observation. [ 11 ] If a theory of knowing starts from the assumption that everything just mentioned is the content of our consciousness, then the question immediately arises of how we get from mere consciousness to knowledge of being, to being aware of being. Where is the springboard that leads us from the subjective to the trans-subjective? For me, the matter is completely different. For me, consciousness and the "I" idea are initially only parts of the immediately given, and what relationship the former has to the latter is only a result of cognitive awareness. We do not want to determine cognition from consciousness, but vice versa; consciousness and the relationship between subjectivity and objectivity is determined by cognition. Since we initially isolate the given without any predicates, we must ask how we even arrive at a characterization of it. How is it possible to begin the activity of knowing? How can we designate one part of the worldview, for example, as perception, and another part as concept, one as being, the other as appearance, one as cause, another as effect. How can we separate ourselves from the objective, and regard ourselves as "I" compared to the "not-I"? [ 12 ] We must find the bridge from the “given” worldview to the one we develop through our knowing. The difficulty is that so long as we just passively stare at what is given, we cannot find a fundamental starting point to build on, on which to continue to develop knowledge. We would have to find a place somewhere in the given where we can intervene, where there is something of the same nature (Homogenes) as cognition. If everything were entirely just given, then it would have to be a matter of simply staring out into the external world and a completely equivalent staring into the world of our individuality. We could then at most describe things as external, but never understand them. Our concepts only have a purely external connection to what they refer to, not an internal one. For true knowing, everything depends on us finding an area somewhere in the given where our knowing activity not only presupposes something given, but actively stands in the middle of the given. In other words, it must turn out, especially when we strictly adhere to what is merely given, that not everything is just given. Our prerequisite, through its strict adherence, must partially cancel itself out. We set it up so that we do not arbitrarily fix any beginning of the theory of knowing, but truly seek it out. Everything can be “the given” in this sense, even what is not given in its innermost nature. It then only appears to us formally as a given, but upon closer inspection it reveals itself to be what it really is. [ 13 ] All the difficulty in understanding knowing lies in the fact that we do not produce the content of the world from within ourselves. If we did that, there would be no recognition at all. A question for me can only arise from a thing if it is “given” to me. Onto whatever I bring forth, I bestow characterizations myself, so I don't need to ask about their authentication. [ 14 ] This is the second point of my epistemology, namely the postulate that there must be something in the realm of the given where our activity does not float in the void, where the content of the world itself is the active agent. [ 15 ] We determined the beginning of the theory of knowing in such a way that we placed it entirely before cognitive activity, so that no prejudice would cloud knowing itself. In the same way we determine the first step that we take in the development of our discourse, so that there can be no question of error or inaccuracy. For we do not make a judgment about anything, but only point out the requirement that must be fulfilled if knowing is to come about at all. It all depends on us being aware, with full consideration (Besonnenheit, basking in the Sun’s clarity), that we put forward as a postulate the characteristics which that part of the world's content must have on which we can use our cognitive skill. [ 16 ] Anything else is quite unthinkable. The content of the world as given would be completely undermined. No part can give the impetus of itself to create order in such a chaos. Therefore, cognitive activity must make a power statement and say that certain parts must be such and such. Such a power statement in no way affects the quality of the given. It does not bring arbitrary assertions into the science of clear thinking. It doesn't claim anything at all, but just says that if knowledge is to be clarified at all, then one must search for an arena as described above. If such is present, then there is a clarification of knowing, otherwise not. While we began the theory of knowing with the "given" in general, we now limit the requirement to keeping a specific viewpoint in mind. [ 17 ] We now should examine this stipulation more closely. Where do we find anything in the world picture that is not just a given, but is a given insofar as it is at the same time something produced, brought forth (Hervorgebrachtes) in the act of knowing? [ 18 ] We must be completely clear that what is brought forth in the act of knowing must have been given fresh and unmodified. Conclusive inferences are not necessary to recognize this. This already shows that the sensory qualities do not satisfy our requirements, because we do not know directly that these do not arise without our activity, but only through physical and physiological considerations. But we do know directly that concepts and ideas always first enter the sphere of unmodified-given in and by the act of knowing. Therefore no one is mistaken about this characterization of concepts and ideas. One can certainly consider hallucinations to be something given from outside, but one will never believe that its concepts are given to us without our own work of thinking. A madman considers certain things and conditions to be real, and endows them with the label “reality”, even though there are no facts to back that up. A madman will never say, however, of his concepts and ideas, that they enter the world of the “given” without his own activity. Everything else in our worldview has such a character that it must be ‘given’ if we want to experience it, and only with concepts and ideas does the reverse hold true. We must produce Ideas and concepts if we want to experience them. Only what we call concepts and ideas have been given to us in a form we call “the intellectual view”. Kant and the more recent philosophers who follow him completely deny that people have this ability, because all thinking is supposed to incorporate only objects standing in the vicinity (Gegenstände) and brings forth absolutely nothing out of itself. In the intellectual view, however, the content must be given along with the think-form (Denkform). But isn't this really the case with pure concepts and ideas? — By concept I mean a rule according to which the unconnected elements of perception are combined into a unity. Causality, for example, is a concept. Idea is just a concept with a larger content. Organism, taken completely abstractly, is an idea. — One only must look at concepts and ideas in the form in which they are still completely free of any empirical content. For example, if you want to grasp the pure concept of causality, you must not stick to any specific causality or to the sum of all causalities, but rather to the mere concept of it. We must look for causes and effects in the world (Ursachen und Wirkungen, primal circumstances and how they work themselves out), but we ourselves must produce causality as thought-form before we can find it in the world. But if one wanted to hold on to Kant's assertion that concepts without intuitions are empty, it would be unthinkable to demonstrate the possibility of characterizing the given world through concepts. Suppose two elements of the world's content are given, a and b. If I am to look for a relationship between them, I must do so with a rule that has a certain content, but I can only produce such a rule in the act of cognition itself. I cannot take the rule from the object, because any characterization of the object is done with the help of the rule. Such a rule for the determination of actuality, of being real (Bestimmung des Wirklichen) arises completely within a being capable of pure inner grasping, of pure inner understanding (der rein begrifflichen Entität). [ 19 ] Before going any further, let's first eliminate a possible objection. It seems as if the idea of the “I”, the “personal subject”, plays a role unconsciously in our thought processes, and that we use this idea in the progress of our thought development without having demonstrated the justification for it. This is the case when we say, for example that we produce concepts, or when we make this or that demand. But nothing in our statements gives reason to see such sentences as more than stylistic twists. As we have already said, the fact that the act of knowing belongs to an “I” and proceeds from it can only be established by cognitive considerations. So, for the time being we should only speak of the act of knowing without even mentioning its bearer. For everything that has been established up to now is limited to the fact that there is something "given" and that the postulate stated above arises from one point of this "given", and finally that concepts and ideas are the in the arena that corresponds to this postulate. This is not to deny that the point from which the postulate arises is the “I”. But for now, we limit ourselves to presenting these two steps of epistemology in their purity.
|
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1916): Moral Imagination (Darwinism and Morality
Translated by R. F. Alfred Hoernlé Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Similarly, Evolutionists suppose that man could have watched the development of the solar system out of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis, if he could have occupied a suitable spot in the world-ether during that infinitely long period. |
| Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of an original nebula had been formed only from the percept of the nebula. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1916): Moral Imagination (Darwinism and Morality
Translated by R. F. Alfred Hoernlé Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A free spirit acts according to his impulses, i.e., intuitions, which his thought has selected out of the whole world of his ideas. For an unfree spirit, the reason why he singles out a particular intuition from his world of ideas, in order to make it the basis of an action, lies in the perceptual world which is given to him, i.e., in his past experiences. He recalls, before making a decision, what some one else has done, or recommended as proper, in an analogous case, or what God has commanded to be done in such a case, etc., and he acts on these recollections. A free spirit dispenses with these preliminaries. His decision is absolutely original. He cares as little what others have done in such a case as what commands they have laid down. He has purely ideal (logical) reasons which determine him to select a particular concept out of the sum of his concepts, and to realize it in action. But his action will belong to perceptible reality. Consequently, what he achieves will coincide with a definite content of perception. His concept will have to be realized in a concrete particular event. As a concept it will not contain this event as particular. It will refer to the event only in its generic character, just as, in general, a concept is related to a percept, e.g., the concept lion to a particular lion. The link between concept and percept is the idea (cp. pp. 68 ff.). To the unfree spirit this intermediate link is given from the outset. Motives exist in his consciousness from the first in the form of ideas. Whenever he intends to do anything he acts as he has seen others act, or he obeys the instructions he receives in each separate case. Hence authority is most effective in the form of examples, i.e., in the form of traditional patterns of particular actions handed down for the guidance of the unfree spirit. A Christian models his conduct less on the teaching than on the pattern of the Saviour. Rules have less value for telling men positively what to do than for telling them what to leave undone. Laws take on the form of universal concepts only when they forbid actions, not when they prescribe actions. Laws concerning what we ought to do must be given to the unfree spirit in wholly concrete form. Clean the street in front of your door! Pay your taxes to such and such an amount to the tax-collector! etc. Conceptual form belongs to laws which inhibit actions. Thou shalt not steal! Thou shalt not commit adultery! But these laws, too, influence the unfree spirit only by means of a concrete idea, e.g., the idea of the punishments attached by human authority, or of the pangs of conscience, or of eternal damnation, etc. Even when the motive to an action exists in universal conceptual form (e.g., Thou shalt do good to thy fellow-men! Thou shalt live so that thou promotest best thy welfare!), there still remains to be found, in the particular case, the concrete idea of the action (the relation of the concept to a content of perception). For a free spirit who is not guided by any model nor by fear of punishment, etc., this translation of the concept into an idea is always necessary. Concrete ideas are formed by us on the basis of our concepts by means of the imagination. Hence what the free spirit needs in order to realize his concepts, in order to assert himself in the world, is moral imagination. This is the source of the free spirit's action. Only those men, therefore, who are endowed with moral imagination are, properly speaking, morally productive. Those who merely preach morality, i.e., those who merely excogitate moral rules without being able to condense them into concrete ideas, are morally unproductive. They are like those critics who can explain very competently how a work of art ought to be made, but who are themselves incapable of the smallest artistic productions. Moral imagination, in order to realize its ideas, must enter into a determinate sphere of percepts. Human action does not create percepts, but transforms already existing percepts and gives them a new character. In order to be able to transform a definite object of perception, or a sum of such objects, in accordance with a moral idea, it is necessary to understand the object's law (its mode of action which one intends to transform, or to which one wants to give a new direction). Further, it is necessary to discover the procedure by which it is possible to change the given law into the new one. This part of effective moral activity depends on knowledge of the particular world of phenomena with which one has got to deal. We shall, therefore, find it in some branch of scientific knowledge. Moral action, then, presupposes, in addition to the faculty of moral concepts1 and of moral imagination, the ability to alter the world of percepts without violating the natural laws by which they are connected. This ability is moral technique. It may be learnt in the same sense in which science in general may be learnt. For, in general, men are better able to find concepts for the world as it is, than productively to originate out of their imaginations future, and as yet non-existing, actions. Hence, it is very well possible for men without moral imagination to receive moral ideas from others, and to embody these skilfully in the actual world. Vice versa, it may happen that men with moral imagination lack technical skill, and are dependent on the service of other men for the realization of their ideas. In so far as we require for moral action knowledge of the objects upon which we are about to act, our action depends upon such knowledge. What we need to know here are the laws of nature. These belong to the Natural Sciences, not to Ethics. Moral imagination and the faculty of moral concepts can become objects of theory only after they have first been employed by the individual. But, thus regarded, they no longer regulate life, but have already regulated it. They must now be treated as efficient causes, like all other causes (they are purposes only for the subject). The study of them is, as it were, the Natural Science of moral ideas. Ethics as a Normative Science, over and above this science, is impossible. Some would maintain the normative character of moral laws at least in the sense that Ethics is to be taken as a kind of dietetic which, from the conditions of the organism's life, deduces general rules, on the basis of which it hopes to give detailed directions to the body (Paulsen, System der Ethik). This comparison is mistaken, because our moral life cannot be compared with the life of the organism. The behaviour of the organism occurs without any volition on our part. Its laws are fixed data in our world; hence we can discover them and apply them when discovered. Moral laws, on the other hand, do not exist until we create them. We cannot apply them until we have created them. The error is due to the fact that moral laws are not at every moment new creations, but are handed down by tradition. Those which we take over from our ancestors appear to be given like the natural laws of the organism. But it does not follow that a later generation has the right to apply them in the same way as dietetic rules. For they apply to individuals, and not, like natural laws, to specimens of a genus. Considered as an organism, I am such a generic specimen, and I shall live in accordance with nature if I apply the laws of my genus to my particular case. As a moral agent I am an individual and have my own private laws.2 The view here upheld appears to contradict that fundamental doctrine of modern Natural Science which is known as the Theory of Evolution. But it only appears to do so. By evolution we mean the real development of the later out of the earlier in accordance with natural law. In the organic world, evolution means that the later (more perfect) organic forms are real descendants of the earlier imperfect forms, and have grown out of them in accordance with natural laws. The upholders of the theory of organic evolution believe that there was once a time on our earth, when we could have observed with our own eyes the gradual evolution of reptiles out of Proto-Amniotes, supposing that we could have been present as men, and had been endowed with a sufficiently long span of life. Similarly, Evolutionists suppose that man could have watched the development of the solar system out of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis, if he could have occupied a suitable spot in the world-ether during that infinitely long period. But no Evolutionist will dream of maintaining that he could from his concept of the primordial Amnion deduce that of the reptile with all its qualities, even if he had never seen a reptile. Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of an original nebula had been formed only from the percept of the nebula. In other words, if the Evolutionist is to think consistently, he is bound to maintain that out of earlier phases of evolution later ones really develop; that once the concept of the imperfect and that of the perfect have been given, we can understand the connection. But in no case will he admit that the concept formed from the earlier phases is, in itself, sufficient for deducing from it the later phases. From this it follows for Ethics that, whilst we can understand the connection of later moral concepts with earlier ones, it is not possible to deduce a single new moral idea from earlier ones. The individual, as a moral being, produces his own content. This content, thus produced, is for Ethics a datum, as much as reptiles are a datum for Natural Science. Reptiles have evolved out of the Proto-Amniotes, but the scientist cannot manufacture the concept of reptiles out of the concept of the Proto-Amniotes. Later moral ideas evolve out of the earlier ones, but Ethics cannot manufacture out of the moral principles of an earlier age those of a later one. The confusion is due to the fact that, as scientists, we start with the facts before us, and then make a theory about them, whereas in moral action we first produce the facts ourselves, and then theorize about them. In the evolution of the moral world-order we accomplish what, at a lower level, Nature accomplishes: we alter some part of the perceptual world. Hence the ethical norm cannot straightway be made an object of knowledge, like a law of nature, for it must first be created. Only when that has been done can the norm become an object of knowledge. But is it not possible to make the old a measure for the new? Is not every man compelled to measure the deliverances of his moral imagination by the standard of traditional moral principles? If he would be truly productive in morality, such measuring is as much an absurdity as it would be an absurdity if one were to measure a new species in nature by an old one and say that reptiles, because they do not agree with the Proto-Amniotes, are an illegitimate (degenerate) species. Ethical Individualism, then, so far from being in opposition to the theory of evolution, is a direct consequence of it. Haeckel's genealogical tree from protozoa up to man as an organic being, ought to be capable of being worked out without a breach of natural law, and without a gap in its uniform evolution, up to the individual as a being with a determinate moral nature. But, whilst it is quite true that the moral ideas of the individual have perceptibly grown out of those of his ancestors, it is also true that the individual is morally barren, unless he has moral ideas of his own. The same Ethical Individualism which I have developed on the basis of the preceding principles, might be equally well developed on the basis of the theory of evolution. The final result would be the same; only the path by which it was reached would be different. That absolutely new moral ideas should be developed by the moral imagination is for the theory of evolution no more inexplicable than the development of one animal species out of another, provided only that this theory, as a Monistic world-view, rejects, in morality as in science, every transcendent (metaphysical) influence. In doing so, it follows the same principle by which it is guided in seeking the causes of new organic forms in forms already existing, but not in the interference of an extra-mundane God, who produces every new species in accordance with a new creative idea through supernatural interference. Just as Monism has no use for supernatural creative ideas in explaining living organisms, so it is equally impossible for it to derive the moral world-order from causes which do not lie within the world. It cannot admit any continuous supernatural influence upon moral life (divine government of the world from the outside), nor an influence through a particular act of revelation at a particular moment in history (giving of the ten commandments), or through God's appearance on the earth (divinity of Christ). Moral processes are, for Monism, natural products like everything else that exists, and their causes must be looked for in nature, i.e., in man, because man is the bearer of morality. Ethical Individualism, then, is the crown of the edifice that Darwin and Haeckel have erected for Natural Science. It is the theory of evolution applied to the moral life. Anyone who restricts the concept of the natural from the outset to an artificially limited and narrowed sphere, is easily tempted not to allow any room within it for free individual action. The consistent Evolutionist does not easily fall a prey to such a narrow-minded view. He cannot let the process of evolution terminate with the ape, and acknowledge for man a supernatural origin. Again, he cannot stop short at the organic reactions of man and regard only these as natural. He has to treat also the life of moral self-determination as the continuation of organic life. The Evolutionist, then, in accordance with his fundamental principles, can maintain only that moral action evolves out of the less perfect forms of natural processes. He must leave the characterization of action, i.e., its determination as free action, to the immediate observation of each agent. All that he maintains is only that men have developed out of monkeys. What the nature of men actually is must be determined by observation of men themselves. The results of this observation cannot possibly contradict the history of evolution. Only the assertion that the results are such as to exclude their being due to a natural world-order would contradict recent developments in the Natural Sciences.3 Ethical Individualism, then, has nothing to fear from a Natural Science which understands itself. Observation yields freedom as the characteristic quality of the perfect form of human action. The establishment of a conceptual connection between this fact of observation and other kinds of processes results in the theory of the natural origin of free actions. What, then, from the standpoint of nature are we to say of the distinction, already mentioned above (p. 13), between the two statements, “To be free means to be able to do what you will,” and “To be able, as you please, to strive or not to strive is the real meaning of the dogma of free will”? Hamerling bases his theory of free will precisely on this distinction, by declaring the first statement to be correct but the second to be an absurd tautology. He says, “I can do what I will, but to say I can will what I will is an empty tautology.” Whether I am able to do, i.e., to make real, what I will, i.e., what I have set before myself as my idea of action, that depends on external circumstances and on my technical skill (cp. p. 118). To be free means to be able to determine by moral imagination out of oneself, those ideas (motives) which lie at the basis of action. Freedom is impossible if anything other than I myself (whether a mechanical process or God) determines my moral ideas. In other words, I am free only when I myself produce these ideas, but not when I am merely able to realize the ideas which another being has implanted in me. A free being is one who can will what he regards as right. Whoever does anything other than what he wills must be impelled to it by motives which do not lie in himself. Such a man is unfree in his action. Accordingly, to be able to will, as you please, what you consider right or wrong means to be free or unfree as you please. This is, of course, just as absurd as to identify freedom with the faculty of doing what one is compelled to will. But this is just what Hamerling maintains when he says, “It is perfectly true that the will is always determined by motives, but it is absurd to say that on this ground it is unfree; for a greater freedom can neither be desired nor conceived than the freedom to realize oneself in proportion to one's own power and strength of will.” On the contrary, it is well possible to desire a greater freedom and that a true freedom, viz., the freedom to determine for oneself the motives of one's volitions. Under certain conditions a man may be induced to abandon the execution of his will; but to allow others to prescribe to him what he shall do—in other words, to will what another and not what he himself regards as right—to this a man will submit only when he does not feel free. External powers may prevent me from doing what I will, but that is only to condemn me to do nothing. Not until they enslave my spirit, drive my motives out of my head, and put their own motives in the place of mine, do they really aim at making me unfree. That is the reason why the church attacks not only the mere doing, but especially the impure thoughts, i.e., motives of my action. And for the church all those motives are impure which she has not herself authorized. A church does not produce genuine slaves until her priests turn themselves into advisers of consciences, i.e., until the faithful depend upon the church, i.e., upon the confessional, for the motives of their actions.
|
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1963): The Fundamental Urge For Knowledge
Translated by Rita Stebbing Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| After a teaching position in Switzerland, and enroute to another in Poland, he met Kant, under whose influence he wrote his Study for a Critique of All Revelation. The printer neglected to place his name on the title-page, and people thought the work had been written by Kant. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1963): The Fundamental Urge For Knowledge
Translated by Rita Stebbing Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] In these words Goethe expresses a characteristic feature belonging to the deepest foundation of human nature. Man is not a uniformly organized being. He always demands more than the world gives him of its own accord. Nature has endowed us with needs; among them are some that are left to our own initiative to satisfy. Abundant are the gifts bestowed upon us, but still more abundant are our desires. We seem born to be dissatisfied. Our thirst for knowledge is but a special instance of this dissatisfaction. If we look twice at a tree and the first time see its branches motionless, the second time in movement, we do not remain satisfied with this observation. Why does the tree appear to us now motionless, now in movement? Thus we ask. Every glance at nature evokes in us a number of questions. Every phenomenon we meet sets us a problem. Every experience contains a riddle. We see emerging from the egg a creature like the mother animal; we ask the reason for this likeness. We notice that living beings grow and develop to a certain degree of perfection and we investigate the conditions for this experience. Nowhere are we satisfied with what nature spreads before our senses. Everywhere we seek what we call explanation of the facts. [ 2 ] The something more which we seek in things, over and above what is given us directly in them, divides our whole being into two aspects; we become conscious of our contrast to the world. We confront the world as independent beings. The universe appears to us to have two opposite poles: I and world. [ 3 ] We erect this barrier between ourselves and the world as soon as consciousness first dawns in us. But we never cease to feel that, in spite of all, we belong to the world, that there is a bond of union between it and us, that we are not beings outside, but within, the universe. [ 4 ] This feeling makes us strive to bridge over the contrast. And in this bridging the whole spiritual striving of mankind ultimately consists. The history of man's spiritual life is an incessant search for unity between us and the world. Religion, art and science all have this same aim. In the revelation God grants him, the religious believer seeks the solution of the problems in the world which his I, dissatisfied with the world of mere phenomena, sets him. The artist seeks to imprint into matter the ideas of his I, in order to reconcile with the world outside what lives within him. He, too, feels dissatisfied with the world as it appears to him, and seeks to embody into the world of mere phenomena that something more which his I, reaching out beyond it, contains. The thinker seeks the laws of phenomena, and strives to penetrate with thinking what he experiences by observing. Only when we have made the world-content into our thought-content do we again find the unity from which we separated ourselves. We shall see later that this goal will be reached only when the task of the scientific investigator is understood at a much deeper level than is usually the case. The whole situation I have described here, presents itself to us on the stage of history in the contrast between a unified view of the world or monism,9 and the theory of two worlds or dualism.10 Dualism pays attention only to the separation between I and world, brought about by man's consciousness. All its efforts consist in a vain struggle to reconcile these opposites, which it calls spirit and matter, subject and object, or thinking and phenomena. The dualist feels that there must be a bridge between the two worlds, but he is unable to find it. In as far as man is aware of himself as “I,” he cannot but think of this “I” as belonging to spirit; and in contrasting this “I” with the world he cannot do otherwise than reckon the perceptions given to the senses, the realm of matter, as belonging to the world. In doing so, man places himself within the contrast of spirit and matter. He must do so all the more because his own body belongs to the material world. Thus the “I” belongs to the realm of spirit, as part of it; the material things and events which are perceived by the senses belong to the “world.” All the problems connected with spirit and matter, man finds again in the fundamental riddle of his own nature. Monism pays attention only to the unity and tries either to deny or to efface the contrasts, which are there nevertheless. Neither of these two views is satisfactory, for they do not do justice to the facts. Dualism sees spirit (I) and matter (world) as two fundamentally different entities and cannot, therefore, understand how they can interact upon each other. How should spirit know what goes on in matter, if the essential nature of matter is quite alien to spirit? And how, in these circumstances, should spirit be able to act upon matter, in order to transform its intentions into actions? The most clever and the most absurd hypotheses have been put forward to solve these problems. But, so far, monism has fared no better. Up to now it has tried to justify itself in three different ways. Either it denies spirit and becomes materialism; or it denies matter and seeks its salvation in spiritualism; 11 or it maintains that since even in the simplest entities in the world spirit and matter are indivisibly bound together, there is no need for surprise if these two kinds of existence are both present in the human being, for they are never found apart. [ 5 ] Materialism 12 can never arrive at a satisfactory explanation of the world. For every attempt at an explanation must of necessity begin with man's forming thoughts about the phenomena of the world. Materialism, therefore, takes its start from thoughts about matter or material processes. In doing so, it straightway confronts two different kinds of facts, namely, the material world and the thoughts about it. The materialist tries to understand thoughts by regarding them as a purely material process. He believes that thinking takes place in the brain much in the same way that digestion takes place in the animal organs. Just as he ascribes to matter mechanical and organic effects, so he also attributes to matter, in certain circumstances, the ability to think. He forgets that in doing this he has merely shifted the problem to another place. Instead of to himself, he ascribes to matter the ability to think. And thus he is back again at his starting-point. How does matter come to reflect about its own nature? Why is it not simply satisfied with itself and with its existence? The materialist has turned his attention away from the definite subject, from our own I, and has arrived at a vague, indefinite image. And here again, the same problem comes to meet him. The materialistic view is unable to solve the problem; it only transfers it to another place. [ 6 ] How does the matter stand with the spiritualistic view? The extreme spiritualist denies to matter its independent existence and regards it merely as product of spirit. But when he tries to apply this view of the world to the solution of the riddle of his own human nature, he finds himself in a corner. Confronting the I, which can be placed on the side of spirit, there stands, without any mediation, the physical world. No spiritual approach to it seems possible; it has to be perceived and experienced by the I by means of material processes. Such material processes the “I” does not find in itself if it regards its own nature as having only spiritual validity. The physical world is never found in what it works out spiritually. It seems as if the “I” would have to admit that the world would remain closed to it if it did not establish a non-spiritual relation to the world. Similarly, when we come to be active, we have to translate our intentions into realities with the help of material substances and forces. In other words, we are dependent upon the outer world. The most extreme spiritualist—or rather, the thinker who, through absolute idealism, appears as an extreme spiritualist—is Johann Gottlieb Fichte.13 He attempts to derive the whole edifice of the world from the “I.” What he has actually accomplished is a magnificent thought-picture of the world, without any content of experience. As little as it is possible for the materialist to argue the spirit away, just as little is it possible for the idealist to argue away the outer world of matter. [ 7 ] The first thing man perceives when he seeks to gain knowledge of his “I” is the activity of this “I” in the conceptual elaboration of the world of ideas. This is the reason why someone who follows a world-view which inclines toward spiritualism may feel tempted, when looking at his own human nature, to acknowledge nothing of spirit except his own world of ideas. In this way spiritualism becomes one-sided idealism. He does not reach the point of seeking through the world of ideas a spiritual world; in the world of his ideas he sees the spiritual world itself. As a result of this, he is driven to remain with his world-view as if chained within the activity of his “I.” [ 8 ] The view of Friedrich Albert Lange 14 is a curious variety of idealism, put forward by him in his widely read History of Materialism. He suggests that the materialists are quite right in declaring all phenomena, including our thinking, to be the product of purely material processes, only, in turn, matter and its processes are themselves the product of our thinking.
That is, our thinking is produced by the material processes, and these by the thinking of the “I.” Lange's philosophy, in other words, is nothing but the story—applied to concepts—of the ingenious Baron Münchhausen,15 who holds himself up in the air by his own pigtail. [ 9 ] The third form of monism is the one which sees the two entities, matter and spirit, already united in the simplest being (the atom). But nothing is gained by this, either, for here again the question, which really originates in our consciousness, is transferred to another place. How does the simple being come to manifest itself in two different ways, if it is an indivisible unity? [ 10 ] To all these viewpoints it must be objected that it is first and foremost in our own consciousness that we meet the basic and original contrast. It is we who detach ourselves from the bosom of nature and contrast ourselves as “I” with the “world.” Goethe 16 has given classic expression to this in his essay On Nature although at first glance his manner may be considered quite unscientific: “We live in the midst of her (nature) yet are we strangers to her. Ceaselessly she speaks to us, and yet betrays not her secrets.” But Goethe knew the other side too: “All human beings are in her and she is in all human beings.” [ 11 ] Just as true as it is that we have estranged ourselves from nature, so is it also true that we feel: We are within nature and we belong to it. That which lives in us can only be nature's own influence. [ 12 ] We must find the way back to nature again. A simple consideration can show us this way. We have, it is true, detached ourselves from nature, but we must have taken something of it over with us, into our own being. This essence of nature in us we must seek out, and then we shall also find the connection with it once again. Dualism neglects this. It considers the inner being of man as a spiritual entity quite alien to nature, and seeks somehow to hitch it onto nature. No wonder it cannot find the connecting link. We can only understand nature outside us when we have first learned to recognize it within us. What within us is akin to nature must be our guide. This points out our path. We shall not speculate about the interaction of nature and spirit. But we shall penetrate the depths of our own being, there to find those elements which we took with us in our flight from nature. [ 13 ] Investigation of our own being must bring the solution of the riddle. We must reach a point where we can say to ourselves: Here I am no longer merely “I,” here I encounter something which is more than “I.” [ 14 ] I am aware that many who have read thus far will not have found my discussion “scientific” in the usual sense. To this I can only reply that so far I have not been concerned with scientific results of any kind, but with the simple description of what everyone experiences in his own consciousness. A few expressions concerning the attempts to reconcile man's consciousness and the world have been used only for the purpose of clarifying the actual facts. I have, therefore, made no attempt to use the expressions “I,” “spirit,” “world,” “nature,” in the precise way that is usual in psychology and philosophy. Ordinary consciousness is unaware of the sharp distinctions made by the sciences, and up to this point it has only been a matter of describing the facts of everyday conditions. I am concerned, not with how science, so far, has interpreted consciousness, but with how we experience it in daily life.
|
| 88. On the Astral World and Devachan: Universal Law and Human Destiny
21 Dec 1903, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| But not only the calculating mind has called the world a microcosm for man, but also the mind, which tells us that we must look up at the stars. Here a word of the philosopher Kant applies: “Two things fill the mind with ever new and increasing admiration and awe...: the starry sky above me and the moral law within me.” |
| Goethe says that he likes to take refuge from the changeability of man in the fixed rules of eternal nature, and the moral law [of Kant] with its categorical imperative seemed to him to be in error. We perceive the difference between the human heart and the world-spirit, the macrocosm, in yet another way. |
| 88. On the Astral World and Devachan: Universal Law and Human Destiny
21 Dec 1903, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Christmas Lecture Follow me for a few moments into the ancient Egyptian temples for a ceremony that was celebrated at midnight on the day that corresponds to our Christmas Day. On this day – or rather at midnight – one of the images that are only shown four times a year was unveiled in the temple and carried before a small crowd that had been prepared for this temple service. This image was locked in the innermost sanctuary of the temple throughout the year and was kept in strict secrecy. On this day, it was carried out by the oldest of the priests, and a ceremony was performed before him, which I will describe to you very briefly. After the eldest of the priests had carried out the radiant image of Horus, son of Isis and Osiris, four priests in white robes approached the image. The first of the priestly sages spoke the following before the image: “Horus, you who are the sun in the spiritual realm and you who give us the light of your wisdom as the sun gives us the light of the world, lead us so that we may no longer be what we are today.” This temple priest had entered from the east. The second of the temple priests entered from the north and spoke roughly the following words: “Horus, you sun in the spiritual realm, you who are the giver of love, as the sun is the giver of the warming power that coaxes out the forces of plants and fruits throughout the year, lead us to a goal so that we may become what we are not yet today.” And the third of the temple priests came from the south and said: “Horus, thou sun in the spiritual realm, bestow thy power upon us, as the sun of the physical world bestows its power, by which it will part the darkest cloud and spread light everywhere.” After this third priest had spoken, a fourth stepped forward and said something like the following: “The three wisest of us have spoken. They are my brothers, but they are beyond the sphere in which I myself still am. I am the representative of you” - and he meant: the representative of the multitude. And he said: “I will lead your voice. I will speak for you who are still standing there as minors. I will tell my older brothers that they long for the great goal of the world, where human destiny and the eternal law of the world will be reconciled.” This should be understood in this hour by those who were sufficiently prepared for it, as once unchanging cosmic law and human destiny were one. If we understand the ceremonies that took place on Christmas in Asia, India and even in China, then we understand what Christmas bells actually mean to us. A macrocosm has always been called the world and a microcosm the human being. This was meant to suggest that the human being contains within himself the forces that are present outside in the great. But not only the calculating mind has called the world a microcosm for man, but also the mind, which tells us that we must look up at the stars. Here a word of the philosopher Kant applies: “Two things fill the mind with ever new and increasing admiration and awe...: the starry sky above me and the moral law within me.” How different macrocosm and microcosm are when we look at them from a different point of view. Especially when faced with the macrocosm with its immutable eternal laws, those who are the most knowledgeable are filled with the deepest admiration and reverence. There have been no knowledgeable people who have seen through the wisdom of the world and not at the same time stood in awe of the creative spirit of the world. And one of those people [in modern times] who for the first time had a confidential relationship with this immutable law, Kepler, spoke the words: Who could look into the wonderful structure of the whole world and not admire the Creator who implanted these laws of the world. - Those who know most admire the eternal laws of the starry sky. It seems to be different when it comes to human destiny. Goethe says that he likes to take refuge from the changeability of man in the fixed rules of eternal nature, and the moral law [of Kant] with its categorical imperative seemed to him to be in error. We perceive the difference between the human heart and the world-spirit, the macrocosm, in yet another way. We perceive this difference when we consider the connection between human destiny and human character. Who would impose responsibility on a volcano? Probably no one. But we must indeed impose responsibility on the man who causes harm. Who would speak of justice and injustice in relation to nature? And how is it that the good suffer while the wicked prosper? We see harmony within the macrocosm. What position do we have in relation to it? What is clearly and distinctly outlined in the ceremony I have described will be enacted in a few days in the festival that is so little understood today. The starry sky with its immutable laws was not always the cosmos that appears to us now. This cosmos emerged out of chaos. Out of the surging and swaying of forces, what we have today first developed. The Copernican-Keplerian laws, which make us marvel at the wisdom of the world spirit, have not always applied. Today it seems to be poured out, exalted above justice and injustice; we cannot ask about good and evil. But we can ask about good and evil in relation to the human being. Today we ask ourselves the deeper question: Why do we ask about good and evil, about justice and injustice in relation to the human being? Why can we not ask this question in relation to the macrocosm? In the beginning, when the world was still a surging sea, there was, in the midst of what the eyes see, the ears hear, the senses perceive, between what appears to us today in the laws of harmony, still a surging sea of surging feelings, of desires and passions out there in the universe. These world passions, which were in the midst of the laws and chaos, had to be overcome first. Today, anyone who tries to visualize this world of cosmic desires and passions from an ancient past can hardly perceive the body of passions. Shiny and transparent, bright as stars, barely perceptible with the seer's finest tools, it shines in every atom after chaos has been overcome. What has brought the astral body of the cosmos to rest has not yet reached the same goal in man. In man, the astral body is still surging. What has already taken place in the cosmos over the course of millions of years, what has reached its goal, is still in the process of becoming in man. And if we follow man from return to return, from re-embodiment to re-embodiment, if we see him in his different bodies and then follow him in his astral bodies, then we see that from embodiment to embodiment the astral body becomes brighter and purer. In the beginning we see it permeated by dull passions. These remind us of the passions of that time when the world was still a chaos. But little by little that brightness and clarity developed, as it has now the astral body of the great universe. Because the sages of ancient times knew about the connection between the development of the human being and the existence of the world, they called the world macrocosm and the human being microcosm. The human being must look at the goal that he can set for himself: to become like the macrocosm, to imbue himself with the same bliss and peace that flows through the cosmos as a universal law today. Just as we cannot ask whether the laws of the cosmos are just or unjust, so neither can man ask whether his destiny coincides with his law. Pure law is the law of the cosmos, and pure human law, pure human spirit, shall one day become man's destiny. This is the path of destiny that the human spirit undergoes in its various embodiments. We become ever more starry and ever more similar to the destiny of the cosmos. Karma is a law by which we all suffer. What we have accomplished in one embodiment bears its fruits in later embodiments. What befalls us today we have caused in previous embodiments. But karma is a law that not only distributes guilt and atonement, disharmony and harmony in the right way, but is a law that leads us up to the highest summit of the human spirit. The great world book of karma will have found its balance on the left and on the right. We will have transformed everything we owe to life back into the bright glow of the astral body. Everything we have felt as deficiencies will be balanced out. Karma is burnt up. When the guilt points of our existence will no longer be there, when we ourselves go our way like the sun, which is not able to step even a little out of its orbit, then we will also follow the laws implanted in us like the sun in the starry sky. That is our way, that is our goal. That will one day be the harmony between the destiny of man and the laws of the world. Not everyone's journey through life is the same. Just as in the natural world, the perfect exists alongside the imperfect, and the higher animal already exists alongside the worm, so too in the spiritual world, the imperfect human spirit exists alongside that which has already reached a higher level. Those who honestly and sincerely believe in evolution must also have faith in spiritual science and its teachings of the first human beings. These are those who have already come further along the path that we all have to travel than we have today. Some have rushed ahead. They have overtaken us from the times of which history tells us; they have reached a higher stage of human development. Thus they have become leaders, guides of humanity. Just as the higher developed animal towers above the worm, so the Rishis, the masters, tower above humanity. They have achieved this in the earlier times because they have taken a different path of knowledge, a steeper, more dangerous path, which is associated with infinite danger. No one may enter it for its own sake. Whoever does so may stumble and fall into deep abysses, or lose his sense of existence for a time, or become a tormentor to people. In short, no one may seek out this path of faster knowledge out of selfishness. Only he who has taken this vow, who has sworn an oath that may never be broken, to powers of which the ordinary person has no inkling, only he who has taken this vow can enter upon the path to becoming a leader of humanity, a forerunner of humanity. Such leaders of men have never used their knowledge for themselves. What is so highly esteemed in the West, the knowledge for the sake of knowing, is not what the adepts, the great masters of knowledge, strive for. They strive for knowledge in order to help humanity, to draw it up to where human destiny and world harmony are in harmony with each other. These human firstlings are those who live in our midst and have lived in all times, who have acquired an astral body cleansed of desires and passions. Buddha already had it, the starry astral body. When he once went out with his disciple Ananda, Buddha dissolved into a bright cloud, into a cloud of light, into radiant light. That was the astral body that had come to rest. The corona of rays is nothing other than the symbol of the radiant astral body of the founder of Christianity. The Firstfruits of Men, as walking brothers of humanity, are an immediate reflection of the macrocosm. It should be shown that they have burnt their karma, that there is nothing more to be redeemed, that the eternal wisdom can no longer stray, that they guide humanity as surely as the sun follows its path across the vault of heaven and cannot stray from this path marked out in the firmament. This is the symbol for the firstfruits of mankind. It expresses that they cannot stray from the path that is laid out for people. As surely as the sun walks across the vault of heaven, they walk their path. And just as the sun sends its light and warmth over the earth, so they send the love of their hearts into the hearts of people, awakening love in the hearts of their fellow brothers. These firstfruits are strong in their powers to resist all temptations. You can show them, you can offer them all the riches of this world, they will not accept them, they only want to be one with the original spirit from which they came forth. These people want to be a macrocosm themselves in this life. That was their consciousness. This is also present in all religions. Those who know the sources of the religions are aware that in all these religions one looks up to the founders of the religions as one looks up to the stars of the macrocosm, as one looks up to the eternal cosmic law that rules the starry sky. These firstfathers of mankind were suns for the initiated and those who had progressed further. If humanity was to be shown how karma works, then they were shown the image of the sun in the temple. This signifies to man his destiny, like the course of the sun in the course of the world. [A-mi-t'o] was the same for the Chinese when they worshipped the Buddha as the “son” among their heavenly gods. And it was the same for the Hindus when they showed Krishna resting in the arms of the Deva-Mother. Christmas permeates all religions. It is the festival that should make man aware that his destiny is once to be an image of the destiny of the macrocosm. In Christianity, the spirit sun lives just as much as in the old religions. The life of Christ should also directly reflect the sun as it rushes across the firmament. His birth was therefore transferred to Christmas. Let us ask ourselves why. What happens to the sun at the time of the winter solstice, at the time of Christmas? The days become longer again after the shortest day has passed. The light struggles out of the darkness again. The sun, which has been in darkness for most of the day, is reborn, and as such a newly born sun it now sends its light. The birth of the light was celebrated at midnight because the light was born out of darkness. Thus, symbolically, the light of wisdom is to be born, which is represented by the firstlings of man. The sun appears again anew - she who moves across the firmament. With her birth, she is a symbol of the firstling of man who is born, who walks just as surely on his path as the universe carries harmony within itself. In the beginning, there were various Christian sects, and they celebrated the Savior's feast at different times. In the early Christian times, there were 135 such days. It was only at the beginning of the 5th century that a uniform date was set, namely our present Christmas. It was deliberately set on this day in order to establish the same symbolism, which resounded throughout the ancient world, for this Christian festival as well. A church father himself, who had been canonized by the church, considered it justified and in the spirit of Christianity. He tells us that the Christians were right to celebrate the birth of Christ at a time when the Romans celebrated the birth of Mithras and the Greeks the birth of Dionysus. The same meaning should be attached to the festival as to the festivals of Mithras and Dionysus, because in them too the birth of the firstlings was celebrated. Thus, in the Christmas festival, Christianity has erected a symbol that is intended to remind people again and again that the karma must be burned so that harmony between the macrocosm and the microcosm, which is not yet present today, will one day be present, so that man will one day also follow the immutable laws from which he must not stray. Just as Horus, the son of Isis and Osiris, the symbol of human existence and human destiny, was shown to the assembled crowd at midnight, and just as it was pointed out by the priests that he was the sun in the spiritual kingdom, that it is equal to the power of warmth and light of the sun, just as the three wise priests have joyfully bowed down, so the Christian legend also presents us with the three wise men bowing down before the Christ child. They follow the star, the light. There is a deep meaning in the visit of the three wise men from the Orient. They are the same three wise men who were active in the service of Horus and who now say: “A child has been born to us who will follow his path as unchangingly as the star that now guides us. The star is still far from us. But when this law will one day be our own, then we will be like the one who carries the unchanging law within himself. Just as the star is our ideal, so he who was born under it is our example. What the Egyptians celebrated became a world fact, a world event. Therefore, he who founded Christianity was allowed to call his disciples together for the Sermon on the Mount. It says: “He led them away from the people, up the mountain.” “Mountain” means the secret place where the inner circle were taught. The King James Version contains a tremendous error at this point: (“Blessed are they that are poor in spirit”). In truth it says: “Blessed are they that are beggars for spirit, for they find within themselves the Kingdoms of Heaven.” What did Jesus want to do for them? He wanted to make them blessed, the beggars for the spirit. Only those who were initiated into the temple mysteries had become partakers of wisdom. The founder of Christianity wanted to carry this wisdom out into the whole world; not only the rich in spirit were to receive the grace of wisdom – no, all those who stand outside and are also beggars for the spirit should find the Kingdoms of Heaven within themselves. In the past, people found this in the temple mysteries. They should not only find bliss within the temple precincts, but should also find the Kingdoms of Heaven within themselves, which were presented to them as the harmonious model of human destiny. They should ascend to the summit where a balance can be struck between the changeable, erring human heart and the unchanging law of the macrocosm. This is what the Christmas bells are meant to make people aware of, according to the original will of the initiates; they are a pointer to what shows us how karma leads to the goal, how the laws of the world and human destiny are connected. And to hear this again is what theosophical deepening is meant to bring us. Many festivals that we celebrate today without thinking about it, without knowing their deeper meaning, have their origin in a deeper wisdom. Because the ancient man was connected to the macrocosmic world, the events of the festival were signs for him. The mystery of the heart and the immutable law resound to us from the sounds of Christmas bells. Theosophy will bring deeper wisdom and the core of religious beliefs into the most direct life; it will show the extent to which these truths are contained in them. And when we recognize this truth, then, in the highest sense, what is expressed in the beautiful word “peace be with all beings” will gradually come true in the harmony between the law of the universe and the destiny of man. |

