| Earthly and Cosmic Man: Foreword
Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Marie Steiner |
|---|
| Only the Group, sculptured in wood, portraying the Representative of Humanity between the vanquished Adversaries, was saved. We are hoping that by Christmas of this year, this Group will stand in a space worthy of it, in the new Goetheanum. There is a moving description of the Representative of Humanity, of the Christ Figure, at the end of one of the lectures of 1912, when there was no thought—even of the possibility—of its execution in sculpture. |
| Earthly and Cosmic Man: Foreword
Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Marie Steiner |
|---|
by Marie Steiner The wealth of ideas and spiritual treasure bestowed upon us by Rudolf Steiner in his lectures often makes it difficult to arrange certain series of lectures under one category and heading. They are like concentrated foci of energy from which sparks shoot out in every direction, lighting up the near and the far, piercing their way to the primal beginnings and again into infinitudes of space and time—then giving sharp definition to details which may seem unessential but are of great symptomatic importance. Out of the cumulative mass of details the necessities of storm-charged destiny arise but also a sustaining power of the Spirit. We discern the play of forces which preceded the sufferings of our present time, discharged itself with unparalleled fury in the world war and its aftermath and will burst out in tempests yet to come. We understand why this had to be, what failings will be forgiven, what demands made of us. A great and impressive tableau of history unrolls from the precision given to details otherwise ignored and from the vast cosmic-human background against which the life of man stands out in bold relief. These vistas of primordial cosmic happenings, of ages of grey antiquity in human history which, nevertheless, shed clearest light upon our present time, are opened up with particular vividness in the lectures given to members of the Anthroposophical Society—with certain interruptions, but in constantly recurring rhythm—in places where Rudolf Steiner made his home between continual travelling: Berlin and Dornach. The lectures were given in order that the conscience of a small group of human beings at least might be made alive to the tasks of the time, to the vital significance of the hour in which we were living before the world war, and are still living today. Rudolf Steiner spoke gravely and impressively, like the voice of destiny itself, like the awakened human conscience, linking his arguments with factual details in every sphere. And then, when in the world outside, all supports hitherto thought secure tottered for every eye to see, as the forces burst upon one another with elemental might, it was he who tried ever and again to formulate the thoughts of deliverance and recovery without which chaos cannot be overcome. Although an unfledged humanity could not understand this voice, a light must somehow be brought into the chaos—even though it might reach only a small group of immature, but eager-hearted people. An attempt had also to be made to penetrate here and there into the field of concrete, practical life. To be sure, the representatives of this “practical side of life” as they are pleased to call it, scornfully and with vicious measures of sabotage, rejected everything that seemed to them so remote from reality in that it spoke of spiritual worlds. Yet the living thought has the power to outlast the moment and to rise up again in a new form. Its duty is to work even where there is no prospect of success; in all its purity it has to find its way to souls who, through constant testing, gradually become open to receive it. Out of the concrete realities of existence from which his spiritual vision was never willing to withdraw, Rudolf Steiner created a science of knowledge embracing every domain of life and able to pour vitalising, creative impulses into the manifold branches of science and art, philosophy and religious activity. To live through this was, and remains, an intense upliftment, like climbing up steep mountain crests in snow-cleansed, sun-pierced air. Deep, refreshing breaths can be drawn in this region of the higher cosmic realities which imbue human life with meaning and even now shape the picture of destiny in those future times, when, out of a quickened consciousness, thought will encompass higher and higher spheres of existence. Treasures of the Spirit of well-nigh frightening brilliance have been bequeathed to us, demonstrating through their very existence that the might of the Dark Age, of Kaliyuga, has been broken and conquered. True, the darkness is within us still, but the Light is there and may not be withheld—not even from a humanity living in shadow. The Light—of which Rudolf Steiner says that it is the Christ Impulse—had first to prepare and shape the vessel of human consciousness into which it can flow; it will bring to men that re-awakening by which alone they can wrest themselves from downfall. Neither the powers of the Sentient Soul, nor the fervent passion of religious experience known to the Middle Ages, to the saints and the mystics along the path of the Christian Initiation, are competent to overcome the obstructions brought by the age of rationalism. But wise Providence, guide and leader of human existence, inaugurated, even before the dawn of the modern age, a second path of Christian Initiation along which souls were gradually to be made ready for the demands of a later future. The call of this, the Christian-Rosicrucian path, went out above all to the powers of the Consciousness Soul, the Spiritual Soul. Hence its mission was also to establish the human being firmly within the personality, to allow him to experience to the full the significance of the single life. Through study, through imagination and contemplation, it led the human being out into the macrocosm—which was discovered again, in image, within his own being. But the full development of the forces of the personality, whereby the “ I ” could be led to conscious realisation of the Spirit, made it necessary that the knowledge of repeated earth-lives should, to begin with, be hidden for a time from the portion of humanity destined to unfold these forces of personality. What the new age needs is not a return to the past through a revival of the methods of Yoga, nor of the Gnostic or Rosicrucian paths in the form in which they served the spiritual weal of men in days gone by. In accordance with the demands of the modern age, a new impulse must be given to the rigorous path of Rosicrucian knowledge which in its true form has nothing whatever to do with the charlatanry that has usurped its name—a new impulse, in the form of the revelation of the great truths of Reincarnation and Karma. Until the task of proclaiming these truths devolved upon Rudolf Steiner, Rosicrucianism concealed them, kept silence about them. But it came about that with the passage of the centuries, these truths were able to flash into the consciousness of minds in Europe, as the result of rigorous and strenuous ways of thought, and as a fruit of knowledge born of alert reason; as a concern, too, of mankind, through which the evolution of human history receives meaning and significance, not as a concern of the single individual whose goal, as in Buddhism, is liberation from the wheel of rebirth. We need only mention the names of Goethe and Lessing. The salvation of the individuality passing onwards and unfolding through the recurrent earthly lives, the rebirth of the Divine “ I ” in man—this is the deed wrought by Christ, and with the stupendous power of knowledge at his command Rudolf Steiner brought this deed ever and again before our eyes. When after long reluctance he had made up his mind to comply with the request of German Theosophists to lead their work, he was able to accept the proposal because of the avowed task of the Theosophical Society: to establish knowledge of Reincarnation and Karma in the world. The lectures leading to the request that he should become the leader of this Movement in Germany were those on Mysticism at the Dawn of Modern Spiritual Life, and Christianity as Mystical Fact. Therewith, the impulse which he was to bring to the Movement had been clearly indicated, and he was assured of absolute freedom to teach as he would. He himself acted in line with the spirit of true occultists of all ages who make a link with the store of spiritual knowledge already existing in order to preserve its life and lead it forward. He still saw hope of being able, through the new impulse, to rescue the Theosophical Society, too, from lapsing into the rigidity of dogma, to imbue it with fresh forces and enrich its very defective understanding of the Mysteries of Christianity. Without overthrowing anything at all, gradually laying stone upon stone, he created the basis for this understanding. For the new insight must be acquired by the listeners only through knowledge consciously put to the test of reason. And so, to begin with, he adopted the terminology current among the Theosophists, gradually widening the ideas and giving them life so that they might conform to the more alert consciousness of the modern mind. The basis once created, wider and wider perspectives could be opened out, until, from the side of the super-sensible, there broke the light which reveals the mission of the earth and the tasks of mankind. Not only from the point of view of their content, but also from that of chronology, the opportunity of studying every such series of lectures given by Rudolf Steiner seems to us to be of great importance for newcomers to Spiritual Science, for only so is it possible to realise the living, organic growth of the work. Remarks interpolated here and there in the lectures about contemporary happenings seeming to have little bearing at a later time, have such moral and educational value that they are of lasting significance. There can be no concealment of the firm stand Rudolf Steiner was compelled to take against the attempts that were clouding objective truth and corrupting the Theosophical Society by the introduction of pet projects and personal ambitions. The warnings given in this connection may not always be understood by the reader today. In the main they were connected with the occult despotism—for so indeed it may be called—which took the form of the announcement of the coming of a World-Saviour in the flesh—to whom they dared to give the name of Christ. The Indian boy Krishnamurti was chosen for this role and the “Order of the Star in the East” founded with a flourish of trumpets. The Theosophical Society was expected to place itself in the service of this new aim. By these crude means it was hoped to win souls who were open to listen to the explanations of Christian Esotericism given by Rudolf Steiner. But a campaign, fought with all the arms of calumny, was launched against him. The International Theosophical Congress which was to have been held in Genoa in the year 1911 and in which Rudolf Steiner was to have given two lectures on “Buddhism in the twentieth century” and “Christ in the twentieth century,” was cancelled at the last minute for inadequate reasons—but in reality because of fear that the influence of Dr. Steiner's words might be too strong. In the lectures that year, many references had to be made to this affair which to very many people was absolutely incomprehensible. It had become necessary to make it clear that methods so grievously degrading the level of the Theosophical Society, could not be countenanced. Dr. Steiner stated this firmly, but with pain, and pouring his very heart's blood into the words, he spoke repeatedly of his one great wish—that the Society led by him might not succumb to the failings into which occult societies so easily lapse when they fall short of the demands of strict truthfulness and drift into vanity and ambition. The words should live like cleansing flames in the souls of those who represent his work and over and over again arise before them as an exhortation and warning. The lectures given in Berlin in the year 1912, contain many references to the struggles Rudolf Steiner was obliged to face in order that in spite of hidden attacks, the spirit of such a Movement might be rescued in its purity, for Spiritual Science. The lapse in the Theosophical Society made it necessary to lay sharp emphasis upon the autonomy of the anthroposophical work in Middle Europe vis-à-vis the Anglo-Indian Theosophical Society, and during the last days of December, 1912, the “Anthroposophical League (Bund)” was officially founded. The rhythms of the years recall such days vividly to the memory. Thirty years ago, on the 20th October, 1902, in Berlin, Rudolf Steiner gave his first lecture on Anthroposophy, and on the 21st translated into German the theosophical lecture delivered by Annie Besant who at that time had not come under the sway of the unhealthy influences to which she afterwards fell victim. Twenty years ago, Rudolf Steiner was obliged to protect the anthroposophical Movement inaugurated by him from the despotic attacks going out from Adyar, and to speak the words which are like a heritage left by the lectures and are now being made available to us once again as a memorial of those days. They rang out in power during the last days of December of that same year, in Cologne, when in Rudolf Steiner's lectures on The Bhagavad Gita and the Epistles of St. Paul, the purest oriental wisdom was presented to the listeners with unprecedented grandeur, in the light of Christian knowledge. Again his concluding words were an impressive appeal for self-knowledge and humility in those belonging to the Movement inaugurated by him. But the opposing powers were not slumbering. Ten years ago, on New Year's night, 1922-23, the Goetheanum was in flames. Only the Group, sculptured in wood, portraying the Representative of Humanity between the vanquished Adversaries, was saved. We are hoping that by Christmas of this year, this Group will stand in a space worthy of it, in the new Goetheanum. There is a moving description of the Representative of Humanity, of the Christ Figure, at the end of one of the lectures of 1912, when there was no thought—even of the possibility—of its execution in sculpture. It came before us then in words, and now it stands before our eyes as a work of Art. Marie Steiner |
| 282. Speech and Drama: The Mystery Character of Dramatic Art
14 Sep 1924, Dornach Translated by Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| If we go back to the time before worldliness began to get the upper hand on the stage, we shall find that dramatic performances were always in connection with worship, with the cult. The Christmas ritual which was intended to lead the people up to a lofty height where they might verily behold the Divine—this Christmas ritual we find continued, either still inside or in front of the church, in the form of a play. |
| 282. Speech and Drama: The Mystery Character of Dramatic Art
14 Sep 1924, Dornach Translated by Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
My dear Friends, It is my intention today to add something to our previous studies that will, I believe, help you to a deeper understanding of dramatic art. For, as I indicated at the end of yesterday's lecture, that is the direction in which our studies are leading us—to an esoteric deepening of our whole conception of drama and of our own part in it. For the community at large, the situation is of course different; we shall be dealing with that later. But speaking for those of us who want to take a share in the work of the stage, we are called upon to fulfil a mission (if I may use such a word in this connection)—a mission on behalf of art and on behalf also of mankind. And before we can begin to have a true perception of that mission, we must learn to see how deeply our art is grounded in man as he is today, and we must also look a little more closely into the whole process of human evolution, in one phase of which we are now living. The actor must be able to experience for himself how the word, the artistically formed and spoken word, can reveal the whole being of man. This penetrating insight that can behold the word as a revelation of man cannot fail to give him a more spiritual conception of his calling; and once he has that, he will be able to arouse within him the necessary energy to make his work increasingly artistic, gradually bringing more and more artistic form into every detail of his acting. I will give you an example. An essential factor in the speaking of consonants is the part played by palate, tongue, lips, etc., in the forming of the word. And by looking a little deeper into the matter, we can see how the word on its part, in order that it shall acquire a fulness of content, catches hold of the experience which is associated with the region of each of the specified organs. We can quite well detect this, if we do not disdain to give our attention first of all to what presents itself to immediate perception, in order to pass on afterwards to its more spiritual aspect. Suppose we take our start from the ordinary physical sense of taste. There is positive ground, you know, for the fact that appreciation of art goes also by the name of taste; although when today we speak of taste in matters of art, and then again of the taste of a cucumber or of a veal cutlet, we have no longer that feeling of necessity which led men of an older time to label both with the same word. Consider how it is when you take some food or drink that can be described as bitter, that ‘tastes bitter’ in the ordinary material sense. Your palate and the back part of your tongue do the sensing of the bitterness for you. While the bitter substance is passing from your mouth into your oesophagus, and you are having the purely physical experience of bitterness, it is the palate that is engaged, in conjunction with the back part of the tongue. It is also possible to feel that something you eat tastes sour. The consumption of such a substance will lead you into a different physical experience. The task of mediating for you this perception of sourness you assign to the edge of the tongue. It is the edge of the tongue that is actively engaged in the experience of sourness. Or again, some food may taste sweet; then the tip of the tongue is mainly concerned. As you see, our relationship to the external world is in strict accordance with laws underlying our organism. We could never cajole the tip of the tongue into communicating to us the sensation of sourness or of bitterness; such foods leave it passive and inert. The tip of the tongue enjoys the distinction of coming into operation only when we take something sweet into our mouth. Now it is, as I have said, not without very good reason that we transfer the expressions sour, bitter, sweet, to the realm of the soul. We apply these terms to impressions that are of a moral nature—and we do so with careful discrimination. For we are not ordinarily inclined to picture, for instance, something sour before us as a result of the words another person speaks in our presence; his countenance however, may well cause us to speak of a sour face, and that out of a perfectly natural instinct. Whilst we do not readily feel a sentence to be sour, we have no compunction about calling a face sour. The fact is, the experience that makes you describe a face as sour calls into action exactly the same region in the mouth—namely the back part of the tongue where it goes toward the throat—as is engaged when you swallow vinegar. The experience is somewhat more spiritual, but it works in the same way. For there is an inner relationship between the two, and the relationship makes itself felt—instinctively, but unmistakably. The unconscious in us knows quite well the connection between vinegar and a sour face. There is just this slight difference in their working, that vinegar lays claim to the small and more passive organs of the tongue, whereas there are occasions when a sour face will call upon the more active parts of the same! We are here verily becoming able to behold the mysterious transition from inner perception or feeling to speech. For there is undoubtedly this real and living connection between them. When something makes an impression upon us in the moral sense and moves us to speech, then what happens is exactly the same as when some physical substance excites our sensation of taste. If you know this, then the knowledge will, evoke in you the power also to dive down into the more hidden regions of external reality. It will, for example, become possible for you to know that supposing you have to speak a sentence that refers, not without artistic feeling, to So-and-so's sour countenance, you will do well to carry in your soul at the same time a distinct after-taste of vinegar. Careful observation of life teaches that this will help; for there is a road that leads straight across from one experience into the other. Or, let us suppose, in the course of my part, I have to say, or am to overhear, that someone has a complaint against me. Then it will be good if I can instinctively arouse in the depths of my soul a sensation that resembles the after-taste of wormwood. Or again, let us say, I have to present on the stage some high official into whose presence a man is admitted who wishes to obtain for himself some office or other. The latter adopts a cringing attitude, and pours out on me words of the most fulsome flattery. This is a situation that may well occur in a play. In addition to all else that it will require—and the ‘all else’ will be substantially helped thereby—I shall do well to carry in me, while speaking, the sweet taste that sugar leaves in the mouth. And that will help with my listening too. If I am there in front of him, feeling in my soul, as it were, the after-taste of sugar, I shall—as the listener—instinctively assume the appropriate gesture. The question might well be raised: In expressing ourselves in this way, are we not adopting a rather realistic and materialistic point of view? Let me tell you, however, that the inducement to speak in this way follows as a direct result from that other study to which I have already alluded—the study, namely, of the historical evolution that has led up to our present drama. If we trace drama right back to the place of its birth, we come ultimately to what are known as the Mysteries. It is, in fact, not possible to have a worthy conception of dramatic art unless we are able to see its origin in the art of the Mysteries. Now, the art of the Mysteries had this aim in view: that what took place on the stage should proceed from those impulses that make their way into man from the spiritual world. But the art of the Mysteries sought also to follow how these spiritual impulses work right down into the details of the material world; so that, for example, those who had to take part in the ancient Mystery Plays would actually be given vinegar or wormwood, or some other substance, in order to prepare them for finding the right words and mime and gesture. And we, on our part, only begin to take our art seriously when, in our quest for artistic form, we do not hesitate to take account also of bodily experience. Otherwise our performances, where the acting must needs, from the very nature of the art, be carried right down to the fingertips—I might even say, to the tip of the tongue, for I have seen actors put out their tongue before now !—can never be more than superficial. Such revivals of primitive drama as can be met with in our time—the sort of drama to which I alluded the other day, for instance, when I told you of the Oriental performance I had witnessed in London—do certainly take us back to quite early stages of dramatic art, but not so far back as to give us any idea of the way things were done in the Mysteries. Plays of that kind we will therefore leave for the moment, we shall return to them later; just now we want to race back the art of drama to its source in the art of the Mysteries. If once the actor of the present day can come to understand the Mystery character of the great and noble art that he is following, he will begin to look on his work in a new way, he will begin to take it seriously. Fundamentally speaking, what the Mystery Play had to do was to show, through the agency of human beings, how the Gods intervene in the life of man on earth. Had we still today a number of plays of Aeschylus that have been lost, we would not, it is true, be able to learn from them the nature and character of the very most ancient Mystery art, but we would have in them echoes of this original art of the Mysteries. And then we would be able to ee that those who had to take part in the plays approached them with a certain awe and reverence. For these plays did not set out to represent events taking place among men on earth. Supersensible events were enacted, events that had indeed connection with human life on earth but took place among the Gods. The object was to show events that happen in supersensible realms among supersensible beings—to show these events in their influence upon the life of man on earth. In the most ancient times men shrank with awe from any direct representation of the supersensible. Rather had they the feeling that their part was to create a kind of framework on the stage for the Gods; everything must be so designed and ordered as to enable the spectators to feel that the Gods themselves have with a part of their being come down upon the stage. How was it sought to bring this about? To begin with, by having not individual actors that should represent Gods or human beings, but Choruses. These Choruses performed a special kind of recitative that was between speaking and singing, and was accompanied by instruments. In this way a form was brought into being and hovered over the stage, a stylised form that was absolutely real and was created out of sound and syllable and sentence, moulded and fashioned with an artistic sensitiveness far surpassing anything known in ordinary life. This form was conjured forth before the spectators, or rather the listeners, conjured forth from the word—the word with all its qualities of music and sculpture and painting. And the listener who lived in these older conceptions perceived—that is to say, did not merely have an idea of what was happening, but saw for himself that these Choruses gave the Gods the possibility of being themselves present, of being present in the musically and plastically formed word. Thus was the forming of the word in all its music and colour, in all its sculpted moulding, brought to such a degree of individualisation that it was able to betoken Divine Beings. This was in very truth attained in the Mysteries of ancient times. And while it was proceeding, the whole space was pervaded with what we today would call fear of the Divine, awe and reverence in the presence of Divine Being. This mood hovered there like an astral aura, mediating between what went on upon the stage and what the spectators were experiencing. The human being felt himself to be in the presence of a supersensible world. And that was what was intended. And it was further intended that in union with this feeling, another should rise up in the human being; he should feel that he is living in his soul together with the Divine. An inner life lived in close relation with the Divine was thus tho second aim that was cherished in these ancient Mysteries. First, fear of the Gods, in the best sense of the word; and then that man should have this experience of living together with the Divine. But now a new development. As time went on, men gradually lost the power to perceive spiritual reality in a form that was not outwardly tangible. The consequence was, it became necessary to put the human being on the stage. In earlier times, men had been able to perceive the contours of the Gods in the word—the word with its colour and its music, the plastically moulded word, the recitative. When they could do so no longer, the human being had to be there on the stage to present in his form and figure the contours of the Gods. But the people must not be allowed to forget that the human being on the stage is a God. Think, for instance, of the Egyptian Gods. Unless there were some special reason for it, they were not given insipid human countenances (I explained in an earlier lecture how I mean this to be understood). The Gods of Egypt, more especially the higher Gods—that is, those who ascend farther into the spiritual—had animal faces, bearing always in their countenance what was intended to typify the eternal. The human countenance is eternal in its mobility; it is eternally changing! Mobility had to be expressed in the gestures of the rest of the person, apart from the head. But there must needs also be duration, constancy; and that must be shown in the physiognomy. A human being cannot let his countenance remain permanently immobile; it would take on the expression of death or look as though he were afflicted with tetanus. If you want to show in the world of the senses that which endures and belongs to the spiritual, if you want to present this in bodily form in contrast to that which is continually changing, then there is no other way, you must have recourse to the animal countenance And so we find in the cult of the Egyptians the supersensible Gods with animal faces. When now the human being begins to appear on the stage, he too comes before us with a mask that is reminiscent of the animal. This development that we can observe on the stage is an outward expression of the inner development that was taking place in man's spiritual life. At his first appearance on the stage, the human being did not present man, he presented the God, and most often the God who stands nearest to man, Dionysos. And we begin then to have, in addition to the Chorus, the actor standing in their midst; first one, then two who carry on a dialogue, and gradually more. Only when we have learned to discern in the whole art of dramatic representation something of the magic of its birthplace in the Mysteries—only then is it possible for us to stand up before an audience as we should, carrying in us the knowledge of how drama has grown up out of the cult of the Mysteries, out of that cult whose whole purpose was to present what belongs to the supersensible world.1 In the Middle Ages there was still an understanding for this. If we go back to the time before worldliness began to get the upper hand on the stage, we shall find that dramatic performances were always in connection with worship, with the cult. The Christmas ritual which was intended to lead the people up to a lofty height where they might verily behold the Divine—this Christmas ritual we find continued, either still inside or in front of the church, in the form of a play. The acting was nothing else than an extension of the ritual that was performed inside the church. The priest who celebrated would afterwards appear as actor and take part in the play. We do not find in these plays the same holy feeling that pervaded the ancient Mysteries, where the drama was an integral part of the cult itself, directly belonging to the Mystery. In mediaeval times it was different; the ritual and the drama had each its own distinct character. One could nevertheless feel that they belonged together. And the sane kind of development went on in connection with the other festivals of the year. Having thus come to see that drama has a sacramental origin, we may now go on to consider the other, more worldly, factor that was brought in later on, and that has not the same close relation to cult and ritual. It has nevertheless a similar origin. When in very early times man looked out into the great world of Nature, he felt there the presence of the Divine, with whom he himself was connected; he felt the God in tho clouds, the God in the thunder and lightning. And still more did he feel the God entering into the word, into the artistically formed and musically modulated word, which the Chorus in the Mysteries placed out into the world as objective, created form. And now, as time went on, this very experience led man to perceive another secret. He began to learn that there is something in himself that is Divine, and that responds like an echo to the Divine that comes to meet him from the far reaches of the universe. And this led man to develop a new feeling about drama which we may describe in the following way. The ground had been prepared in far-off times by the Chorus, who produced the word wherein the God was able, not of course to incarnate, but to be incorporated. That was how it was in the Mystery Play, the original Mystery Play. Then came the time when, man being no longer equal to this experience, the actor was brought forward, not yet, however, for any other purpose than to represent the God. But now, as evolution proceeded further, the perception began to dawn upon man that when the human being presents his own innermost soul, then too he is presenting something Divine; if he can present on the stage the Divine that is in the external world, he can also present the Divine that is in himself. And so, from being a manifestation of the Gods, dramatic art became a manifestation of the inner being of man; it presented on the stage the human soul. And this inevitably led to the need to bring innermost human experience into the forming of the speech, to bring this same intimate human experience into the gesturing also that was done on the stage. And then there developed, in a time when its significance could still be instinctively felt, all that way of working with voice and gesture which I have been putting before you in these lectures, impressing upon you the need to renew it in our day, to put your whole will into getting it restored to the technique of the stage. We have seen how it takes us, on the one hand, to such things as Discus-throwing, and on the other hand to a sensitive perception of the after-taste, for example, of sour and bitter. Yes, we have to go on paths that may seem at first to lead us far afield, in order to find again the foundations upon which alone can be built the drama that portrays man. It will be helpful if at this point we make a kind of picture of how the evolution of drama has taken its course. Contemplate the picture, meditate upon it, and it will inspire you to enter with deeper understanding into the things that I have been expounding in these days in considerable detail and that will, I hope, become much clearer to you as I help you now to see them in a larger perspective. We can for the moment imagine that we have before us the stage of the present day (only, obviously no more than its barest outlines, if we are thinking of primeval times); and in the centre of the stage the word, produced by the Chorus in all its fulness of colour and tone and form. In the word men feel the presence of the God. The God appears in the word—in the music, in the painting, in the sculpture of the word. It is His will to appear to those who are present there, beholding. That is the first phase. The next phase is that in amongst the Chorus the human being begins to take a place, the real and actual human being. Before, it was the God—the God who was only `incorporated’ in the formed word. Now, man stands there; yet we still have the God, for man is only there to represent the God. He will accordingly have to learn how to speak from the Chorus, who used even to employ instruments in order to give greater strength to the voice. Man will have to learn from the Chorus; for his voice must not reveal what is within him, must not utter forth any human experience, no, it has to imitate what the Chorus places out objectively into the world. His recitative is to be a continuation of what was in the Chorus. In comparison with the mighty development of voice that was striven for here and that was rendered yet more powerful by the use of all manner of instruments (and this was not simply because they were acting in the open air and needed on that account to reinforce the voice, but for the reason I have explained, namely, that upon that stage should be heard speak the voice of the Gods)—in comparison, I say, with this development of voice in the earliest Mystery Plays, the speaking on our modern stage would sound to some Greek of ancient times who had understanding for these things like the squeaking of a mouse. Yes, it would indeed! For through what took place upon that stage of olden time, the Divine World rushed storming like a mighty wind. But now comes this further development, where man begins to grow aware that the Divine is also within himself. Representation of the God gives place to representation of man. It follows as a necessary consequence that man will have to learn to stylise his prose; for he has to carry into the external world the revelation of his own inner experiences. But for this it is by no means enough that we should behave on the stage as we do in real life. After all, what occasion is there to show that on the stage? We have enough of it around us all the time. No one with artistic feeling will be interested in a mere imitation of life, since life itself is always far richer than the poor husk which is all that imitation can produce. Consider for a moment how it is with some other art—say, the art of landscape painting. There would not be much sense in a painter's setting out to paint trees with the object of painting them so as to show whether they had needles or leaves, and then putting in some clouds up in the sky of various shapes, adding below a meadow and carefully reproducing there the colours of the different flowers. No one with artistic feeling could bear to look at such a picture. And why not? Because there are much more beautiful views to look at outside in Nature. Landscape painting of this kind does not justify its existence. No question but Nature can show us pictures of far greater beauty. But now suppose you have a painter who begins by feeling all around him a mood of evening time. The tree that stands there in the landscape is nothing to him, but the light on the tree, how the tree catches the light of the setting sun—that has a mood of its own, a mood that comes and goes in a moment. It will probably make no great impression on the dry and prosaic passer-by, but the painter can seize upon the momentary experience and hold it fast, if he have sufficient presence of mind (I mean that in the best sense of the word2). Then landscape painting begins to have meaning. For if we have before us such a painting, we are looking at the momentary inspiration of a fellow human being, at the momentary spiritualising of his sight. Through and beyond the painted landscape, we are looking into the very heart of the painter's temperament. For according as is a man's temperament, so does the landscape show itself to him, down to the very colours he finds there. With a genuine and elemental painter, it will really be so, that if the fundamental mood of his soul is melancholy, he will show us the shadow side of things with their darker nuances of colour. If again in his deepest being he is of sanguine temperament, then shades of red and yellow will dance for him upon the leaves wheresoever the sunshine strikes them. And if you should happen to look at paintings where these bright colours are seen dancing in the sunshine, and on making the acquaintance afterwards of the man who painted them discover that he is a melancholic, then that man is no painter; he has merely learned to paint. And there is a vast difference between being a painter and learning to paint—although one who is a painter must also learn to paint! This last fact is too often forgotten nowadays, and people jump to the conclusion that one who has learned to paint is no painter, and that he alone is a painter who has never learned to paint. That is, however, not correct. If you want to characterise the true painter, he is the one of whom you are bound to say when you see his pictures: He must indeed be a painter! And then you have to add, a little diffidently: And he must also have learned to paint! But if you meet with someone like I described just now, who paints. a picture that is entirely out of tune with his temperament, then you will have to say, taking care not to give offence (for one must always be polite): He has learned to paint!—adding, silently, to yourself: But he is, for all that, no painter ! I don't mean you to take this as a piece of advice! I am merely quoting what you will frequently hear people say in order to get out of the dilemma in which they find themselves when faced with the pretensions of would-be painters. Well then, it will, I think, be clear to us all that there is no point in reproducing on the stage what we have immediately present before us in real life. What is wanted is that the one who is there on the stage shall for the time let his ordinary self be forgotten, and become the human being who lives in speech in the way I have described. The spectator will then instinctively perceive around the actor an aura; as he listens to the formed speech, he will see before him the auric contours—perhaps of the incisive word, or perhaps of the slowly spoken, or again of the word that is abrupt, or the word that is energetically flung out. Living in this way in the speech, the actor becomes something quite different from what he is in life. In extreme instances you will recognise at once that this has to be so. Suppose you want to assign the part of a simpleton. It would never do to give it to an actor who is one already. A producer who allowed a rather silly, idiotic person to play the part would be the worst producer imaginable. To play the role of a simpleton requires the highest art; least of all is a simpleton equal to it. From a purely naturalistic point of view, it might, of course, seem best to look round for an actor who would play the part out of his own natural silliness. For the part to be played as it should be, however, something quite different is required. The actor has to know that the condition is due to an incapacity to let the forming of the speech make contact with the sour, bitter and sweet in the way I have explained. The simpleton does not succeed in building the bridge from these sensations to speech. The dramatist ought to take this into consideration in his composition of the text; he ought to know that such a person remains at the sensation, cannot get across to the speech which should result from the soul experience that belongs to the sensation. What will a good dramatist do in such a situation? (And the actor, you know, should always have the insight to see what the dramatist is doing; it should be quite clear to him from the whole setting of the play.) A good dramatist will want the role to be played by an actor who is a true artist and possesses to a rare degree the gift of gesture in the way I have described it, so that his gestures come right out of inner experience, bringing this inner experience to expression in style, in true artistic style. The art of listening—that is what the actor of the part will have to develop particularly, the art of listening with gesture. It may be the dramatist will not help him here; for the dramatists of the present day are not exactly great artists. But, although it is true that one cannot ‘corriger la fortune’, one can ‘corriger’ life, which means in the present instance one can ensure that art appears on the stage in a genuine and worthy manner by having the ‘foolish’ part acted with full complement of gesture, and especially of those gestures I described yesterday for the listener or onlooker. The main point is that the simpleton, when he is conscious of some sensation within him, should show by his whole attitude and gesture that he expects his environment to tell him how he is to put it into words. Get your actor to make listening’ gestures and be all the time gazing open-mouthed at the people around him, in the position for a; and your audience will not fail to receive the impression of a simpleton. Let him even try to caricature this a position right from the back of the mouth, looking intently on the people around, as though it were they, and not he, who should really be doing the speaking. And if the dramatist has failed to do his part in the matter, the producer should none the less require the actor to employ the relevant gestures; even if something quite different is being said around him, the actor can still make as though he were hearing from the talk of the others what he himself has to say. You have only to let him be perpetually giving the impression of being the echo of those who are standing around and be making also at the same time appropriate gestures, and you will have placed on the stage a faithful presentation of a simpleton. In real life you won't find it exactly like that. But now suppose you want to show on the stage the ‘wise’ man, generally a popular part with actors—but I myself would sooner play the simpleton. An actor who is playing the wise or ‘knowing’ man should show by his gestures that for his own understanding he is not very dependent on the others with whom he is conversing. His gestures will in fact be lacking in the very quality that I have said ought to characterise gesture; they will be lacking in life, being no more than lightly indicated, and containing always a subtle hint of the gesture of rejection that we saw must accompany the word of rejection or brushing aside. The wise man goes with the other speaker, follows what he is saying, but along with his gesture of understanding there will always be a touch of the gesture of rejection. And then, when his partner has finished speaking, he will wait awhile, and whereas before, when he was the listener, he inclined his head to hear what the other had to say, he will now perhaps throw it back; even the eyelids too can be held back a little. This will always >mean that the audience will instinctively have the impression that the ‘wise’ man is not going to enter fully into what the other has been saying, but intends rather to draw upon his own store of wisdom in order to show what is really essential in the matter. The audience will feel that he is talking more out of his memory than in response to what he has heard the other say. Your wise man should always give this impression. If he does not, the acting has been lacking in style. A very different kind of gesturing will have to be employed if you want to represent on the stage a gossipy old lady. She has, let us say, just come from an afternoon tea-party, and brings with her the manners of the tea-table. This old lady will have to accompany what she hears said with a motion of stout resistance, indicating that nothing the other has to say is right. And then, before the other has finished speaking, she should break in, with complete corresponding accompaniment of gesture to accord with every shade of speech formation. She must break in so suddenly that you feel she has no need to stop to think; she knows right away, as soon as ever she is confronted with the situation, what she will say to it. She should be beginning with gesture and word while the other's last syllable is being spoken. One must, however, be careful to let this last syllable be heard, so that the audience do not lose the thread. You must really ensure that such a scene is treated in the way I have described, for then it will have style. This gossipy old lady, coming in straight from the tea-table, is, you see, the exact opposite of the wise man. It could also quite well be a gossipy old gentleman, come straight from his evening glass with his pals; in that case the male quality of the talk would have to be brought out. And where the lady from the tea-party, before her partner has finished speaking, pokes out a finger, the old gentleman who also bursts in on the last syllable, will gesticulate with his whole hand, or his whole arm. That will be rendering the scene in style.
|
| 343. The Foundation Course: Anthroposophy and Religion
28 Sep 1921, Dornach Translated by Hanna von Maltitz Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| [ 14 ] Today in our inner reflections we have a weak memory of what at that time had been lived through instinctively. We celebrate Christmas and a historic glance reveals to us the connection of the inner memory life of individuals who, during winter, had felt abandoned by heaven, and so nursed their memories in solitude. |
| What is revealed in our abstract minds and calculations to determine the Easter festival, this was a direct experience for earlier man; it was observed in the heavens after the completion of winter and the time of St John in the soulful feeling of the divine weaving in the heavens, to unite in divine blessedness with the truly Spiritual-Divine which had been only a memory at Christmas time and into which they lived at springtime. The old summer solstice was primarily celebrated as the inner search for the union with the Divine in which man could empathise with how, if the earth would not be enclosed, the earth would be an active being working in the cosmos together with the entire being of humanity towards this cosmic experience. |
| 343. The Foundation Course: Anthroposophy and Religion
28 Sep 1921, Dornach Translated by Hanna von Maltitz Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] My dear friends! Last night I received a letter from Reverend Dr Schairer in Nagold which contains a number of theses regarding how Anthroposophy can conduct itself regarding religion, and religion conduct itself regarding Anthroposophy, and how a way must be found to initiate this behaviour. Dr Schairer thinks a discussion could be based on this. That also seems to be quite right following on from the first part of the letter—I couldn't read the whole thing, I haven't yet read the last pages—because a lot will be clarified in an exceedingly exact manner. Perhaps this could in some respects provide a good basis for a discussion because it will be a priority in our future work, if I may say so, to bring these fundamental issues in order. [ 2 ] In addition to what I want to say to you today—everything is for the time being still introductory—depends from one side on the main issue of this question, certainly from one specific side. We have to be perfectly clear that Anthroposophy as such must arrive in a positive way at the Mystery of Golgotha so that the manner and way in which this happens regarding this event, can really be ascribed to a concept of knowledge, a knowledge which, if the term is taken seriously, this concept of "knowledge" is also applicable in the modern scientific sense. It is on the other hand right that this special way, first of all—I stress first of all—Anthroposophy needs to get to the Mystery of Golgotha, that at first the Protestant sense of religion from certain foundations need to be brought to consciousness, which can take offence. Only complete clarity about these things can lead to some healing goal. [ 3 ] I must therefore, even if it appears somewhat remote, enter into what I want to say to you today. Anthroposophy or spiritual science actually creates out of supersensible knowledge, and rejects—in principle rejects—anything from older traditions, let's say, the oriental wisdom or historic Gnosticism, through somehow assembling a content, or expanding the content. Anthroposophy quite decisively rejects this because it focuses above all in its comprehensive task of practically answering the question: How much can a person today, who has in his soul, latent, or in ordinary life, not conscious forces in his awareness, how can he now in full consciousness and with full human discretion, recognise the supersensible world instantly?—Spiritual science would like to proceed with this cognition similarly to a mathematician who wants to prove the theory of Pythagoras. He proves it out of something which one can recognise today, and he doesn't reject purely from historical writers what he had encountered before, when he obviously later, in his historic studies, entered into the way the theorem had been found. If you research spiritual science in this way you will certainly conclude that an abyss lies between the way and manner in which current spiritual science arrives at its results through fully conscious research, and what still remains in Gnosticism or oriental wisdom, which has a more instinctive character on the other hand. Precisely what people want as unmixed knowledge brought to realization, even this, as I've said, needs to be researched. In the course of this research it becomes apparent that something is needed which makes an appearance as if one had reverted back to the old. In the course of research spiritual experiences take place namely for which modern people—the entire modern civilization—the concise words are missing. Our modern language has definitely connected to material thinking patterns; our modern speech has been learnt as linked either to mere outer material or intellectual matters—both these belong together. Inner intellectualism is nothing other than correlations to the materialistic methods of observation of the external world. What can be recognised about matter is that when one uses the materialistic method, it reflects inwardly as intellectualism. It is like this, that any philosophy which wants to prove its spirit through mere intellect or a spirit comprised from the intellect, will be wafting around in the wind; these would hardly be able to acknowledge that the intellectual is quite rightly spiritual, but that the content of what is intellectual can be nothing other than that of the material world. One must always speak clearly about these things. By expressing a sentence like: "The content of the intellectual can be nothing other than that of the material world," I'm only saying it can be nothing other than the content of the world, which can be viewed as the sum of material beings and phenomena; whether this is what it is, is not yet agreed upon. The intellectual material world could be through and through spiritual and what comprises intellectualism could be an illusion. Therefore, it is important for spiritual scientific discussions there should already be an unusually powerful conscientiousness existing towards knowledge otherwise there will be no progress in spiritual science. This conscientiousness is also noticed by people of the present; they find it necessary to hackle through their sentences in all directions in order to be concise, and people of the present day who are used to the journalistic handling of a style, call this wrestling for conciseness a bad style. [ 4 ] Such things we certainly must understand out of the peculiarities of the time. So, while current materialism and intellectualism have hassled speech/language to such a degree that language only operates in terms of the material, one can hardly find the right words needed to describe one's experiences and then one grasps for the old words which come from instinctive observation, to express that which needs expression. This results in the misunderstanding: people who cling only to words now believe that in the word one borrows what is contained in the translation of the word. This is not the case. The words "lotus flower" is a borrowed expression from oriental wisdom but what I have indicated (in my book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and its Attainment) is certainly not borrowed from oriental wisdom. This is what I'm asking, for you to always take this into consideration, when on occasion I need through necessity to borrow expressions from history, as I have to do today. [ 5 ] You see, spiritual science first and foremost wants to gain human knowledge through Anthroposophy, modern physiology and biology need to some extent be considered as the most unsuitable instrument for acquiring real human knowledge. Modern physiology and biology unfortunately base their knowledge on what can be seen in man's corpse. Also, when living people are studied, they are unfortunately only studying the corpse. At most they indulge in a certain deception, which extraordinarily characteristically was revealed when Du Bois-Reymond held his famous lecture on the Ignorabimus. He is quite clear that nothing—because he was besides a scientific researcher also a thinker—of this modern manner of research of the soul—he called it consciousness—can be gained; so that one actually through natural science, according to Du Bois-Reymond, can't find out anything about the actual being of man. He is submitting himself to an ever-greater deception; he says that with outer scientific beings we will never be able to recognise conscious people, at most only those who are asleep. When a person lies sleeping in bed, according to Du Bois-Reymond, the sum of all processes is within the person, but at the moment of waking, when the spark of consciousness jumps in, the possibility of observation ends. It would be correct if one was able today, to scientifically understand the life and development of the plant world. The life and development of the plant world is still not comprehensible through science today because the method is not recognised through which this would be understood. So that too, is an illusion, what current science explains about sleeping people; it can only be in their domain to explain sleeping people, the corpse; further than this they don't go. They can only explain those who are sleeping; the ones who are lively they can't explain. [ 6 ] Anthroposophy doesn't follow philosophic speculation about people, but the way which I outline in my book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and its Attainment, in the withdrawal of the soul into observation, and then the attainment towards not remaining stuck in the mineral element in man, which is perpetually dead and is incorporated as a dead mineral element in the being of man, but that one gets to, through what could be called the ether body or creative force, observe what the real foundation of the sleeping human being is. [ 7 ] Now people come along out of the current philosophic consciousness; I can refer to one case. When my Occult Science was published, there was talk about a Polish philosopher, Lutoslawski, in an old German monthly publication. In this discussion it was said, among other things, that it is only an abstraction to divide a human being into members of the physical body, the ether body, the astral body and the I, one can certainly as an abstraction divide man into these, but it goes no further.—As far as Lutoslawski at that time regarded it, he was correct in his assertion, but he remained in the field of abstraction, and this depends on the following: As soon as a one moves up to contemplate the ether body one can't remain in the physical body of the human being; as long as one only contemplates the physical body then one doesn't need anything but to investigate within the human skin and at most go as far as to examine the interaction with the outside world through breathing and so on; but nothing further is examined, basically nothing more than by beginning with the boundary of the human skin. [ 8 ] This characteristic I'm offering, you will quite rightly find if you only think about it. One can, if one remains confined in examining the physical body only by what is enclosed by the skin, but one can no longer remain in what is contained by the physical skin when one thoroughly looks at the ether body. Obviously, the basic outlines need to be drawn first, as I have done in my Occult Science, so attention can be drawn to man's physical body, ether body, astral body and so on. However, Anthroposophy doesn't remain stuck here; Anthroposophy must now expand these things. As soon as knowledge of the ether body is extended one can no longer remain within the human being, but one needs to observe the human being as a single being in connection with everything earthy. One must examine the human being in connection with the earthly. This means as long as the human being is enclosed in his physical body, he leads a relatively independent life, a relatively independent life. To a high degree man is dependent on everything possible, air, light and so on, for the physical body; man is dependent on these to a high degree. You can see this in the following example. When materialism was at the height of its blossoming, Wolff, Büchner and Czolbe very often referred to the dependency of man on the physical environment and one of these writers once listed everything, from gravity, light, the climate and so on and concluded that the human being was the result of every breath of air he breathes. He meant by this—the person concerned was a materialist—the physical organism is dependent on every breath of air. Yes, my dear friends, if one considers the depiction of materialism in this reference in all earnest and contemplate how the human being was as depicted by materialism, then one will become aware that the human being at its highest potency could be a hysteric or a cripple. The materialists have already described the material human being but not what happens in the world, a being who at its highest potency would be an hysteric. The hysteric at his highest power would be as dependent on his environment as the materialist has described him.—The actual human being in his highest power is independent on what the physical earth environment offers. One can't say this about the etheric man. As soon as one rises to the etheric in man, one can't observe the etheric body as isolated from the entire earth's etheric which needs to be examined, and here man lives in a far higher—naturally not in the physical sense higher—level as his physical body. When one comes to the realm of the etheric while observing the earth, then one can no longer hold on to concepts of chemistry, or mineralogy and so on, but one must now search for completely different conceptions; now one will be confronted with the necessity of wanting to say what one wants to say, at least prove it with expressions which the Greeks had, because it is not possible to do so in today's language. [ 9 ] The (ancient) Greek would, if you demonstrated current chemistry to him, express himself in the following way. Just imagine we have on the one hand a really modern chemist and on the other hand a Greek, an educated ancient Greek, who would like to talk to the chemist, and the modern scientist would say something like the following: "You Greeks come from far back, you took the four elements of fire, earth, water and air. Those are for us at most, aggregate conditions: fire as all penetrating warmth, air as aeriform, the water as liquid and the earth in a solid physical state. We acknowledge that from you. However, we have placed some seventy elements in place of your four." If the Greek would study what has been presented as some seventy elements, he would say: "What we understand under the four elements will not touch many of your seventy elements. We have for what you have in your seventy elements, the collective name of 'earth': we call all of that 'earth.' With our four elements we are referring to something else, we indicate through it how some things express themselves from out of their inner being. What you are pouring out regarding your elements, that is for us aeriform and such further conditions of the earth. Something far more internal than what you acknowledge with your elements, describe for us the expressions of earth, water, fire or heat." [ 10 ] Exactly to these four elements one is guided when one considers everything surging and weaving which has been spun into the earthy etheric and human etheric. Only when you follow this etheric, which lives in the four elements, as an experience within the circling of the earth's weaving existence, will you understand spring, summer, autumn and winter. In spring, summer, autumn and winter which exist as the foundation of the etheric processes of the earth—not merely as the physical processes of the earth—in this etheric weaving of the earth the human ether body is woven so that one, when one in a sense advances to the etheric body, one must find the etheric body rooted in the earthly-etheric. [ 11 ] What we rediscover again—I have explained this whole relationship in detail in the Hague—sounds like instinctive wisdom of the ancients, which continued right into Greek times. We don't understand the continuity in humanity if we don't, in our way, discover what the content of these instincts were. [ 12 ] Now we will go further and come to the astral body of the human being. The terminology doesn't mean anything to me; the astral body had been spoken about much later, right into the middle ages and even up to present time, but it must have some formulation. When one rises up into the astral body, the actual carrier of thinking, feeling and will in man, then you again come to realise that man cannot be regarded in isolation. Just as one makes the etheric a member of the etheric weaving of the earth, so one needs to make the astral—in quite a spiritual manner—as basically incorporated in what is expressed in the movement and positioning of the stars. The astral in man is simply the expression of the cosmic, the astral relationships; how the stars move and are positioned to one another, this is expressed in the human astral body. Just like the human being through his etheric body is interrelated to the earthly etheric, so man through his astral body is associated through his astral to the earth's surroundings; it lives further in the earthly surrounding, they continue to live in the events, in the processes of his astral body. [ 13 ] You see, it is not an abstraction to structure the human being; we are required to structure the human being because in this structuring we rise from human knowledge to cosmic knowledge, quite naturally. Now we can go back in human evolution to more ancient times which had not actually reached into the Greek times any more. Here we find an instinctive awareness of people's relationship to the starry worlds. Not as if Astronomy was carried on in these ancient times, and if it was, that it could be considered serious, but the connection happened as a direct experience. Human beings experienced themselves in certain times of their earth evolution far less as earthlings than as heavenly beings. In our research we easily reach a time where people, certainly inwardly, lived into the growing and flourishing of the plant world, also in the animal world where everything offered in air and in water were experienced, but as being independent. Similar to how the human being in current times experiences inner processes of nutrition and digestion, processes taking place independently, so the human being once took in all that he experienced in the physical world, as independent, but he didn't take what he lived through in his astral body as independent from the influences of the heavenly worlds. That was something that differentiated itself, imposed itself too strongly upon him, to be taken as independently. When winter shifted closer, when nights lengthened and a person found frost had arrived all around him, he sensed in a certain way how he simply depended on his placement in the world, he felt something within him, like a memory of heaven. During winter he felt himself separated from heaven in a way, he sensed something within him which was like a mere memory of heaven. When by contrast spring approached and the warmth of the earth was interwoven with man, then he felt something dissolve within him as when he shares in the experience, I would call it, of a spreading out breath, the events of the heavens. Now he had heavenly reality, not just a memory of heaven which he had in winter. In this differentiated way he experienced the other seasons also; he actually participated in the seasons. [ 14 ] Today in our inner reflections we have a weak memory of what at that time had been lived through instinctively. We celebrate Christmas and a historic glance reveals to us the connection of the inner memory life of individuals who, during winter, had felt abandoned by heaven, and so nursed their memories in solitude. We still have echoes of experiences, not at one time through astronomical speculation or astronomy, but direct experiences in the determination of the Easter spring celebration according to the relationship of the sun to the moon. What is revealed in our abstract minds and calculations to determine the Easter festival, this was a direct experience for earlier man; it was observed in the heavens after the completion of winter and the time of St John in the soulful feeling of the divine weaving in the heavens, to unite in divine blessedness with the truly Spiritual-Divine which had been only a memory at Christmas time and into which they lived at springtime. The old summer solstice was primarily celebrated as the inner search for the union with the Divine in which man could empathise with how, if the earth would not be enclosed, the earth would be an active being working in the cosmos together with the entire being of humanity towards this cosmic experience. [ 15 ] In other words, what we refer to in spiritual science as an objective experience when we refer to the astral body, this would have been a direct experience for ancient mankind, but such that it didn't only occur in a moment but that it spanned time; from which one knew the stars worked here in their laws, in their movement. Not that man took much notice of sun and moon eclipses; that only happened when religion was transferred to science. In olden times people looked up to the heavens with religious simplicity, but also sensed the heavens within them, for a certain time. [ 16 ] You see, my dear friends, consider what one can think when theology comes forward today and says: What human beings primarily experience through the senses can hardly lead over to the super-sensible; what we have in science, can hardly lead over into the super-sensible; something quite extraordinary must happen in a person if he wants to become accessible to the spiritual worlds.—Such an examination of current theology shows that people are advised to justify religion while life, because we participate in life in the outer world, has no religious character; in a sense it needs to be removed out of ordinary life and placed in a special life in order to feel religious. There once was a time on earth where religious feelings were direct, in the present, and independent, and where one had turned life on earth out of religion. Just as we sense materialistically when we look at the plant world, the animal world and the stars and then need to turn within if we want to have religious experiences, just so once upon a time religious life was the given and if one wanted to turn away from what was given, one would go primarily out from the religious life. [ 17 ] As long as these things are not fully examined, there would be no clarity about the relationship of science, daily life and religious experience. At least once in life one should look at how human evolution is linked to these things, that at one stage in old world imagery there came the appearance of the outer sun, moon and stars which were relatively indifferent, these appearances coming from outside only addressed feeling; but was inwardly experienced. What took place in heaven was an inner experience for man which he could settle with himself, the effect still came from the heavenly realm and that was given to him as a matter of course. [ 18 ] Of course, there was a time where what lived and weaved in the astral body as the result of star activity was to some extent interlinked with an experience that takes place inwardly, in relation to the earth, which we can penetrate recognizably when we move forward to the ether body today. Human beings felt themselves more in the soul-spiritual when, through their astrality, they experienced celestial processes. Then one sees the human being indeed in the earthly, but he wasn't penetrating it as we do today; he penetrated the etheric, into what ruled in fire, water, air and earth. Here he maintains a relationship of which he is deprived according to today's viewpoint and particularly the view of science. Right in the experiences the human being has in these relationships, refer back to the ritual acts which of course for our confessions are actually only inherited traditions. [ 19 ] Yesterday I introduced you to how the Ritual Acts can be grasped out of human understanding. It can also be understood through insight into every interplay between possible experiences through the astral body and those through the etheric body; they go back to the sense which one can have when one follows the celestial vitality and weaving in the earthly etheric. What is revealed as a result is that man is placed in a cosmic process, in a cosmic movement which I can express in the following way. You see, when we turn to the tone which rings out of words, when we thus approach them, for example in the Greek Logos, what lies in the words of the Logos—this what I'm saying right now was certainly still experienced in (ancient) Greece and certainly felt in the composing of the St John's Gospel—when one approaches what lives as tone, what rings out as tone and then turn it to the outside, then one is involved in processes which are about to happen, which are revealed in the air. When we hear a tone or the words and the process is created which I indicated yesterday as it entering into the human being, then we are considering the movement of air being breathed in, which then hits the spinal cord and the brain fluid and continues as a movement; we also have this continuation in the air penetrating into the human being here. When we do further research, we don't only have to deal with this, but, because words manifest an effect in the human being, it acts on the human being's state of warmth. The human being becomes inwardly imbued with warmth, he contains the element of warmth differentiated by the sound entering him, of the word entering inward. This means on the outside warmth or cold is at most a by-product of sound, when the tone is too high or too low; remaining with one tone has no meaning. In the human being actually every differentiation in the word and in the tone is differentiated within, through engendering warmth or cooling, so that we can now say: In our understanding of the Word, we find it manifests outwardly in air and we find it manifest inwardly in warmth. [ 20 ] If we now go from what we learnt yesterday, we now approach the Sacrificial Act. These things, like many others, we later will clarify more, but this will be able to give you an indication. In olden times the actual characteristic could be found in the Sacrificial Act, of people experiencing the Sacrificial Act as a total reality. Actually for the more ancient presentation, the Sacrificial Act obviously connected to the smoke-like, to the airy; it was because, while the Sacrificial Act flows from within the human beings people knew—as one can also today really experience this in a Sacrificial Act—that just in this way, how the word sounds inwardly and lives itself out in warmth, the Sacrificial Act realises itself in air. Inwardly it lives itself out in the air. Towards the outside the true Sacrificial Act can't manifest without it somehow or other appearing through light. However, we will speak about these things again later. [ 21 ] When we now go to what we called the Transformation yesterday, we find that with the Transformation we refer to something which already penetrates matter, which already strongly approaches substantiality, but which has not yet been configured, which has not yet taken in an outline; this is experienced in the transformation as characteristic and one refers, in the same sense, to how the Word refers to the warmth, the Offering to the air, the Transformation, the transubstantiation to the water. [ 22 ] What is experienced as living in Communion, in the union, is felt now as through the connection with the etheric and its connection with the earth; one experiences oneself as an earthling, as a true earthling only because one feels so connected to the earthly, that one feels this union as related to the earth. [ 23 ] In the Old Mysteries this was the result: they had seen how the Word outwardly manifested in the air, and inwardly as warmth. (This was written on the blackboard.) 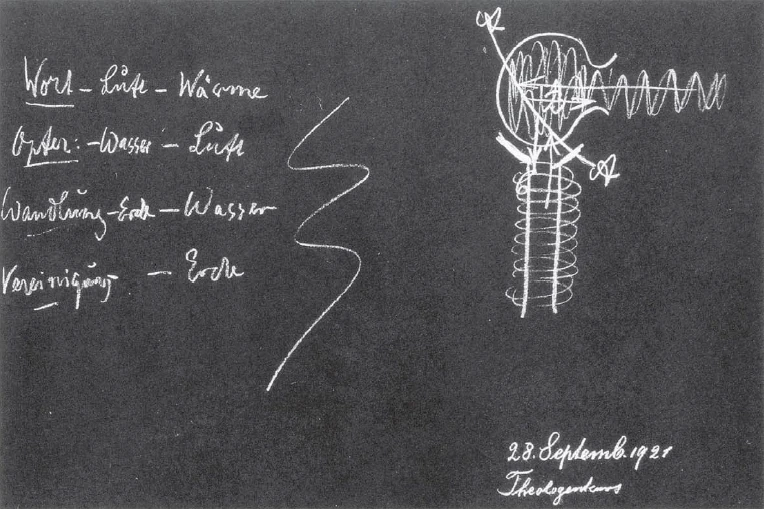
[ 24 ] The Offering manifests itself inwardly, as we've seen, as air. When you come to examine the following things, you could later say: I'm taking notice of these things so that I can say that what referred to water in the Sacrificial Mass of the old Mysteries, has now been retained as a residue in the Baptism. How the spoken word referred outwardly to the air and inwardly to warmth, so the Transformation could accordingly refer to the earth, to what is firm, and only inwardly to water; and what had corresponded to unification, one had nothing. In the human being, one could say to oneself, the connection with the elements shifts. However, already in the Transformation to the extra-terrestrial, the earth is available, which man experiences by turning to be united with it. How can he then experience being united with the earthly?—This was the great question of the Old Mysteries. How can one somehow feel anything at all about the truly earthly? [ 25 ] I've even spoke about it from another point of view. One looks around and it becomes obvious that people take their inner processes for granted, but they don't find anything which they want to take up into their consciousness. Symbolic action took on unification, but on the outside the place remained empty, something was necessary, so people said to themselves, for this place to be filled, if one wanted to turn to something within the earthly element itself it could correspond to the uniting taking place in communion. People felt they could look down on the earth. What presented itself within the earth, this could be fulfilled in the communion, but something outwardly was not possible. This is how people basically felt in the Old Mysteries, when they spoke of communion. They spoke about it this way, but they felt it could not be a concluded event. We basically feel this way when are instructed according to the outer statements of the Old Mysteries, how in images the event of Golgotha was foreseen, how it was symbolically carried out, which current research always refer to when they want to show that the Mystery of Golgotha was only something which can be compared to later developments when various sacrificial acts took place in temples, by presenting a sensory image of the representative of man having died, buried and resurrected three days later. [ 26 ] You know how the real crux of the Christ conception resulted from people noticing some similarities between the symbolic religious practices and the event of Golgotha, that they believed, even theologians believed they must speak about Christ as a myth or as something which had developed and reached fulfillment in the temples. The whole thing has now reached a point where this same way of thinking is appearing in other areas: the Our Father prayer has been examined in the same way and now nearly every sentence can be shown to have existed in pre-Christian times. This is regarded as a special catch for religious research. For someone who admits, truly admits to this way of closed thinking, it would be the same as to draw conclusions about people from their clothes. When a father allows his child to inherit his clothes, one can't say the son has become the father, because the son is someone quite different from the father even when he wears the same clothing. Just so the wording of the Our Father has passed over on to Christianity, but the content has essentially become something new. In order to examine these things, one must first look even deeper into all the connections: one needs to know the foundations from which the Old Mystery priests retained something like an expectation, which resembled something which could not yet have been accomplished on earth. [ 27 ] So there we will, I'd like to say, be led, in the first element, even through quite careful considerations, to a mood of expectation in the Old Mysteries, certainly out of an instinctive science which was completely permeated by religion, how in all Old Mysteries a Christ-expectation mood was there, and then it was fulfilled though the Mystery of Golgotha. [ 28 ] Tomorrow we will look at the entire problem from another side, when we will enter into it more profoundly. However, you see how Anthroposophy approaches the Christ-problem in what could be called a certain scientific manner, by making a lively observation of the ether and astral bodes and also what results from their cooperation. You see, by discovering, so to speak the Christ-experience in the boundary between the astral and etheric bodies, you must arrive in a positive way to the Christ-experience. I must say to you, my dear friends, this is largely the biggest difficulty of Anthroposophy and its task in the present. You see, the somewhat washed out Theosophy which you find for instance in the Theosophical Society, finds this reference far easier. It doesn't enter into the Christ-experience but stops just before it. Therefore, it's easier. To some extent they laid down all religions as equally valid and seek within it the common human element which of course every science must be based on. [ 29 ] Anthroposophy is determined in its own evolution, through the nerve of its entire being, to approach the Mystery of Golgotha in a positive way, and because it wants to remain scientific, to make the task of the events of Golgotha clear to humanity, as clearly as mathematics states the theory of Pythagoras. All religious confessions are in line with this rejection of the event of Golgotha as such. As a result, the world task of Anthroposophy necessary for our time is not easy. How difficult it is, I ask you to read the in words of a poet from Prague, Max Brod, who writes—he has also written some other things—in "Paganism, Christianity, Judaism" about how these things need to be handled; how out of the re-enlivened Jewish consciousness everything that makes Jesus into Christ must be removed, and only to keep Jesus as what does not make him into Christ. What is at the foundation of this tendency? It is the tendency to make it possible for modern Jews to have a relationship with Jesus, in which Jesus can be admitted but in which it is not necessary to see Him as the bearer of the Christ. [ 30 ] Anthroposophy is compelled—and we will still talk about this a great deal—to recognise Jesus as Christ. For Jesus to be taken as valid is what the Jews also strive, as well as the Indians; the entire East is striving for this, but they only strive to accept Him as he is, and not for being Christ. [ 31 ] Now my dear friends, Harnack's book about the Essentials of Christianity and the Weinel's research about Jesus you can take all in a way in which they could be accepted by all non-Christians to a certain degree. I know there can be some objections, so for this reason I say you could take it in this way—of course they are not like this. However, what we have as a task is this: To fully understand Christianity—not to keep Jesus at the expense of the fact that He is the bearer of the Christ. [ 32 ] Here lies the complete other side of a basis for the true, earnest Christianity through Anthroposophy, because one has to admit, that a communal world task has to be dealt with which encounters the most frightening prejudices. This world task is connected to what we today experience as dissatisfactory in religious experiences. For this reason, this can't be understood in the narrowest sense, but one must allow oneself to enter into what penetrates our religious life as unsatisfactory and look at this from a higher perspective. We will speak further about this tomorrow. |
| 318. Pastoral Medicine: Lecture XI
18 Sep 1924, Dornach Translated by Gladys Hahn Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Ich werde gehen den Weg, Der die Elemente in Geschehen löst Und mich führt nach unten zum Vater Der die Krankheit schickt zum Ausgleich des Karma Und mich führt nach oben zum Geiste Der die Seele in Irrtum zum Erwerb der Freiheit leitet Christus führt nach unten und nach oben Harmonisch Geistesmensch in Erdenmenschen zeugend. When you have become completely permeated by the content of this brief meditation, you will have taken livingly into your spirit what I wanted to give in this Pastoral Medicine course. |
| 318. Pastoral Medicine: Lecture XI
18 Sep 1924, Dornach Translated by Gladys Hahn Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Dear friends, Pastoral medicine as we think of it here will only be recognized as something from spiritual research that has meaning when humankind once more possesses a common consciousness of a spiritual realm containing positive, active forces. For naturally in an age that has developed materialism, it is inconceivable to the ordinary human being that anyone could have seen something worthy of notice in the spiritual world. But this really happened in the old mysteries. Individuals saw into spiritual realms and found knowledge there that led to valuable cures. And what we still have to say today to round off our studies may perhaps provide a connection to that old mystery wisdom for the medical stream that should now emanate from the Goetheanum. Indeed this impulse is understood most correctly in its historical connection if what is intended here is thought of as having developed out of the research methods (although, of course, quite different in form) and the artistic healing practices of the old mysteries. Obviously you will have to regard what has been offered in this short course as just a stimulus, as in a certain sense just the first chapter, the beginning of a pastoral medicine that will develop further through the work that is still to be done here by Dr. Wegman and me. So first I would like to point out how the initiates in the old mysteries described their path of initiation, particularly that path that was pursued at the place where the mysteries were most involved in the secrets of healing. Actually all the mysteries were connected with secrets of healing, but some more than others. They were all connected with them because healing was regarded as related to the entire evolution of human civilization. There were deep reasons for this. People of those ancient times said: When the human being comes down out of spiritual worlds into the physical-earth world through conception and birth, the soul-spiritual entity undergoes a transformation by which it is able to form a physical human body. We have described how this achievement takes place for the first time through the activity of the individual during the first seven years of life. The first body had been given through heredity, the body that in the course of the first seven or eight years is entirely stripped off. Thus it was conceived very exactly in the ancient mysteries how one came out of spiritual worlds into the world of the physical senses. But there was a universal recognition that a person does not in the first place unite with the physical body in the way that was originally intended by the spiritual powers who direct humanity. It was always believed that through some anomaly of the general evolution the forces that a human being inherits overpower in a certain sense the forces that are brought through the individuality from former earth-lives. This seemed to show a lack of harmony. It was said: If there were complete harmony between soul-and-spirit and physical body in earthly humans, death would not have the form it now has; nor would illness come in the way it now comes. Illness and death were regarded as the symptoms that show that human beings indeed have more to do with the physical-earth world than they were originally meant to. Although today this can no longer be completely understood, still it is an extremely profound idea in which there is very much truth. For the moment one reaches a higher level of consciousness even to a slight degree, one sees at once that death is quite different in character. It appears as a metamorphosis rather than the end of a phase of life. Therefore for the entire ancient consciousness the education of the human being was related to healing. The entire educational process in very ancient times of human evolution was thought of primarily from a medical point of view. Connected with this was the recognition that the mysteries united the professions of physician and priest, both of whom should be concerned with the healing of human beings on earth. Usually in olden times physician and priest were united in one person. This could only happen out of the old instinctive consciousness; today it would not be possible, at least not as an accepted custom. This recognition of the importance of healing, which was strong even in normally healthy persons, was related for every human being to their knowledge that after the metamorphosis they would undergo through death, they would be guided through their life between death and rebirth on their path to the sun by souls who on earth had been physicians or priests. The first need of every human being after death was to find the sun path—because there they would work out part of what they had to experience between death and rebirth. And these first steps had to be shown to them by a physician or a priest. So it was thought in ancient times. This was included in the deepest mystery wisdom. For us today this wisdom must be regarded differently because the old methods are no longer suitable for us. However, at this present time they can be renewed. Indeed that renewal is to be attempted right here. When ancient initiates described their initiation they would say that after they had crossed the threshold they were first made acquainted with the activity of the elements. In olden times, “elements” was the name given to what today would be called physical conditions. That is, the solid, which was called “earth”; all fluids, which were called “water”; everything gaseous, which was called “air”; and everything to do with “warmth,” which was ascribed to the warmth ether and which was called an element. Modern physicists deny all this. For them these four elements do not exist. For them there are from sixty to eighty elements, which have qualities. Under certain conditions one is fluid, another solid or gaseous. The condition of warmth belongs to all. What was described as an element in olden times does not exist today. There are now only qualities of things; the qualities have no existence of their own. What today are called elements are actually only “real” in the coarse, tangible physical world. And what in olden times were called elements were understood not as reaching down into tangible matter itself, but only to the intangible, living activity of matter. It was of no particular importance to an ancient physician whether something was this or that substance with this or that name. Naturally this is important, but it only becomes so after one has first obtained full view of something else, of the living, weaving activity of the substance. Thus one can study a substance in a place where it is exposed to weather conditions. The ancient physicians laid great value on studying a substance while it was being exposed to the weather, to the whole earth process. Also they took care that they did not simply take some substance out of the mineral kingdom if it could be obtained from the plant kingdom. In other words, they looked at the position the substance had in the world process by virtue of its living activity. But to understand that, one needs to accept the concept of the four elements. For then it is of prime importance in what temperature a substance becomes earth, for instance; in what temperature it becomes solid, or fluid, or air. That was the important thing in olden times, to observe what world process must happen so that some substance or other would take on a particular form. That was the first requirement. After that, the substance was examined without restriction. Today one starts out from the substance; formerly one started out from the process. And in fact any substance is only a process suspended at a certain stage. Formerly people were above all concerned with the whole weaving life within the material substance. And so initiates described how they were led to a vision of the weaving life of matter and of how it appeared to them as a fabric woven of the four elements. That was the first experience. The second description everyone gave, which presented the second step for them, was this: they were led to a place where they could learn to know the “upper and lower gods.” What does that mean? We have already described that, but in a modern way. I told you that if the soul-spiritual entity enters too deeply into the physical and etheric bodies, these bodies overpower the soul-spiritual entity, creating a pathological condition—an aberration of the soul-spiritual entity in the physical-etheric organism. There is, then, this pathological situation, that such people have descended more deeply into the physical organism than they should in ordinary waking life, and down below encounter nonhuman, subnatural activity. For only when we have a normal relation between our soul and spirit and our physical-etheric organism do we live in the natural world. The moment we descend too deeply, too intensely into physical corporeality, we come into relation with the subnatural. We fall to a level at which elemental beings, beings of higher hierarchies at various stages of their development, are all active. We come into relation with those gods who are unfolding their activity below the level of nature. How would ancient initiates have spoken if they had wanted to use a more neutral expression, veiling the facts so that no one would understand them except other initiates? How could they have implied that they had been led to the lower gods? An ancient initiate would have said: I have learned to know the nature of human illnesses. For that leads to the lower gods. Now look in the other direction, at the life of the saint: this also, as I have shown you, can be at the borderline between normal and pathological. It can happen that the soul-spiritual entity goes out farther than it should, enhancing the sleep condition. The ancient initiates described their introduction to this state as meeting with the upper gods. Put schematically (see drawing), this corresponds to the facts: nature, subnature, supernature. Visionary life, through the clairvoyant faculty that leads an individual into the spiritual world: the initiate called this “meeting with the upper gods.”  Now when we speak of upper and lower gods someone can very easily entertain the false idea that it concerns rank. You must think of it in this way: if I simply say nature, subnature, supernature, illness, visionary life, then I am tempted to think of the lower gods as being of a lower order. But that is not true. In reality it is like the drawing below. Imagine we have nature; then above, it leads to a circle; below, it leads to a circle; and what is above joins what is below. If we draw the circle larger and larger, and continue to draw it larger, we finally get a straight line. A piece of circle that continues on, after it has gone into infinity, comes back from the other side. This shows that the terms “upper” and “lower” are not to be understood as signs of rank, but simply as different ways that the gods come to human beings. They have been thought of as working in equal rank with one another, of striving to unite at a point in infinity. Therefore everything in olden times that was either illness or clairvoyance was thought to show that those who gained an understanding of those two human conditions, would then see into the spiritual world. One way to know about the spiritual world was to become well acquainted with illness and with clairvoyance.  When we understand this, we are able to bring into our own modern age what was present in human consciousness in olden times. If we ask what can be identified in modern consciousness with the realm of the lower gods, the answer must be—the Being whom we call the Father when we think of the divine Trinity. The Father belongs in the most eminent sense to subnature. How are we to think about the Father God with truly spiritual comprehension? Let us consider human beings, first in day-waking consciousness, then in night-sleeping consciousness, and let us compare the two states. We know that in full waking consciousness individuals are living as they have been placed to live within the order of this physical world. Just as the earth has had earlier stages of evolution—Saturn, Sun, Moon—and will undergo further evolution, so must humans themselves be recognized as the result of those earlier evolutionary periods. In this sense they belong in their waking state to the earth; by their nature they stand within the sphere of the earth. In waking condition they stand on a level with nature. It is not the same when human beings sleep. When we are asleep our physical and etheric bodies lie on the bed, and our astral body and ego are outside them. Let us look at the physical and etheric bodies. Of what do we consist, lying there in our physical and etheric bodies? We have—of course, at a more advanced stage—what we received in the old Saturn evolution and the old Sun evolution. That is now further evolved; we have the further development of our Saturn and Sun existence now during sleep. We do not have our Moon existence in what lies there on the bed. Nature has progressed from Moon existence to Earth existence. And the fact that the sleep condition is essential to us means that nature preserves in the sleeping human being a nature that is now below, a nature that only existed during the Saturn and Sun periods. That is subnature. That lies at the foundation of all beings through the fact that there is a human race. Humans fall during sleep into subnature, and from this fall illnesses appear. That is the realm of the Father God. When we sleep we enter the realm of the Father God, we enter subnature, the realm of the Father. Human clairvoyance helps illuminate the members of the human being that during sleep are outside the physical and etheric bodies: that is, the ego and astral body. When we become conscious in them, we are in the opposite condition, the opposite pole to illness and have entered the realm of the Spirit with the astral body and ego. So we can see that the human being is organized on earth in such a way that one is able to go out from nature in two directions, in the direction of subnature to the Father, and in the direction of supernature to the Spirit. Since the Mystery of Golgotha, Christ has been the mediator for both worlds. He is the one who permeates the world of nature, the one who permeates normal human existence. He has always to create harmony between subnature and supernature. Subnature is always kept in balance by the normal course of sleeping and waking. Supernature is kept in balance by those seers who are able to return to their ordinary human life at will. If someone is unable upon waking from sleep to balance what is experienced in subnature, then there is illness in the physical and etheric bodies. If someone is unable to bring back into the full waking state, into the natural course of earth-life, what is experienced clairvoyantly in the realm of the spirit, then there are soul illnesses or spiritual illnesses. This is the other pole. Let us now consider physical illness. What happens when the healing process starts? The human being is led from the experience of subnature to the experience of nature, from the Father to Christ. For Christ is the spiritual life in nature. That is in reality what the physician does. It is the physician's task to know how a person fallen to subnature is brought back to Christ, after the Father has given the leadership over to Christ the Son. That puts into modern speech what mystery wisdom would express. After initiates have attained a Christ-consciousness here on earth, they are led on the one side to the Father, on the other side to the Spirit. If then they are aware how their path leads from the Father to Christ, they will find all the healing processes on this path. Here the modern mystery begins, the mystery that creates a great test for real medical science. It is this to which I must point at the conclusion of this pastoral medicine course, so that there shall flow from it what should first of all bestow healing upon physicians. We can assume that they will gradually learn the separate healing measures that we have shown in this course by learning which are the defective organs and then what in outer nature corresponds to them and will work with spiritual power. Thus we introduce spirit as the healing agent into the human body. The physicians will learn how it is done in a given case. This will all build up for them into a complete knowledge. This living knowledge that they attain will be different from the current conventional knowledge. If today you open your pathology text or a medical textbook and study it thoroughly, at the end you are no further along than you were at the beginning. Granted, you have digested the entire contents, but even while you worked at it chapter after chapter, still you were making no progress in your general human attitude. It is the nature of real knowledge that it impels one to grow in one's entire human attitude. If you take up medicine in this sense and as it was meant in this pastoral medicine course, you will advance step by step. And the result will be nothing less than that you can say to yourselves: Now that I have my medical training behind me, I understand all that transpired at the Mystery of Golgotha, up to the moment when Christ went through the gate of death. You will understand the passage of Christ from the Father to the death on Golgotha. That is the mystery. One may not believe at first that medicine is related to this mystery, but it is. It is so truly related that through your understanding of the processes of healing, you will grasp what happened in the cosmos when the Father sent the Son to undergo the death on Golgotha. You will see in the death on Golgotha not death but the working together of all that happened at the death. That was not a death but the overcoming of death and the healing of all mankind. That is the path of the physician, from Father to Son until the Son dies on Golgotha. All separate pieces of medical knowledge bring one a step further toward the final comprehension of this Mystery. Pastoral medicine is not only what the pastor and the physician are to practice together, it is what is to be brought together so that first through the physician one part of the Mystery of Golgotha can be really understood. That is the high point, the ultimate achievement of medicine: to comprehend all human illness in such a way that one sees the Mystery of Golgotha up to the death as a tremendous healing process. The pathology of evolving humanity and the therapy, the dying on the cross—these will be seen in their true connection when we have real medicine. The priest has to follow all that is experienced by human beings when they leave their body and enter the other world, the world of the spirit. Thereby priests become more and more aware of the relation of a human being to the Spirit, to the spiritus sanctus, the Holy Spirit. And their path is that of mediation between the Spirit and the Son, the Christ, of developing theology so it will find the way from Christ to the Spirit, from the Spirit to Christ. A great sum of knowledge and life experience can be acquired on this path along which one has to lead one's fellow humans from the Spirit to Christ, from Christ to the Spirit. Its highest service must be that the successive stages of theology are able to clarify the meaning of Christ's path after the death on Golgotha. For his going through the death on Golgotha was the great healing event. Then the question arises: what faculty does this healing event create in human beings that will help them to enter the spiritual world? Theology must have for its crowning endeavor the comprehension of what is happening to the Christ individuality since He went through the death on Golgotha. Christ's path to Golgotha: the peak of the physician's path. For many contemporary theologians, the two paths seem to have no connection whatever. There are theologians today who do not want to know anything about the risen Spirit and the further activity of the Christ. But if we speak in the sense of a renewal of the mysteries, then the event of Golgotha, the Mystery of Golgotha belongs to it. And then we can say that the path by which the ancient initiate came to initiation could be described in this way: I was led through the elements to the lower and higher gods. The modern initiate would describe it as follows: I have been led through what dissolves the elements into their active processes—the elements are now the chemical elements, eighty of them, that dissolve when they enter into any process—and I am led further, to the Father below and the Spirit above. I perceive the activity of Christ on both paths. If you would like to take a summary of this course with you for your esoteric study, then take these words:
 When you have become completely permeated by the content of this brief meditation, you will have taken livingly into your spirit what I wanted to give in this Pastoral Medicine course.  |
| Cosmic Memory: Introduction
Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Today the Goetheanum is the world headquarters of General Anthroposophical Society, which was founded at Dornach at Christmas, 1923, with Rudolf Steiner as President. Audiences of many thousands come there each year to attend performances of Steiner's dramas, of Goethe's Faust (Parts I and II in their entirety), and of plays by other authors, presented on the Goetheanum stage, one of the finest in Europe. |
| Cosmic Memory: Introduction
Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Rudolf Steiner: The Man and His WorkRudolf Steiner is one of those figures who appear at critical moments in human history, and whose contribution places them in the vanguard of the progress of mankind. Born in Austria in 1861, educated at the Technische Hochschule in Vienna, where he specialized in the study of mathematics and science, Steiner received recognition as a scholar when he was invited to edit the well-known Kurschner edition of the natural scientific writings of Goethe. Already in 1886 at the age of twenty-five, he had shown his comprehensive grasp of the deeper implications of Goethe's way of thinking by writing his Grundlinien einer Erkenntnistheorie der Goetheschen Weltanschauung (Theory of Knowledge Implicit in Goethe's Conception of the World). Four years later he was called to join the group of eminent scholars in residence at Weimar, where he worked with them at the Goethe-Schiller Archives for some years. A further result of these activities was the writing of his Goethes Weltanschauung (Goethe's Conception of the World) which, together with his introductions and commentary on Goethe's scientific writings, established Steiner as one of the outstanding exponents of Goethe's methodology. In these years Steiner came into the circle of those around the aged Nietzsche. Out of the profound impression which this experience made upon him, he wrote his Friedrich Nietzsche, Ein Kampfer gegen seine Zeit (Friedrich Nietzsche, a Fighter Against his Time), published in 1895. This work evaluates the achievements of the great philosopher against the background of his tragic life-experience on the one hand, and the spirit of the nineteenth century on the other. In 1891 Steiner received his Ph.D. at the University of Rostock. His thesis dealt with the scientific teaching of Fichte, and is further evidence of Steiner's ability to evaluate the work of men whose influence has gone far to shape the thinking of the modern world. In somewhat enlarged form, this thesis appeared under the title, Wahrheit und Wissenschaft (Truth and Science), as the preface to Steiner's chief philosophical work, Die Philosophie der Freiheit, 1894. Later he suggested The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity as the title of the English translation of this book. At about this time Steiner began his work as a lecturer. This activity was eventually to occupy the major portion of his time and was to take him on repeated lecture tours throughout Western Europe. These journeys extended from Norway, Sweden and Finland in the north to Italy and Sicily in the South, and included several visits to the British Isles. From about the turn of the century to his death in 1925, Steiner gave well over 6,000 lectures before audiences of most diverse backgrounds and from every walk of life. First in Vienna, later in Weimar and Berlin, Steiner wrote for various periodicals and for the daily press. For nearly twenty years, observations on current affairs, reviews of books and plays, along with comment on scientific and philosophical developments flowed from his pen. Finally, upon completion of his work at Weimar, Steiner moved to Berlin in 1897 to assume the editorship of Das Magazin fur Litteratur, a well-known literary periodical which had been founded by Joseph Lehmann in 1832, the year of Goethe's death. Steiner's written works, which eventually included over fifty titles, together with his extensive lecturing activity brought him into contact with increasing numbers of people in many countries. The sheer physical and mental vigor required to carry on a life of such broad, constant activity would alone be sufficient to mark him as one of the most creatively productive men of our time. The philosophical outlook of Rudolf Steiner embraces such fundamental questions as the being of man, the nature and purpose of freedom, the meaning of evolution, the relation of man to nature, the life after death and before birth. On these and similar subjects, Steiner had unexpectedly new, inspiring and thought-provoking things to say. Through a study of his writings one can come to a clear, reasonable, comprehensive understanding of the human being and his place in the universe. It is noteworthy that in all his years of work, Steiner made no appeal to emotionalism or sectarianism in his readers or hearers. His scrupulous regard and deep respect for the freedom of every man shines through everything he produced. The slightest compulsion or persuasion he considered an affront to the dignity and ability of the human being. Therefore, he confined himself to objective statements in his writing and speaking, leaving his readers and hearers entirely free to reject or accept his words. Rudolf Steiner repeatedly emphasized that it is not educational background alone, but the healthy, sound, judgment and good will of each individual that enables the latter to comprehend what he has to say. While men and women eminent in cultural, social, political and scientific life have been and are among those who have studied and have found value in Steiner's work, experience has shown repeatedly that his ideas can be grasped by the simplest people. His ability to reach, without exception, all who come to meet his ideas with the willingness to understand, is another example of the well-known hallmark of genius. The ideas of Rudolf Steiner address themselves to the humanity in men and women of every race and of every religious and philosophical point of view, and included them. However, it should be observed that for Steiner the decisive event in world development and the meaning of the historical process is centered in the life and activity of the Christ. Thus, his point of view is essentially Christian, but not in a limited or doctrinal sense. The ideas expressed in his Das Christentum als mystische Tatsache und die Mysterien des Altertums (Christianity as Mystical Fact and the Mysteries of Antiquity), 1902, and in other works, especially his cycles of lectures on the Gospels (1908-1912), have brought to many a totally new relationship to Christianity, sufficiently broad to include men of every religious background in full tolerance, yet more deeply grounded in basic reality than are many of the creeds current today. From his student days, Steiner had been occupied with the education of children. Through his own experience as tutor in Vienna and later as instructor in a school for working men and women in Berlin, he had ample opportunity to gain first-hand experience in dealing with the needs and interests of young people. In his Berlin teaching work he saw how closely related are the problems of education and of social life. Some of the fundamental starting-points for an educational praxis suited to the needs of children and young people today, Steiner set forth in a small work titled Die Erziehung des Kindes vom Gesichtspunkte der Geisteswssenshaft (The Education of the Child in the Light of the Science of the Spirit), published in 1907. Just forty years ago, in response to an invitation arising from the need of the time and from some of the ideas expressed in the essay mentioned above, Rudolf Steiner inaugurated a system of education of children and young people based upon factors inherent in the nature of the growing child, the learning process, and the requirements of modern life. He himself outlined the curriculum, selected the faculty, and, despite constant demands for his assistance in many other directions, he carefully supervised the initial years of activity of the first Rudolf Steiner Schools in Germany, Switzerland and England. The story of the successful development of the educational movement over the past forty years cannot be told here. However, from the opening of the first Rudolf Steiner School, the Waldorf School in Stuttgart, Germany, to the present time, the success of Rudolf Steiner Education sometimes referred to as Waldorf Education) has proven the correctness of Steiner's concept of the way in which to prepare the child for his eventual adult role in his contribution to modern society, existence in seventeen countries of the world, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, and South America. In 1913, at Dornach near Basel, Switzerland, Rudolf Steiner laid the foundation of the Goetheanum, a unique building erected in consonance with his design and under his personal supervision. Intended as the building in which Steiner's four dramas would be performed, the Goetheanum also became the center of the Anthroposophical Society which had been founded by students of Rudolf Steiner in 1912. The original building was destroyed by fire in 1922, and subsequently was replaced prepared by Rudolf Steiner. Today the Goetheanum is the world headquarters of General Anthroposophical Society, which was founded at Dornach at Christmas, 1923, with Rudolf Steiner as President. Audiences of many thousands come there each year to attend performances of Steiner's dramas, of Goethe's Faust (Parts I and II in their entirety), and of plays by other authors, presented on the Goetheanum stage, one of the finest in Europe. Eurythmy performances, musical events, conferences and lectures on many subjects, as well as courses of study in various fields attract people to the Goetheanum from many countries of the world, including the United States. Among activities springing from the work of Rudolf Steiner are Bio-Dynamic Farming and Gardening, which aims at improved nutrition resulting from methods of agriculture outlined by him; the art of Eurythmy, created and described by him as “visible speech and visible song”; the work of the Clinical and Therapeutical Institute at Arlesheim, Switzerland, with related institutions in other countries, where for the past thirty years the indications given by Rudolf Steiner in the fields of Medicine and Pharmacology have been applied; the Homes for Children in need of special care, which exist in many countries for the treatment of mentally retarded children along lines developed under Steiner's direction; the further development of Steiner's indications of new directions of work in such fields as Mathematics, Physics, Painting, Sculpture, Music Therapy, Drama, Speech Formation, Astronomy, Economics, Psychology, and so on. Indeed, one cannot but wonder at the breadth, the scope of the benefits which have resulted from the work of this one man! A full evaluation of what Rudolf Steiner accomplished for the good of mankind in so many directions can come about only when one comprehends the ideas which motivated him. He expressed these in his writings, of which the present volume is one. Taken together, these written works comprise the body of knowledge to which Steiner gave the name, the science of the spirit, or Anthroposophy. On page 249 of this book he writes of the benefits of this science of the spirit: “When correctly understood, the truths of the science of the spirit will give man a true foundation for his life, will let him recognize his value, his dignity, and his essence, and will give him the highest zest for living. For these truths enlighten him about his connection with the world around him; they show him his highest goals, his true destiny. And they do this in a way which corresponds to the demands of the present, so that he need not remain caught in the contradiction between belief and knowledge.” Many of the thoughts expressed in this book may at first appear startling, even fantastic in their implications. Yet when the prospect of space travel, as well as modern developments in technology, psychology, medicine and philosophy challenge our entire understanding of life and the nature of the living, strangeness as such should be no valid reason for the serious reader to turn away from a book of this kind. For example, while the word “occult” or “supersensible” may have undesirable connotations for many, current developments are fast bringing re-examination of knowledge previously shunned by conventional research. The challenge of the atomic age has made serious re-evaluation of all knowledge imperative, and it is recognized that no single area of that knowledge can be left out of consideration. Steiner himself anticipated the reader's initial difficulties with this book, as he indicates on page 112: “The reader is requested to bear with much that is dark and difficult to comprehend, and to struggle toward an understanding, just as the writer has struggled toward a generally understandable manner of presentation. Many a difficulty in reading will be rewarded when one looks upon the deep mysteries, the important human enigmas which are indicated.” On the other hand, a further problem arises as a result of Steiner's conviction regarding the purpose for which a book dealing with the science of the spirit is designed. This involves the form of the book as against its content. Steiner stressed repeatedly that a book on the science of the spirit does not exist only for the purpose of conveying information to the reader. With painstaking effort, he elaborated his books in such a manner that while the reader receives certain information from the pages, he also experiences a kind of awakening of spiritual life within himself. Steiner describes this awakening as “...an experiencing with inner shocks, tensions and resolutions.” In his autobiography he speaks of his striving to bring about such an awakening in the readers of his books: “I know that with every page my inner battle has been to reach the utmost possible in this direction. In the matter of style, I do not so describe that my subjective feelings can be detected in the sentences. In writing I subdue to a dry mathematical style what has come out of warm and profound feeling. But only such a style can be an awakener, for the reader must cause warmth and feeling to awaken in himself. He cannot simply allow these to flow into him from the one setting forth the truth, while he remains passively composed.” (The Course of My Life, p. 330) In the present translation, therefore, careful effort has been made to preserve as much as possible such external form details as sentence and paragraph arrangement, italics, and even some of the more characteristic punctuation of the original, regardless of currently accepted English usage. The essays contained in this book occupy a significant place in the life-work of Rudolf Steiner. They are his first written expression of a cosmology resulting from that spiritual perception which he described as “a fully conscious standing-within the spiritual world.” In his autobiography he refers to the early years of the present century as the time when, “Out of the experience of the spiritual world in general developed specific details of knowledge.” (Op. cit. pp. 326, 328.) Steiner has stated that from his early childhood he knew the reality of the spiritual world because he could experience this spiritual world directly. However, only after nearly forty years was it possible for him to transmit to others concrete, detailed information regarding this spiritual world. As they appear in the present essays, these “specific details” touch upon processes and events of extraordinary sweep and magnitude. They include essential elements of man's prehistory and early history, and shed light upon the evolutionary development of our earth. Published now for the first time in America, just a century after Darwin's Origin of the Species began its transformation of Man's view of himself and of his environment, these essays clarify and complement the pioneer work of the great English scientist. Rudolf Steiner shows that the insoluble link between man and cosmos is the fundamental basis of evolution. As man has participated in the development of the world we know today, so his achievements are directly connected with the ultimate destiny of the universe. In his hands rests the freedom to shape the future course of creation. Knowledge of his exalted origins and of the path he followed in forfeiting divine direction for the attainment of his present self-dependent freedom, are indispensable if man is to evolve a future worthy of a responsible human being. This book appears now because of its particular significance at a moment when imperative and grave decisions are being made in the interests of the future of mankind. Paul Marshall Allen |
| Curative Eurythmy: refer
Translated by Kristina Krohn, Anthony Degenaar |
|---|
| And what gave rise to it? The natural science course in Stuttgart at Christmas 1920/21. Frau Baumann and I went to this course—more as visitors really—since we could not understand a lot of what Dr. |
| Curative Eurythmy: refer
Translated by Kristina Krohn, Anthony Degenaar |
|---|
The basis for the text: The course was taken down in short-hand by the professional shorthand writer Helene Finckh (1883–1963) and then written out in longhand. The Stuttgart lecture of October 28, 1922, which is included as the eighth lecture, was probably taken down by participants. There is no shorthand report. For the first edition (manuscript of lectures 1–6) the material was arranged by the curative eurythmist Elisabeth Baumann-Dollfus. For the second edition (manuscript of lectures 1–6, with the addition of lecture 7) the first publication was revised by Isabella de Jaager. For the third edition (first edition in the complete works) the publisher, Dr. Hans W. Zbinden, used Helene Finckh's original shorthand notes as a reference. The present (fourth) edition is an unaltered impression of the third edition, the only additions being the summary of the contents and the subject index. Concerning lectures 7 and 8: The lecture of April 18, 1921, which was included as the seventh lecture of this course, was given in connection with the so-called second doctors' course and is contained in the volume “The Spiritual Scientific Aspect of Therapy”. In that context Rudolf Steiner refers to this lecture by saying “After a short pause we shall continue by going more in the direction of eurythmy.” The lecture given in Stuttgart on October 28, 1922, and which has been included in this course as the eighth lecture, was given in connection with the “Medical Week” held in Stuttgart from October 26–28, 1922, (see “Anthroposophical Approach to Medicine”). The lecture has been published in the present volume only, however. How the course came about and the ladies to whom the abbreviations “Frau B. and Frl. W.” refer: Frau B. is Elisabeth Baumann-Dollfus (1895–1947) who actively participated in the development of eurythmy as from the summer of 1913. Later on she was the first eurythmy teacher at the Independent Waldorf School in Stuttgart, and she was an active member of the curative eurythmy course. Frl. W. is Erna van Deventer, née Wolfram (1894–1976), one of the first eurythmists, and, together with Elisabeth Baumann, an active member of the curative eurythmy course. In a memorial essay of the year 1961 in the periodical “Blätter für Anthroposophie” she makes the following reference to it: “I have two rather faded pieces of paper in front of me; one is a small drawing of the curve of Cassini and the other is a postcard dated February 1921 from Dr. Roman Boos1 in Dornach. Two modest pieces of paper, and yet they are almost the only visible testimonies of the events that led up to the curative eurythmy course that Dr. Steiner gave in Dornach in the Spring of 1921 alongside the second doctors' course. If I want to go back in memory to the time when Dr. Steiner gave the first therapeutic eurythmy exercises I have to go much further back than 1921. As early as 1915 and even earlier Dr. Steiner gave me, and probably other eurythmy teachers too, in answer to our questions, various eurythmy exercises for speaking, and hints for using in special cases we had encountered in towns all over Germany. The expression curative eurythmy did not even exist then, and Dr. Steiner called these exercises “therapeutic” eurythmy and said that these arose out of the Greek Mysteries. This remark will perhaps show how earnest Dr. Steiner was even at that time about healing by means of eurythmy movements, and it will also show how deeply it was impressed upon the consciousness of us still very young teachers that “healing” is connected with “holy”, and that our movements in this therapeutic eurythmy would really have to be carried by “the will to heal” if we wanted to achieve any success with this therapy. (Dr. Steiner did not coin the expression “the will to heal” until later; it was actually on the occasion of our asking him for advice, in 1923–24, whereupon he entered into our problems and gave the course for young medical students.) Anyone who worked with Dr. Steiner in any way will remember that everything he gave was in answer to a question, a wish, or sometimes even a vague aspiration that came his way. It was the same with curative eurythmy. For instance two children with speech defects were brought to him, and he gave what we would later on have called “curative eurythmy exercises”. In 1919 I met a child with curvature of the spine. Dr. Steiner entered into my questions very thoroughly and gave me the help I warned. I could give lots more examples like this. Yet at the same time I myself was also learning, in the course of giving lessons, to observe people, and I learnt to unite the various phenomena I observed in a person, and to become aware of how many people actually in the numerous eurythmy courses round about were in need of help. ... During those years I often met Elisabeth Baumann-Dollfus, who was also one of the first eurythmists, and a deep love for the work we shared united us for many years. In 1919, after the end of the First World War, we encountered one another again when the Waldorf School was being founded. So we began to exchange our experiences, she being a teacher at the Waldorf School where she worked with Dr. Schubert's remedial class, and I being a eurythmist who in the course of the year gave eurythmy courses in almost all the big towns in Germany, and I had the privilege when I was in Stuttgart of standing in for Frau Baumann at the Waldorf School when she was ill. We each had much joy in the other, because we were aware of our common bond. We were both searching for the same thing, and what were we looking for? The healing element in or behind eurythmy! This was one of the threads of destiny that hound us together. The other one was my engagement and marriage to H.A.R. van Deventer, who was himself a doctor, and who approached eurythmy from a background of medicine with the same enthusiasm that we approached medicine from a background of eurythmy. And what gave rise to it? The natural science course in Stuttgart at Christmas 1920/21. Frau Baumann and I went to this course—more as visitors really—since we could not understand a lot of what Dr. Steiner was saying, and as eurythmists we hardly even belonged to that enlightened gathering of students and scholars! But—even if we did not understand it all with our intellect—our enthusiasm for the astronomical drawings made up for it. And one day Dr. Steiner drew something on the blackboard that made us fall on top of one another and nearly jump into the air, and that was the curve of Cassini. This was the external occurrence that we needed to make us aware that the paths of the stars and the flow of forces within us, both sprang from the same source! For this curve of Cassini that Dr. Steiner was now describing in connection with natural science and astronomy, why, we eurythmists knew it too! As early as 1915, in the White Room of the old Goetheanum, Dr. Steiner had given four to six eurythmy teachers a series of lessons, and on this occasion he taught us “children's forms, good for children and young people from the age of three to eighty, to stop their thoughts scattering”. Those were his words, and one of these forms was the curve of Cassini, to the words “We will seek one another, we feel near one another, we know one another well”. In 1915 we young people did not have the least idea why he gave this form as a pedagogical exercise, in fact we hardly knew the “Why” of any of the eurythmy teaching material—and to be honest do we know it that much better today? And yet it should be our task to pass not only the exercises but also the “Why” on to our successors. The only way to do this seems to be that in the eurythmy of the future we must separate truth from error, and the source of eurythmy from a watering down of it. This experience of “recognizing” such an apparently insignificant form was what drew me to Elisabeth Baumann and what caused her and my husband to sit together for hours discussing the problem “If this form which Dr. Steiner was illustrating in the natural science course is so important for both macrocosmic man and microcosmic man, then does not everything given us in eurythmy come from the same source, and should it not be applicable for healing?” For just as with the curve of Cassini, we had also over the years learnt about the cosmic and the human healing effect of vowels, for instance AUM. Our experience of the curve of Cassini was really only the corner-stone of the building of our surmises and experiences in the realm of eurythmy! But how was it to be done? How were we to acquire a knowledge of “therapeutic eurythmy”? What we knew up till then—Elisabeth Baumann and I—were only small building stones that Dr. Steiner had given us on occasion. Through the fact that my husband supported us in our ideas, as a doctor—he had done quite a lot of eurythmy himself and could understand and support our endeavours from both the medical and the eurythmic side—this gave us courage to ask Dr. Steiner whilst he was still in Stuttgart whether he would like to teach us a kind of therapeutic eurythmy in a systematic way just like he had taught us ordinary eurythmy. Dr. Steiner was very kind, looked at us somewhat astonished at our bold plans, and said he would discuss the matter further with my husband in Holland, and then we would hear. And thus it happened. Dr. Steiner was in Holland at the beginning of 1921, and as my husband had a strong connection with our work through his medical studies, he had a good deal of opportunity to talk with Dr. Steiner. Frau Baumann was in Stuttgart at the time and I was in Breslau, but we had both set down our wishes very clearly in writing and sent them to my husband (He was still my fiance then). At any rate I)r. Steiner asked him one day in Holland “Do you actually have some eurythmists who would really put their backs into therapeutic eurythmy?”—to which my husband replied “Yes indeed, two at present, Frau Baumann and my future wife”. “Then we can start with it” said Dr. Steiner, and instructed my husband to do the necessary organizing. This brings me back to the beginning, for the little drawing was the “curve of Cassini” which came from an evening's discussion with Dr. Steiner, and the faded postcard from Roman Boos was his announcement from Domach to say that the “Curative Eurythmy Course” (Dr. Steiner had now coined the name) was due to take place in Dornach at the beginning of April, along with the second doctor's course, that was also due to be given then. In an article for the periodical “Beiträge zu einer Erweiterung der lleilkunst nach Geisteswissenschaftlichen Erkenntnissen” (1971, volume 4) headed “Curative Eurythmy: 1921–71. Its Origins, Development and Task” she describes the following: During the second doctors' course, from April 12 to 17, 1921, Dr. Steiner gave the curative eurythmy course in six lectures, for doctors, and also for eurythmists who had been training for more than two years. Not one of us could imagine what the course would be like! Dr. Steiner stood on the platform, and Frau Baumann and 1, sitting on two chairs in front of it, felt very uncomfortable, for we had instigated the situation, and in the meantime, from February till April, we had heard no word from Dr. Steiner as to how he would establish this new branch of medical science with the likes of us, who had not the slightest preparatory training in the realm of medicine! We certainly did not have the necessary knowledge for curative eurythmy work—would it not have been much more practical and sensible for Dr. Steiner to have chosen a small group of doctors for this work? Or did Frau Baumann and I, being eurythmists, really bring something with us out of our past that seemed important to him? In the instructions he gave me shortly after the course, about the training necessary for curative eurythmy, I had my answer. He answered our question by saying “The prerequisite for the curative eurythmy profession is that you first of all know the whole foundation of artistic eurythmy, in theory and practice. You must he capable of performing a dramatic poem on the stage, for example “der Zauberlehrling” (sorcerer's apprentice) by Goethe, and carry out all the eurythmic indications for word meaning and sentence construction, with all the forms and postures you have learnt. Not until you have mastered all the aspects of artistic eurythmy are you ready to change over to curative eurythmy. He made it clear to us that we would first of all have to master all the possibilities of artistic eurythmy, be able to find them in the cosmos as the forces of the planets and the fixed stars, then in their reflection in human speech and music, then through movements of the human body itself, and in this way we would get to know the human being, that is, ourselves, as beings who reflect macrocosm and microcosm in our own body. Not until we had grasped our situation and task would we be able to advance from the periphery of eurythmy to the centre of the healing aspect of eurythmy. Yet “first of all you must know the periphery, and then you can move on to the centre of man!” What a perspective for us, who had already been actively engaged in artistic and pedagogical eurythmy for eight years, though more in a practical way, and by learning from doing it rather than filling it with our consciousness. The vowels, consonants, parts of speech, rhymes—how much more significant they now appeared to be! ...What a eurythmist should know was also clearly defined by Dr. Steiner telling me what and how I would have to learn from my husband's textbooks, the “Spalteholz”2 and the textbook by Professor Broesicke3 of Breslau. Dr. Steiner told us this shortly after the curative eurythmy course, so that it was with a deep feeling of responsibility that we took our departure from Dornach.
|
| 300a. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner I: Sixteenth Meeting
30 Jul 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Steiner: I already noticed it some time ago, and mentioned it at Christmas and in February. I didn’t go into it then because it is so difficult for me, but it comes up so often, namely, that we shut people out. |
| 300a. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner I: Sixteenth Meeting
30 Jul 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A teacher: We need to discuss hiring new teachers. Dr. Steiner: Yes, we have the personnel problem. The problem is that our present shop teacher has not done what we expected, so we need to think of a replacement. We probably do not need to go into the details. I am not certain to what extent you are familiar with the problem that he could not handle the large classes. He has said that the children in the upper grades did not do the work. You can see that, since the children in the upper grades did not finish what they should. He found it difficult to work in that area. What I have seen indicated that he does not have sufficient practical talent so that the children could not do their work well because he himself did not have an eye for what the craft demanded. Many of the projects remained at the level of tinkering and were not what they should have been. The children did not learn how to work precisely with him. In the gardening class, the work remained with each child having a small garden where each did what he or she wanted, with the result that it was more like a number of small children’s gardens than a school garden. The worst thing was that he simply had no heart for his work. His main interest is in studying, but what we actually needed, namely, someone who could teach gardening thoroughly, did not occur. From my perspective, there is nothing else to do other than look for a better teacher. I don’t believe he is able to really bring the artistic into the shop instruction. As things have developed, it is impossible to keep him on the faculty. He doesn’t seem able to find his way into the spirit of the school. A teacher: Since we brought him here, we should, of course, find a way to take care of him so that he does not become an enemy of the school when we remove him from the faculty. Emil Molt: I will see that he is taken care of in some way. A teacher: I need to say that I don’t quite understand all this. He certainly gave considerable effort to finding his way into the spirit of the school. He definitely handled my children well and in the gardening class, my class also did well. He will find his way into the artistic aspect. Dr. Steiner: That will be difficult. What I said about the artistic was in connection with the shop instruction. He will hardly find his way into that. A teacher: He has the best will, and it will be difficult for him to understand. During the holidays he wants to learn cabinetmaking better and also shoemaking. Marie Steiner: There is something trusting about him. Dr. Steiner: There is no doubt that he likes to work with children, and that he is serious about it, but there are some things lacking. When I saw certain things that occurred, I had to conclude that it was impossible to leave this work to him. A teacher: Is there a reason we would need to get rid of him or could we employ him somewhere else, for example in the library? Dr. Steiner: It is certainly difficult to make a clear decision. I think it will be difficult for him to find his way into the real spirit of the school because he hasn’t the spirit in him. It is certainly possible to carry someone along, but do you really believe that he could do the shop class alone permanently? He could never teach all of the shop classes. Possibly he could teach the four lower classes if we had a teacher for the upper grades. I have my doubts whether he has the spiritual capacity to handle the upper grades in shop. I have watched how he works, and it is really quite nice for the younger children if they put themselves to it. However, for later, when a certain feeling for the craft is necessary, it is a question whether he can gain that feeling. This is very difficult, and we would need to change our thinking if he were to remain. My impression is that this is the general opinion of the faculty. He has poetic ambitions, but he imagines himself to be much better than he is. He has a wonderful amount of goodwill. I feel sorry for him because I think he will probably develop a lot of resentment. It is always difficult when someone brings a certain personal quality to things when they work at the school. He injects a personal note into everything and is not as objective as he should be. He wants to be someone who becomes a Waldorf teacher, he wants to be a poet. He wants the children to trust him. All of the characteristics he has certainly bring out sympathy for him. We will need to find another position for him. Nevertheless, it would remain difficult since he does not understand certain things about the spirit of the Waldorf School, particularly the shop class. In an area where objectivity is necessary, it is very difficult when sympathy plays a role. All that leads off the path. Is there some possibility that we could resolve the situation by having him in the lower four grades? That would be desirable, but we would end up with a huge budget. The school is getting bigger. Emil Molt: We don’t have the money to give him a soft job. As we saw recently, we must count every penny. What we need to do is to take care of him somewhere in the company so that he is not harmed, and we don’t hurt him. Dr. Steiner: We certainly must take care of him, but we will need to see how to do that. A difficult situation. We can objectively say that he was not fit for the task. He does not have an artistic feel. I don’t think he would find his way into the subject. As I said, it would hurt nothing if he took the lower grades and someone else, the upper classes. Often, that is the best way and the children will simply work. Later, when they need to show what they can do, things will be better. There is certainly nothing to object to for the lower grades, but for the upper classes, he simply will not do. A teacher: Do you intend to have one person do it all? Dr. Steiner: That is a budget question. In the shop class, we must stretch to the limit. It would be best if we strongly developed shop. If we had a good shop teacher, we could start in the sixth grade, but it is a different situation in the gardening class. That needs someone who really understands the subject. If we had two teachers, I would prefer that each would give shop in one year and gardening in the other. We must realize that if we retain him, other difficulties will arise in the school. I had the impression that was the opinion of the whole faculty. At the beginning, I thought this was already decided, but now I see that is not so. It is good we have discussed the matter so that we all understand it. A teacher: Isn’t it possible to see that someone is inadequate for a position earlier? Dr. Steiner: I already noticed it some time ago, and mentioned it at Christmas and in February. I didn’t go into it then because it is so difficult for me, but it comes up so often, namely, that we shut people out. Recently, there have been many times when the situation seemed to have improved. Well, there is nothing left to do other than look for another solution. We will need to find another solution. A teacher: In any event, we will need to find a first-rate shop teacher. It would be possible to have him as an assistant to the main teacher. Some time ago, Mr. X. wanted to take over the shop class. Dr. Steiner: I already said that it would be best if someone who is one the faculty would learn how to make shoes. I didn’t think we should employ a shoemaker. The instruction in shop must come from the faculty, but suddenly Y. was there. It was only fleetingly mentioned to me, and it was certainly not intended that he completely take over the teaching of shop. A teacher: He sort of grew into the faculty without a decision that he should become a part. Dr. Steiner: Now we’re rather caught in the situation. We shouldn’t allow such things to happen. Recently when we were talking, I was quite surprised that someone who was not at all under consideration for the faculty was at the meeting. Those who are not on the faculty should not be at the meetings. A teacher: I certainly think we can take him on as an assistant. Dr. Steiner: It would be too much for one teacher to do the gardening and the shoemaking, but then we would have to be able to pay him. Emil Molt: I would say that budget considerations should be subordinate to the major considerations. Dr. Steiner: It was certainly not harmful that he was there, but the harm may first arise when he is left out. He has become a teacher in a way I have often encountered in Stuttgart. If you ask how they reach their position, you find out that people have simply pushed their way in. They suddenly appear. I don’t understand how people move up. It is certainly true that we cannot continue in that way. You need to realize, Mr. X., that one thing builds upon the other. As we decided, you were to create the shop instruction. Mr. Molt asked if we could consider Y. as an assistant for you, then, suddenly, he was sitting here in the faculty. He was never under consideration as a teacher for the Waldorf School. We can see that clearly because he is an employee of the Waldorf-Astoria Company that they sent over. Thus, there was not the least justification for him to be on the faculty. A teacher: I don’t think we can work intimately if someone is here who does not belong. Dr. Steiner: If he is already here, we can’t do that. If he has been teaching the subject and if other difficulties did not arise, we could not say that Y. is no longer on the faculty. A teacher: It was a mistake to let him in. A teacher: Yes, but we were the ones who made the mistake. Dr. Steiner: The Waldorf School will pay for it. Just as people have made mistakes in the Anthroposophical Society, and in spite of the fact that people make these same mistakes time and again, I was the one who had to suffer. I had to suffer for each person we threw out. It is clear that in this case, the Waldorf School will have to suffer, but I think it is better that it suffer outwardly rather than within. Following further discussion: Dr. Steiner: Well, we will just have to try to keep him if there is no other way. [After further discussion on the next day, of which there are no notes, Y. was told that he would no longer work in the Waldorf School.] Dr. Steiner: It is certainly not so that we will include every specialty teacher in the faculty. The intent is that the inner faculty includes the class teachers and the older specialty teachers, and that we also have an extended faculty. A teacher: My perspective is that we should include only those whom Dr. Steiner called to the faculty, and thus that someone’s mere presence in some position does not mean that he or she will automatically be part of the faculty. A teacher: Who should be on the faculty? Dr. Steiner: Only the main teachers, those who are practicing, not on leave, should be on the faculty. In principle, the faculty should consist of those who originally were part of the school and those who came later but whom we wish had participated in the course last year. We have always discussed who is to be here as a real teacher. If someone is to sit with us, he or she must be practicing and must be a true teacher. Berta Molt: Well, then, I don’t belong here, either. Dr. Steiner: You are the school mother. That was always the intent. Mrs. Steiner is here as the head of the eurythmy department and Mr. Molt as the patron of the school, that was always the intent from the very beginning. If we have discussed it, then there is not much to say. That was the case with Baravalle. He was here as a substitute, but we discussed that. It was also clear that he would eventually come into a relationship to the school, because he would eventually be a primary teacher. We still have the question of whom to consider as a teacher. A teacher: Must the new teacher be an anthroposophist, or can it be someone outside? Dr. Steiner: That is something I do not absolutely demand, we have already discussed it. I propose that we talk with Wolffhügel regarding the shop class and see if he wants to take it. I think that Wolffhügel would be quite appropriate. That would be really good. He is a painter and works as a furniture maker. That would be excellent. Now we need know only which of the new teachers should attend our meetings. Of course, Wolffhügel should. I was only in the handwork class a few times, but once I had to ask myself why a child did not have a thimble on. I have always said that we must get the children accustomed to sewing with a thimble. They should not do it without a thimble. We cannot allow that. We cannot know ahead of time whether a teacher can keep the children quiet. Often we can know that, I think, but we can also experience some surprises. You just don’t always know. We need two teachers for the first grade. For the 1B class, I would propose Miss Maria Uhland and for the 1A class, Killian. I think we should hire them provisionally and not bring them into the faculty meetings. We then have Miss von Mirbach for the second grade, for the third grade, Pastor Geyer, for the fourth grade, Miss Lang, for the fifth grade, Mrs. Koegel. Dr. Schubert will have the weaker children, the remedial class, and Dr. von Heydebrand, the sixth grade. We still need someone. Baravalle would be good for the second sixth-grade class. I think we should take him. He can also do his doctoral work here. Dr. Kolisko will take over the whole seventh grade. I also think we should do the eighth and ninth grades as we did the seventh and eighth. How did that work? A teacher: We took the classes in alternating weeks. Our impression is that if we alternate it daily, we would not know the class well enough. Dr. Steiner: Then your perspective is that it is better to teach for a week, better than alternating daily? A teacher: The reason why we two did not know our classes very well is unclear to me. The fact is that I knew the children the least of all our colleagues. Could you perhaps say what the problem was? Dr. Steiner: That will not be better until you are more efficient in regard to the subject matter and how you treat it. You felt under pressure. You had, in general, too little contact with the children and lectured too much. |
| 300b. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner I: Twenth-Seventh Meeting
11 Sep 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Those who are less advanced will not be able to read A Christmas Carol. A new teacher: I think Dickens is much too difficult for this grade. Could we obtain a textbook for teaching language? |
| 300b. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner I: Twenth-Seventh Meeting
11 Sep 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Dr. Steiner: School begins on the thirteenth. Now that we have more teachers, we need to discuss the classes again. Do you have a plan here? We could go according to that. A final decision is made about who will be the main teacher for each class. Dr. Steiner: The first thing we need to talk about is the remedial class. We definitely need it, but the question is, who can do it? I would be happy if Dr. Schubert could take over the remedial class. Don’t you think you would just die if you could no longer have your old class? Dr. Schubert: Did I do poorly? Dr. Steiner: No, the children are quite lively. I think that Dr. Kolisko should step in for Dr. Schubert in history for the upper three grades. I would also like to see if Dr. Schwebsch could give a kind of aesthetics class, a class in art for the upper three grades, eighth, ninth, and tenth. Thus, we would add Dr. Schwebsch to the three main lesson teachers for the upper classes, and he would teach aesthetics. We already spoke of that to an extent. That would not continue indefinitely, but would merge into other teaching in a few weeks. The four of you would then rotate. A teacher: That would mean that one of us would be free for a period of time. Dr. Steiner: That does not matter since the upper grades need that. We need to speak about the foreign languages. They discuss how to divide the modern languages. Dr. Steiner: Dr. Schubert should take over the younger children for Latin and Greek, and I would ask Dr. Röschl to take over the remaining Latin and Greek classes. I will say something more about that later. A teacher: Isn’t it better to place the students in Latin and Greek by class? Dr. Steiner: With the confusion we now have, we can do that only slowly. Our goal could be to achieve some balance by the age of sixteen or seventeen. I would like to talk about that tomorrow at 2 o’clock. The teachers who are no longer responsible for Latin could help in the teachers’ library. Today there was some talk about hiring a librarian, something I consider pure nonsense. If you work at it, you could finish the entire library. I think it would be silly. I could keep the whole thing in order with three hours a week. We need to consider how we can save some time. I think it would be a good idea if the faculty took that up. We can’t create a library and then hire a librarian who will need at least a palace. That talk is pure fantasy. Someone like Dr. R. would cost 30,000 Marks, money we could save if you would spend some of your free time in the library. I think that would be best and most efficient. The theology course will take place in Dornach from September 26 until October 10. Hahn, Uehli, Ruhtenberg, and Mirbach will attend, and thus the independent religious instruction will not take place. We will have to teach something else in their place. It would be interesting if, for example, Dr. Schwebsch is free during that period, and if he could do something appropriate for the children concerning history or art history. It could also be something else. I would now like to hear what else has been happening. A teacher: What should we read in the seventh grade? Dr. Steiner: We cannot hold the whole class back simply because there are a few new children. Those who are less advanced will not be able to read A Christmas Carol. A new teacher: I think Dickens is much too difficult for this grade. Could we obtain a textbook for teaching language? Dr. Steiner: I have nothing against using a textbook, but all of them are bad. The class does not have one book that unites them. Look for a textbook, and show it to me when I come back. With regard to Dickens, I do not agree. The seventh grade can certainly read him. You could also choose some other prose, that was only given as an example. There are a number of good students’ editions. Of course, you’ll have to use something appropriate to the students’ age. A teacher: In other schools, we began Dickens in the tenth grade. Dr. Steiner: Find some texts you feel you can work with. A teacher: I would be grateful if you would say something about rhythm and verse. Dr. Steiner: It is difficult to hold a course about individual topics in teaching. Why can’t you find anything reasonable? A teacher: I cannot say precisely. Dr. Steiner: The children need to learn the poetic meter and rhyme that you know. They should understand the relationship of the individual meters to the pulse and breathing rhythms. That is the goal. I can hardly believe you cannot find anything. We cannot say that all books are bad. You can make them good by using them. A teacher: I would like to ask a question about algebra. I think it would be good if we gave the children homework. It is certainly clear in this case that the children should do some problems at home. Dr. Steiner: We need to emphasize what results from a good pedagogy. One basic principle is that we know the children do the homework, and that we never find that they do not do it. You should never give children homework unless you know they will bring the solved problems back, and that they have done them with zeal. A liveliness needs to come into the work, and we need to encourage the children so that their inner attitude is not paralyzed. For example, you should do it so that when you have covered some material, and you want to assign them some work in connection with it, you say, “Tomorrow I will do the following arithmetic operations.” Then wait and see if the children prepare the work at home. Some will be interested enough to do it and then others will become interested. You should bring it about that the children want to do what they need to do in school. What you need to do from day to day should come from what the children want to do. A teacher: Can we also give homework such as multiplication problems and so forth? Dr. Steiner: Only in that way. It’s the same story in the other subjects, and together we would then have a great deal of homework. We would then have pale children. Our goal must be to cover the material in such a way that we don’t need anything outside of school.A teacher: I also wanted to ask what we could do following mathematics. Dr. Steiner: Afterward, when the children are tired, you could go on to something simpler. You could do something like what you had originally thought of as homework. A teacher: I have not had the impression that even the most strenuous things in mathematics tire the children. Dr. Steiner: In spite of that, we should not keep the children under the same stress for two hours. You could help the children or give them a hint that they should do this or that at home. But do not demand it. A teacher: Could you give me some help in teaching aesthetics? Dr. Steiner: These are fourteen- to sixteen-year-old children. Through examples, I would try use art itself to give them the concept of beauty. Look at the metamorphosis of beauty through the various style periods: Greek beauty, Renaissance beauty, and so forth. It is particularly important for children at that age that you bring a certain concrete form to what is otherwise abstract. If you study the aesthetics of people like Vischer and Carrière, all that is simply chaff in regard to concepts. On the other hand, you ennoble the children regarding ideals if you can give them an understanding of what is beautiful or what is great. What is comedy and how does music or poetry achieve it? The child’s soul cannot take in generalized concepts in this period. For that reason, at that age you must include such things as what it means to declaim and recite. At the time when I was lecturing about declamation and recitation, I discovered that most people do not even know there is a difference. If you take the way you should speak Greek verses, then you have the archetype of reciting, because what is important is the meter, how things are extended or contracted. When the important point is the highs and lows, and that is what you need to emphasize, for instance, in The Song of the Niebelungs, then you have declamation. I showed that through an example, that there is a radical difference between the first form of Goethe’s Iphigenia, that he later reworked into a Roman form. The German Iphigenia should be declaimed and the Roman, recited. A teacher: If we are to integrate our work with that of Dr. Schwebsch, I would like to ask approximately how much time we should allow for teaching aesthetics? Dr. Steiner: It would be good to allow equal times. In that way, the German class would be less work. We need to have somewhat different concepts. Think about the Austrian college preparatory schools. They have eight periods of Latin in the fifth grade. That is the result of terribly inefficient teaching. We, of course, must limit that. The Austrian schools have only very few periods of mathematics. Three in the 4th, 5th, and sixth grades and two in the seventh and eighth. If you work in these periods so that you correctly distribute the material you have to cover during the time available, the children will get the most from your instruction. These are children of fifteen or sixteen years of age. Thus, in geometry, if you can see that the children have the basic concepts, including the law of duality and perspective geometry, so that the children are perplexed and amazed and have some interest in what you say about some of the figures, then you will have achieved everything that you can. Have you begun with descriptive geometry yet? A teacher: I have done the constructions with a point and a line, Cavalieri’s perspective and shadow construction, so that the children have an idea of them. Now we are only doing shadow construction. Then, we will do technical drawing. We have done relatively little of that. Dr. Steiner: Then, you should do mechanical drawing including trajectory, simple machines, and trigonometry. Trajectory is better if you treat it with equations. Do the children understand parabolic equations? If you develop concrete examples, then you do not need to go into detail there. From a pedagogical perspective, the whole treatment of a trajectory is only so that the children learn parabolic equations and understand parabolas. The coinciding of reality with mathematical equations is the goal you need to strive for. “Philosophy begins with awe,” is partially incorrect. In teaching, awe must come at the end of a block, whereas in philosophy, it is at the beginning. You need to direct the children toward having awe. They need something that will completely occupy them. They need to understand that it is something that, in the presence of its greatness, even Novalis would fall to his knees. I would particularly like to remind all of you who are involved with drawing to study Baravalle’s dissertation thoroughly. I have attempted to mention it several times. Copies were available at the conference. Baravalle’s dissertation is extremely important for aesthetics. You should all study it. Baravalle’s dissertation could have a very deep effect, particularly in the handwork class. There is certainly a great deal in it that would help in understanding how a collar or a belt should be shaped. Things like this from Baravalle—now don’t let this go to your head—things like this dissertation have a fundamental importance for Waldorf teachers, since they show how to pictorially present mathematical ideas and thus make them easier. That is something we could extend. What he has done for forms could be done in a similar way for colors or even tone. You could find a number of helpful ideas about Goethe’s thoughts about the world of tone in my last volume of the Kürschner edition. The table contained there is very informative. Certainly the theory of color could be treated in the same way. A teacher: It may be possible to create a parallel in the moral and perceptible side of tones. Color perception follows the order of the spectrum. Everything in the blue range corresponds to sharps, and the remainder, to flats. Dr. Steiner: That would be an interesting topic. A teacher: In looking at both spectra, there is a certain parallel between them. Dr. Steiner: The thought is nearly correct, but we must avoid simple analogies. I would like to say something more that will hopefully strike an anthroposophical chord with you. I said that it would be a good idea to study Baravalle’s dissertation. I would like to mention that there is an occult significance in enlivening instruction when a lively interest exists for the work done by members of the faculty. This is extremely important. The entire faculty is enlivened when you take an interest in some original work by a colleague. That is also a basic thought of many of the various school programs, but it has been corrupted. Each year discussion of the program should be published, but the whole faculty should be concerned with it. The fact is that the spiritual forces within the faculty carry the faculty through a communal inner experience. We should not try to do things individually, the whole should participate. Of course, here, through lively presentation, there is a significant general interest. However, there is an assumption that many others are also hiding their work. I would like to remind you to make that work fruitful for others as well. A teacher: Sometime ago we spoke about a gymnastics teacher. Dr. Steiner: Mr. Baumann told me we could no longer consider the business regarding a gymnastics teacher because we have no rooms. When we have room, then Englert will be here. A teacher: He wrote that he could not do that. He is now in Norway. Dr. Steiner: We haven’t the slightest need in the next half-year. He will need to wait until something else occurs. We will need to make an effort that the boys get better. We cannot say anything about gymnastics since Baumann is not here. They discuss the public conference in Stuttgart from August 29 until September 6, “Cultural Perspectives of the Anthroposophical Movement.”Dr. Steiner: The conference was such a success that it far exceeded our expectations. It was really quite a success. Only the members’ meeting on Sunday, September 4, was poor. It was the worst thing imaginable. The meeting of the local threefold groups was still worse. I had thought that just those people would bring new life into Anthroposophy. We should have been able to see that on Sunday. You can be certain that a great deal was wanted. People were sitting in all the corners having small meetings, but the whole was lost. It would have been better had it all been visible at the surface. Hopefully, further development will be better. |
| 295. Discussions with Teachers: Discussion Ten
01 Sep 1919, Stuttgart Translated by Helen Fox, Catherine E. Creeger Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| This was known to the people of ancient times, and that was why they placed Christmas—the time when we look for soul life—not in the summer, but during winter. “Just as a person’s soul life passes out of the body when falling asleep, and again turns inward when a person wakens, so it is also for the Earth. |
| 295. Discussions with Teachers: Discussion Ten
01 Sep 1919, Stuttgart Translated by Helen Fox, Catherine E. Creeger Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Speech Exercises:
RUDOLF STEINER: The “ch” should be sounded in a thoroughly active way, like a gymnastic exercise.1 The following is a piece in which you have to pay attention both to the form and the content. From “Galgenlieder” by Christian Morgenstern:
RUDOLF STEINER: Now we will continue our talk about the plant world. Various contributions were offered by those present. RUDOLF STEINER: Later there will be students in the school who will study the plant kingdom on a more scientific basis, in which case they would learn to distinguish mosses, lichens, algae, monocotyledons, dicotyledons, and so on. All children, who in their youth learn to know plants according to scientific principles, should first learn about them as we have described—that is, by comparing them with soul qualities. Later they can study the plant system more scientifically. It makes a difference whether we try first to describe the plants and then later study them scientifically, or vice versa. You can do much harm by teaching scientific botany first, instead of first presenting ideas that relate to the feeling life, as I have tried to show you. In the latter case the children can tackle the study of scientific botanical systems with a truly human understanding. The plant realm is the soul world of the Earth made visible. The carnation is a flirt. The sunflower an old peasant. The sunflower’s shining face is like a jolly old country rustic. Plants with very big leaves would express, in terms of soul life, lack of success in a job, taking a long time with everything, clumsiness, and especially an inability to finish anything; we think that someone has finished, but the person is still at it. Look for the soul element in the plant forms! When summer approaches, or even earlier, sleep spreads over the Earth; this sleep becomes heavier and heavier, but it only spreads out spatially, and in autumn passes away again. The plants are no longer there, and sleep no longer spreads over the Earth. The feelings, passions, and emotions of people pass with them into sleep, but once they are there, those feelings have the appearance of plants. What we have invisible within the soul, our hidden qualities—flirtatiousness, for example—become visible in plants. We don’t see this in a person who is awake, but it can be observed clairvoyantly in people who are sleeping. Flirtation, for example, looks like a carnation. A flirt continually produces carnations from the nose! A tedious, boring person produces gigantic leaves from the whole body, if you could see them. When we express the thought that the Earth sleeps, we must go further: the plant world grows in the summer. Earth sleeps in the summer and is awake during winter. The plant world is the Earth’s soul. Human soul life ceases during sleep, but when the Earth goes to sleep its soul life actually begins. But the human soul does not express itself in a sleeping person. How are we going to get over this difficulty with children? One of the teachers suggested that plants could be considered the Earth’s dreams. RUDOLF STEINER: But plants during high summer are not the Earth’s dreams, because the Earth is in a deep sleep in the summer. It is only how the plant world appears during spring and autumn that you can call dreams. Only when the flowers are first beginning to sprout—when the March violet, for example, is still green, before flowers appear, and again when leaves are falling—that the plant world can be compared to dreams. With this in mind, try to make the transition to a real understanding of the plant. For example, you can begin by saying, “Look at this buttercup,” or any plant we can dig out of the soil, showing the root below, the stalk, leaves, blossoms, and then the stamens and pistil, from which the fruit will develop. Let the child look at a plant like this. Then show a tree and say, “Imagine this tree next to the plant. What can you tell me about the tree? Yes, it also has roots below of course; but instead of a stalk, it has a trunk. Then it spreads its branches, and it’s as if the real plants grew on these branches, because many leaves and flowers can be found there; it’s as if little plants were growing on the branches above. So, we could actually look at a meadow this way: We see yellow buttercups growing all over the meadow; it is covered with individual plants with their roots in the Earth, and they cover the whole meadow. But when we look at the tree, it’s as if someone had taken the meadow, lifted it up, and rounded it into an arch; only then do we find many flowers growing very high all over it. The trunk is a bit of the Earth itself. So we may say that the tree is the same as the meadow where the flowers grow. “Now we go from the tree to the dandelion or daisy. Here there is a root-like form in the soil, and from it grows something like a stalk and leaves, but at the top there is a little basket of flowers, tiny little blossoms close together. It’s as though the dandelion made a little basket up there with nothing in it but little flowers, perfect flowers that can be found in the dandelion-head. So we have the tree, the little ‘basket-bloomers,’ and the ordinary plant, a plant with a stalk. In the tree it’s as though the plants were only high up on the branches; in the compound flowers the blossom is at the top of the plant, except that these are not petals, but countless fully-developed flowers. “Now imagine that the plant kept everything down in the Earth; suppose it wanted to develop roots, but that it was unsuccessful—or perhaps leaves, but could not do this either; imagine that the only thing to unfold above ground were what one usually finds in the blossom; you would then have a mushroom. At least, if the roots down below fail and only leaves come up, you would then have ferns. So you find all kinds of different forms, but they are all plants.” Show the children the buttercup, how it spreads its little roots, how it has its five yellow-fringed petals, then show them the tree, where the “plant” only grows on it, then the composite flowers, the mushroom, and the fern; do not do this in a very scientific way, but so that the children get to know the form in general. Then you can say, “Why do you think the mushroom remained a mushroom, and why did the tree become a tree? Let’s compare the mushroom with the tree. What is the difference between them? Take the tree. Isn’t it as though the Earth had pushed itself out with all its might—as though the inner being of the tree had forced its way up into the outside world in order to develop its blossoms and fruits away from the Earth? But in the mushroom the Earth has kept within itself what usually grows up out of it, and only the uppermost parts of the plant appear in the form of mushrooms. In the mushroom the ‘tree’ is below the soil and only exists as forces. In the mushroom itself we find something similar to the tree’s outermost part. When lots and lots of mushrooms are spread over the Earth, it is as though you had a tree growing down below them, inside the Earth. And when we look at a tree it is as though the Earth had forced itself up, turning itself inside out, as it were, bringing its inner self into the outer world.” Now you are coming nearer to the reality: “When you see mushrooms growing you know that the Earth is holding something within itself that, in the case of a growing tree, it pushes up outside itself. So in producing mushrooms the Earth keeps the force of the growing tree within itself. But when the Earth lets the trees grow it turns the growing-force of the tree outward.” Now here you have something not found within the Earth during summer, because it rises out of the Earth then and when winter comes it goes down into the Earth again. “During summer the Earth, through the force of the tree, sends its own force up into the blossoms, causing them to unfold, and in winter it draws this force back again into itself. Now let us think of this force, which during the summer circles up in the trees—a force so small and delicate in the violet but so powerful in the tree. Where can it be found in winter? It is under the surface of the Earth. What happens during the depth of winter to all these plants—the trees, the composite flowers, and all the others? They unfold right under the Earth’s surface; they are there within the Earth and develop the Earth’s soul life. This was known to the people of ancient times, and that was why they placed Christmas—the time when we look for soul life—not in the summer, but during winter. “Just as a person’s soul life passes out of the body when falling asleep, and again turns inward when a person wakens, so it is also for the Earth. During summer while asleep it sends its sap-bearing force out, and during winter takes it back again when it awakens—that is, it gathers all its various forces into itself. Just think, children, our Earth feels and experiences everything that happens within it; what you see all the summer long in flowers and leaves, the abundance of growth and blossom, in the daisies, the roses, or the carnations—this all dwells under the Earth during winter, and there it has feelings like you have, and can be angry or happy like you.” In this way you gradually form a view of life lived under the Earth during winter. That is the truth. And it is good to tell the children these things. This is something that even materialists could not argue with or consider an extravagant flight of fancy. But now you can continue from this and consider the whole plant. The children are led away from a subjective attitude toward plants, and they are shown what drives the sap over the Earth during summer heat and draws it back again into itself in winter; they come to see the ebb and flow in plant life. In this way you find the Earth’s real soul life mirrored in plants. Beneath the Earth ferns, mosses, and fungi unfold all that they fail to develop as growing plants, but this all remains etheric substance and does not become physical. When this etheric plant appears above the Earth’s surface, the external forces work on it and transform it into the rudiments of leaves we find in fungi, mosses, and ferns. But under a patch of moss or mushrooms there is something like a gigantic tree, and if the Earth cannot absorb it, cannot keep it within itself, then it pushes up into the outer world. The tree is a little piece of the Earth itself. But what remains underground in mushrooms and ferns is now raised out of the Earth, so that if the tree were slowly pushed down into the Earth everything would be different, and if it were to be thus submerged then ferns, mosses, and mushrooms would appear; for the tree it would be a kind of winter. But the tree withdraws from this experience of winter. It is the nature of a tree to avoid the experience of winter to some extent, but if I could take hold of a fern or a mushroom by the head and draw it further and further out of the Earth so that the etheric element in it reached the air, then I would draw out a whole tree, and what would otherwise become a mushroom would now turn into a tree. Annual plants are midway between these two. A composite flower is merely another form of what happens in a tree. If I could press a composite flower down into the Earth it would bear only single blossoms. A composite flower could almost be called a tree that has shot up too quickly. And so we can also find a wish, a desire, living in the Earth. The Earth feels compelled to let this wish sink into sleep. The Earth puts it to sleep in summer, and then the wish rises as a plant. It is not visible above the Earth until it appears as a water-lily. Down below it lives as a wish in the Earth, and then up above it becomes a plant. The plant world is the Earth’s soul world made visible, and this is why we can compare it with human beings. But you should not merely make comparisons; you must also teach the children about the actual forms of the plants. Starting with a general comparison you can then lead to the single plant species. Light sleep can be compared with ordinary plants, a kind of waking during sleep with mushrooms (where there are very many mushrooms, the Earth is awake during the summer), and you can compare really sound deep sleep with the trees. From this you see that the Earth does not sleep as people do, but in one part it is more asleep and in another more awake; here more asleep, there more awake. People, in their eyes and other sense organs, also have sleeping, waking, and, dreaming side by side, all at the same time. Now here is your task for tomorrow. Please make out a table; on the left place a list of the human soul characteristics, from thoughts down through all the emotions of the soul—feelings of pleasure and displeasure, actively violent emotions, anger, grief, and so on, right down to the will; certain specific plant forms can be compared with the human soul realm. On the right you can then fill in the corresponding plant species, so that in the table you have the thought plants above, the will plants below, and all the others in between. Rudolf Steiner then gave a graphic explanation of the Pythagorean theorem and referred to an article by Dr. Ernst Müller in Ostwald’s magazine for natural philosophy, Annalen der Naturphilosophie, entitled “Some Observations on a Theory of Knowledge underlying the Pythagorean theorem.”  In the drawing, the red parts of the two smaller squares already lie within the square on the hypotenuse. By moving the blue and the green triangles in the direction of the arrows, the remaining parts of the two smaller squares will cover those parts of the square on the hypotenuse still uncovered. You should cut out the whole thing in cardboard and then you can see it clearly.3
|
| 261. Our Dead: Memorial speech for Sophie Stinde
26 Dec 1915, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Among the many things we may remember in these days of the Christmas season, the world's earthly motto stands before our soul above all: Revelation of divine powers in the heights And peace on earth to men, Who are of good will. |
| 261. Our Dead: Memorial speech for Sophie Stinde
26 Dec 1915, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
When I last spoke to you here in this place, the person who is most intimately connected with this building was still among us: our dear Sophie Stinde. You have commemorated the great, painful loss here, and in the time when Sophie Stinde's soul left us, you have evoked in your own souls those feelings that arose from the deep, intimate connection that existed between your souls and Sophie Stinde's soul in relation to our spiritual work. Nevertheless, my dear friends, I cannot resume these lectures here without mentioning the departure of Sophie Stinde's soul from the physical plane, which had such a profound impact on our lives. Only a few words are needed, for our souls, each one's soul, speaks to us so much when we think of the soul that has left us, and the more abundantly, the more fully perhaps the soul has to say to itself at this point, the shorter may be what is expressed with outer physical words. My dear friends, for many years we here in the physical world were faithfully connected with this soul that had passed away from us in a way that we can say, in the highest sense of the word, was exemplary for us and to us. For the way in which Miss Stinde has placed herself in our spiritual endeavor is so connected with the deepest, most inner soul impulse of this personality, with that in this personality which, within this incarnation, constitutes its essential character of existence. It was only a short time since we had begun our work in Central Europe, and our task was to establish this work in various places. In the house of Fräulein Stinde and her dear friend, Countess Kalckreuth, it was possible for me to speak the first intimate words to a community in Munich that was willing to receive them at that time. And from that moment on, Fräulein Stinde was with our work out of the very abundance of her beautiful will, was with our work in a sense that our work needs it. For we must distinguish between two things. The content of our work must be taken from the spiritual world; if the earth is to reach its goal, it must belong to what will flow into the spiritual development of humanity in the course of future earthly ages. This is what we must humbly face in our soul. In our time we can be convinced of this content, or we can reject it. It is a matter that can be said to belong to something that may already now, but will certainly one day, flow into the spiritual development of humanity, even if our efforts, as they are being attempted by us in the present, should fail due to the resistance of souls that are too weak for our cause. But working within our own circle, with those who strive with us to incorporate the spiritual content of our world view into the spiritual heritage of humanity, to bring this content to the souls and hearts of those who need it, is something else entirely within our society. There is no possibility of saying: if not now, then later. There is only the one possibility of committing oneself with one's whole, undivided soul. And anyone who is committed to this, who puts everything he has and can do at the service of the cause, as if this work were one of the most necessary things he has to do in life, can be said to have grasped the full meaning of how our work is to flow into the spiritual culture of the world through a socially organized circle. For the time being, for the content of our world view, no goodwill is required of people; only the inner truth of the matter is needed. But it is true that under certain circumstances the matter can fail, and the time may lie further in the future when this content can be incorporated into the spiritual culture of humanity. There is nothing but understanding of the content, nothing but learning to recognize, there is no need to speak of trust, of this or that kind of will, there is only need to speak of the inner truth of the matter. The situation is different when we look at the instrument through which this spiritual content is to enter the world. This has nothing to do with the truth content of our world view. But this truth must be carried into the present day in the mutual trust that the souls of the members have for one another, and the goodwill that is connected with the warmth and light of the cause must extend into that which, as if in a necessary stream of development, must be brought into the present day. For those who, so to speak, have a special task to work on, there are many things to consider. The first thing is that they have the good will to gather together what karma has brought them in this incarnation up to the moment when they enter our spiritual house through the gate of our spiritual aspirations, so that they know how to transform and transmute everything that has presented itself to them in the present incarnation in order to put it at the service of our cause. Some will bring this, others that; some were capable when they came, others when they go. There is no path in the life of present-day humanity that does not lead to the center as if it came from the ends of a circle: to the place where the gate to that house stands. And so was Fräulein Stinde. And she had important and essential things to bring, and she had goodwill, the best of intentions, to bring through our gate that which she has become with this incarnation. Among the many things we may remember in these days of the Christmas season, the world's earthly motto stands before our soul above all:
Yes, this soul was of good will. She had a goal in life when she came to us, and this goal was embraced by her artistic endeavors. A heartfelt artistic sense lived in her soul and expressed itself to all who came to know what this soul had attempted and created in the field of art through the heartfelt way in which she worked artistically. But it was of infinite value that she could bring this through the gate to our spiritual home. For that which blossoms in artistic fantasy may find its way more easily than from many other starting points to the spiritual secrets that must be brought down from the realms of imagination. And what this soul was able to experience, what it was able to acquire from art, it brought to us. Only in this way was it possible to unfold that will, which then spreads and takes hold of many, that will to develop, which finds expression in this our building. Sophie Stinde was among the very first to whom the idea of this our building arose, and one can feel that we would hardly have found the way to this building from our Munich mystery thoughts if her strong will had not been at the starting point of the thought of this building. A second thing, my dear friends, may come to our minds when we see Sophie Stinde's soul, which is intimately connected with the work and life in our society: her trust. Within the second, that is, within the context of where trust is necessary because cooperation is necessary, Miss Stinde can be an example to us. And where cooperation is necessary, mutual trust is necessary, quite independently of the teaching and the world view, which include the striving for truth and the striving for knowledge and not, for example, trust. But trust is part of working together. Yes, those who knew how to work with Sophie Stinde were able to learn from her how the kind of trust that is needed for working together in our field is particularly special. I would like to say something here that I wish would sink into many souls so that they would fully understand it: When working together towards a certain goal, a goal that often only reveals itself to the outside world after a long time, that can only be manifested in the outside world after a long time, it is necessary to work together towards a goal that cannot be presented to others, but that wants to develop. People must work together who can trust each other to want to work together, even if the goal cannot be presented in a programmatic, abstract, theoretical way in a few sentences. Not trust in work, not trust in theories, but trust in souls, from which one feels and experiences that one will achieve with them what is to be achieved, even if one cannot yet determine it in the outer world, because it will show itself in the development itself. One must know, one is dealing with people who are not only able to grasp this deeper trust, which is not based on external formulations, but are also able to grasp the coexistence of souls that want to walk together, even if they do not know the goal. This goal will be the right one. That means: being connected to the living core of the work; that means: experiencing loyalty to the work in this core of life; that means: being selflessly connected to the work. We will perhaps only agree with each other on the things that lie years ahead of us, which we would ruin now if we wanted to put them in front of us in an externally formulated way: you have to be able to say that to each other if you have trust in such a context, as our context should be. That such trust existed between them and Sophie Stinde was known to those who really got to know Sophie Stinde in this regard. Thus, above all, the thought that comes to mind when we think about her is: because we know how she is with us in our souls, because we know how she belongs to those souls who, after passing through the gate of death, work in our midst with all the means of power that are then available to their souls and which are the flowering of what the souls have acquired here in earthly incarnation. Their place in the external physical world will be empty in the future. But for those who have learned to understand her, this place will be the source of the idea of exemplary, dedicated, sacrificial work within our ranks. And this idea must live in particular in the rooms under the double dome, in the rooms where Sophie Stinde's soul already worked as her co-work during this incarnation on earth. If we grasp our relationship to her in the right sense, it will be impossible to turn our gaze to our forms without feeling connected to her, who first turned her gaze to him to whom she dedicated her own work, and in whom Sophie Stinde's soul will continue to work. My dear friends, spiritual science cannot be there to dull the pain that weighs on our soul when we suffer a great loss, for pain is a world principle. And the great and the sublime in the world, as we have explained in various places in our world view, arise as blossoms and fruits from the mother soil of pain. If we were to sin against pain, we would sin against the meaning of the world. But we may look up to the words that she spoke as Sophie Stinde's spirit, the words that we can learn from her: “I will be with you as I was with you! Our relationship will have changed as a result of passing through the gate of death, changed only, not changed, and one may think that our understanding of the connection with the departed souls may then increase our overall understanding of the human connection with the spiritual world. For the understanding that we may have of such personalities as Sophie Stinde is interwoven with and sustained by love and mutual trust. I do not think that there will ever be a significant occasion within this building where we will not have to remember how Sophie Stinde's soul has prevailed at the starting point of this reasoning, how she has connected with it. Of course, souls of this kind, who clearly recognize the task that is inwardly incumbent upon those who unite with our work, must accept many misunderstandings and go through many difficulties; they are not easily understood by others, misunderstood by many. This must be borne. But there are enough souls in our ranks who, in their deepest inner being, carry a flame of love, a beautiful flame of love, which shines towards Sophie Stinde's soul. The flames of love that Sophie Stinde's nature has kindled in the hearts of our members appear to me especially before the soul. Just think how many a soul has searched, has come to her, and with those words that it was able to speak, has found that love, loyalty and friendship that such a soul needs. And then the flames of love are kindled by such love, loyalty and friendship, and they are especially kindled to a lasting degree where they flare up in the right way, where they can be kindled by a soul that seizes what it has to seize for the world in the highest sense of duty, and whose sense of duty never speaks, even when it must speak in the negative, without this sense of duty being crossed by the mitigating love. We must never let ourselves be tempted by love to dispense with duty. Love must be warmed by duty, duty must be strengthened by love. This could be seen in Sophie Stinde's soul. And so she also ruled within these rooms, so she ruled for the benefit of our building, and so the spirit of her soul will continue to rule as the soul of our building. May the souls be quite numerous who look with understanding at the way Sophie Stinde's soul is connected to this, our spiritual work. My dear friends, I did not want to speak again within these rooms, where Sophie Stinde's soul ruled, without first mentioning her. If we loved her when she walked among us in the physical body, we will love her as a spirit that warms and illuminates us without end. Let us seek her among those to whom we look up with particular loyalty in the times when the spiritual realms shine even more brightly than at other times of the year. Let us seek in particular those effective forces that emanate from Sophie Stinde's soul, and in relation to which we want to make ourselves so worthy that they can always be effective through our work, especially in these rooms. |

