The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education
GA 306
Lecture I
15 April 1923, Dornach
At the opening of this conference, I want to extend my warmest greetings to you all. Had you come some four or five months earlier, I would have welcomed you in the building we called the Goetheanum, which stood over there. The artistic forms of its architecture and its interior design would have been a constant reminder of what was intended to go out into the world from this Goetheanum. However, the misfortune that befell us on New Year's night and inflicted such grievous pain on all who loved this building, has robbed us of the Goetheanum. And so, for the time being, we shall have to nurture the spirit—without its proper earthly home—that would have reigned within this material, artistic sheath.
It gives me great joy to welcome those of you who have come from Switzerland, and who have displayed, through your coming, real evidence of your interest in our educational goals, even though they have been received recently in Switzerland with enmity. With equal joy and gratification I want to welcome the many friends of Waldorf Education—or those wishing to become its friends—who have come from Czechoslovakia. Your presence confirms to me that education involves one of the most crucial questions of our time, and that it will receive the impetus it needs and deserves only if it is seen in this light by the various members of the teaching profession.
Furthermore, I welcome those of you who have come from other countries, and who show, through your presence, that what is being worked toward here in Dornach is not just a matter of cosmopolitan interest, but is also a matter of concern for all of humanity.
And finally I want to greet our friends, the teachers of the Waldorf School. Their primary goal in coming here is to contribute to this conference from their own personal experience. They are deeply connected with our cause, and expressed the wish to support this conference. This is greatly appreciated.
Today, as an introduction, I want to prepare the ground for what will concern us during the next few days. Education is very much in the news today, and many people connected with educating the young are discussing the need for reform. Many different views are expressed—often with considerable enthusiasm—about how education should go through a change, a renewal. And yet, when hearing the various ideas on the subject, one cannot help feeling a certain trepidation, because it is difficult to see how such different views could ever lead to any kind of unity and common purpose, especially since each viewpoint claims to be the only valid one.
But there is another reason for concern. New ideas for education do not cause undue concern in themselves, for the necessities of life usually blunt the sharp edges, causing their own compensations. When one hears nearly everyone call for a renewal in education, yet another problem comes to mind—that is, where does this praiseworthy enthusiasm for better education spring from?
Isn't it prompted by people's memories of unhappy childhood days, of their own deep-seated memories of an unsatisfactory education? But as long as the call for educational reform comes only from these or similar feelings, it merely serves to emphasize personal discontent with one's own schooling. Even if certain educational reformers would not admit this to themselves or to others, by the very nuance of their words they imply dissatisfaction with their own education. And how many people today share this dissatisfaction! It is little wonder if the call for a change in education grows stronger every day.
This educational dilemma, however, raises two questions, neither of which is comforting. First, if one's education was bad, and if as a child one was exposed to its many harmful effects, how can one know what constitutes proper educational reform? Where can better ways of educating the young be found? The second question arises from listening to what certain people say about their own education. And here I want to give you a practical example because, rather than presenting theories during this conference, I want to approach our theme in practical terms.
A few days ago a book appeared on the market that, in itself, did not draw my particular interest. Nevertheless it is interesting because in the first few chapters the author, an outstanding person who has become world-famous, speaks very much about his early school days. I am referring to the memoirs of Rabindranath Tagore,1Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941) Indian Bengali poet and novelist; won Nobel prize for literature in 1913; knighted by England, but resigned knighthood (1919) in protest against English repression in Punjab. which have just been published. Although I do not have the same interest in this person that many Europeans do, in regard to educational matters his memoirs do contain some noteworthy and pertinent details.
I am sure that you would agree that the most beautiful memories of one's early school days—however wonderful these may have been—will hardly consist of fragmentary details of what happened in certain lessons. Indeed, it would be sad if this were so, because what affects children during lessons should become transformed into life habits and skills. In later life we should not be plagued by the details of what we once learned at school, for these must flow together into the great stream of life. Couldn't we say that our most beautiful recollections of school are concerned with the different teachers we had? It is a blessing if, in later years, one can look back with deep, inner satisfaction at having been taught by one or another admired teacher. Such an education is of value for the whole of one's life. It is important that teachers call forth such feelings in their pupils; this also belongs to the art of education.
If we look at some of the passages in Tagore's memoirs from this perspective, we find that he does not talk of his teachers with much reverence and admiration. To quote an example, he says, “One of our teachers in the elementary school also gave us private lessons at home. His body was emaciated, his face desiccated, and his voice sharp. He looked like a veritable cane.” One might easily imagine—especially here in our Western civilization, often criticized strongly in the East—that the wrongs of education would hardly be so vehemently emphasized by an Asian. But here you have an example of how an Eastern personality, now world-famous, looks back at his school days in India. And so I shall use a word that Tagore also mentions in his book—that is, “miserable school.” The meaning of this expression is not confined to European countries, but seems to express a worldwide cultural problem. Later on we shall have to say much more about what teachers must do to kindle genuine interest for what they bring to their pupils.
But now I shall give you another example from Tagore's memoirs of how his English teacher approached this task. Tagore writes, “When I think back on his lessons, I cannot really say that Aghor Babu was a hard taskmaster. He did not rule us with the cane.” To us, such a remark would point to times long past, long superseded. The fact that Tagore speaks so much in his book about the cane indicates something we would consider culturally primitive. I believe that such a comment is justified when reading Tagore's description, not just about one of his teachers “looking like a veritable cane,” but also when he points out that another teacher actually did not use the cane. Speaking of this other teacher, Tagore continues, “Even when reprimanding us he did not shout at us. But, whatever his positive sides may have been, his lessons were given in the evening, and his subject was English. I am sure that even an angel would have appeared to a Bengali boy like a true messenger of Mamas (The God of Death), had he come to him in the evening after the `miserable school' of the day, kindling a comfortless, dim lamp, in order to teach English.”
Well, here you have an example of how a famous Indian speaks about his education. But Tagore also writes about how each child brings certain needs to education. He points out in a very practical way how such needs should be met, and how this did not happen in his case. I will leave it to you to interpret this situation in Western terms. To me it seems very good to look at such matters from a global perspective, matters that—if quoted in a European context—could very well arouse strong criticism. Tagore continues:
From time to time Aghor Babu tried to introduce a refreshing scientific breeze into the dry routine of the class room. One day he pulled from his pocket a little parcel wrapped in paper, saying, “Today I want to show you one of the Creator's wonderful works of art.” Unwrapping the paper, he showed a human larynx, which he used to explain to us the wonders of its mechanism.
I still remember the shock this gave me, for I had always thought that speech came from the entire human being. I did not have the slightest inkling that the activity of speaking could thus be isolated from the whole human organism. However perfect the mechanism of each single part might be, surely it would always amount to less than the complete human being. Not that I consciously realized this, but at the bottom of my feelings it was distasteful. The fact that the teacher had lost sight of such a truth must have been the reason why his pupil could not share in his enthusiasm for this kind of demonstration.
Well, this was the first shock when the nature of the human being was introduced to the boy. But another one, worse still, was to follow. Tagore continues:
On another occasion he took us into the dissecting room of the local medical school.2There can be no doubt that Aghor Babu wanted to give his boys a special treat. The corpse of an old woman was lying on a table. This in itself did not particularly disturb me. But an amputated leg, which was lying on the floor, completely threw me off my balance. The sight of a human being in such a state of fragmentation seemed so dreadful, so utterly lacking in sense to me, that I could not shake off the impression of this dark and expressionless leg for many days to come.
This example illustrates the reaction of a young person introduced to anatomy. Fundamentally speaking, this procedure is adopted in education only because it is in line with the orthodox scientific approach. And since the teacher has indeed gone through scientific training, it is naturally assumed to be a wonderful idea to demonstrate the mechanics of human speech with a model of the larynx, or to explain physiological anatomy with the aid of an amputated leg, for contemporary scientific thinking does not consider it necessary to look at the human being as a whole.
However, these are not yet the primary reasons for selecting certain passages from Tagore's memoirs—of which we will say more later on, not because of their connection with Tagore, but because they belong to the theme of our conference. First, I want to make another point.
Anyone judging Tagore's literary merits will correctly recognize in him an outstanding individual. In the autobiography of this distinguished author we read about his dreadful education. Doesn't this encourage a strange thought—that his poor education did not seem to harm his further development? Couldn't one conclude that a thoroughly bad education doesn't necessarily inflict permanent or serious harm? For did Tagore not demonstrate that despite this, he was able to grow into a good, even a famous person? (Examples like this could be multiplied by the hundreds, though they may be less spectacular.)
Considering the myriad impulses for educational reform, one could easily be pulled in two directions. On the one hand, how can anyone possibly be in a position to improve education if one has had the misfortune of suffering from a bad one? On the other hand, if “miserable school” has not prevented someone from becoming, not just a good, but even a great and famous person, then a bad education cannot do permanent harm. Is there any point in lavishing so much care on attempts to improve education? From a superficial perspective, one might conclude that it would be better to occupy oneself with matters that are more useful than educational reform.
If anthroposophy, which has been much maligned, were merely to offer even more ideas for educational reform, as is generally done, I would not even consider it worthwhile to attempt these in practice. But in reality, anthroposophy is something very different from what most people imagine it to be, for it springs from the deepest needs of our present culture.
Anthroposophy does not proceed, as so many of its enemies do, by shamefully denigrating everything that does not agree with its own principles. Anthroposophy is more than prepared to recognize and acknowledge what is good, wherever it is found. More of this later, for, as I have said already, today's content is intended only as an introduction.
Anthroposophy points to the importance of the scientific achievements of the last three to four centuries and, above all, to those of the nineteenth century, all of which it fully recognizes. At the same time, however, anthroposophy also has the task of observing how these great scientific successes affect the human soul. It would be foolish to think that the ideas of a relatively few scientifically trained experts have little consequence for society as a whole; for even people who know little or nothing about science are influenced by contemporary science in their soul mood and in their life's orientation. Even people of a strictly orthodox religious faith, born of tradition and habit, nevertheless owe their world orientation to the results of orthodox science. The attitude of modern people is colored increasingly by the scientific view with all its tremendous achievements, which cannot be praised highly enough.
Yet the constitution of the human soul has been strangely affected by modern science. Having revealed more and more of outer nature, science has, at the same time, alienated human beings from themselves. What happens when the human being is observed from a scientific perspective? Our attention is drawn first to what has already been discovered very thoroughly in the inert, lifeless world. Then the human being is analyzed according to physiological and chemical components and what was established in the laboratories is then applied to the living human being.
Or else our attention is directed to other realms of nature, to the plant and animal kingdoms. Here scientists are fully aware that they have not been able to establish laws as convincing as those applied to inorganic nature. Nevertheless—at least in the animal realm—what has been discovered is then also related to the human being. This is the reason why “the man in the street” sees the human being as the final evolutionary stage of animals. The evolutionary ladder of the animal species ends with the emergence of the human being. The animals are understood up to a certain point. Their bony structures or muscular configurations are then simply transferred to the human being who, as a result, is considered to represent the most developed animal.
As yet, no true picture of the human being has arisen from these methods, and this will become poignantly clear to us when we focus on education. One could say that whereas in earlier times human beings occupied a central position within the existing world order, they have been displaced, crushed by the weight of geological data, and eliminated from their own sphere by the theory of animal evolution. Merely to trace back one of the ossicles of the human middle ear to the square-bone (Quadratbein) of a lower animal is praised as real progress. This is only one small example, but the way human physical nature reflects the soul and spiritual nature seems to have been entirely disregarded by modern research.
This kind of thing easily escapes notice, because the orthodox approach is simply taken for granted. It is a by-product of our modern culture, and properly so. Indeed, it would have been a sad situation if this change had not occurred, for, with the soul attitude that prevailed before the age of science, humanity could not have progressed properly. Yet today a new insight into human nature is called for, insight based on a scientific mode of thinking, and one that will also shed light on the nature of the entire universe.
I have often tried to show how the general scientific viewpoint—which in itself, can be highly praised—nevertheless can lead to great illusions, simply because of its innate claims of infallibility. If one can prove science wrong on any specific point, the whole thing is relatively simple. But a far more difficult situation arises when, within its own bounds, a scientific claim is correct.
Let me indicate what I mean. What led to a theory such as that of Kant-Laplace?3Pierre Simon Marquis de Laplace (1749–1827) French astronomer and mathematician. Immanuel Kant (1724–1895) German philosopher. Using this theory—which has been modified recently, and is known to practically every educated person—scientists attempt to explain the origin of our Earth and planetary system. In their calculations, some of these scientists went back over long periods of time. When one scientist spoke of some twenty million years, soon enough he was considered naïve by others who spoke in terms of two hundred million years. Then other scientists began to calculate the length of time of certain processes taking place on Earth today. This is a perfectly correct thing to do, because from a strictly material point of view there is nothing else one can do. Sedimentation or metamorphosis of rocks was observed and, from the data gained, a picture was built up that explained certain changes, and the length of time involved was then calculated. For example, if the waters of Niagara Falls have been falling on the rocks below for such and such a period of time, one can calculate the degree of erosion of these rocks. If one now transfers this calculation to another spot somewhere else where considerably more erosion has been found, one can calculate the time this must have required through simple multiplication. Using this method, one might arrive at, let's say, twenty million years, which is quite correct as far as the calculation is concerned.
Similarly, one may start with the present time and, according to another well-known theory, calculate the time it will take for the Earth to become subject to heat death, and so on.
Yet, such a procedure might equally well be applied to a very different situation. Observe, for example, how the human heart changes from year to year. Noting the differences, one could investigate—following the same method applied in the case of Niagara Falls—how this heart must have looked some three hundred years ago, and what it would look like some three hundred years from now. Technically speaking, this method would be analogous to that of determining the times of geological changes and in this sense it would be correct. Observing the heart of a person aged about thirty-five, one would be basing one's calculations on an organ that has been functioning for a considerable length of time. However, one obvious detail has been overlooked—that this particular heart did not exist three hundred years ago, nor will it be there three hundred years from now. Though mathematically speaking the calculation is correct, it has no relationship to reality.
In our current intellectual age we are too preoccupied with whether or not something is correct, whether or not it is logically correct; but we have lost the habit of asking whether it conforms to actual real-life situations. We will confront this problem again and again this week. But it can happen sometimes that, when we follow apparently correct theories, even fundamental issues are simply overlooked. For example, you may have witnessed—I am not implying that as teachers you have actually carried out this experiment yourselves, for present company is always excluded when negative assertions are being made—you may have witnessed how the rotation of the planets around the Sun was graphically illustrated even to a class of young children. A piece of cardboard is cut into a disc and its center is pierced with a pin. A drip of oil is then put onto its surface before the disc is floated on water. When the pin is twirled around to rotate the floating disc, little droplets of oil will shoot off at a tangent, making “little planets”—little oil planets—and in this way a most convincing model of a planetary system has been fabricated. Needless to say, this experiment is supposed to prove the accuracy of the Kant-Laplace theory. Well, as far as one's own morality is concerned, it is virtuous enough to be self-effacing, but in a scientific experiment of this sort, the first requirement is certainly not to omit any essential detail—however small—and to include all existing criteria. And isn't the teacher spinning the disc the most important factor involved? Therefore, this hypothesis would make sense only if it were assumed that, long, long ago, a gigantic schoolmaster once twirled round an immense world-pin, thus spinning our entire planetary system! Otherwise one should not use such a hypothetical experiment.
And so, many elements of an unrealistic soul attitude can be detected where science appears to be most correct, where its findings cannot be contested. Consequently these elements of error easily creep into education. For those who teach are inevitably a product of their own time, and this is as it should be. When they come across such geological calculations or astronomical analogies, everything seems to fit together very nicely. Sometimes one cannot help but feel amazed at the incredible ingenuity of scientific interpretations that, despite their apparent power of conviction, nevertheless, can lead us away from reality. However, as educators we must never deviate from actual reality. In teaching, we face reality all the time, and this must spur us on to greater knowledge of human nature as it really is. In a certain sense this failure to penetrate human nature has already crept into modern-day educational thinking and practice.
I would like to illustrate this point with an example. Whenever you are dealing with children in the classroom, you will find that some are more gifted in one or another subject than others. Most of you will be familiar with the current thoughts and methods regarding this problem. I am referring to them here only to establish mutual understanding. There are different degrees of abilities in children. And how are these dealt with, especially in today's most progressive centers for educational science? From your study of educational literature you probably know about the so-called correlation coefficients recently introduced in schools. According to this method, the correlation coefficient one is written down if a pupil shows an equal aptitude for two different subjects. (Such a thing actually never occurs, but hypothetically it is simply assumed.) If, on the other hand, a natural gift exists for two subjects that are mutually incompatible, the correlation coefficient zero is given. The idea of this method is to test and measure the pupils' various gifts. For example, you may find that drawing and writing carry the correlation coefficient of, let us say, .7. This means that more than half the children who are gifted in drawing also have a natural skill for writing. One also looks for correlation coefficients in other combinations of talents. For example, writing is linked to a pupil's ability to deal with the mother tongue and, in this case, the correlation coefficient is .54. Arithmetic and writing carry the correlation coefficient of .2, arithmetic and drawing .19, and so on. From this it can be seen that arithmetic and drawing are the least compatible partners, whereas writing and drawing are matched most frequently. A natural gift for both the mother tongue and for drawing is found to be equally present in approximately fifty percent of the pupils.
Please note that, on principle, I do not object to this kind of scientific research. It would be wrong to declare that such things should not be investigated. As a matter of fact, I find these things extraordinarily interesting. I am not in the least against such experimental or statistical methods of psychology.
But if their results are directly implemented in education, it is as if you were to ask someone to become a painter without mentioning the importance of having to deal with color. It is as if one were to say instead to such a person, “Look, here is a good book on esthetics. Read the chapter about painting and, in itself, that will make you into a good painter.”
A well-known painter in Munich once told me a story that I have quoted several times. While he was a student at the local arts school, Carriere, [Moritz Carriere (1817–1895) German thinker; published Aesthetics in 1815.] the famous professor of esthetics, was lecturing in Munich. One day the painter and some of his fellow students decided to go and see this famous expert who also lectured on painting. But one visit was enough for them, because, as they put it, all he did was “crow with esthetic delight.”
This is how it strikes me if people think they can benefit their educational practice with the kind of thing mentioned above. Though these experiments may be interesting from a scientific perspective, something very different is needed for the practical classroom situation. It is necessary, for example, that teachers can penetrate human nature so deeply that they can recognize the origin of the skills for drawing and writing within the inner functions, or recognize what enables a pupil to speak the mother tongue well. To achieve such a faculty, a living observation of the human being is required, which eventually may lead one to discover how specific capacities flow out of some children for, let us say, drawing or the skill for their native language. Here, statistics are of little use. One must take a cue from what children reveal of themselves. At most, such statistical evidence may serve as an interesting confirmation afterward. Statistics do have their value, but to believe that they are tools for educational practice only shows the degree of one's alienation from real human nature.
Today, many people look at statistics as a key to understanding human beings. In certain areas of life this is justified. It is possible to build a statistical picture of the human being, but such a picture will not allow us to understand the human being in depth. Think, for instance, of how useful statistics are in their appropriate sphere, such as in insurance. If I want to take out a life insurance policy, I will be asked how old I am, and I must give evidence for the state of my health, and so on. From such data the level of my premium can be worked out very neatly, depending on whether I happen to be a youngster or an old fogy. My life expectancy is then calculated and these details meet exactly the needs of the insurance business. But what if, in my thirty-seventh year, I had taken out a life insurance policy for, let us say, twenty years? Would this make me feel obliged to die at the age of fifty-seven, simply because of what was calculated on paper? To enter fully into the stream of life is something very different from following certain established criteria, however logically correct they may be, or however beneficial they may be in their proper sphere.
When considering the question of aptitude for writing and drawing in children who have recently entered school, one must remember that they have reached the stage of their second dentition. In the coming lectures you will hear more about the different stages of children's development, and about how their ages can be divided into three groups: the period from birth to the change of teeth; from the second dentition to puberty; and the time following puberty. Later we shall go into more detail about what happens in children during these three periods.
For now let us consider this question of writing and drawing. Science, having scrutinized so minutely the three kingdoms of nature that surround us, now transfers the knowledge gained to the human being. Knowledge of the outer world and the mode of thinking about outer nature now becomes the key to understanding the human individual. And yet, if one observes the human being within the human sphere, one will come to recognize the true situation. One only needs the courage to do so with the same accuracy and objectivity used to study outer nature. Current research shows such courage only when observing external nature, but shrinks from applying the same methods in the study of the human being.
Let's look at how the child develops from birth to the change of teeth. This change of teeth is a unique event in life, inasmuch as it occurs only once in life. Now, if you can experience something similar to the feelings Tagore expressed when he saw the amputated leg, you will realize that what is revealed in the change of teeth does not just happen in the jaws, but encompasses the entire human being. You will feel that something must be pervading the whole child until around the age of seven, and that some activity must reach a climax in the change of teeth. This activity is there in its original form until the seventh year, and then it is no longer present in its original state.
When studying physics, for example, scientists have the courage to speak of latent heat as distinct from the various forms of liberated heat. According to this concept, there must be some form of heat that cannot be determined with a thermometer, but can be measured after it has been released. When characterizing these phenomena that occur in nature, scientists have shown courage in their interpretations. However, when the human being becomes the object of study, this courage is no longer there. Otherwise they would not hesitate to state: What has been working until the seventh year in the child, working toward liberation during the change of teeth, must have been connected with the physical organism before becoming freed and reappearing in a different guise as the child's inner soul properties. This same process can also be recognized in other areas of the child's bone formation. One would realize that these newly emerging powers must be the same, although transformed, as what had been active previously in the child's physical organism.
Only courage is needed to look at the human being with the same cognitive powers used to study outer nature, but modern science will not do this. However, if we do this, our attention is drawn toward all that belongs to the bony system, to everything that hardens the human form to give it structure and support. Orthodox physiology might eventually go this far—if not today, then certainly in due time. The most important branches of science are going through considerable changes just now, and the time will come when they will follow the course indicated.
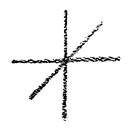
But something else must also be considered. In later years, the child will be introduced to many different subjects, such as geometry. In today's intellectual age, one has an abstract concept of three-dimensional space, to choose a very simple example. One imagines: three lines at right angles to one another hovering about in space and extending to infinity. It is possible to form such a concept abstractly, but in such a case it is not inwardly experienced. And yet, three-dimensional space wants to be experienced as reality. This does happen in a young child, although unconsciously, at the crawling stage when, losing its balance time and again, it will eventually learn to acquire the upright position and achieve equilibrium in the world. Here we have a case of actual experience of three-dimensional space. This is not merely a question of drawing three lines in space, because one of these three dimensions is identical with the human upright position (which we can test by no longer assuming it—that is, by lying horizontally or sleeping). This upright position signals the most fundamental difference between the human being and the animal, because, unlike the human backbone, the animal's spinal column runs parallel to Earth's surface. We experience the second dimension unconsciously every time we stretch our arms sideways. The third dimension moves from our front toward the back.
In reality these three dimensions are experienced concretely as above and below, right and left, forward and backward. What is done in geometry is merely an abstraction. Human beings do experience with their bodies what is shown in geometrical constructions, but only during the age when they are still largely unconscious and dreamy. Later on, these experiences rise into consciousness and assume abstract forms.
With the change of teeth, the forces that cause an inner firmness, an inner consolidation and support, have reached a certain climax. From the moment when the child can stand upright until the inner hardening processes manifest in the change of teeth, the child inwardly tries, although unconsciously, “body geometry” as an activity akin to drawing. When the teeth change, this becomes a soul activity—that is, it enters the realm of the child's soul. We might understand this transformation better through an analogy; just as a sediment falls to the bottom when a chemical solution cools, and leaves the upper part clearer, so there is also a physiological aspect to the hardening process—the sediment, as well as its counterpart: the clear solution within the child's soul realm, which manifests as a faculty for geometrizing, for drawing, and so on.

After this period, we can see the child's soul qualities streaming outward. Just think about how such a discovery engenders real interest in the human being. We shall observe this streaming out in greater detail, and how it is reflected back again, later on.
In this respect everything in life is linked together. What we do to the child not only has an immediate effect, but influences the whole lifetime. Only a few people are prepared to observe a human life as a whole, but most focus their attention on present circumstances only. This is the case, for example, when one creates an experiment concerned only with the present. On the other hand, have you ever observed how the mere presence of some old people can be like a blessing for the others present? They need not even say a word. Goodness radiates from their presence simply through what they have become. And if you now search the biography of such old people, you may find that when they were children they learned to feel reverence quite naturally, without any outer compulsion. I could say equally that they learned how to pray, by which I mean praying in its widest sense, which includes a deep respect and admiration for another human being. I would like to express this thought in the form of a picture. Those who have not learned to fold their hands in prayer during childhood, cannot spread them in blessing in old age.
The different phases of life are all interconnected and it is of great importance in education to take this into full account. We learn a great deal about the child when we recognize how soul forces well forth after they have completed their task of working in the physical body up to the end of the first seven-year period.
Psychologists have made the strangest hypotheses about the interplay of soul and body, whereas one period of life actually sheds light on another. What we can see in the child between the change of teeth and puberty will tell us something about the soul forces previously engaged in working within the child's physical realm. Facts speak for themselves and shed light on one another. Think of how such things will stimulate interest in education! And genuine interest in the human being is needed in education today. Far too many people think about the relationship of body and soul—or of soul and body—only in abstract terms. And because so little of real value has emerged, a rather amusing theory has been formulated—that is, the theory of the so-called psycho-physical parallelism. According to this theory, processes of soul and body run side by side on a parallel course. There is no need to bother about points of intersection, no need to bother about the relationship between body and soul at all, because they supposedly meet at infinity! That is why this theory sounds like a joke.
However, if one allows the guidance of practical experience, one can discover the actual interrelationship between body and soul. One only needs to look over a person's whole life-span. Let us take the example of someone who develops diabetes or rheumatism at a certain age. When trying to find a remedy for such an illness, usually only the present conditions are considered; this, in itself, is quite justified. It is certainly proper to make every effort to heal a sickness whenever it occurs. But if one surveys the whole life of the patient, one may discover that many times diabetes is due to a memory that was overtaxed or developed in the wrong way between the change of teeth and puberty. Health during later years is largely conditioned by the way a person's soul life was developed during childhood. The way a child's memory is trained will affect the metabolism after a certain period of time. For example, if undigested vestiges of memory remain in the soul of a child between seven and fourteen, they will be released approximately between the ages of thirty-five and forty-five as physical residues, which can then lead to rheumatism or diabetes.
It is not an understatement to suggest that teachers should have at least a modicum of medical knowledge at their disposal. It is not right for them to leave everything concerning the child's health to the school doctor, who usually doesn't even know the children. If any profession in our time requires a wider background, education needs it most of all.
This is what I wanted to tell you as an introduction to our conference theme, so that you can judge for yourselves when you hear people say that anthroposophy now dabbles also in education, whereas others believe that it has something valid to say on the subject. Those who are ready to listen will not be swayed by those who have the opinion that there is no real need for education, or that there is no point in discussing it simply because their own experiences in this area have been so frustrating. Anthroposophy begins with an entirely different attitude. It does not simply want to correct old ideas, but begins with a true picture and knowledge of the human being, because, in keeping with human progress, these things have become necessary today.
If you go back to the earlier forms of education, you will discover that they have all arisen from the general culture of their time, from the universal nature of human feelings and experiences. We must rediscover a universal approach, flowing from human nature itself. If I had my way, I would give anthroposophy a new name every day to prevent people from hanging on to its literal meaning, from translating it from the Greek, so they can form judgments accordingly. It is immaterial what name we attach to what is being done here. The only thing that matters is that everything we do here is focused on life's realities and that we never lose sight of them. We must never be tempted to implement sectarian ideas.
And so, looking at education in general, we encounter the opinion that there are already plenty of well-considered educational systems; but since we are all suffering so much from the intellectualism of our times, it would be best if the intellect were banished from education. This is very correct, but then it is concluded that, instead of developing a science of education, again we should appeal to our inherent pedagogical instincts. However desirable this may sound, it is no longer possible today because humankind has moved to a further stage of development. The healthy instincts of the past are no longer with us today. A new and unbiased look at education has to be backed by fully conscious cognition, and this is possible only if our understanding can penetrate the very nature of the human being. This is what anthroposophy is all about.
One more point: intellectualism and abstractions are rampant today to the degree where there is a general feeling that children should be protected from an education that is too intellectual, that their hearts and feelings should also be educated. This is entirely correct, but when looking into educational literature and current practice, one cannot help noticing that such good intentions are not likely to go very far because, once again, they are formulated in a theoretical and abstract way. It is even less clear that this request should be made, not just on behalf of the child, but should be addressed also to the teachers and, most of all, to the pedagogical principles themselves. To do this is my goal. We must not give mere lip service when stating how we wish to educate the heart of the child and not just the intellect, but we should ask ourselves how we can best meet this challenge.
What do we have to do so that education can have a heart again?

