Soul Economy
Body, Soul and Spirit in Waldorf Education
GA 303
VI. Health and Illness II
28 December 1921, Stuttgart
It was not my intention in yesterday’s lecture to single out certain types of illnesses nor to specify differing degrees of health, nor is it my aim to do so today as we continue this subject. I merely wish to point out how important it is for teachers to learn to recognize both healing and harmful influences in the lives of their students. True educators, above all else, must have acquired real understanding of the entire human organization. They must not allow abstract educational theories or methods to cause them deviate from their natural or (as we could also call it) natural, intuitive understanding. Abstract theories will only hamper teachers in their efforts. They must be able to look at the children without preconceived ideas.
There is a saying often heard in Central Europe (perhaps this is also known in the West): “There is only one health, but there are numerous illnesses.” Many people believe in this saying, but it really does not stand up to scrutiny. Human beings are so individualized that we all, including children, have our own specific states of health, representing individual variations of the general notion of health. One might just as well coin the saying, “There are as many kinds of health and illness as there are people in the world.” This alone indicates how we must always consider the individual nature of each person. But this is possible only when we have learned to see human beings in their wholeness.
In every human being, soul and spiritual forces continually interact with physical forces, just as hydrogen and oxygen interact in water. We cannot see hydrogen and oxygen as separate elements in water, and similarly we cannot ordinarily see the human soul and spirit as separate from the physical and material aspects of a human being when we look at someone. To recognize the true relationship between the soul and spiritual aspect and the physical nature of a human being, one must first get to know them intimately, but we cannot do this through just our ordinary means of knowledge. Today we are used to seeing the human being from two points of view. One involves the study of physiology and anatomy, in which our image is not based on the living human being at all, but upon the human corpse, with the human soul and spirit excluded. The other point of view comes from psychology, the study of our inner life. But psychologists can form only abstractions, thin and cold concepts for our naturalistic and intellectualistic era. Such researchers warm up only when they try to plumb the depths of human emotions and will impulses. In their true essence, however, these are also beyond their grasp; in a vague way, they see only waves surging up from within.
It is obvious that cold, thin, and pale concepts of the human psyche will not give us a true sense of reality. What I am about to say might seem strange from the modern point of view, but it is true nevertheless. People today adopt a materialistic attitude, because for them spirit has become too attenuated and distant; as a result, when people observe the human inner life, it no longer has any sense of reality. The very individuals who live with the most abstract thoughts have become the most materialistic people during our cultural epoch. Contemporary thinking—and thinking is a spiritual activity—turns people into materialists. On the other hand, those who are relatively untouched by today’s scientific thinking, people whose minds turn more toward outer material events, are the ones who sense some of the mystery behind external processes. Scientific thinking today leaves little room for life’s mysteries. Its thoughts are thin and transparent and, for the most part, terribly precise; consequently, they are not grounded in the realities of life. The material processes of nature, on the other hand, are full of mysteries. They need more than the clarity of intellectual thoughts, since they can evoke a sense of wonder, in which our feelings also become engaged.
Those who have not been influenced by today’s sterile thinking and have remained aloof from the rigorous discipline of a scientific training are more open to the mysteries of the material processes of nature. But here there is a certain danger; in their longing to find spirit in nature, they look for the spiritual as if it, too, were only matter. They become spiritualists. Modern scientific thinking, on the other hand, will not produce people who are directed to the spiritual, but people who are materialists. A natural openness toward the material world, however, easily produces a spiritualistic approach, and here lies a strange contradiction typical of our time. But neither the materialistic view nor the spiritualistic view can provide a true picture of the human being. This is accomplished only by discriminating how—in every organ of the human being—the soul and spiritual element interacts with the material nature of the human being.
People do talk about soul and spirit today, and they talk about our physical aspect. They then philosophize about the relationship between these two aspects. Experts have presented detailed theories, which may be ingenious but never touch reality, merely because we find reality only when we perceive the complete interpenetration of the soul and spiritual element and the physical, material element of the whole human being. If we look at the results of today’s investigations, both in physiology and in psychology, we always find them vague and colorless.
Today, when people look at another person, they have the feeling they are confronted by a unified whole, because the other person is neatly wrapped up in skin. One generally fails to realize that this seeming singularity is the result of the cooperation of the most diverse organs. And if we say that this unity must not be assumed, opponents quickly arise and accuse us of destroying the idea that the human being is unified, which they consider fundamental. However, their concept of human oneness is still just an abstract thought unless they can harmonize the manifold members of the human being into a single organization.
When people look inward, they sum up all that lives within them with the little word I. Eminent people such as John Stuart Mill worked hard to formulate theories about the nature of this inner feeling of identity, which we express with the word I. Just stop and think, however, how vague this idea of a point-like I really is. You will soon see that you no longer grasp concrete reality with this concept. In German, only three letters form this little word (ich), and in English even fewer. People seldom manage to get beyond the outer meaning of these letters, and consequently today’s knowledge of the human being remains vague, regardless of whether you look at the inner life or the physical constituents.
It is the ability to see the spiritual and physical working together that enriches our efforts at comprehending the nature of the human being. There are many today who are inwardly satisfied by Goethe’s words, “Matter in spirit, spirit in matter.” It is good if these words make people happy, since they certainly express a truth. But for anyone who has the habit of seeing spirit and matter working together everywhere, these words express a mere triviality; they extol the obvious. The fact that so many receive this somewhat theoretical dictum with such acclaim just goes to show that they no longer experience its underlying reality. Theoretical explanations usually hide the loss of concrete inner experience. We find an example of this in history when we look at theories about the holy communion, theories that were widely discussed beginning at the very point in time when people had lost their ability to experience its reality. In general, theories are formed to explain what is no longer experienced in practice.
The attitude of mind expressed so far will be helpful to those who wish to practice education as an art. It will enable you to acquire a concrete image of the manifold members of the human being instead of having to work with some vague notion of human oneness. An image of the human being as an organic whole will emerge, but in it you can see how the various members work together in harmony. Such a picture inevitably leads to what I have indicated in my book Riddles of the Soul: the discovery of the three fundamental human aspects, each different from the others in both functions and character. Externally, the head as an organization appears very different from, say, the organism of the limbs and metabolic system. I link these two latter systems together, because the metabolism shows its real nature in the activity of a person’s limbs. In morphological terms, we can see the digestive system as a kind of continuation (though perhaps only inwardly) of a person in movement. There is an intimate relationship between the limbs and the digestive systems. For instance, the metabolism is more lively when the limbs are active. This relationship could be demonstrated in detail, but I am merely indicating it here. Because of their close affinity, I group these two systems together, although, when each one is seen individually, they also represent certain polarities.
Now let us look at the human shape, beginning with the head. For the moment, we will ignore the hair, which, in any case, grows away from the head and, because it is a dead substance, remains outside the living head organization. Human hair is really a very interesting substance, but further details of this would only lead us away from our main considerations.
The head is encased in the skull, which is formed most powerfully at the periphery, whereas the soft, living parts are enclosed within. Now compare the head with its opposite, the limb system. Here we find tubular bones enclosing marrow, which is typically not considered as important for the entire organism as the brain mass in the skull. On the other hand, here we find the most important parts—the muscles—attached on the outside, and from this point of view we see a polarity characteristic of human nature. This polarity consists of the nerves and senses, centered primarily (though not exclusively) in the head, and the metabolism localized in the metabolic and limb systems.
Despite this polarity, the human being is of course a unity. At this point, however, we must not be tempted to make up diagrams that divide the human being into three parts (as though these parts could exist separately), which we then define as the nervous-sensory system, a second part, which will be discussed shortly, and, finally, the metabolic and limb organization. It is not like this at all. Metabolic as well as muscular activities constantly take place in the head, and yet we can say that the head is the center of the organization of nerves and senses. Conversely, the organization of digestion and limbs are also permeated by forces emanating from the head, but we can nevertheless call it the seat of the “metabolic-limb system.”
Midway between these two regions, we find what we can call the rhythmic system of the human being, located in the chest, where the most fundamental rhythms take place: breathing and blood circulation. Each follows its own speed; the rhythm visible in a person’s breathing is slower, and the blood circulation, felt as the pulse, is faster. This “rhythmic organization” acts as a mediator between the other two poles. It would be tempting to go into further detail, but since we have gathered to study the principles and methods of Waldorf education, I must refrain. However, if you can see the chest organization from the point of view just indicated, you find in every one of its parts—whether in the skeletal formation or in the structure of the inner organs—a transition between the head organization and the metabolic-limb system. This is the image that emerges when we observe human beings according to their inner structure rather than foggy notions about human unity. But there is more, for we are also led to understand the various functions within the human being, and here I would like to give you an example. One could mention countless examples, but this must suffice to show how important it is for real educators to follow the directions indicated here.
Imagine that a person suffers from sudden outbursts of temper. Such eruptions may already occur in childhood, and then a good teacher must find ways of dealing with them. Those who follow the usual methods of physiology and anatomy might also consider the psychological effects in this person. Furthermore they may include the fact that, along with extreme anger, there is an excess of gall secretion. However, these two aspects—the physical and psychological—are not generally seen as two sides of the same phenomenon. The soul-spiritual aspect of anger and the physically overactive secretion of bile are not seen as a unity. In a normal person, bile is of course a necessary for the nutritive process. In one who is angry, this gall activity becomes imbalanced and, if left alone, such a person will finally suffer from jaundice, as you all know.
If we consider both the soul-spiritual and the physical aspects, we see that a tendency toward a certain illness may develop, but this alone is still not enough to assess human nature, because, while bile is being secreted in the metabolism, an accompanying but polar opposite process occurs in the head organization. We are not observing human nature fully unless we realize that while bile is secreted, an opposite process is taking place at the same time in the head organization. In the head, a milk-like sap, produced in other parts of the body, is being absorbed. In an abnormal case, if too much bile is secreted into the metabolism, the head organization will try to fill itself with too much of this fluid; consequently, once the temper has cooled down, one feels as if one’s head were bursting. And whereas an excess of bile will cause this milky sap to flow into the head, once the temper has cooled down this person’s face may turn somewhat blue. If we study not just the external forms of bones and organs but also their organic processes, we certainly can find a polarity between the nervoussensory organization centered in the head and the limb-metabolic system. Between these lives the rhythmic system with its lung and heart activities, which always regulate and mediate between the two outer poles.
If we keep our images flexible and avoid becoming too simplistic by picturing the various organs in a static way—perhaps by making accurate, sharp illustrations—we are certain to be captivated by the multifarious relationships and constant interplay within these three members of the human being. If we look at the rhythmic activity of breathing, we see how during inhalation the thrust is led to the cerebrospinal fluid. While receiving these breathing rhythms, this fluid passes the vibrations right up into the brain fluid, which fills the various cavities of the brain. This “lapping” against the brain, so to speak, caused by rhythmic breathing, stimulates the human being to become active in the nervous-sensory organization. The rhythms caused by the process of breathing are constantly passed on via the vertebral canal into the brain fluid. Thus the stimuli activated by breathing constantly strive toward the region of the head.
If we look downward, we see how rhythmic breathing, in a certain sense, becomes more “pointed” and “excited” in the rhythm of the pulse and how the blood’s circulation affects the metabolism with each exhalation—that is, while the brain and cerebrospinal fluid push downward. If we look with lively, artistically sensitive understanding at the breathing process and blood circulation, we can follow the effects of the pulsing blood upon both the nervous-sensory organization and the metabolic-limb system. We see how, on the one side, the processes of breathing and blood circulation reach up into the brain and the region of the head, and, on the other, in the opposite direction into the metabolic-limb system. If we gradually gain a living picture of the human being in this way, we can make real progress in our research. We can form concepts that accord fully with the nature of the human central system. Such concepts must not be so simple that we can make them into diagrams; schemes and diagrams are always problematic when it comes to understanding the constant, elemental weaving and flowing of human nature.
In the early days of our anthroposophic endeavors, when we were still operating within theosophical groups (permit me to mention this), we were faced again and again with all sorts of diagrams, generously equipped with plenty of data. Everything seemed to fit into elaborate, neat schematic ladders, high enough for anyone to climb to the highest regions of existence. Some members seemed to view such diagrammatic ladders as a kind of spiritual gym equipment, with which they hoped to reach Olympic heights; everything was neatly enclosed in boxes. These things made one’s limbs twitch convulsively. They were hardly bearable for those who knew that, to get hold of our constantly mobile human nature in a suprasensory way, we must keep our ideas flexible and alive. Fixed habits of thinking made us want to flee. What matters is that, in our quest for real knowledge of the human being, we must keep our thinking and ideation flexible, and then we can advance yet another step.
Now, as we try to build mental images of how this rhythm between breathing and blood circulation becomes changed and transformed in the upper regions, we are led to the following idea, which I will sketch on the blackboard—not as a fixed scheme but merely as an indication (see drawing). Let the thick line represent the mental image of some sort of rope, which will help us imagine, roughly, the processes in our breathing and blood circulation. This is one way we can get hold of what exists beyond the physical blood in a much finer and imponderable substance of the “etheric nerves.”
Now, using our imagination, we can go further by looking from the chest organization upward, feeling inwardly compelled, as it were, to “fray” our images and transform them into fine threads that interweave and form a delicate network. Thus we can grasp through mental images—turned upward and modified—something that occurs externally and physically. We find that we simply have to fray these thick cords into threads. Imagining this process, we gradually experience the white, fibrous brain substance under the grey matter. In our mental images we become as flexible as the very processes that pervade human nature.
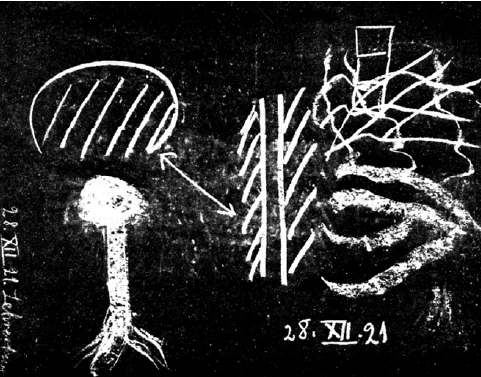
Directing your image making in the opposite direction, downward, you will find it impossible to split up or fray your mental images into fine threads to be woven into some sort of texture, as seen externally in the nervous system; such threads simply vanish, and you lose all traces of them. Otherwise, you would be led astray into forming images that no longer correspond to external reality. If you follow the brain as it continues downward into the spinal cord through the twelve dorsal vertebrae—through the lumbar and sacral vertebrae and so on—you find that the nerve substance, which now is white on the outside and grey inside, gradually dissolves toward the region of the metabolism. Somehow it becomes impossible to imagine the nerves continuing downward. We cannot get a true and comprehensive picture of the human being unless our images are able to transform; we must keep our images flexible.
If we look upward, our mental pictures change from those we find when looking down. We can recreate in images the flexibility of human nature, and this is the beginning of an artistic activity that eventually leads researchers to what we find externally in the physical human being. So we avoid the schism caused by looking first at the outer physical world and forming abstract concepts about it. Rather, we dive right into human nature. Our concepts become lively and stay in harmony with what actually exists in the human being. There is no other way to understand the true nature of the human being, and this is an essential prerequisite in the art of education.
To know the human being, we have to become inwardly flexible, and then we can correctly discover these three members of the human organization and how they work together to create a healthy equilibrium. We will learn to recognize how a disturbance of this equilibrium leads to all kinds of illnesses and to discriminate, in a living way, between the causes of health and illness in human life. If you look at the creation of the human being with the reverence it deserves, you will not oversimplify this intricate human organization by calling it a natural unity. And, when looking at the chest region, if you imagine coarse, rope-like shapes that become more refined as you approach the region of the head, until they fray into simple threads, you begin to reach the material reality. You find your imagination confirmed outwardly by the physical nerve fibers and by the way they interweave.
This is especially important when we consider the entire span of human life, because these three members of the human organization are interrelated in different ways during the various stages of life. During childhood the soul-spiritual element works into the physical organization in a completely different way than it does during the later stages. It is essential that we pay enough attention to these subtle changes. How94 ever, if we are willing to develop the kind of mental images indicated here, we gradually learn to broaden and deepen previous concepts.
It seem I offended many readers of my book The Spiritual Guidance of the Individual and Humanity when I pointed out that children have a kind of wisdom that adults no longer possess. I certainly do not wish to belittle adult wisdom and abilities, but just imagine what would happen if, at an early stage when the brain and the other organs are still relatively unformed, our whole organization had to come about and form itself by relying solely on our personal wisdom. I am afraid we would turn out rather poorly. Certainly, children form their brains and other organs entirely subconsciously, but there is great wisdom at work nonetheless.
When you consider the whole of human life as described in previous lectures, you can recognize this wisdom, especially if you have a sense for what children’s dreams can tell you. Adults tend to dismiss these dreams as childish nonsense, but if you can experience their underlying reality, children’s dreams, so different from adult dreams, are in fact very interesting. Of course, children cannot express themselves clearly when speaking about their dreams, but there are ways of discovering what they are trying to say. And then we find that, through images of spirit beings in their dreams, children dimly experience the sublime powers of wisdom that help shape the brain and other physical organs. If we approach children’s dreams with a reverence in tune with their experience, we see a pervading cosmic wisdom at work in them. From this point of view (forgive this somewhat offensive statement), children are much wiser, much smarter than adults. And when teachers enter the classroom, they should be fully aware of this abundance of wisdom in the children. Teachers themselves have outgrown it, and what they have gained instead—knowledge of their own experience—cannot compare with it in the least.
Adult dreams have lost that quality; they carry everyday life into their dreams. I have spoken of this from a different perspective. When adults dream, they carry daytime wisdom into their life at night, where it affects them in return. But when children dream, sublime wisdom flows through them. Though unaware of what is happening, children nevertheless retain a dim awareness upon awaking. And, during the day, when they sit in school, they still have an indistinct sense of this cosmic wisdom, which they cannot find it in the teacher. Teachers, on the other hand, feel superior to children in terms of knowledge and wisdom. This is natural, of course, since otherwise they could not teach. Teachers are conscious of their own wisdom, and from this point of view, they certainly are superior. But this kind of wisdom is not as full and sublime as that of the child.
If we put into words what happens when a young child, pervaded by wisdom, meets the teacher, who has lost this primordial wisdom, the following image might emerge. The abstract knowledge that is typical of our times, and with which teachers have been closely linked for so many years of life, tends to make them into somewhat dry and pedantic adults. In some cases, their demeanor and outer appearance reveal these traits. Children, on the other hand, have retained the freshness and sprightliness that spring from spiritual wisdom.
Now, when teachers enter the classroom, children have to control their high spirits. Teachers feel that they are intelligent and that their students are ignorant. But in the subconscious realms of both teachers and students, a very different picture emerges. And if dreams were allowed to speak, the picture again would be quite different. Children, somewhere in their subconscious, feel how stupid the teacher is. And in their subconscious, teachers feel how wise the children are.
All this becomes a part of the classroom atmosphere and belongs to the imponderables that play a very important role in education. Because of this, children cannot help confronting their teachers with a certain arrogance, however slight, of which they remain completely unaware. Its innate attitude toward the teacher is one of amusement; they cannot help feeling this flow of wisdom pervading their own bodies and how little has survived in the teacher. Instinctively, children contrast their own wisdom with that of their teachers, who enter the classroom somewhat stiff and pedantic—the face grown morose from living so long with abstract intellectual concepts, the coat so heavy with the dust of libraries that it defies the clothes brush. Mild amusement is the uppermost feeling of a child at this sorry sight.
This is how the teacher is seen through the eyes of a child, however unaware the child may be. And we cannot help seeing a certain justification in this attitude. After all, such a reaction is a form of self-protection, preserving the child’s state of health. A dream about teachers would hardly be an elevating experience for young students, who can still dream of the powers of wisdom that permeate their whole being.
In a teacher’s subconscious regions, an opposite kind of feeling develops that is also very real, and it, too, belongs to the imponderables of the classroom. In the child, we can speak of dim awareness, but in the teacher, there lurks a subconscious desire. Though teachers will never admit this consciously, an inner yearning arises for the vital forces of wisdom that bless children. If psychoanalysts of the human soul were more aware of spiritual realities than is usually the case, they would quickly discover the important role that children’s fresh, vital growth and other human forces play in a teacher’s subconscious.
These are some of the invisible elements that pervade the classroom. And if you are able to look a little behind the scenes, you will find that children turn away from the teacher because of a certain disenchantment. They dimly sense an unspoken question: In this adult, who is my teacher, what became of all that flows through me? But in teachers, on the other hand, a subconscious longing begins to stir. Like vampires, they want to prey on these young souls. If you look a little closer, in many cases you can see how strongly this vampire-like urge works beneath an otherwise orderly appearance. Here lies the origin of various tendencies toward ill health in young children. One only needs to look with open eyes at the psychological disposition of some teachers to see how such tendencies can result from life in the classroom.
As teachers, we cannot overcome these harmful influences unless we are sustained by a knowledge of the human being that is imbued with love for humankind—knowledge both flexible and alive and in harmony with the human organism as I have described it. Only genuine love of humankind can overcome and balance the various forces in human nature that have become onesided. And such knowledge of the human being enables us to recognize not just the way human nature is expressed differently in various individuals, but also its characteristic changes through childhood, maturity, and old age. The three members of the human being have completely different working relationships during the three main stages of life, and each member must adapt accordingly.
We need to keep this in mind, especially when we make up the schedule. Obviously, we must cater to the whole being of a child—to the head as well as the limbs—and we must allow for the fact that, in each of the three members, processes that spring from the other two continue all the time. For example, metabolic processes are always occurring in the head.
If children have to sit still at their desks to do head work (more on this and classroom desks later), if their activities do not flow into their limbs and metabolism, we create an imbalance in them. We must balance this by letting the head relax—by allowing them to enjoy free movement later during gym lessons. If you are aware of the polar processes in the head and in the limbs and metabolism, you will appreciate the importance of providing the right changes in the schedule.
But if, after a boisterous gym lesson, we take our students back to the classroom to continue the lessons, what do we do then? You must realize that, while a person is engaged in limb activities that stimulate the metabolism, thoughts that were artificially planted in the head during previous years are no longer there. When children jump and run around and are active in the limbs and metabolism, all thoughts previously planted in the head simply fly away. But the forces that manifest only in children’s dreams—the forces of suprasensory wisdom—now enter the head and claiming their place. If, after a movement lesson, we take the children back to the classroom to replace those forces with something else that must appear inferior to their subconscious minds, a mood of resentment will make itself felt in the class. During the previous lesson, sensory and, above all, suprasensory forces have been affecting the children. The students may not appear unwilling externally, but an inner resentment is certainly present. By resuming ordinary lessons right after a movement lesson, we go against the child’s nature and, by doing so, we implant the potential seeds of illness in children. According to a physiologist, this is a fact that has been known for a long time. I have explained this from an anthroposophic perspective to show you how much it is up to teachers to nurture the health of children, provided they have gained the right knowledge of the human being. Naturally, if we approach this in the wrong way, we can, in fact, plant all sorts of illnesses in children, and we must always be fully aware of this.
As you may have noticed by now, I do not glorify ordinary worldly wisdom, which is so highly prized these days. That sort of wisdom hardly suffices for shaping the inner organs of young people for their coming years. If we have not become stiff in our whole being by the time we mature, the knowledge we have impressed into our minds through naturalistic and intellectual concepts—which is thrown back as memory pictures—all that would eventually flow down into the rest of our organism. However absurd this may sound, a person would become ill if what belongs in the head under ordinary conditions were to flow down into limb and metabolic regions. The head forces act like poison when they enter the lower spheres. Brain wisdom, in fact, becomes a kind of poison as soon as it enters the wrong sphere, or at least when it reaches the metabolism. The only way we can live with our brain knowledge—and I use this term concretely and not as a moral judgment—is by preventing this poison from entering our metabolic and limb system, since it would have a devastating effect there.
But children are not protected by the stiffness of adults. If we press our kind of knowledge into children, our concepts can invade and poison their metabolic and limb system. You can see how important it is to recognize, from practical experience, how much head knowledge we can expect children to absorb without exposing them to the dangers of being poisoned in the metabolic-limb organization.
So it is in teachers’ hands to promote either health or illness in children. If teachers insist on making students smart intellectually according to modern standards, if they crams children’s heads with all sorts of intellectuality, they prevent subconscious forces of wisdom from permeating those children. Cosmic wisdom, on the other hand, is immediately set in motion when children run around and move more or less rhythmically. Because of its unique position between head and limb-metabolism, rhythmic activity brings about physical unity with the cosmic forces of wisdom. Herbert Spencer was quite correct when he spoke of the negative effects of a monastic education aimed at making the young excel intellectually. He pointed out that in later years those scholars would be unable to use their intellectual prowess, because during their school years they had been impregnated with the seeds of all sorts of illnesses.
These matters cannot be weighed by some special scales. They are revealed only to an open mind and to the kind of flexible thinking achieved through anthroposophic training; this kind of thinking must stay in touch with practical life. So much for the importance of teachers getting to know the fundamentals that govern health and illness in human beings. Here it must be emphasized again that, to avoid becoming trapped by external criteria and fixed concepts, you must learn to recognize the ever-changing processes of human nature, which always tend toward either health or illness. Teachers will encounter these things in their classes, and they must learn to deal with them correctly. We will go into more detail when we focus on the changing stages of the child and the growing human being.

